- 重要な情報
- はじめに
- 用語集
- Standard Attributes
- ガイド
- インテグレーション
- エージェント
- OpenTelemetry
- 開発者
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- DDSQL Reference
- モバイルアプリケーション
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft
- アプリ内
- ダッシュボード
- ノートブック
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Watchdog
- アラート設定
- メトリクス
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- インフラストラクチャー
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- ユニバーサル サービス モニタリング
- Hosts
- コンテナ
- Processes
- サーバーレス
- ネットワークモニタリング
- Cloud Cost
- アプリケーションパフォーマンス
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- データベース モニタリング
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- RUM & セッションリプレイ
- Synthetic モニタリング
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility (CI/CDの可視化)
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Visibility
- Code Coverage
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- セキュリティ
- セキュリティの概要
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- クラウド セキュリティ マネジメント
- Application Security Management
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- ログ管理
- Observability Pipelines(観測データの制御)
- ログ管理
- CloudPrem
- 管理
未許可または異常なプロセスの特定
Workload Protection を使用すると、IT システム上で未許可または異常なプロセスが実行中、または実行されたかどうかを特定できます。
たとえば、プロセス許可リストを作成し、ホストやコンテナで実行されている許可リスト未登録のプロセスを照会することができます。
Workload Protection では、カスタム ルールを定義することでプロセス実行を監視し、ホストまたはコンテナ上の悪意のあるアクティビティをリアルタイムで検出できます。ユーザーに通知するために使用できるセキュリティ シグナルを生成するプロセス名や引数のリストを定義できます。
このガイドでは、静的許可リストと動的許可リストを例に、未許可または異常なプロセスを照会する方法を説明します。
許可リストにないプロセスの検出
既知の許可リストに含まれないプロセスを検出するルールを作成できます。
こちらはホストを対象とした例です。
exec.file.name not in [ "0anacron", "agent", "aide", "airflow", "anacron", "appstart.sh", "appstop.sh", "arping", "aws", "awslogs-nanny.sh", "basename", "bash", "blkid", "bounce", "capsh", "cat", "certwatch", "chcon", "chmod", "chown", ~"*chrony", "chronyc", ~"*chrony-dhcp", "chrony-helper", ~"*chrony-onoffline", "classification_move_archive.sh", "cleanup", "clear", "consoletype", "consul", "cp", "curl", "cut", "date", "dbus-send", "df", ~"*dhclient", "dhclient-script", "dircolors", "dirname", "dmidecode", "dnf-3", "du", "echo", "embedded_logrotate.sh", "ethtool", "file", "find", "findmnt", "flock", "gawk", "getconf", "git", "gpg", "gpg2", "gpgconf", "gpgsm", "grep", "grepconf.sh", "groupadd", "grub2-set-bootflag", "gzip", "head", "hostname", "hostnamectl", "httpd", "httpd_daily_logs_gzip.sh", "iconv", "id", "ionice", "ip", "ipcalc", "java", "java_version.sh", "jboss_66_log_rotate.sh", "ldconfig", "less", "ln", "local", "locale", "logger", "logrotate", "ls", "lsattr", "lsblk", "lscpu", "lspci", "mandb", "man-db.cron", "md5sum", "mkdir", "mktemp", "mlocate", "mon-put-instance-data.pl", "more", "moveFilesFromSourceToTarget.sh", "mv", ~"*netreport", "nice", "nm-cloud-setup", ~"*nm-cloud-setup.sh", "nm-dhcp-helper", "nm-dispatcher", "nohup", "on_ac_power", "oracle", "perl", "pickup", "pip", "postdrop", "printenv", "proxymap", "ps", "psql", "pyenv", ~"pyenv-*", ~"python*", "python2.7", "python3.9", "readlink", "renice", "rhn_check-2.7", "rhsmcertd-worker", "rm", "rmdir", "rpm", "rsync", "run-parts", "sa1", "sa2", "sadc", "sar", "_script.sh", "sed", ~"*sendmail", "sendmail.postfix", "setup-policy-routes", "sftp-server", "sg_inq", "sleep", "smtp", "smtpd", "snowsql", "sort", "sqlite3", "ssh", "sshd", "ssm-document-worker", "ssm-session-worker", "stat", "su", "sudo", "systemctl", "systemd", "systemd-coredump", ~"*systemd-environment-d-generator", "systemd-hostnamed", "systemd-networkd-wait-online", "systemd-tmpfiles", "systemd-tty-ask-password-agent", "systemd-user-runtime-dir", "systemd-userwork", "systemd-xdg-autostart-generator", "tail", "tar", "time", "tlsmgr", "touch", "tput", "tr", "trivial-rewrite", "tty", "udevadm", "uname", "unbound-anchor", "unix_chkpwd", "unzip_rename_files.sh", "updatedb", "updater", "urlgrabber-ext-down", "useradd", "usermod", "vault", "vi", "wc", "which", "wkhtmltoimage", "xargs", "yum", "ping", "get_latest_version.sh", ~"rbenv*", "uniq", "diff", "ruby", "get_hosts_for_app_component.sh", "update_health_status.rb", "check.pl", "check_all_pool_db_version.rb", ~"gitaly-git-v*", ~"gitlab-*", "upload_host_info.rb", "sshpass", ~"splunk*", "killall5", "php", "run", "env", "chpst", ~"jenkins*" ]
コンテナ向けの例は次のとおりです。
exec.file.name not in ["vault"] && container.id == "ca5534a51dd04bbcebe9b23ba05f389466cf0c190f1f8f182d7eea92a9671d00"
この例では、container.id により、そのコンテナに対してのみイベントが生成されます。
vault ではないプロセスを実行するすべてのコンテナを対象にイベントを生成したい場合は、次のような式になります。
exec.file.name not in ["vault"] && container.id == ""
動的な異常の検出
動的な異常の検出はコンテナでのみサポートされています。
プロセスを照会する際に許可リストを作成したくない場合は、カスタム ルールを作成して、動的にドリフト イベントを照会できます。
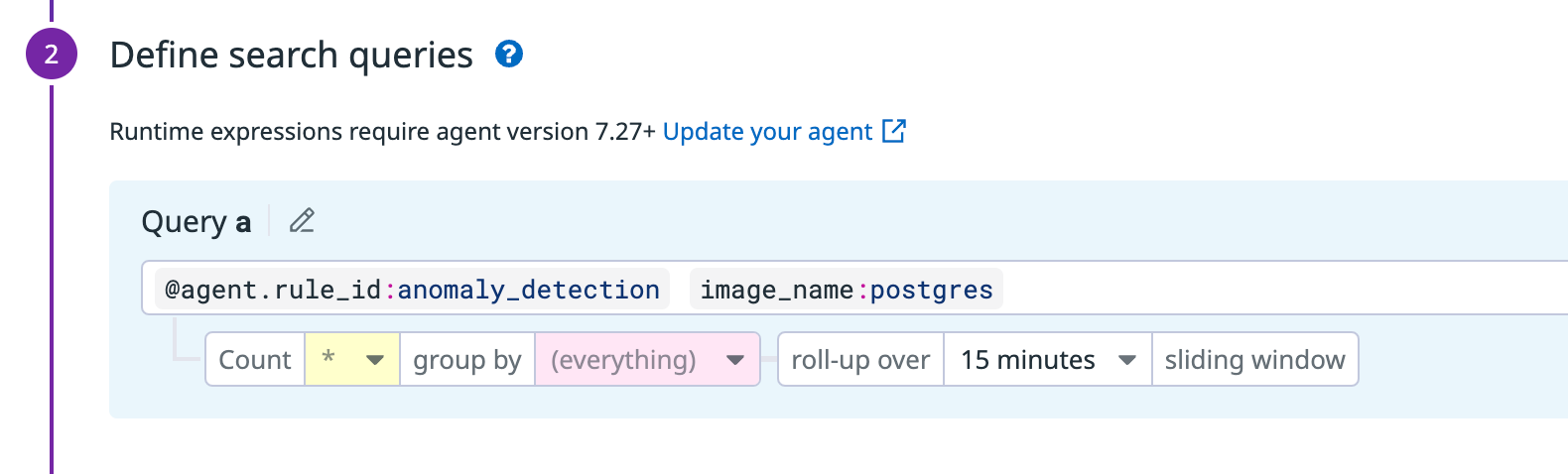
カスタム ルールのクエリは @agent.rule_id:anomaly_detection です。
特定のコンテナ イメージの異常を照会したい場合は、image_name タグを使用します。例: @agent.rule_id:anomaly_detection image_name:IMAGE_NAME
参考資料
お役に立つドキュメント、リンクや記事: