- Esenciales
- Empezando
- Agent
- API
- Rastreo de APM
- Contenedores
- Dashboards
- Monitorización de bases de datos
- Datadog
- Sitio web de Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Gestión de incidencias
- Integraciones
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitores
- OpenTelemetry
- Generador de perfiles
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless para Lambda AWS
- Software Delivery
- Monitorización Synthetic
- Etiquetas (tags)
- Workflow Automation
- Centro de aprendizaje
- Compatibilidad
- Glosario
- Atributos estándar
- Guías
- Agent
- Arquitectura
- IoT
- Plataformas compatibles
- Recopilación de logs
- Configuración
- Automatización de flotas
- Solucionar problemas
- Detección de nombres de host en contenedores
- Modo de depuración
- Flare del Agent
- Estado del check del Agent
- Problemas de NTP
- Problemas de permisos
- Problemas de integraciones
- Problemas del sitio
- Problemas de Autodiscovery
- Problemas de contenedores de Windows
- Configuración del tiempo de ejecución del Agent
- Consumo elevado de memoria o CPU
- Guías
- Seguridad de datos
- Integraciones
- Desarrolladores
- Autorización
- DogStatsD
- Checks personalizados
- Integraciones
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Crear una integración basada en el Agent
- Crear una integración API
- Crear un pipeline de logs
- Referencia de activos de integración
- Crear una oferta de mercado
- Crear un dashboard de integración
- Create a Monitor Template
- Crear una regla de detección Cloud SIEM
- Instalar la herramienta de desarrollo de integraciones del Agente
- Checks de servicio
- Complementos de IDE
- Comunidad
- Guías
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Aplicación móvil de Datadog
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft
- En la aplicación
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- Editor DDSQL
- Reference Tables
- Hojas
- Monitores y alertas
- Watchdog
- Métricas
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Explorador
- Estados de problemas
- Detección de regresión
- Suspected Causes
- Error Grouping
- Bits AI Dev Agent
- Monitores
- Issue Correlation
- Identificar confirmaciones sospechosas
- Auto Assign
- Issue Team Ownership
- Rastrear errores del navegador y móviles
- Rastrear errores de backend
- Manage Data Collection
- Solucionar problemas
- Guides
- Change Tracking
- Gestión de servicios
- Objetivos de nivel de servicio (SLOs)
- Gestión de incidentes
- De guardia
- Status Pages
- Gestión de eventos
- Gestión de casos
- Actions & Remediations
- Infraestructura
- Cloudcraft
- Catálogo de recursos
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Contenedores
- Processes
- Serverless
- Monitorización de red
- Cloud Cost
- Rendimiento de las aplicaciones
- APM
- Términos y conceptos de APM
- Instrumentación de aplicación
- Recopilación de métricas de APM
- Configuración de pipelines de trazas
- Correlacionar trazas (traces) y otros datos de telemetría
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origin for Spans
- Observabilidad del servicio
- Endpoint Observability
- Instrumentación dinámica
- Live Debugger
- Error Tracking
- Seguridad de los datos
- Guías
- Solucionar problemas
- Límites de tasa del Agent
- Métricas de APM del Agent
- Uso de recursos del Agent
- Logs correlacionados
- Stacks tecnológicos de llamada en profundidad PHP 5
- Herramienta de diagnóstico de .NET
- Cuantificación de APM
- Go Compile-Time Instrumentation
- Logs de inicio del rastreador
- Logs de depuración del rastreador
- Errores de conexión
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Gastos generales de integración del Agent
- Arquitecturas de configuración
- Configuración de Postgres
- Configuración de MySQL
- Configuración de SQL Server
- Configuración de Oracle
- Configuración de MongoDB
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Conexión de DBM y trazas
- Datos recopilados
- Explorar hosts de bases de datos
- Explorar métricas de consultas
- Explorar ejemplos de consulta
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Solucionar problemas
- Guías
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Experiencia digital
- Real User Monitoring
- Pruebas y monitorización de Synthetics
- Continuous Testing
- Análisis de productos
- Entrega de software
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Visibility
- Configuración
- Network Settings
- Tests en contenedores
- Repositories
- Explorador
- Monitores
- Test Health
- Flaky Test Management
- Working with Flaky Tests
- Test Impact Analysis
- Flujos de trabajo de desarrolladores
- Cobertura de código
- Instrumentar tests de navegador con RUM
- Instrumentar tests de Swift con RUM
- Correlacionar logs y tests
- Guías
- Solucionar problemas
- Code Coverage
- Quality Gates
- Métricas de DORA
- Feature Flags
- Seguridad
- Información general de seguridad
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- Observabilidad de la IA
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Gestión de logs
- CloudPrem
- Administración
- Gestión de cuentas
- Seguridad de los datos
- Ayuda
Rigor
Supported OS
Información general
Rigor proporciona monitorización y optimización Synthetic durante todo el ciclo del desarrollo.
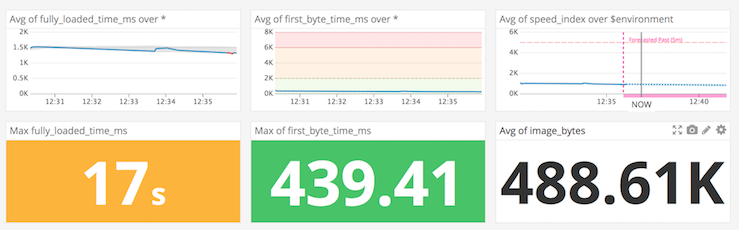
Con Rigor, puedes recopilar métricas de rendimiento del front-end Synthetic y enviarlas a Datadog. También puedes enviar alertas a Datadog como eventos.
Configuración
Rigor tiene dos integraciones diferentes con Datadog, una integración de métricas y una integración de eventos.
Configuración
Recopilación de métricas
Como administrador, haz clic en el menú “Admin Tools” (Herramientas de administración) en la parte superior derecha de tu pantalla y selecciona “Integrations” (integraciones).
Añade una nueva integración, haciendo clic en el botón “New” (Nuevo) para habilitar la configuración de la integración.
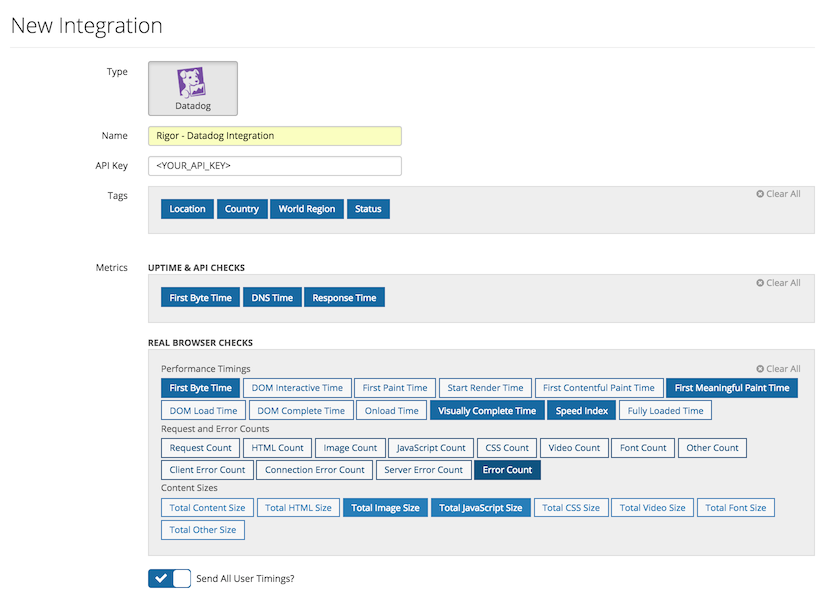
Añade un nombre único para esta integración y tu clave de API de Datadog. A continuación, elige qué etiquetas (tags) y métricas quieres enviar. Algunas cosas para recordar:
- Se incluye una versión normalizada del nombre del check como etiqueta predeterminada.
- En el caso de los checks de varios pasos (checks de Real Browser y de API), se incluye la posición de la solicitud de la que proceden las métricas.
- Los checks de tiempo de actividad incluyen HTTP, puerto y checks de API
- Los checks de puertos sólo informan de la métrica “Tiempo de respuesta”.
- No todos los navegadores admiten todas las métricas
Si quieres que los checks de Real Browser informen de la temporización de la API de temporización de usuario, asegúrate de que la opción “¿Enviar todas las temporizaciones de usuarios?” está seleccionada. Las marcas se notifican en el espacio de nombresrigor.real_browser.marks y las medidas en el espacio de nombres rigor.real_browser.measures. Nota: La selección de esta opción podría enviar muchas series nuevas a Datadog, especialmente si las marcas y medidas del sitio que está probando se generan dinámicamente.
Una vez que hayas configurado la integración, puedes añadirla a cualquier check de navegador real, HTTP, puerto o API. Sólo tienes que editar el check, ir a la pestaña “Notifications” (Notificaciones) y añadir allí la integración que acabas de crear.

Recopilación de eventos
Como administrador, haz clic en el menú “Admin Tools” (Herramientas de administración) en la parte superior derecha de tu pantalla y selecciona “Alert Webhooks” (Webhooks de alerta).
Añade una nueva integración, haciendo clic en el botón “New” (Nuevo) y luego en el cuadro de Datadog.
Añade un nombre único para este webhook y asegúrate de actualizar los activadores con tu clave de API Datadog.
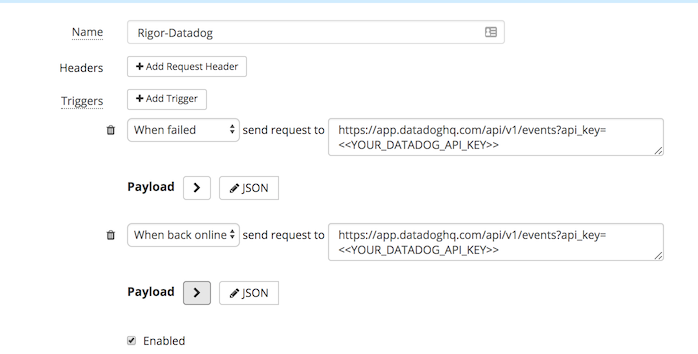
Una vez que hayas configurado la integración, puedes añadirla a cualquier check de navegador real, HTTP, puerto o API. Sólo tienes que editar el check, ir a la pestaña “Notifications” (Notificaciones) y añadir allí el webhook que acabas de crear.

Datos recopilados
Métricas
Any of Rigor’s metrics can be sent to Datadog. The metrics that are actually sent depend on how the integration was configured. The possible metrics are:
Eventos
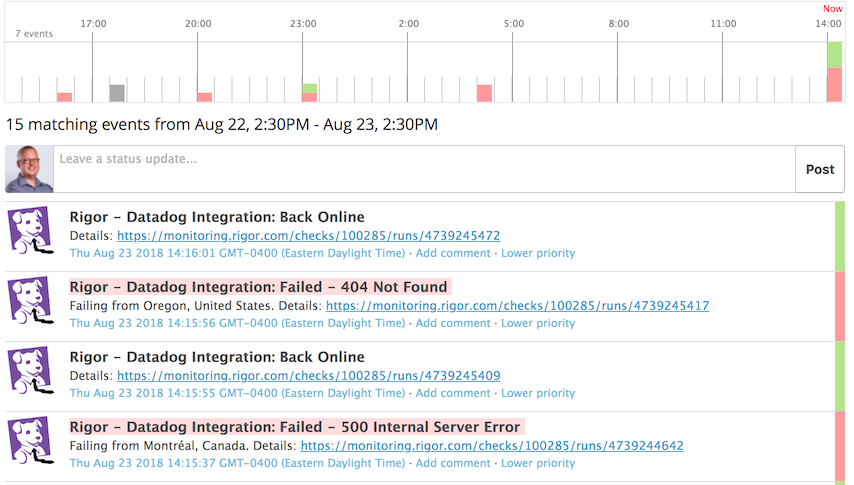
Cuando un check se configura para alertar mediante un evento Datadog, se envían dos tipos de eventos a Datadog:
- Fallido: Cuando el check falla lo suficiente como para superar el umbral y enviar una alerta.
- Nuevamente en línea: Cuando el check se ejecuta correctamente mientras se encuentra en estado de laerta
Checks de servicio
La integración Rigor no incluye checks de servicio.
Solucionar problemas
¿Necesitas ayuda? Ponte en contacto con el servicio de asistencia de Datadog.
