- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- Notebooks
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Search
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API-based Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Service Level Objectives
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Event Management
- Incident Response
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- End User Device Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Storage Management
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Session Replay
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Code Coverage
- PR Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- AI Guard
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Configuration
- Sources
- Processors
- Destinations
- Packs
- Akamai CDN
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs
- AWS Application Load Balancer Logs
- AWS CloudTrail
- AWS Elastic Load Balancer Logs
- AWS Network Load Balancer Logs
- Cisco ASA
- Cloudflare
- F5
- Fastly
- Fortinet Firewall
- HAProxy Ingress
- Istio Proxy
- Juniper SRX Firewall Traffic Logs
- Netskope
- NGINX
- Okta
- Palo Alto Firewall
- Windows XML
- ZScaler ZIA DNS
- Zscaler ZIA Firewall
- Zscaler ZIA Tunnel
- Zscaler ZIA Web Logs
- Search Syntax
- Scaling and Performance
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Guides and Resources
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
Log Search Syntax
Overview
A query filter is composed of terms and operators.
There are two types of terms:
A single term is a single word such as
testorhello.A sequence is a group of words surrounded by double quotes, such as
"hello dolly".
To combine multiple terms into a complex query, you can use any of the following case sensitive Boolean operators:
| Operator | Description | Example |
AND | Intersection: both terms are in the selected events (if nothing is added, AND is taken by default) | authentication AND failure |
OR | Union: either term is contained in the selected events | authentication OR password |
- | Exclusion: the following term is NOT in the event (apply to each individual raw text search) | authentication AND -password |
Full-text search
The full-text search feature is only available in Log Management and works in monitor, dashboard, and notebook queries. The full-text search syntax cannot be used to define index filters, archive filters, log pipeline filters, rehydration filters, or in Live Tail.
Use the syntax *:search_term to perform a full-text search across all log attributes, including the log message.
Single term example
| Search syntax | Search type | Description |
|---|---|---|
*:hello | Full-text | Searches all log attributes for the exact string hello. |
hello | Free text | Searches only the message, @title, @error.message, and @error.stack attributes for the exact string hello. |
Search term with wildcard example
| Search syntax | Search type | Description |
|---|---|---|
*:hello | Full-text | Searches all log attributes for the exact string hello. |
*:hello* | Full-text | Searches all log attributes for strings starting with hello. For example, hello_world. |
Multiple terms with exact match example
| Search syntax | Search type | Description |
|---|---|---|
*:"hello world" | Full-text | Searches all log attributes for the exact string hello world. |
hello world | Free text | Searches only the log message for hello and world words. For example hello beautiful world. |
Escape special characters and spaces
The following characters are considered special and require escaping with the \ character: - ! && || > >= < <= ( ) { } [ ] " * ? : \ #, and spaces.
/is not considered a special character and doesn’t need to be escaped.@cannot be used in search queries within Logs Explorer because it is reserved for Attribute Search.
You cannot search for special characters in a log message. You can search for special characters when they are inside of an attribute.
To search for special characters, parse them into an attribute with the Grok Parser, and search for logs that contain that attribute.
Attributes search
To search on a specific attribute, add @ to specify you are searching on an attribute.
For instance, if your attribute name is url and you want to filter on the url value www.datadoghq.com, enter:
@url:www.datadoghq.com
Reserved attributes
Reserved attributes such as host, source, status, service, trace_id, and message do not require the @ prefix. You can search these attributes directly:
service:web-app
status:error
host:i-1234567890abcdef0
Notes:
It is not required to define a facet to search on attributes and tags.
Attributes searches are case sensitive. Use full-text search to get case insensitive results. Another option is to use the
lowercasefilter with your Grok parser while parsing to get case insensitive results during search.Searching for an attribute value that contains special characters requires escaping or double quotes.
- For example, for an attribute
my_attributewith the valuehello:world, search using:@my_attribute:hello\:worldor@my_attribute:"hello:world". - To match a single special character or space, use the
?wildcard. For example, for an attributemy_attributewith the valuehello world, search using:@my_attribute:hello?world.
- For example, for an attribute
Examples:
| Search query | Description |
|---|---|
@http.url_details.path:"/api/v1/test" | Searches all logs matching /api/v1/test in the attribute http.url_details.path. |
@http.url:/api\-v1/* | Searches all logs containing a value in http.url attribute that start with /api-v1/ |
@http.status_code:[200 TO 299] @http.url_details.path:/api\-v1/* | Searches all logs containing a http.status_code value between 200 and 299, and containing a value in http.url_details.path attribute that start with /api-v1/ |
-@http.status_code:* | Searches all logs not containing the http.status_code attribute |
Search using CIDR notation
Classless Inter Domain Routing (CIDR) is a notation that allows users to define a range of IP addresses (also called CIDR blocks) succinctly. CIDR is most commonly used to define a network (such as a VPC) or a subnetwork (such as public/private subnet within a VPC).
Users can use the CIDR() function to query attributes in logs using CIDR notation. The CIDR() function needs to be passed in a log attribute as a parameter to filter against, followed by one or multiple CIDR blocks.
Examples
CIDR(@network.client.ip,13.0.0.0/8)matches and filters logs that have IP addresses in the fieldnetwork.client.ipthat fall under the 13.0.0.0/8 CIDR block.CIDR(@network.ip.list,13.0.0.0/8, 15.0.0.0/8)matches and filters logs that have any IP addresses in an array attributenetwork.ip.listthat fall under the 13.0.0.0/8 or 15.0.0.0/8 CIDR blocks.source:pan.firewall evt.name:reject CIDR(@network.client.ip, 13.0.0.0/8)would match and filter reject events from palo alto firewall that originate in the 13.0.0.0/8 subnetsource:vpc NOT(CIDR(@network.client.ip, 13.0.0.0/8)) CIDR(@network.destination.ip, 15.0.0.0/8)will show all VPC logs that do not originate in subnet 13.0.0.0/8 but are designated for destination subnet 15.0.0.0/8 because you want to analyze network traffic in your environments between subnets
The CIDR() function supports both IPv4 and IPv6 CIDR notations and works in Log Explorer, Live Tail, log widgets in Dashboards, log monitors, and log configurations.
Wildcards
You can use wildcards with free text search. However, it only searches for terms in the log message, the text in the content column in Log Explorer. See Full-text search if you want to search for a value in a log attribute.
Multi-character wildcard
To perform a multi-character wildcard search in the log message (the content column in Log Explorer), use the * symbol as follows:
service:web*matches every log message that has a service starting withweb.web*matches all log messages starting withweb.*webmatches all log messages that end withweb.
Note: Wildcards only work as wildcards outside of double quotes. For example, "*test*" matches a log which has the string *test* in its message. *test* matches a log which has the string test anywhere in its message.
Wildcard searches work within tags and attributes (faceted or not) with this syntax. This query returns all the services that end with the string mongo:
service:*mongo
Wildcard searches can also be used to search in the plain text of a log that is not part of a log attribute. For example, this query returns all logs with content (message) that contain the string NETWORK:
*NETWORK*
However, this search term does not return logs that contain the string NETWORK if it is in a log attribute and not part of the log message.
Search wildcard
When searching for an attribute or tag value that contains special characters or requires escaping or double quotes, use the ? wildcard to match a single special character or space. For example, to search for an attribute my_attribute with the value hello world: @my_attribute:hello?world.
Numerical values
In order to search on a numerical attribute, first add it as a facet. You can then use numerical operators (<,>, <=, or >=) to perform a search on numerical facets.
For instance, retrieve all logs that have a response time over 100ms with:
@http.response_time:>100
You can search for numerical attribute within a specific range. For instance, retrieve all your 4xx errors with:
@http.status_code:[400 TO 499]
Tags
Your logs inherit tags from hosts and integrations that generate them. They can be used in the search and as facets as well:
testis searching for the string “test”.env:(prod OR test)matches all logs with the tagenv:prodor the tagenv:test(env:prod AND -version:beta)matches all logs that contain tagenv:prodand that do not contain tagversion:beta
If your tags don’t follow tags best practices and don’t use the key:value syntax, use this search query:
tags:<MY_TAG>
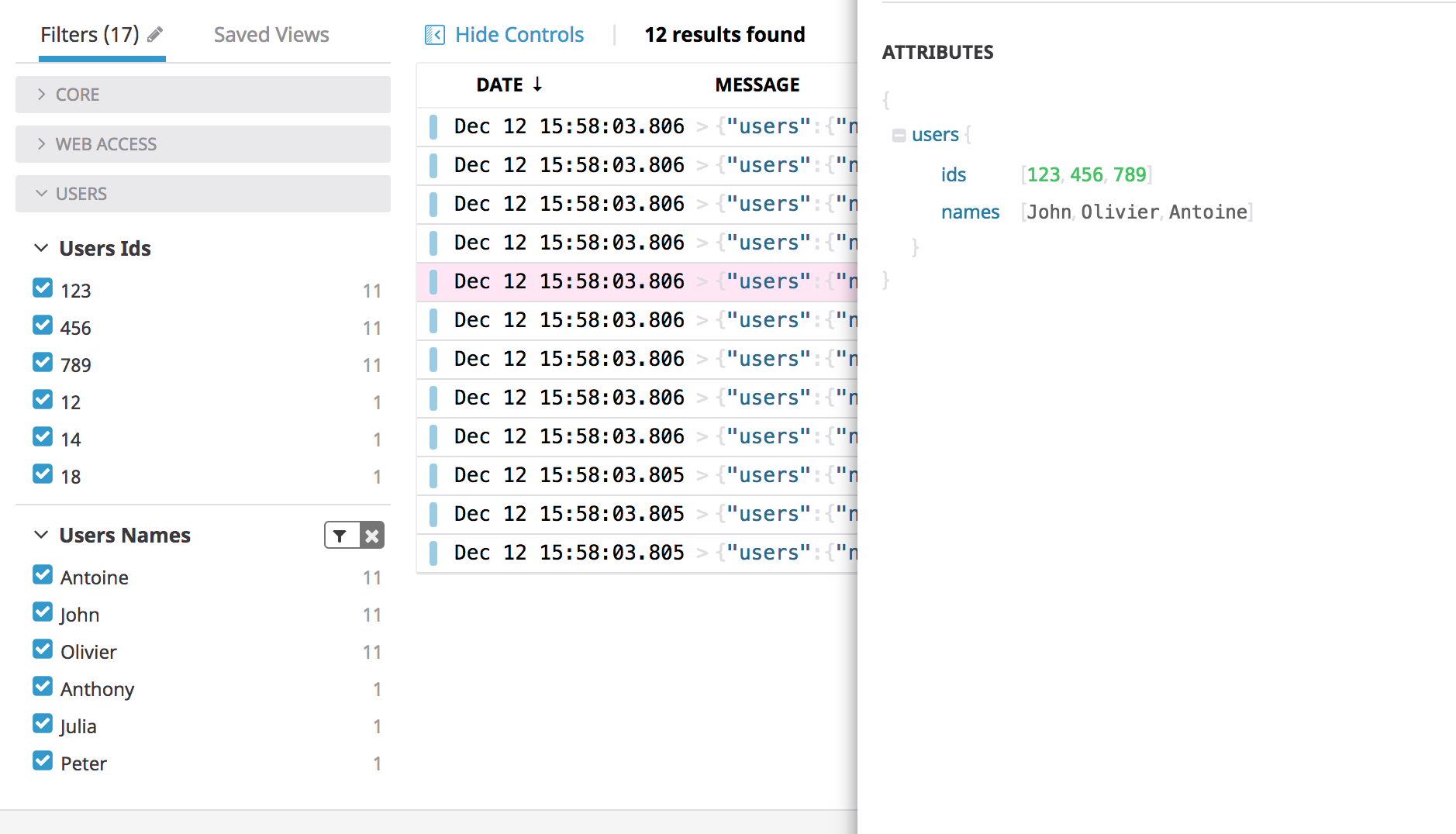
Arrays
In the below example, clicking on the Peter value in the facet returns all the logs that contains a users.names attribute, whose value is either Peter or an array that contains Peter:
Note: Search can also be used on non-faceted array attributes using an equivalent syntax.
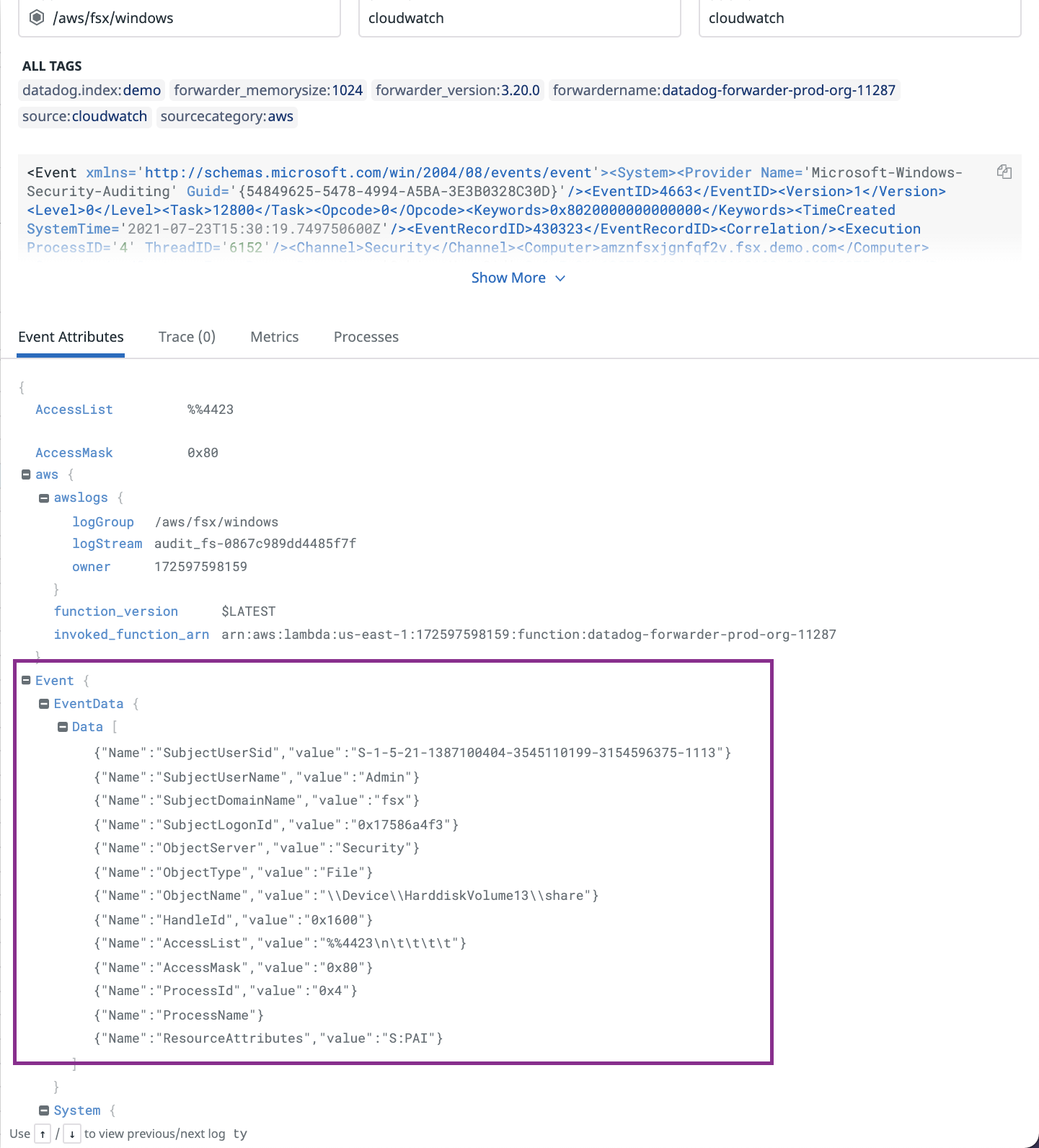
In the following example, CloudWatch logs for Windows contain an array of JSON objects under @Event.EventData.Data. You cannot create a facet on array of JSON objects, but you can search using the following syntax.
@Event.EventData.Data.Name:ObjectServermatches all logs with the keyNameand valueObjectServer.
Calculated fields
Calculated fields function like log attributes and can be used for search, aggregation, visualization, and defining other calculated fields. Use the # prefix to reference calculated field names.
Saved searches
Saved Views contain your search query, columns, time horizon, and facet.
Further Reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: