- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- APM Terms and Concepts
- Application Instrumentation
- APM Metrics Collection
- Trace Pipeline Configuration
- Correlate Traces with Other Telemetry
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origins for Spans
- Service Observability
- Endpoint Observability
- Dynamic Instrumentation
- Live Debugger
- Error Tracking
- Data Security
- Guides
- Troubleshooting
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Log Management
- Administration
Glossary
Welcome to our Glossary! This is a work in progress and we are actively building up a complete term list, which will take time. If you have feedback about how this glossary works, or terms you'd like to see defined, please click Feedback and let us know.
A
absolute change
CI-CD
Related terms: baseline mean , test duration , relative change
In Datadog Test Optimization, an absolute change is the absolute difference between the test duration and the baseline mean. For more information, see the documentation.
action
REAL USER MONITORING
In Datadog RUM, an action is a type of event. Action events track user interactions during a user journey.
administrative status
Synonyms: admin status
The administrative status of a port (up/down) refers to whether the port is disabled.
Agent
DATADOG AGENT
Synonyms: Datadog Agent
The Datadog Agent is an open source software that runs on a host. It collects metrics and events from the host and sends them to Datadog. It can run on your local hosts (Windows, macOS), containerized environments (Docker, Kubernetes), and in on-premises data centers. For more information, see the documentation.
alert
ALERTS
Datadog monitors generate alerts, indicating that a set condition has been reached.
alert graph
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: timeseries , dashboard
Alert graphs are timeseries graphs showing the current status of most monitors defined on your system. For more information, see the documentation.
alert value
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: alert , dashboard
The Alert value widget displays the current query value from a simple-alert metric monitor. Simple-alert monitors have a metric query that is not grouped and returns one value.
Use Alert value widgets in your dashboard to get an overview of your monitor behaviors and alert statuses. For more information, see the documentation.
alerting type
ALERTS
Related terms: simple alert , multi alert
Synonyms: alert grouping
Alerts are grouped automatically based on your selection of the group by aggregation step when defining your metric. Any added aggregations result in a “multi alert” type, and no aggregation is a “simple alert” type. For more information, see the documentation.
Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS)
INFRASTRUCTURE MONITORING
ECS is a container orchestration service.
Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)
INFRASTRUCTURE MONITORING
EKS is a managed Kubernetes service.
Amazon Resource Name (ARN)
INFRASTRUCTURE MONITORING
An ARN is a string that uniquely identifies an AWS resource. See the AWS documentation for more information.
analytics
LOG MANAGEMENT
Log analytics is the process of querying, grouping, and visualizing logs for investigation and exploration.
Annotation
INFRASTRUCTURE MONITORING
In Kubernetes, annotations are key/value maps that can be used to attach metadata to Kubernetes objects.
anomaly
ALERTS
METRICS
Related terms: outlier
Anomaly detection is an algorithmic feature that identifies when a metric behaves differently than it has in the past. It takes into account trends, seasonal day-of-week, and time-of-day patterns. It is suited for metrics with strong trends and recurring patterns that are hard to monitor with threshold-based alerting. For more information, see the documentation.
API key
An API key is a token used to authenticate a user or an application. The Datadog Agent requires an API key to submit metrics and events to Datadog.
api test
SYNTHETIC MONITORING
Related terms: multistep api test
In Datadog Synthetic Monitoring, an API test allows you to launch requests through individual network protocols. For more information, see the documentation.
APM
APM
Synonyms: Tracing, Distributed Tracing
Application Performance Monitoring (APM) monitors requests, errors, and latency in your application. Add distributed traces throughout your application to correlate to browser sessions, logs, profiles, synthetic checks, network, processes, and infrastructure metrics across your hosts, containers, proxies, and server less functions.
For more information about APM, see the APM documentation.
approval wait time
CI-CD
Related terms: queue time
Approval wait time is the duration that pipelines and jobs or stages within a pipeline are blocked, pending manual approval. For more information, see the documentation.
archive
LOG MANAGEMENT
An archive is a long-term cloud storage solution to store logs, whether they are indexed or not, for longer periods.
attribute
LOG MANAGEMENT
An attribute is a piece of information about a log.
Autodiscovery
DATADOG AGENT
In Datadog, Autodiscovery is a feature that automatically identifies the services running on containers. This enables you to define configuration templates for Agent checks and specify which containers each check should apply.
AWS Fargate
SERVERLESS MONITORING
Synonyms: Fargate
AWS Fargate is a serverless compute engine.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
INFRASTRUCTURE MONITORING
AKS is a managed Kubernetes service.
B
baseline mean
CI-CD
Related terms: test run
In Datadog Test Optimization, a baseline mean is the mean duration of the same test in the default branch, calculated over the last week of test runs. For more information, see the documentation.
baseline standard deviation
CI-CD
Related terms: test run
In Datadog Test Optimization, a baseline standard deviation is the standard deviation of the same test in the default branch, calculated over the last week of test runs. For more information, see the documentation.
browser test
SYNTHETIC MONITORING
Related terms: mobile app test
In Datadog Synthetic Monitoring, a browser test monitors web business transactions or web user journeys. A single test may involve several actions and pages to verify that users can successfully complete processes such as signing up for an account and checking out. For more information, see the documentation.
C
cardinality
METRICS
In Datadog, cardinality is the number of tag values associated with a tag key for a metric.
Center for Internet Security (CIS)
SECURITY
The CIS is an organization that maintains CIS Controls and CIS Benchmarks, which are recommendations and guidelines for best security practices.
change
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: metric
The change visualization shows you the change in a metric over a period of time. It compares the absolute or relative (%) change in value between N minutes ago and now against a given threshold. For more information, see the documentation.
change alert
ALERTS
Related terms: threshold alert
A change alert compares the absolute or relative (%) change in value between N minutes ago and now against a given threshold. The compared data points aren’t single points but are computed using the parameters in the alert conditions section. For more information, see the documentation.
Check
DATADOG AGENT
Checks are small Python programs run periodically by the Agent. A Check performs an action and then gathers the result, which the Agent then stores and reports to the Datadog platform. These programs are freeform and are generally used to collect metrics from custom environments or applications. Note that the word “check” - when not capitalized - refers to the generic act of taking a measurement.
check status
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: check , dashboard
The check status widget shows the current status or number of results for any check performed. For more information, see the documentation.
child org
A child org belongs to a parent org and maintains its own data separate from the parent org and other child orgs.
Cloud Network Monitoring (CNM)
CLOUD NETWORK MONITORING
Datadog’s Cloud Network Monitoring (CNM) provides visibility into network traffic between services, containers, availability zones, etc. For more information, see the documentation.
Cluster Agent
DATADOG AGENT
The Cluster Agent is a version of the Datadog Agent that provides a streamlined, centralized approach to collecting cluster-level monitoring data.
cold start
SERVERLESS MONITORING
INFRASTRUCTURE MONITORING
In computing, a cold start refers to when a system or component was recently created or restarted. In serverless computing, a cold start refers specifically to the problems (such as increased latency) that may arise when a function is invoked for the first time or after an idle period.
collection interval
Related terms: minimum resolution , granularity
The collection interval is the frequency at which Datadog gathers and processes data from a source. For example, if the collection interval is 10 seconds, Datadog collects data every 10 seconds, regardless of how frequently the data is generated.
collector
DATADOG AGENT
The collector is the Agent process that runs checks on the machine and collects metrics. For more information, see the documentation.
conditional variables
ALERTS
Conditional variables use if-else logic to display a different message depending on the state of the monitor and the details of how it was triggered. For more information, see the documentation.
ConfigMap
INFRASTRUCTURE MONITORING
A ConfigMap is an API object that stores data in key-value pairs. ConfigMaps can be supplied to Pods as environment variables, command-line arguments, or configuration files in a volume.
Container Agent
DATADOG AGENT
The Container Agent is the version of the Datadog Agent that runs on a containerized environment.
container runtime
INFRASTRUCTURE MONITORING
A container runtime is the part of a container engine that mounts the container and stops/starts containerization.
Container Runtime Interface (CRI)
INFRASTRUCTURE MONITORING
The CRI interface allows a kubelet to use different container runtimes.
control
SECURITY
CLOUD SECURITY
A specific recommendation for how technology, people, and processes should be managed. A control is typically based on a regulation or industry standard.
Core Web Vitals
REAL USER MONITORING
SYNTHETIC MONITORING
Core Web Vitals are a set of metrics that Google has identified as meaningful signals for UX testing. These metrics concern how long it takes for a page to load, how long it takes for a user to interact, how stable a page is as it loads, and more. For more information, see the documentation.
count
METRICS
“Count” is a metric type that adds up all the submitted values in a time interval. For more information, see the documentation.
crawler delay
INFRASTRUCTURE MONITORING
A crawler delay is a delay in metrics for Datadog cloud integrations due to constraints with the cloud provider API. For more information, see the documentation.
cross-site request forgery (CSRF)
SECURITY
Synonyms: XSRF
CSRF is a type of exploit where an attacker uses a web client, such as a browser, to access or manipulate information.
custom measure
CI-CD
Related terms: custom tag
A custom measure is a quantitative facet (a numerical value) that can be used to aggregate values from multiple pipeline traces, filter pipeline traces using a range, or sort pipeline traces against a value. For more information, see the documentation.
custom span
CI-CD
A custom span is the ability to integrate command-level events in CI Pipeline Visibility, which are displayed in a pipeline’s flame graph visualization. For more information, see the documentation.
custom tag
CI-CD
Related terms: custom measure
A custom tag is a qualitative facet (a string value) that can be used to aggregate values from multiple pipeline traces, filter pipeline traces using a range, or sort pipeline traces against a value. For more information, see the documentation.
D
DaemonSet
INFRASTRUCTURE MONITORING
In Kubernetes, a DaemonSet is a controller that manages groups of Pods. You can describe a DaemonSet in a YAML file.
dashboard
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: screenboard , timeboard
A dashboard is Datadog’s tool for visually tracking, analyzing, and displaying key performance metrics, enabling you to monitor the health of your infrastructure.
Dashboards are on a grid-based layout, which can include a variety of objects such as images, graphs, and logs. They have a maximum width of 12 grid squares and work well for debugging. For more information, see the documentation.
datadog.yaml
DATADOG AGENT
The datadog.yaml is the main Agent configuration file for enabling and disabling different features.
For more information, see the documentation.
delay
ALERTS
An evaluation delay tells the monitor to wait a specified number of seconds before it begins evaluation. For more information, see the Advanced alert conditions.
device namespace
NETWORK DEVICE MONITORING
Namespace of the device. Namespaces can be used as tags to differentiate between multiple network devices that may share the same private IP.
device profile
NETWORK DEVICE MONITORING
A profile is a collection of OIDs associated with a device. Profiles allow NDM to reuse metric definitions across several device types or instances.
distributed tracing
APM
Distributed tracing is a method of tracking application requests as they flow from frontend devices to backend services and databases. Developers can use distributed tracing to troubleshoot requests that exhibit high latency or errors.
distribution
METRICS
Related terms: flush interval , heatmap
A distribution is a metric type that aggregates values (such as count, min, max, sum, avg, p50, p75, p90, p95, and p99) sent from multiple hosts during a flush interval.
The distribution visualization shows data aggregated across one or several tags, such as hosts. Unlike the heatmap, a distribution graph’s x-axis is quantity rather than time. For more information, see the documentation.
DogStatsD
DATADOG AGENT
DogStatsD refers to two related things: a protocol based on StatsD, and an application for reporting metrics which implements that protocol. The DogStatsD protocol is an extension of the StatsD protocol, with some modifications that are specific to the Datadog platform. The DogStatsD application is a service that is bundled with the Agent, and is used as a lightweight mechanism for reporting metrics.
See the DogStatsD documentation for more information.
downtime
ALERTS
SLOS
INCIDENT MANAGEMENT
Downtimes are scheduled periods during which monitors’ alerts and notifications are silenced. For more information, see the documentation.
dynamic application security testing (DAST)
SECURITY
APPSEC
DAST is a security testing methodology that analyzes a running application without looking at its source code.
E
eBPF
eBPF is a Linux kernel technology that allows users to run bytecode without changing the kernel or adding kernel modules.
enhanced metric
SERVERLESS MONITORING
Synonyms: enhanced Lambda metric
Datadog generates a set of enhanced Lambda metrics from your Lambda runtime. These are in addition to the default Lambda metrics provided by the AWS Lambda integration. Enhanced Lambda metrics are prepended with aws.lambda.enhanced.*.
error
REAL USER MONITORING
ERROR TRACKING
In Datadog RUM, an error is a type of event. An error event is generated when the browser emits a frontend error.
evaluation frequency
ALERTS
Related terms: evaluation window
The evaluation frequency defines how often Datadog performs the monitor query. For most configurations, the evaluation frequency is 1 minute, which means that every minute, the monitor queries the selected data over the selected evaluation window and compares the aggregated value against the defined thresholds. For more information, see the documentation.
evaluation window
ALERTS
Related terms: evaluation window
The evaluation window is the look back timeframe of the data that the monitor aggregates and uses to compare against the defined thresholds. For more information, see the documentation.
exclusion filter
LOG MANAGEMENT
An exclusion filter determines which logs should not be indexed. These logs still show in Live Tail.
execution time
APM
In APM, execution time is the total time that a span is considered active, or not waiting for a child span to complete.
Execution time is calculated by adding up the time that a span is active, meaning it has no child spans. For non-concurrent work, this is straightforward. In the following image, the execution time for Span 1 is $\D1 + \D2 + \D3$. The execution time for Spans 2 and 3 are their respective widths.
When child spans are concurrent, execution time is calculated by dividing the overlapping time by the number of concurrently active spans. In the following image, Spans 2 and 3 are concurrent (both are children of Span 1), overlapping for the duration of Span 3, so the execution time of Span 2 is $\D2 ÷ 2 + \D3$, and the execution time of Span 3 is $\D2 ÷ 2$.
explorer
Events Explorer is a page in Datadog where you can view and aggregate events. Events Explorer displays the most recent events generated by the user’s infrastructure and services, such as code deployments, service health, configuration changes, or monitoring alerts. For more information, see the Events Explorer documentation.
Trace Explorer is a page in Datadog where you can view and create analytics on 100% of ingested traces for 15 minutes, and all indexed spans for 15 days.
extract, transform, and load (ETL)
An established system where you pull data, transform the data, and load the output into a data warehouse. For more information, see the blog post.
F
facet
LOG MANAGEMENT
A facet is a user-defined tag or attribute of indexed logs. It can be quantitative or qualitative and is used in Log Explorer to search logs, define log patterns, and perform log analytics.
faceted search
A faceted search uses filters to narrow down search results.
finding
SECURITY
WORKLOAD PROTECTION
CLOUD SECURITY
A finding is the primary primitive for a rule evaluation against a resource. Every time a resource is evaluated against a rule, a finding is generated with a pass or fail status.
flaky test
CI-CD
A flaky test is a test that exhibits both a passing and failing status across multiple test runs for the same commit. If you commit some code and run it through CI, and a test fails, and you run it through CI again and the test passes, that test is unreliable as proof of quality code. For more information, see the documentation.
flame graph
APM
CONTINUOUS PROFILER
A flame graph is a visualization of a trace, where bars represent spans and show the span’s execution time as well as what called it and what calls it made.
A flame graph is also the default visualization for Continuous Profiler. It shows resource consumption (such as CPU usage) per method, and how each method was called.
flare
DATADOG AGENT
The flare command is a quick way to send troubleshooting information to the Datadog support team. flare gathers all of the Agent’s configuration files and logs into an archive file, removes sensitive information like passwords, and then sends the archive file to Datadog support.
flow
CLOUD NETWORK MONITORING
In computer networks, a flow is the path taken when one endpoint communicates with another. Datadog’s network map provides a visualization for network data flow. For more information, see the documentation.
flush interval
DATADOG AGENT
METRICS
Related terms: variance
The Datadog Agent doesn’t make a separate request to Datadog’s servers for every single data point you send.
Instead, it reports values collected over a flush time interval. For more information, see the documentation.
forecast
Forecasts use algorithms to predict the future behavior and values of a metric.
forwarder (Agent)
DATADOG AGENT
The forwarder is the Agent process that sends metrics over HTTPS to Datadog. For more information, see the documentation.
framework
SECURITY
CLOUD SECURITY
Synonyms: compliance framework, compliance standard, compliance benchmark
A collection of requirements that map to an industry benchmark or regulatory standard.
free text
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: screenboard , dashboard
Free text is a widget that allows you to add headings to your screenboard. For more information, see the documentation.
function
SERVERLESS MONITORING
In serverless computing, a function is a programmatic function hosted on managed infrastructure.
funnel
DASHBOARDS
REAL USER MONITORING
Related terms: metric
Funnel analysis helps you track conversion rates across key workflows to identify and address any bottlenecks in end-to-end user journeys.
The funnel widget visualizes conversion rates across user workflows and end-to-end user journeys. For more information, see the documentation.
funnel analysis
REAL USER MONITORING
Funnel analysis analyzes a user’s journey towards a defined outcome, such as signup or purchase. Funnel analysis looks at the sequence of events along this journey.
G
gauge
METRICS
Gauge is a metric type that takes the last value reported during the interval. For more information, see the documentation.
geomap
DASHBOARDS
REAL USER MONITORING
Related terms: metric
The Geomap widget visualizes geographic data with shaded regions or points. Use this widget to view user sessions by country, filter to see a list of all sessions in a new tab, or monitor performance metrics like load time, core web vitals, and percent of views with errors. For more information, see the documentation.
global variable
SYNTHETIC MONITORING
In Datadog Synthetic Monitoring, a global variable is a variable that is accessible from all of a user’s Synthetic tests. For more information, see the documentation.
Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
INFRASTRUCTURE MONITORING
GKE is a managed Kubernetes service.
granularity
DASHBOARDS
METRICS
Granularity is the frequency at which data is collected or displayed on graphs. For more information, see the documentation.
grok
LOG MANAGEMENT
Grok is a method for parsing and extracting attributes from semi-structured log messages.
group
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: metric , dashboard
The groups widget allows you to keep similar graphs together on your dashboard. Each group has a custom header, can hold one to many graphs, and is collapsible. Use groups to organize the widgets on your dashboard. For more information, see the documentation.
H
heatmap
DASHBOARDS
REAL USER MONITORING
Related terms: metric
The heatmap widget shows metrics aggregated across multiple tags.
Use heatmap widgets to visualize OpenTelemetry histograms, distribution metrics, high resolution and data display. For more information, see the documentation.
Helm
INFRASTRUCTURE MONITORING
Helm is a tool for managing pre-configured Kubernetes resources.
histogram
METRICS
A histogram reports five different values that summarize the submitted values: the average, count, median, 95th percentile, and max. For more information, see the documentation.
HorizontalPodAutoscaler (HPA)
INFRASTRUCTURE MONITORING
In Kubernetes, an HPA automatically deploys more Pods to meet demand.
host
INFRASTRUCTURE MONITORING
A host is a computer or a virtual machine.
hostmap
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: host , metric , dashboard
The host map widget graphs any metric across your hosts using the same visualization available from the main Host Map page. For more information, see the documentation.
I
iframe
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: dashboard
An inline frame (iframe) is a HTML element that loads another HTML page within the document. The iframe widget allows you to embed a portion of any other web page on your dashboard. For more information, see the documentation.
image
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: dashboard
The image widget allows you to embed an image on your dashboard. An image can be a PNG, JPG, or animated GIF, hosted where it can be accessed by URL. For more information, see the documentation.
impossible travel
CLOUD SIEM
Impossible travel is a detection method that identifies access events from different locations, where the distance between the locations is greater than the distance a human can travel in the time elapsed between the two access events.
indexed
LOG MANAGEMENT
APM
Indexed logs are logs that have been collected, processed, and retained for analysis, alerting, and troubleshooting.
Indexed spans represent spans indexed by a retention filter stored in Datadog for 15 days that can be used to search, query, and monitor in Search Spans by the tags included on the span.
Creating tag-based retention filters after ingestion allows you to control and visualize exactly how many spans are being indexed per service.
In this example, the requests (merchant.store_name and merchant.tier) have been added as tags to the span.
To get started with tagging spans in your application, see the Adding span tags guide.
After a tag has been added to a span, search and query on the tag in Analytics by clicking on the tag to add it as a facet. Once this is done, the value of this tag is stored for all new traces and can be used in the search bar, facet panel, and trace graph query.
ingested
LOG MANAGEMENT
APM
Ingested logs and spans are all logs and spans collected throughout your environment.
ingestion control
APM
Ingestion control refers to the mechanisms and rules in the Agent and in tracing libraries for determining what traces are sent from an application to Datadog.
instrumentation
APM
Instrumentation is the process of adding code to your application to capture and report observability data to Datadog, such as traces, metrics, and logs. Datadog provides instrumentation libraries for various programming languages and frameworks.
Intelligent Retention Filter
APM
A Datadog default retention filter that is always active, keeping a representative proportion of traces, true high latency, and diverse error traces to help you monitor the health of your applications. It ensures that you always see individual sample traces in any service and resource page.
interactive application security testing (IAST)
SECURITY
IAST is a security testing methodology that combines static and dynamic testing.
Investigator
CLOUD SIEM
Investigator is a graphical interface that users can use to pivot from one affected entity to another and see user behavior and its impact on their cloud environment.
invocation
SERVERLESS MONITORING
In serverless computing, an invocation is when a deployed function is called.
J
job log
CI-CD
LOG MANAGEMENT
A job log is a record of all events, outputs, and actions that occur when a job executes in a CI/CD pipeline. Job logs include information such as command outputs, system messages, error messages, and status updates. For more information, see the documentation.
K
Kubernetes
INFRASTRUCTURE MONITORING
Kubernetes is a platform for managing containers.
L
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
REAL USER MONITORING
In Datadog RUM, Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) is a web performance indicator that measures how long it takes for the largest piece of content on a webpage to become visible to the user. It is a Core Web Vital metric, which Google uses to assess a website’s loading experience.
layer 2
NETWORK DEVICE MONITORING
CLOUD NETWORK MONITORING
Synonyms: data link layer
In the OSI model of computer networking, layer 2 defines the network data format. Layer 2 concerns frames and physical addressing.
layer 3
NETWORK DEVICE MONITORING
CLOUD NETWORK MONITORING
Synonyms: network layer
In the OSI model of computer networking, layer 3 determines how data is physically routed from source to destination. Layer 3 concerns packets and logical addressing.
list
DASHBOARDS
LOG MANAGEMENT
Related terms: dashboard
The list widget displays a list of events and issues, which can come from a variety of sources such as Logs, RUM, or Events. Search and query across sources to narrow down the events you want the widget to highlight and display. For more information, see the documentation.
Live Tail
LOG MANAGEMENT
Live Tail is all logs ingested by Datadog after processing but before indexing or archiving.
log indexing
LOG MANAGEMENT
Log indexing filters logs into value groups for different retention periods, quotas, usage monitoring, and billing.
M
managed information base (MIB)
NETWORK DEVICE MONITORING
A database or list of all the possible OIDs and their definitions that are related to the MIB. For example, the IF-MIB (interface MIB) contains all the OIDs for descriptive information about a device’s interface.
manifest (Kubernetes)
INFRASTRUCTURE MONITORING
In Kubernetes, a manifest is a file that describes the creation and management of resources in a cluster.
manual step
CI-CD
A manual step is when there is a job with a manual approval phase in the pipeline. For more information, see the documentation.
measure
LOG MANAGEMENT
A measure is a quantitative facet that can be used to aggregate values from multiple logs, filter logs using a range, or sort logs against a value.
metric
METRICS
Metrics are numerical values that can track anything about your environment over time, from latency to error rates to user signups. For more information, see the documentation.
minified code
APM
SYNTHETIC MONITORING
REAL USER MONITORING
Minified code is code (often JavaScript) stripped of comments, extra whitespace, unused code, and anything else that does not affect functionality. Minified code is less human-readable, but its smaller size improves website performance.
minimum resolution
Related terms: collection interval
Minimum resolution is the shortest interval between datapoints for which Datadog can retain unique records. For example, if the minimum resolution is 1 second, only one value per unique combination of tags and metrics can be stored within each 1-second window. Any subsequent value sent within the same second overwrites the previous value.
While minimum resolution defines the minimum time granularity Datadog can support, the collection interval defines the default frequency at which Datadog reports datapoints.
MITRE Adversarial Tactics, Techniques, and Common Knowledge (ATT&CK)
SECURITY
MITRE ATT&CK is a knowledge base of cyber adversary tactics and techniques.
mobile app test
SYNTHETIC MONITORING
Related terms: browser test
In Datadog Synthetic Monitoring, a mobile app test monitors key business flows that may involve several actions and pages to verify that users can successfully complete processes such as signing up for an account and checking out. For more information, see the documentation.
monitor summary
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: dashboard
The monitor summary widget displays a summary view of all your Datadog monitors, or a subset based on a query. For more information, see the documentation.
multi alert
ALERTS
Related terms: simple alert , alerting type
A multi alert applies the alert to each source according to the monitor’s group parameter. An alert notification is sent for each group that meets the set conditions. For more information, see the documentation.
multi-org
Multi-org is an account feature to manage multiple child organizations from one parent organization account. Users can be added to the parent-org and multiple child-orgs.
multistep API test
SYNTHETIC MONITORING
Related terms: api test
In Datadog Synthetic Monitoring, a multistep API test has several HTTP requests chained together to monitor user journeys on your services. For more information, see the documentation.
mute
ALERTS
Mute a monitor to silence a monitor’s alerts and notifications.
N
NetFlow
CLOUD NETWORK MONITORING
NetFlow is a network protocol system that collects IP network traffic as it enters or exits an interface. It was introduced by Cisco in 1996.
Network Device Monitoring (NDM)
NETWORK DEVICE MONITORING
Datadog’s Network Device Monitoring (NDM) provides visibility into on-premise and virtual network devices, such as routers, switches, and firewalls. For more information, see the documentation.
network profile
CLOUD NETWORK MONITORING
NETWORK DEVICE MONITORING
A network profile is set of attributes that describe how a network is configured.
new
NEW indicates a fully developed, production-ready product or feature that has been recently released. New features are complete, thoroughly tested, and fully supported for regular production workloads.
No Data
No Data is when an integration or application is no longer submitting metrics to Datadog.
Node Agent
DATADOG AGENT
The Node Agent is the version of the Datadog Agent that runs on a host.
notes and links
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: free text , dashboard
The Notes and Links widget is similar to the free text widget but contains more formatting and display options. For more information, see the documentation.
notification rule
SECURITY
CLOUD SIEM
APPSEC
WORKLOAD PROTECTION
CLOUD SECURITY
A notification rule determines who should be notified about security issues based on the source type, severity, tags, and attributes.
O
object identifier (OID)
NETWORK DEVICE MONITORING
A unique ID or address on a device that when polled returns the response code of that value. For example, OIDs are CPU or device fan speed.
Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP)
SECURITY
APPSEC
OWASP is an organization that provides web application security resources.
operational status
The operational status of a port (up/down) refers to whether the port is up or down.
orchestrator
INFRASTRUCTURE MONITORING
In a containerized infrastructure, an orchestrator automates the management of containers. This includes the provisioning, deploying, scaling, and networking of containers.
outlier
ALERTS
Related terms: anomaly
Outlier detection is an algorithmic feature that allows you to detect when a specific metric group behaves differently than its peers. For more information, see the documentation.
P
parallelization
SYNTHETIC MONITORING
Related terms: test run
In Datadog Synthetic Monitoring, parallelization allows you to execute multiple tests in your CI/CD pipelines simultaneously rather than sequentially to help speed up your building, testing, and deployment processes. For more information, see the documentation.
parameter
CI-CD
A parameter is any user-defined value that can be passed to a CI pipeline at runtime. Parameters allow you to customize and control a pipeline’s execution behavior, and are useful for situations such as deploying to different environments, selecting specific test suites to run, or defining build versions. For more information, see the documentation.
parent org
A parent org can manage and view the usage of multiple child organizations.
partial retry
CI-CD
Related terms: running pipeline
A partial retry is when a subset of stages, jobs, or steps in a CI pipeline are re-executed after a failure, as opposed to retrying the entire pipeline. For more information, see the documentation.
pattern
LOG MANAGEMENT
A pattern is when log messages have a similar structure. Pattern aggregation groups these logs together and displays them in the patterns view.
percentile
DASHBOARDS
A percentile describes how a score compares to other scores from the same dataset, or the percentage of values in a dataset that fall below a given value.
performance regression
CI-CD
Related terms: test regression , test service
In Datadog Test Optimization, a performance regression is a measurable decline in performance metrics for a test service. For more information, see the documentation.
pie chart
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: metric
The pie chart widget can display a single dataset with corresponding proportions, or multiple datasets with nested proportions. For more information, see the documentation.
ping
NETWORK DEVICE MONITORING
A network tool that measures how long it takes for a signal to travel from one device to another over a network and back again.
pipeline
LOG MANAGEMENT
OBSERVABILITY PIPELINES
In Log Management, a pipeline is an ordered set of processors applied to a filtered subset of logs, which happens after the collection of logs but before indexing.
In Observability Pipelines, a pipeline is a sequential path of sources, transforms, and destinations for your observability data.
pipeline breakdown execution time
CI-CD
For the CI jobs on the critical path, the total amount of time dedicated to executing tasks.
The sum of all the pipeline breakdown metrics is equal to the pipeline duration (@duration).
Note that this metric is different from the overall pipeline execution time since this metric only takes into account the jobs on the critical path, while the overall pipeline execution time includes all jobs in the pipeline.
Tag: @ci.pipeline.critical_path.execution_time.
pipeline breakdown queue time
CI-CD
For the CI jobs on the critical path, the total amount of time spent in the queue.
The sum of all the pipeline breakdown metrics is equal to the pipeline duration (@duration).
Tag: @ci.pipeline.critical_path.queue_time.
pipeline breakdown uncategorized time
CI-CD
Amount of time that is not categorized by the other breakdown metrics. This could be due to downstream pipelines, job teardown time, or other activities.
The sum of all the pipeline breakdown metrics is equal to the pipeline duration (@duration).
Tag: @ci.pipeline.critical_path.uncategorized_time.
pipeline breakdown wait time
CI-CD
For the CI jobs on the critical path, the total amount of time spent waiting for a manual approval.
The sum of all the pipeline breakdown metrics is equal to the pipeline duration (@duration).
Tag: @ci.pipeline.critical_path.wait_time.
pipeline execution time
CI-CD
Pipeline execution time is the amount of time a pipeline has been actively running jobs. Pipeline execution time represents a pipeline trace, which provides an overview of the pipeline’s execution history, including the start and end times of each job and any idle periods between jobs.
For example, consider a pipeline with 3 jobs: A, B, and C. During the first minute both A and B are running, so that minute counts towards execution time. The next 30 seconds, A stops while B is still running, so that time also counts. Then, there is a gap until C starts running, so the execution time is not increased during this period since there are no jobs running. Finally, C runs for 15 seconds.
The final execution time calculation is $\1m30s + 15s = 1m45s$.
This metric is available at the pipeline level only under the name @ci.execution_time.
pipeline failure
CI-CD
A pipeline failure occurs when one or more stages or jobs in a CI/CD pipeline does not complete successfully. For more information, see the documentation.
Pod
INFRASTRUCTURE MONITORING
In Kubernetes, a Pod is the smallest deployable unit of computing.
policy-based routing (PBR)
CLOUD NETWORK MONITORING
In computer networks, PBR is a technique for routing data according to policies and filters.
powerpack
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: group , dashboard
Powerpacks are templated groups of widgets that scale graphing expertise as reusable dashboard building blocks.
Powerpacks are either preset (created by Datadog, available to all customers) or custom (created by a user, and only available within their organization). For more information, see the documentation.
preview
PREVIEW indicates an early access version of a major product or feature that you can opt into before its official release. Previews allow you to explore new functionalities, provide valuable feedback, and help shape the final product. While using a feature in Preview, you might encounter limited features or minor issues, as the product is still under active development.
private location
SYNTHETIC MONITORING
In Datadog Synthetic Monitoring, a private location is a Docker container that a user can install inside a private network. This enables users to monitor internal-facing applications or private URLs that are not accessible from the public internet. For more information, see the documentation.
processing pipeline
Related terms: processor , pipeline
For Datadog Events, a processing pipeline is a set sequence of data-structuring actions on event attributes when they are ingested. Users can configure processing pipelines to normalize and enrich events. For more information, see the documentation.
processor
LOG MANAGEMENT
A processor is a set of instructions executed in a log pipeline to restructure log data and generate attributes to enrich logs.
profile
CONTINUOUS PROFILER
A profile is snapshot in time of how much work (CPU usage, memory usage) is being done by code.
profiling flame graph
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: trace , resource , dashboard
The profiling flame graph visualization represents a breakdown of top consuming lines of code such as CPU and Memory.
Add this widget to visualize stack traces of your profiled applications and accurately identify frequent resource requests. For more information, see the documentation.
Q
quartile
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: median
Quartiles organize data into four sections with 25% of the data in each.
Quartiles are used to calculate the interquartile range, which is a measure of variability around the median.
query
METRICS
A query is composed of the metric name, the time aggregator, the space aggregator, and the scope. For more information, see the documentation.
query value
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: metric
Query values display the current value of a given metric, APM, or log query. They come with conditional formatting (such as a green/yellow/red background) to convey whether the value is in the expected range. This can be supplemented with optional backgrounds of timeseries data.
The values displayed by a query value do not require an instantaneous measurement. The widget can display the latest value reported, or an aggregate computed from all query values across the time window. For more information, see the documentation.
queue time
CI-CD
Queue time is the amount of time a pipeline or job is in the queue before execution. For more information, see the documentation.
R
rate
METRICS
Rate is a metric type that takes the count and divides it by the length of the time interval. For more information, see the documentation.
real user monitoring (RUM)
REAL USER MONITORING
RUM is a UX monitoring technology that records user interactions with a website or application.
RED metrics
RED stands for “Rate, errors, and duration,” three key metrics for evaluating the performance of some code.
reference table
LOG MANAGEMENT
A reference table lists entities in Datadog like customer details, service names, and information, or IP addresses. The information is represented by a primary key and the associated metadata. For more information, see the documentation.
Rehydration
LOG MANAGEMENT
Rehydration is when archived logs are recalled back into Datadog.
relative change
CI-CD
Related terms: baseline mean , test duration , absolute change
In Datadog Test Optimization, a relative change is the relative difference between the test duration and the baseline mean. For more information, see the documentation.
Remote Configuration
APM
APPSEC
OBSERVABILITY PIPELINES
Synonyms: RC
Remote Configuration enables users to remotely configure and change the behavior of Datadog components (for example Agents, tracing libraries, and Observability Pipelines Workers) deployed in their environment.
requirement
SECURITY
CLOUD SECURITY
A group of controls representing a single technical or operational topic, such as access management or networking. The regulatory framework PCI DSS, for example, has 12 requirements.
resource
APM
REAL USER MONITORING
- In APM, a resource is a particular domain of an application, typically an instrumented web endpoint, database query, or background job.
- In RUM, a resource is a type of event. A resource event is generated for images, XHR, Fetch, CSS, or JS libraries loaded on a page.
- In Cloud Security Misconfigurations, a resource is a configurable entity that needs to be continuously scanned for adherence with one or more controls. Examples of AWS instance resources include hosts, containers, security groups, users, and customer-managed IAM policies.
retention filter
APM
Synonyms: indexing
Mechanisms and rules for determining what traces are retained for 15 day storage. Datadog retains a certain amount (Intelligent Retention) and users can create custom filters.
role
A role defines the account permissions for users. In Datadog, there are three default roles: Admin, Standard, and Read-only. For more information, see the documentation.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
RBAC is a method to control read and write access to account assets based on roles that are granted permissions and assigned to users. For more information, see the documentation.
rule
SECURITY
WORKLOAD PROTECTION
CLOUD SECURITY
Synonyms: detection rule, compliance rule
A security rule evaluates the configuration of a resource to validate an element related to one or more controls. Rules may map to multiple controls, requirements, and frameworks.
run workflow
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: dashboard
The run workflow widget allows you to automate critical tasks from dashboards.
Trigger your workflows from a dashboard at the point you become aware of an issue affecting the health of your system. This keeps your systems up and running by improving the time to resolution and reducing the possibility of errors. For more information, see the documentation.
running pipeline
CI-CD
Related terms: partial retry
A running pipeline is a pipeline that is executing in a CI/CD environment. During its execution, the pipeline processes various jobs or tasks sequentially or in parallel, depending on the pipeline configuration. For more information, see the documentation.
runtime application self-protection (RASP)
SECURITY
APPSEC
RASP is a security technology that detects and prevents attacks in real time.
For more information about RASP, see the App and API Protection documentation.
S
Saved Views
APM
LOG MANAGEMENT
In an Explorer view, saved views keep track of different search queries, customized default visualizations, and a selected subset of facets. Saved views are shared across your organization.
scatter plot
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: metric
A scatter plot identifies a possible relationship between changes observed in two different sets of variables. It provides a visual and statistical means to test the strength of a relationship between two variables. For more information, see the documentation.
scope
METRICS
ALERTS
The scope uses tag(s) to filter the query. For more information, see the documentation.
screenboard
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: dashboard , timeboard
Screenboards are dashboards with free-form layouts which can include a variety of objects such as images, graphs, and logs. They are commonly used as status boards or storytelling views that update in real-time or represent fixed points in the past. For more information, see the documentation.
Secrets (Kubernetes)
INFRASTRUCTURE MONITORING
In Kubernetes, a Secret is an object that can be used to store sensitive data, such as passwords, tokens, and keys.
Security Agent
WORKLOAD PROTECTION
SECURITY
The Security Agent is a component of the Datadog platform designed to provide security observability for your infrastructure. It collects security-related data, such as system and network activity, to help detect potential security threats and vulnerabilities across your environment.
security information and event management (SIEM)
SECURITY
CLOUD SIEM
SIEM is a field in computer security that uses data from security events to support threat detection, security incident management, and compliance.
security posture score
SECURITY
CLOUD SECURITY
Synonyms: posture score, compliance score
Available for Cloud Security Misconfigurations, the security posture score represents the percentage of your environment that satisfies all of your active Datadog out-of-the-box Cloud and Infrastructure compliance rules.
Formula:
$${{({\text"Pcritical"/\text"Pcritical + Fcritical"})^2 *8}+{(\text"Phigh"/\text"Phigh + Fhigh") *6}+{(\text"Pmedium"/\text"Pmedium + Fmedium") *3}+{(\text"Plow"/\text"Plow + Flow") *2}+{(\text"Pinfo"/\text"Pinfo + Finfo") *1}}/{8+6+3+2+1}$$
- P is the number of misconfiguration findings that evaluate to pass.
- F is the number of misconfiguration findings that evaluate to fail.
The formula uses a weighted ratio that considers the severity of the misconfiguration and the number of passing/failing findings for each severity. Only rules and findings that have the tag scored:true are included in the calculation.
If there are no findings for a given severity, the severity is not included in the calculation. For example, if there are no critical findings, the denominators would be 6+3+2+1 (excluding 8 for critical).
You can improve your score by remediating misconfigurations, either by fixing the underlying issues or by muting the rule for the impacted resource. The posture score is updated every hour.
security signal
SECURITY
CLOUD SIEM
APPSEC
WORKLOAD PROTECTION
Synonyms: signal
A security signal is a an event that is generated when Datadog detects a threat based on a security rule.
Sensitive Data Scanner
The Sensitive Data Scanner is a stream-based, pattern matching service to identify, tag, and optionally redact or hash sensitive data.
server-side request forgery (SSRF)
SECURITY
APPSEC
SSRF is a type of exploit where an attacker uses a server to access or manipulate information.
serverless
SERVERLESS MONITORING
Serverless is a cloud development and execution model in which a cloud service provider handles server infrastructure.
Serverless Insights
SERVERLESS MONITORING
Serverless insights are automatically-generated indicators (such as high memory usage, cold start, out of memory, etc.) that Datadog uses to identify and flag Lambda functions that are failing or performing poorly.
service
APM
SERVERLESS MONITORING
SOFTWARE CATALOG
- In APM, a service is a group of related endpoints, queries, or jobs that perform a piece of work for your application. A microservices-based architecture is built from multiple services, each performing part of the operation of the application.
- In serverless computing, a service is an independently-deployed piece of functionality in your architecture. Serverless applications are powered by managed services.
service account
A service account is a non-human user that can be assigned a role and own application keys. For more information, see the documentation.
service check
A service check monitors whether the status of a specific service is up or down. For more information, see the documentation.
service entry span
APM
A span is a service entry span when it is the entrypoint method for a request to a service. You can visualize this in APM when the color of the immediate parent on a flame graph is a different color.
Service Level Agreement (SLA)
SLOS
An SLA is an explicit or implicit agreement between a client and service provider stipulating the client’s reliability expectations and the service provider’s consequences for not meeting them.
Service Level Objective (SLO)
SLOS
An SLO is a target percentage for application performance over a specific period of time. For more information, see the documentation.
Service Map
APM
SOFTWARE CATALOG
In APM, the Service Map visualization provides an overview of your services and their health. It decomposes your application into its component services and draws observed dependencies between them.
service summary
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: service , dashboard
A service is a set of processes that do the same job, for example, a web framework or database. Datadog provides out-of-the-box graphs to display service information, as seen on the Service page.
Use the service summary widget to display the graphs of a chosen service in your dashboard. For more information, see the documentation.
session
REAL USER MONITORING
In Datadog RUM, a session is a type of event. A user session begins when a user starts browsing the web application. It contains high-level information about the user, including their browser and device.
Session Replay
REAL USER MONITORING
Session replay is a technique in UX testing that replays a user’s journey on a website or application.
short image
INFRASTRUCTURE MONITORING
A short image is a container image name that does not include the registry hostname, namespace, or tag. You can also think of a short image as a substring between the last slash (/) and the last colon (:) of a full container image string. For example: for the container image gcr.io/datadoghq/agent:latest, the short image is agent.
signal correlation
SECURITY
CLOUD SIEM
A signal correlation rule combines multiple signals together to generate a new signal so that users can alert on more complex use cases.
simple alert
ALERTS
Related terms: multi alert , alerting type
Monitor alerts that aggregate over all reporting sources. You receive one alert when the aggregated value meets the set conditions. For more information, see the documentation.
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
NETWORK DEVICE MONITORING
SNMP is a protocol for collecting, organizing, and modifying information about managed devices on IP networks.
slo list widget
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: service level objective (SLO) , dashboard
The SLO List widget displays a subset of SLOs over their primary time window. All other configured time windows are available in the SLO’s side panel on the SLO page. For more information, see the documentation.
slo widget
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: service level objective (SLO) , dashboard
The SLO widget visualizes the status, budget, and remaining error budget of the existing SLOs. It displays all underlying groups of the SLO and lets you sort the groups by any of the time windows in the widget.
Use this widget to build out meaningful dashboards with the most critical SLO information. For more information, see the documentation.
SNMP Management Information Base (MIB)
NETWORK DEVICE MONITORING
An SNMP MIB is a collection of definitions for a managed object’s properties (such as data types, access permissions, etc.) For more information, see the documentation.
SNMP trap
NETWORK DEVICE MONITORING
SNMP Traps are notifications sent from an SNMP-enabled device to an SNMP manager. When a network device encounters unusual activity, such as a sudden state change on a piece of equipment, the device triggers an SNMP Trap event. For more information, see the documentation.
software development kit (SDK)
An SDK is a set of tools that enable developers to create applications for a specific technology, such as an operating system or a programming language.
software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN)
NETWORK DEVICE MONITORING
A wide area network (WAN) that uses software-defined networking (SDN). SD-WAN is often used to interconnect remote offices and data centers across different transports (MPLS, broadband, 5G, and so on).
source
LOG MANAGEMENT
A log source is where logs are collected and ingested into Datadog.
source map
A source map is a file that maps minified JavaScript code to the original source.
space aggregation
METRICS
Space aggregation splits a single metric into multiple timeseries by tags such as host, container, and region. There are four aggregation options: sum, min, max, and avg.
For more information, see the documentation.
span
APM
A span is a logical unit of work in a distributed system for a given period. Multiple spans construct a trace.
span ID
APM
A span ID is a numerical identifier generated by the tracing library for a span. Together with trace IDs, they are used to correlate traces and logs in Datadog.
span summary
APM
The span summary table in APM shows metrics for spans aggregated across all traces, including how often the span shows up among all traces, what percent of traces contain the span, the average duration for the span, and its typical share of total execution time of the requests. This helps you detect N+1 problems in your code so you can improve your application performance.
The span summary table is only available for resources containing service entry spans, and contains the following information:
- Average spans per trace
- Average number of occurrences of the span for traces, including the current resource, where the span is present at least once.
- Percentage of traces
- Percentage of traces, including the current resource, where the span is present at least once.
- Average duration
- Average duration of the span for traces, including the current resource, where the span is present at least once.
- Average percentage of execution time
- Average ratio of execution time for which the span was active for traces, including the current resource, where the span is present at least once.
span tag
APM
A span tag is a tag that is applied to a span, in the form of a key-value pair, to correlate a request with other telemetry (or to filter it in searches). Tags can be added to a single span or globally to all spans.
split graph
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: metric , facet , dashboard
A split graph allows you to break down a query across multiple tag values to identify outliers and patterns.
Use this feature to investigate metrics performance across multiple facets, compare events across multiple tags, or create dynamic visualizations. For more information, see the documentation.
standard attribute
A standard attribute is from a default set of attributes. These default attributes can be customized to create a naming convention for your organization.
standard deviation
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: variance
A standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation of a random variable relative to its mean.
The standard deviation is calculated as the square root of variance by determining each data point’s deviation relative to the mean.
standard deviation change
CI-CD
Related terms: baseline mean
In Datadog Test Optimization, a standard deviation change is the number of standard deviation above the baseline mean. For more information, see the documentation.
static application security testing (SAST)
SECURITY
APPSEC
Synonyms: static analysis, Code Security
SAST is a security testing methodology that analyzes a program’s source code or binaries.
sublayer metric
APM
A sublayer metric is the execution duration of a given type or service within a trace.
Some Tracing Application Metrics are tagged with sublayer_service and sublayer_type so that you can see the execution time for individual services within a trace.
Sublayer metrics are only available if a service has downstream dependencies.
system object identifier (sysOID)
NETWORK DEVICE MONITORING
A specific address that defines the device type. All devices have a unique ID that defines it. For example, the Meraki base sysOID is 1.3.6.1.4.1.29671.
System Probe
WORKLOAD PROTECTION
SECURITY
System Probe is a component of the Datadog Agent that is used to monitor and collect system-level metrics, such as networking and performance data, from the hosts where your Kubernetes workloads are running. System Probe provides detailed insights into the system and container-level activity and helps with monitoring infrastructure and application health within Kubernetes clusters.
T
table
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: metric
The table visualization displays columns of aggregated data grouped by tag key.
Use tables to compare values across many groups of data and see trends, changes, and outliers. For more information, see the documentation.
tail
LOG MANAGEMENT
The term tail is derived from the tail command in Unix and Linux operating systems. Tailing is an alternative to printing the entire contents of a file. When you tail a file, you print the last few lines of the file to the terminal. Tailing is commonly used with log files to find the most recently logged events for a process or service. You can set the Datadog Agent up to tail a log file. For more information see Custom log collection.
template variable
ALERTS
DASHBOARDS
A template variable is an attribute used to customize and route monitor notifications based on the alert details, or to provide multiple views on a single dashboard. For more information, see the monitor notifications and dashboard documentation.
test batch
SYNTHETIC MONITORING
In Datadog Synthetic Monitoring, a test batch is a batch of CI jobs running in your CI pipelines. For more information, see the documentation.
test duration
CI-CD
Related terms: absolute change , relative change
In Datadog Test Optimization, a test duration is the length of time for a CI test to complete. For more information, see the documentation.
test regression
CI-CD
Related terms: performance regression
In Datadog Test Optimization, a test run is marked as a regression when its duration is both five times the mean and greater than the max duration for the same test in the default branch. Additionally, the test run must have a minimum duration of 500ms to be considered a regression. A benchmark test run (@test.type:benchmark) is marked as a regression when its duration is five times the standard deviation above the mean for the same test in the default branch.
The mean and maximum durations of the default branch are calculated based on the test runs from the past week. For the algorithm to consider a test run, there must be a minimum of 100 test runs on the default branch. For benchmark test runs, the minimum number of test runs is 10. For more information on Test Optimization, see the documentation.
test run
SYNTHETIC MONITORING
CI-CD
In Datadog Synthetic Monitoring and Test Optimization, a test run is an executed set of tests on software to ensure its functionality. A browser test run is a simulation of a web transaction, up to 25 steps. For more information, see the documentation.
test service
CI-CD
SYNTHETIC MONITORING
Related terms: test suite
In Datadog Test Optimization, a test service is generally a group of tests associated with, for example, a project or repo. It contains all the individual tests for your code, optionally organized into test suites, which are like folders for your tests. For more information on Test Optimization, see the documentation.
test suite
CI-CD
SYNTHETIC MONITORING
Related terms: test service
In Datadog Synthetic Monitoring and Test Optimization, a test suite is generally a group of tests exercising the same unit of code depending on your language and testing framework. You can access an example of a test suite which corresponds to a test file in the datadog-ci repository. For more information, see the documentation.
threshold alert
ALERTS
Related terms: change alert
Monitor detection method that compares metric values to a static threshold. Threshold alerts are the default detection method for metric monitors. For more information, see the documentation.
time aggregation
METRICS
Synonyms: rollup
Time aggregation is how Datadog combines data points into time buckets. There are five aggregation options: sum, min, max, avg, and count. For more information, see the documentation.
timeboard
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: dashboard , screenboard
Timeboards have automatic layouts, and represent a single point in time—either fixed or real time—across the entire dashboard. They are commonly used for troubleshooting, correlation, and general data exploration. For more information, see the documentation.
timeline view
CONTINUOUS PROFILER
A timeline view is the equivalent of a flame graph, with a distribution over time.
Each lane represents a thread (or a goroutine for Go applications). In contrast to the flame graph, you can use the timeline view to:
- Isolate spiky methods
- Investigate complex interactions between threads
- Surface runtime activity impacting the process
timeseries
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: metric
The timeseries visualization allows you to display the evolution of one or more metrics, log events, or Indexed Spans over time. For more information, see the documentation.
top list
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: metric
The top list visualization enables you to display a list of tag values with the most or least of any metric or event value, such as highest consumers of CPU, hosts with the least disk space, or cloud products with the highest costs. For more information, see the documentation.
topology
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: dashboard
The Topology Map widget displays a visualization of data sources and their relationships to help understand how data flows through your architecture. For more information, see the documentation.
trace
APM
A trace tracks the time spent processing a request, and the status of this request. Each trace consists of one or more spans.
trace context propagation
APM
Trace context propagation is the method of passing trace identifiers between services in a distributed system. It enables Datadog to stitch together individual spans from different services into a single distributed trace. Trace context propagation works by injecting identifiers, such as the trace ID and parent span ID, into HTTP headers as the request flows through the system. The downstream service then extracts these identifiers and continues the trace. This allows the Datadog to reconstruct the full path of a request across multiple services.
For more information, see propagating the trace context for your application’s language.
trace ID
APM
The trace ID is a numerical identifier generated by the tracing library for a trace. Together with span IDs, they are used to correlate traces and logs in Datadog.
trace metric
APM
Trace metrics are automatically collected and kept with a 15-month retention policy similar to any other Datadog metric. They can be used to identify and alert on hits, errors, or latency. Statistics and metrics are always calculated based on all traces, and are not impacted by ingestion controls.
Trace metrics are tagged by the host receiving traces along with the service or resource. For example, after instrumenting a web service trace metrics are collected for the entry-point span web.request on the Metrics Summary page.
Trace metrics can be exported to a dashboard from the Service or Resource page. Additionally, trace metrics can be queried from an existing dashboard.
Trace metrics are useful for monitoring. APM monitors can be set up on the New Monitors, Service, or Resource page. A set of suggested monitors is available on the Service or Resource page.
trace root span
APM
A span is a trace root span when it is the first span of a trace. The root span is the entry-point method of the traced request. Its start marks the beginning of the trace.
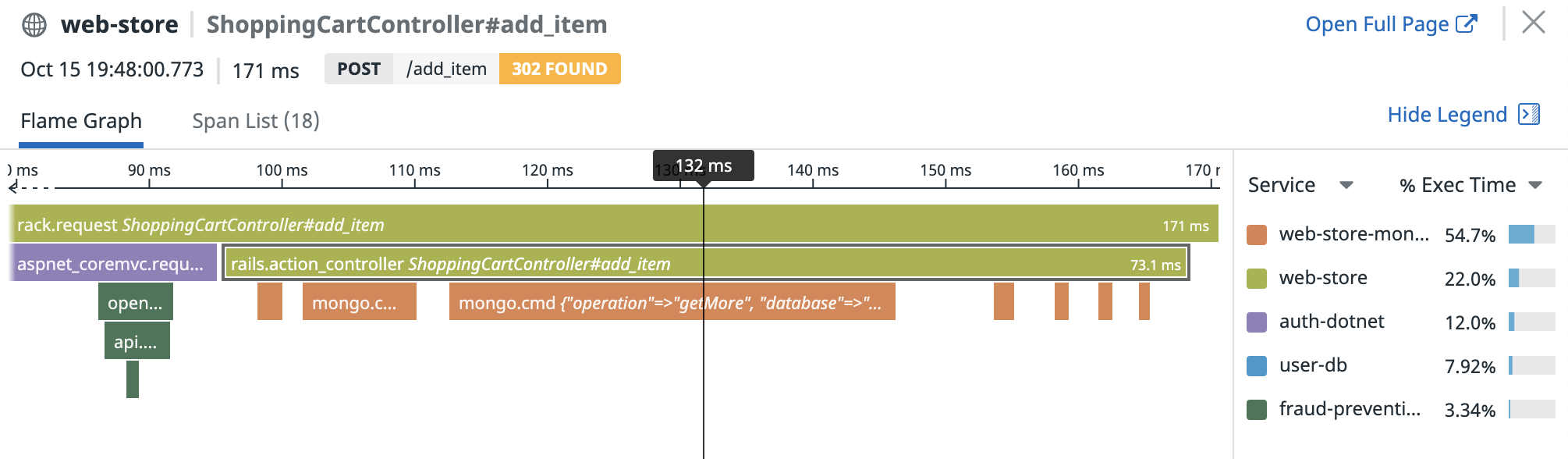
In this example, the service entry spans are:
rack.request(which is also the root span)aspnet_coremvc.request- The topmost green span below
aspnet_coremvc.request - Every orange
mongodbspan
transaction
LOG MANAGEMENT
A transaction aggregates indexed logs based on an instance of a sequence of events, such as a user session or a request processed across multiple micro-services.
treemap
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: metric
The treemap widget allows you to display proportions of one or more datasets.
This widget can display a single dataset with corresponding proportions, or multiple datasets with nested proportions. For more information, see the documentation.
U
user
A user is someone who has access to data in Datadog based on their assigned role.
V
variance
DASHBOARDS
Related terms: standard deviation
Variance is a measurement of the spread between numbers in a dataset.
The square root of the variance is the standard deviation.
view
REAL USER MONITORING
In Datadog RUM, a view is a type of event. A view event is generated each time a user visits a web application page.
W
warning
ALERTS
A warning is an optional monitor threshold setting for sending a warning notification, where the priority level is lower than an alert.
web application firewall (WAF)
SECURITY
APPSEC
A WAF is a security tool that monitors and filters HTTP traffic from a web application.
webhook
A webhook uses a URL to connect your services, and alerts your services when a metric alert is triggered. For more information, see the documentation.