- Principales informations
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- Tracing
- Conteneurs
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Site Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Intégrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- OpenTelemetry
- Profileur
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Intégrations
- Développeurs
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Application mobile
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Alertes
- Watchdog
- Métriques
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Conteneurs
- Processes
- Sans serveur
- Surveillance réseau
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Termes et concepts de l'APM
- Sending Traces to Datadog
- APM Metrics Collection
- Trace Pipeline Configuration
- Connect Traces with Other Telemetry
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origin for Spans
- Observabilité des services
- Endpoint Observability
- Dynamic Instrumentation
- Live Debugger
- Suivi des erreurs
- Sécurité des données
- Guides
- Dépannage
- Profileur en continu
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Configuration de Postgres
- Configuration de MySQL
- Configuration de SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Données collectées
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Explorer les métriques de requête
- Explorer des échantillons de requêtes
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Dépannage
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- RUM et Session Replay
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Visibility
- Code Coverage
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Securité
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Pipelines d'observabilité
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
Kafka Destination
Ce produit n'est pas pris en charge par le site Datadog que vous avez sélectionné. ().
Cette page n'est pas encore disponible en français, sa traduction est en cours.
Si vous avez des questions ou des retours sur notre projet de traduction actuel, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter.
Si vous avez des questions ou des retours sur notre projet de traduction actuel, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter.
Overview
Use Observability Pipelines’ Kafka destination to send logs to Kafka topics.
When to use this destination
Common scenarios when you might use this destination:
- To route logs to the following destinations:
- Clickhouse: An open-source column-oriented database management system used for analyzing large volumes of logs.
- Snowflake: A data warehouse used for storage and query.
- Snowflake’s API integration utilizes Kafka as a method to ingest logs into their platform.
- Databricks: A data lakehouse for analytics and storage.
- Azure Event Hub: An ingest and processing service in the Microsoft and Azure ecosystem.
- To route data to Kafka and use the Kafka Connect ecosystem.
- To process and normalize your data with Observability Pipelines before routing to Apache Spark with Kafka to analyze data and run machine learning workloads.
Setup
Set up the Kafka destination and its environment variables when you set up a pipeline. The information below is configured in the pipelines UI.
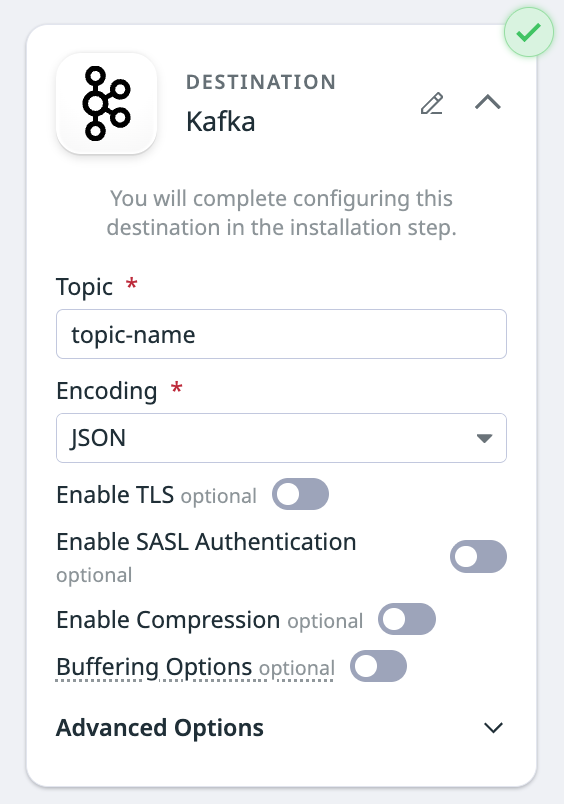
Set up the destination
- Enter the name of the topic you want to send logs to.
- In the Encoding dropdown menu, select either
JSONorRaw messageas the output format.
Optional settings
Enable TLS
Toggle the switch to enable TLS. The following certificate and key files are required.
Note: All file paths are made relative to the configuration data directory, which is /var/lib/observability-pipelines-worker/config/ by default. See Advanced Worker Configurations for more information. The file must be owned by the observability-pipelines-worker group and observability-pipelines-worker user, or at least readable by the group or user.
Server Certificate Path: The path to the certificate file that has been signed by your Certificate Authority (CA) root file in DER or PEM (X.509).CA Certificate Path: The path to the certificate file that is your Certificate Authority (CA) root file in DER or PEM (X.509).Private Key Path: The path to the.keyprivate key file that belongs to your Server Certificate Path in DER or PEM (PKCS#8) format.
Enable SASL authentication
- Toggle the switch to enable SASL Authentication.
- Select the mechanism (PLAIN, SCHRAM-SHA-256, or SCHRAM-SHA-512) in the dropdown menu.
Enable compression
- Toggle switch to Enable Compression.
- In the Compression Algorithm dropdown menu, select a compression algorithm (gzip, zstd, lz4, or snappy).
- (Optional) Select a Compression Level in the dropdown menu. If the level is not specified, the algorithm’s default level is used.
Buffering options
Toggle the switch to enable Buffering Options. Enable a configurable buffer on your destination to ensure intermittent latency or an outage at the destination doesn’t create immediate backpressure, and allow events to continue to be ingested from your source. Disk buffers can also increase pipeline durability by writing logs to disk, ensuring buffered logs persist through a Worker restart. See Configurable buffers for destinations for more information.
- If left unconfigured, your destination uses a memory buffer with a capacity of 500 events.
- To configure a buffer on your destination:
- Select the buffer type you want to set (Memory or Disk).
- Enter the buffer size and select the unit.
- Maximum memory buffer size is 128 GB.
- Maximum disk buffer size is 500 GB.
Advanced options
Click Advanced if you want to set any of the following fields:
- Message Key Field: Specify which log field contains the message key for partitioning, grouping, and ordering.
- Headers Key: Specify which log field contains your Kafka headers. If left blank, no headers are written.
- Message Timeout (ms): Local message timeout, in milliseconds. Default is
300,000 ms. - Socket Timeout (ms): Default timeout, in milliseconds, for network requests. Default is
60,000 ms. - Rate Limit Events: The maximum number of requests the Kafka client can send within the rate limit time window. Default is no rate limit.
- Rate Limit Time Window (secs): The time window used for the rate limit option.
- This setting has no effect if the rate limit for events is not set.
- Default is
1 secondif Rate Limit Events is set, but Rate Limit Time Window is not set.
- To add additional librdkafka options, click Add Option and select an option in the dropdown menu.
- Enter a value for that option.
- Check your values against the librdkafka documentation to make sure they have the correct type and are within the set range.
- Click Add Option to add another librdkafka option.
Set secrets
These are the defaults used for secret identifiers and environment variables.
Note: If you enter identifiers for your secrets and then choose to use environment variables, the environment variable is the identifier entered and prepended with DD_OP. For example, if you entered PASSWORD_1 for a password identifier, the environment variable for that password is DD_OP_PASSWORD_1.
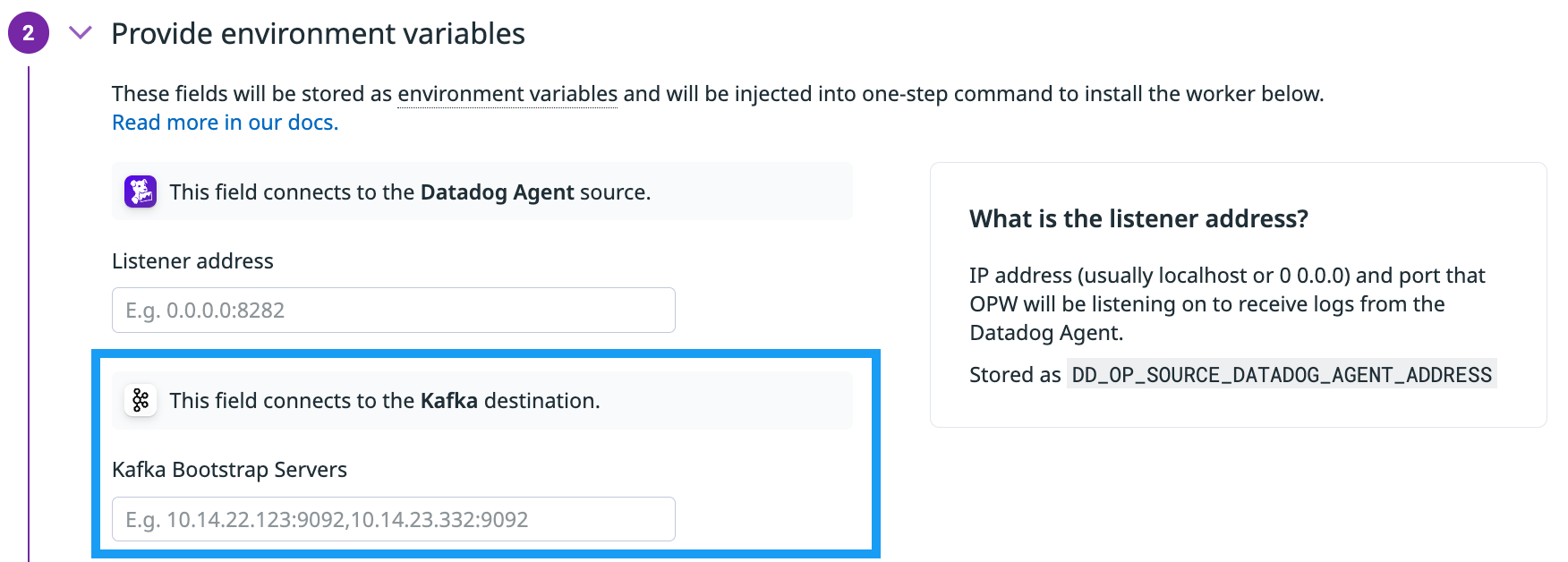
- Kafka bootstrap servers identifier:
- References the bootstrap server that the client uses to connect to the Kafka cluster and discover all the other hosts in the cluster.
- In your secrets manager, the host and port must be entered in the format of
host:port, such as10.14.22.123:9092. If there is more than one server, use commas to separate them. - The default identifier is
DESTINATION_KAFKA_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS.
- Kafka TLS passphrase identifier (when TLS is enabled):
- The default identifier is
DESTINATION_KAFKA_KEY_PASS.
- The default identifier is
- SASL authentication (when enabled):
- Kafka SASL username identifier:
- The default identifier is
DESTINATION_KAFKA_SASL_USERNAME.
- The default identifier is
- Kafka SASL password identifier:
- The default identifier is
DESTINATION_KAFKA_SASL_PASSWORD.
- The default identifier is
- Kafka SASL username identifier:
Kafka bootstrap servers
- The host and port of the Kafka bootstrap servers.
- This is the bootstrap server that the client uses to connect to the Kafka cluster and discover all the other hosts in the cluster. The host and port must be entered in the format of
host:port, such as10.14.22.123:9092. If there is more than one server, use commas to separate them. - The default environment variable is
DD_OP_DESTINATION_KAFKA_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS.
TLS (when enabled)
- If TLS is enabled, the Kafka TLS passphrase is needed.
- The default environment variable is
DD_OP_DESTINATION_KAFKA_KEY_PASS.
SASL (when enabled)
- Kafka SASL username
- The default environment variable is
DD_OP_DESTINATION_KAFKA_SASL_USERNAME.
- The default environment variable is
- Kafka SASL password
- The default environment variable is
DD_OP_DESTINATION_KAFKA_SASL_PASSWORD.
- The default environment variable is
librdkafka options
These are the available librdkafka options:
- client.id
- queue.buffering.max_messages
- transactional.id
- enable.idempotence
- acks
See the librdkafka documentation for more information and to ensure your values have the correct type and are within range.
How the destination works
See the Observability Pipelines Metrics for a full list of available health metrics.
Worker health metrics
Component metrics
Monitor the health of your destination with the following key metrics:
pipelines.component_sent_events_total- Events successfully delivered.
pipelines.component_discarded_events_total- Events dropped.
pipelines.component_errors_total- Errors in the destination component.
pipelines.component_sent_events_bytes_total- Total event bytes sent.
pipelines.utilization- Worker resource usage.
Buffer metrics (when buffering is enabled)
Use these metrics to analyze buffer performance. All metrics are emitted on a one-second interval, unless otherwise stated. Note: counter metrics, such as pipelines.buffer_received_events_total, represent the count per second and not the cumulative total, even though total is in the metric name.
Tags for metrics
- Use the
component_idtag to filter or group by individual components. - Use the
component_typetag to filter or group by sources, processors, or destinations. Note: For processors, usecomponent_type:transform.
Destination buffer metrics
These metrics are specific to destination buffers, located upstream of a destination. Each destination emits its own respective buffer metrics.
pipelines.buffer_size_events- Description: Number of events in a destination’s buffer.
- Metric type: gauge
pipelines.buffer_size_bytes- Description: Number of bytes in a destination’s buffer.
- Metric type: gauge
pipelines.buffer_received_events_total- Description: Events received by a destination’s buffer.
- Metric type: counter
pipelines.buffer_received_bytes_total- Description: Bytes received by a destination’s buffer.
- Metric type: counter
pipelines.buffer_sent_events_total- Description: Events sent downstream by a destination’s buffer.
- Metric type: counter
pipelines.buffer_sent_bytes_total- Description: Bytes sent downstream by a destination’s buffer.
- Metric type: counter
pipelines.buffer_discarded_events_total- Description: Events discarded by the buffer.
- Metric type: counter
- Additional tags:
intentional:truemeans an incoming event was dropped because the buffer was configured to drop the newest logs when it’s full.intentional:falsemeans the event was dropped due to an error. pipelines.buffer_discarded_bytes_total- Description: Bytes discarded by the buffer.
- Metric type: counter
- Additional tags:
intentional:truemeans an incoming event was dropped because the buffer was configured to drop the newest logs when it’s full.intentional:falsemeans the event was dropped due to an error.
Source buffer metrics
These metrics are specific to source buffers, located downstream of a source. Each source emits its own respective buffer metrics. Note: Source buffers are not configurable, but these metrics can help monitor backpressure as it propagates to your pipeline’s source.
pipelines.source_buffer_utilization- Description: Event count in a source’s buffer.
- Metric type: histogram
pipelines.source_buffer_utilization_level- Description: Number of events in a source’s buffer.
- Metric type: gauge
pipelines.source_buffer_utilization_mean- Description: The exponentially weighted moving average (EWMA) of the number of events in the source’s buffer.
- Metric type: gauge
pipelines.source_buffer_max_size_events- Description: A source buffer’s maximum event capacity.
- Metric type: gauge
Processor buffer metrics
These metrics are specific to processor buffers, located upstream of a processor. Each processor emits its own respective buffer metrics. Note: Processor buffers are not configurable, but these metrics can help monitor backpressure as it propagates through your pipeline’s processors.
pipelines.transform_buffer_utilization- Description: Event count in a processor’s buffer.
- Metric type: histogram
pipelines.transform_buffer_utilization_level- Description: Event count in a processor’s buffer.
- Metric type: gauge
pipelines.transform_buffer_utilization_mean- Description: The exponentially weighted moving average (EWMA) of the number of events in a processor’s buffer.
- Metric type: gauge
pipelines.transform_buffer_max_size_events- Description: A processor buffer’s maximum event capacity.
- Metric type: gauge
Deprecated buffer metrics
These metrics are still emitted by the Observability Pipelines Worker for backwards compatibility. Datadog recommends using the replacements when possible.
pipelines.buffer_events- Description: Number of events in a destination’s buffer. Use
pipelines.buffer_size_eventsinstead. - Metric type: gauge
pipelines.buffer_byte_size- Description: Number of bytes in a destination’s buffer. Use
pipelines.buffer_size_bytesinstead. - Metric type: gauge
Event batching
A batch of events is flushed when one of these parameters is met. See event batching for more information.
| Max Events | Max Bytes | Timeout (seconds) |
|---|---|---|
| 10,000 | 1,000,000 | 1 |