- 重要な情報
- はじめに
- 用語集
- Standard Attributes
- ガイド
- インテグレーション
- エージェント
- OpenTelemetry
- 開発者
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- DDSQL Reference
- モバイルアプリケーション
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft
- アプリ内
- ダッシュボード
- ノートブック
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Watchdog
- アラート設定
- メトリクス
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- インフラストラクチャー
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- ユニバーサル サービス モニタリング
- Hosts
- コンテナ
- Processes
- サーバーレス
- ネットワークモニタリング
- Cloud Cost
- アプリケーションパフォーマンス
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- データベース モニタリング
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- RUM & セッションリプレイ
- Synthetic モニタリング
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility (CI/CDの可視化)
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Visibility
- Code Coverage
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- セキュリティ
- セキュリティの概要
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- クラウド セキュリティ マネジメント
- Application Security Management
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- ログ管理
- Observability Pipelines(観測データの制御)
- ログ管理
- CloudPrem
- 管理
Go 向け Test Impact Analysis
This product is not supported for your selected Datadog site. ().
互換性
Test Impact Analysis は、orchestrion >= 0.9.4 + dd-trace-go >= 1.70.0 でのみサポートされています。
セットアップ
テスト最適化
Test Impact Analysis を設定する前に、Go 向け Test Optimization をセットアップしてください。Datadog Agent 経由でデータを送信する場合は、v6.40 以降または v7.40 以降を使用してください。
Activate Test Impact Analysis for the test service
You, or a user in your organization with the Intelligent Test Runner Activation (intelligent_test_runner_activation_write) permission, must activate Test Impact Analysis on the Test Service Settings page.
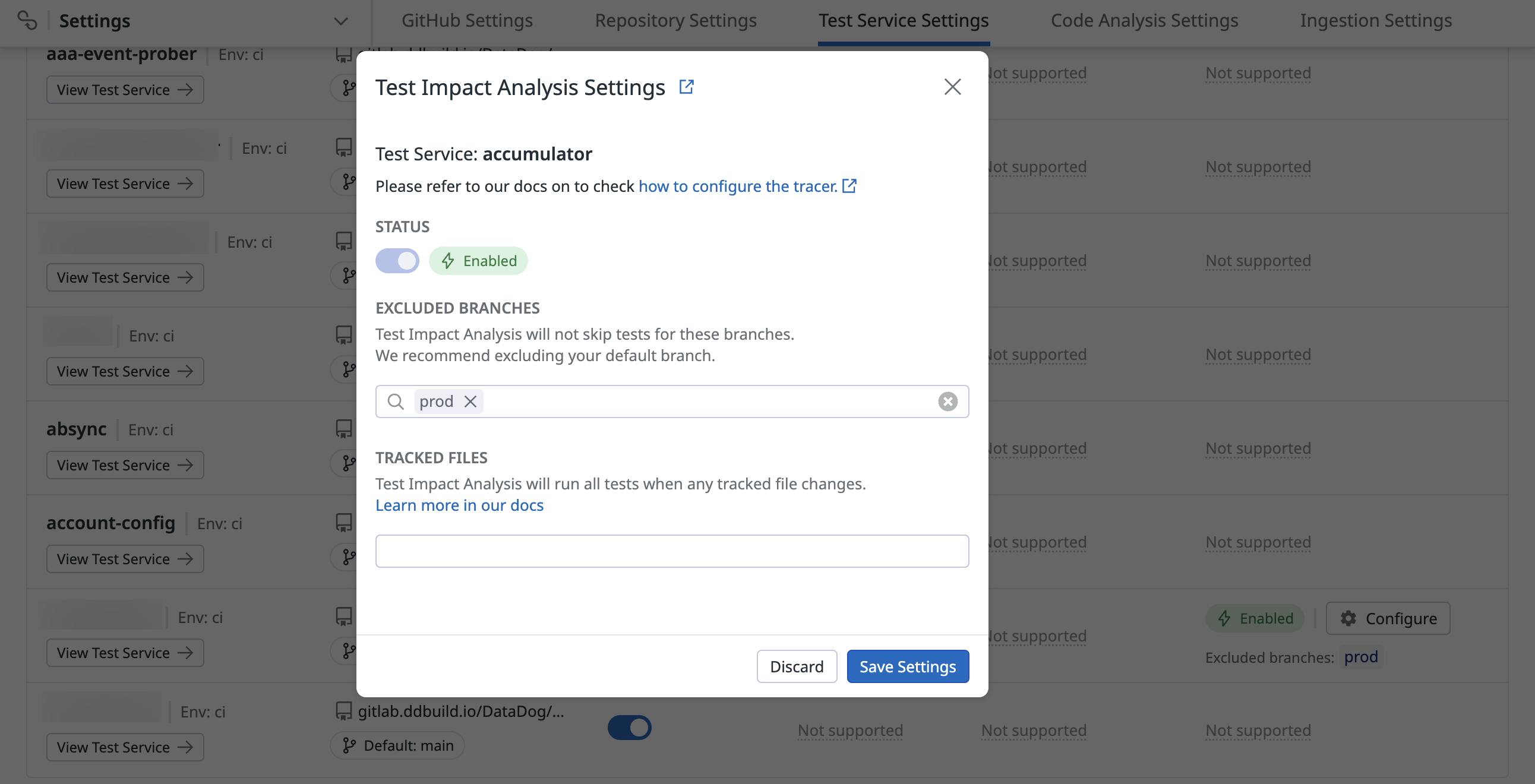
Run tests with Test Impact Analysis enabled
セットアップが完了したら、go test に以下のコード カバレッジ オプションを指定してテストを実行します。
orchestrion go test ./... -cover -covermode=count -coverpkg ./...
-cover: Test Impact Analysis 機能は、Go に組み込まれたコード カバレッジ プロセッサーを使用するため、go testコマンドでコード カバレッジの収集を有効にする必要があります。-covermode:countまたはatomicのいずれかを指定する必要があります。setはサポートされていないため、値にsetを指定すると Test Impact Analysis が無効になります。-coverpkg: 各テストのコード カバレッジ分析は、テスト対象のパッケージだけでなく、すべての依存パッケージにも適用されるように構成する必要があります。こうすることで、依存関係が変更された場合に、その変更の影響を受けるテストを特定できます。プロジェクト ルート (go.mod ファイルのあるディレクトリ) でgo testを実行する場合は、ワイルド カードの./...を使用できます。そうでない場合は、すべての依存パッケージをカンマ区切りで手動で列挙する必要があります (pattern1, pattern2, pattern3, ...)。その際は、go list ./...コマンドで、すべてのパッケージ名を取得できます。
-coverpkg の値が正しくない場合、Test Impact Analysis はテスト カバレッジを正しく追跡できなくなります。
特定のテストに対するスキップの無効化
You can override the Test Impact Analysis behavior and prevent specific tests from being skipped. These tests are referred to as unskippable tests.
テストをスキップできないようにする理由は?
Test Impact Analysis uses code coverage data to determine whether or not tests should be skipped. In some cases, this data may not be sufficient to make this determination.
例:
- テキストファイルからデータを読み込むテスト。
- テスト対象のコード以外の API とやりとりするテスト (リモートの REST API など)。
- Designating tests as unskippable ensures that Test Impact Analysis runs them regardless of coverage data.
Marking tests as unskippable
Individual test case
テスト ケースをスキップ不可にするには、テスト ケースに //dd:test.unskippable コメントを追加します。
import (
"testing"
)
//dd:test.unskippable
func TestMyCustomTest(t *testing.T) {
...
}
テストスイート
テスト スイートをスキップ不可にするには、ファイルの先頭に //dd:suite.unskippable コメントを追加します。
If a suite is marked as unskippable, none of the test cases from that suite can be skipped by Test Impact Analysis.
import (
"testing"
)
//dd:suite.unskippable
func TestMyCustomTest(t *testing.T) {
...
}
func TestMyCustomTest2(t *testing.T) {
...
}
その他の参考資料
お役に立つドキュメント、リンクや記事:
