- Principales informations
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- Tracing
- Conteneurs
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Site Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Intégrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- OpenTelemetry
- Profileur
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Intégrations
- Développeurs
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Application mobile
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Alertes
- Watchdog
- Métriques
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Conteneurs
- Processes
- Sans serveur
- Surveillance réseau
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Termes et concepts de l'APM
- Sending Traces to Datadog
- APM Metrics Collection
- Trace Pipeline Configuration
- Connect Traces with Other Telemetry
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origin for Spans
- Observabilité des services
- Endpoint Observability
- Dynamic Instrumentation
- Live Debugger
- Suivi des erreurs
- Sécurité des données
- Guides
- Dépannage
- Profileur en continu
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Configuration de Postgres
- Configuration de MySQL
- Configuration de SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Données collectées
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Explorer les métriques de requête
- Explorer des échantillons de requêtes
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Dépannage
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- RUM et Session Replay
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Visibility
- Code Coverage
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Securité
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Pipelines d'observabilité
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
Gatekeeper
Supported OS
Intégration0.0.1
Présentation
Ce check recueille des métriques à partir de Gatekeeper OPA.
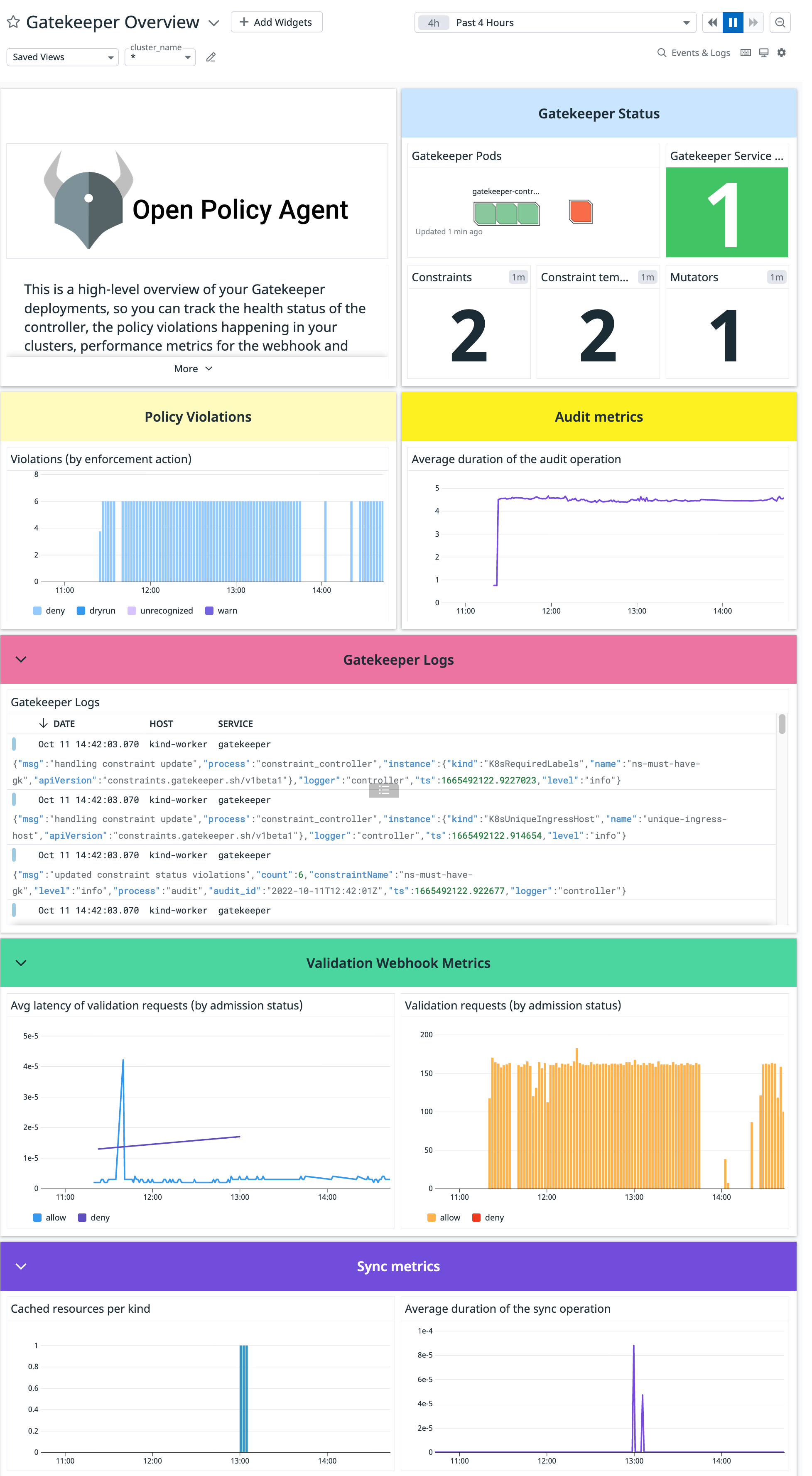
Configuration
Suivez les instructions ci-dessous pour installer et configurer ce check pour un Agent exécuté sur un cluster Kubernetes. Consultez également la documentation relative aux modèles d’intégration Autodiscovery pour découvrir comment appliquer ces instructions.
Installation
Agent v7.26.0/v6.26.0 ou ultérieur
Pour utiliser une intégration provenant du référentiel integrations-extra avec l’Agent Docker, nous vous recommandons de générer l’Agent avec l’intégration installée. Utilisez le Dockerfile suivant pour créer une version mise à jour de l’Agent comprenant l’intégration gatekeeper issue de integrations-extras :
FROM gcr.io/datadoghq/agent:latest
RUN agent integration install -r -t datadog-gatekeeper==<VERSION_INTÉGRATION>
Versions antérieures de l’Agent
Pour installer le check gatekeeper sur votre cluster Kubernetes :
Installez le kit de développement.
Clonez le dépôt
integrations-extras:git clone https://github.com/DataDog/integrations-extras.git.Mettez à jour votre configuration
ddevavec le cheminintegrations-extras/:ddev config set extras ./integrations-extrasPour générer le package
gatekeeper, exécutez :ddev -e release build gatekeeperTéléchargez le manifeste de l’Agent pour installer l’Agent Datadog en tant que DaemonSet.
Créez deux
PersistentVolumeClaim, un pour le code des checks et l’autre pour la configuration.Ajoutez-les en tant que volumes au modèle de pod de l’Agent, puis utilisez-les pour vos checks et votre configuration :
env: - name: DD_CONFD_PATH value: "/confd" - name: DD_ADDITIONAL_CHECKSD value: "/checksd" [...] volumeMounts: - name: agent-code-storage mountPath: /checksd - name: agent-conf-storage mountPath: /confd [...] volumes: - name: agent-code-storage persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: agent-code-claim - name: agent-conf-storage persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: agent-conf-claimDéployez l’Agent Datadog sur votre cluster Kubernetes :
kubectl apply -f agent.yamlCopiez le fichier d’artefact de l’intégration (.whl) sur vos nœuds Kubernetes ou importez-le sur une URL publique.
Exécutez la commande suivante pour installer le wheel de l’intégration à l’aide de l’Agent :
kubectl exec ds/datadog -- agent integration install -w <PATH_OF_GATEKEEPER_ARTIFACT_>/<GATEKEEPER_ARTIFACT_NAME>.whlExécutez les commandes suivantes pour copier les checks et la configuration sur les PVC correspondants :
kubectl exec ds/datadog -- sh # cp -R /opt/datadog-agent/embedded/lib/python3.8/site-packages/datadog_checks/* /checksd # cp -R /etc/datadog-agent/conf.d/* /confdRedémarrez les pods de l’Agent Datadog.
Configuration
Modifiez le fichier
gatekeeper/conf.yamldans le dossier/confdque vous avez ajouté au pod de l’Agent pour commencer à recueillir vos données de performance gatekeeper. Consultez le fichier d’exemple gatekeeper/conf.yaml pour découvrir toutes les options de configuration disponibles.
Validation
Lancez la sous-commande status de l’Agent et cherchez gatekeeper dans la section Checks.
Données collectées
Métriques
| gatekeeper.audit.duration.seconds.sum (count) | Latency of audit operation in seconds Shown as second |
| gatekeeper.audit.duration.seconds.count (count) | Latency of audit operation in seconds Shown as second |
| gatekeeper.audit.last_run_time (gauge) | Timestamp of last audit operation |
| gatekeeper.constraint_template_ingestion.duration.seconds.sum (count) | Distribution of how long it took to ingest a constraint template in seconds Shown as second |
| gatekeeper.constraint_template_ingestion.duration.seconds.count (count) | Distribution of how long it took to ingest a constraint template in seconds Shown as second |
| gatekeeper.constraint_template_ingestion.count (count) | Total number of constraint template ingestion actions |
| gatekeeper.violations (gauge) | Total number of violations per constraint |
| gatekeeper.constraints (gauge) | Current number of known constraints |
| gatekeeper.constraint_templates (gauge) | Number of observed constraint templates |
| gatekeeper.request.duration.seconds.sum (count) | [Deprecated since Gatekeeper v3.4.0] The response time in seconds Shown as second |
| gatekeeper.request.duration.seconds.count (count) | [Deprecated since Gatekeeper v3.4.0] The response time in seconds Shown as second |
| gatekeeper.request.count (count) | [Deprecated since Gatekeeper v3.4.0] Total number of requests that are routed to webhook |
| gatekeeper.sync (gauge) | Total number of resources of each kind being cached |
| gatekeeper.sync.duration.seconds.sum (count) | Latency of sync operation in seconds Shown as second |
| gatekeeper.sync.duration.seconds.count (count) | Latency of sync operation in seconds Shown as second |
| gatekeeper.sync.last_run_time (gauge) | Timestamp of last sync operation |
| gatekeeper.watch.intended (gauge) | The total number of Group/Version/Kinds that the watch manager has instructions to watch |
| gatekeeper.watch.watched (gauge) | The total number of Group/Version/Kinds currently watched by the watch manager |
| gatekeeper.validation.request.count (count) | The number of requests that are routed to validation webhook |
| gatekeeper.validation.request.duration.seconds.sum (count) | The response time in second Shown as second |
| gatekeeper.validation.request.duration.seconds.count (count) | The response time in second Shown as second |
| gatekeeper.mutator.ingestion.count (count) | Total number of Mutator ingestion actions |
| gatekeeper.mutator.ingestion.duration.seconds.sum (count) | The distribution of Mutator ingestion durations Shown as second |
| gatekeeper.mutator.ingestion.duration.seconds.count (count) | The distribution of Mutator ingestion durations Shown as second |
| gatekeeper.mutators (gauge) | The current number of Mutator objects |
| gatekeeper.mutator.conflicting.count (gauge) | The current number of conflicting Mutator objects |
Événements
Gatekeeper n’inclut aucun événement.
Checks de service
gatekeeper.prometheus.health
Returns CRITICAL if the agent fails to connect to the Prometheus metrics endpoint, otherwise OK.
Statuses: ok, critical
gatekeeper.health
Returns CRITICAL if the agent fails to connect to the gatekeeper health endpoint, OK if it returns 200, WARNING otherwise.
Statuses: ok, warning, critical
Dépannage
Besoin d’aide ? Contactez l’assistance Datadog.
