- 重要な情報
- はじめに
- 用語集
- Standard Attributes
- ガイド
- インテグレーション
- エージェント
- OpenTelemetry
- 開発者
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- DDSQL Reference
- モバイルアプリケーション
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft
- アプリ内
- ダッシュボード
- ノートブック
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Watchdog
- アラート設定
- メトリクス
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- インフラストラクチャー
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- ユニバーサル サービス モニタリング
- Hosts
- コンテナ
- Processes
- サーバーレス
- ネットワークモニタリング
- Cloud Cost
- アプリケーションパフォーマンス
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- データベース モニタリング
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- RUM & セッションリプレイ
- Synthetic モニタリング
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility (CI/CDの可視化)
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Visibility
- Code Coverage
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- セキュリティ
- セキュリティの概要
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- クラウド セキュリティ マネジメント
- Application Security Management
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- ログ管理
- Observability Pipelines(観測データの制御)
- ログ管理
- CloudPrem
- 管理
AWS Step Functions のサーバーレスモニタリングのトラブルシューティング
トレースが表示されない
Step Function がすべてのログを送信するように構成されていることを検証する
- AWS コンソール上の Step Function で
DD_TRACE_ENABLEDタグがtrueに設定されていることを確認してください。 - AWS コンソールで、Step Function の logging タブを開きます。Log level が
ALLに設定され、Include execution data が選択されていることを確認します。 - CloudWatch のロググループ (logging タブにもある) に、同じリージョンの Datadog Lambda Forwarder へのサブスクリプションフィルターがあることを確認します。
ログが Datadog に正常に転送されることを検証する
- Datadog Lambda Forwarder のエラーメッセージを確認します。API キーと Datadog サイトが正しく設定されていることを確認します。
- 環境変数
DD_LOG_LEVELをdebugに設定することで、Datadog Lambda Forwarder でDEBUGログを有効にします。
ログが Live Search で検索でき、DD_TRACE_ENABLED タグが付与されていることを確認する
Datadog の Logs > Log Stream に移動し、source:stepfunction を検索します。ステートマシンを数回トリガーする必要があるかもしれません。古いバージョンから Datadog Lambda Forwarder をアップグレードする場合は、アップグレード後に Forwarder に DD_FETCH_STEP_FUNCTIONS_TAGS タグが true と設定されているか確認してください。もしこのタグがない場合は、Forwarder が正しくアップグレードされていない可能性があります。
Forwarder とステートマシンのタグが前のステップで正しく設定されていれば、ログには DD_TRACE_ENABLED:true タグが付与されます。
Step Function が最新バージョンを使用していることを確認する
- AWS は Step Function API を更新したり、新しいバージョンの Step Function 定義を導入したりします。古いバージョンではログの形式や動作に想定外の問題が起こる可能性があります。
- また、ログの転送に不整合が起きないよう、Datadog Lambda Forwarder も最新バージョンを使用することが推奨されます。
カスタムログパイプラインの使用には注意
- カスタムログパイプラインはログ処理に柔軟性を提供しますが、ログ形式を大きく変更すると、ログがパースされなくなったり認識されなくなったりするなどの問題が発生する可能性があります。
- Step Function のログ構造を JSON 形式が変わるほど大幅に変更することは避けてください。
Lambda のトレースが Step Function のトレースにマージされない
- Lambda のトレースと Step Function のトレースの両方が Datadog で確認できることを検証します。
- トレースのマージガイドに従って正しいレイヤーやトレーサーバージョンを使用していることを確認し、ステートマシン定義で Lambda ステップがインストルメントされていることも確認します。
- Step Function を一度実行し、Lambda ステップの
TaskScheduledイベントログに Step Function のコンテキストオブジェクトのデータを含むペイロードがあるか確認してください。 - Lambda に
DD_TRACE_EXTRACTOR環境変数が設定されている場合、そのトレースはマージできません。
aws.stepfunctions の root スパンは見えるが、ステップスパンが見えない
ステートマシンのロギングで Include execution data オプションを有効にしてください。このオプションを有効にすると、ログ実行入力、ステート間で渡されたデータ、および実行出力がログに記録されます。Datadog バックエンドは、ログを使用してこれらのステップスパンを自動的に構築します。
トレースが断続的に欠落する
トレースを検索するときは、右上の Live Search オプションを選択してください。Live Search にトレースが表示される場合、リテンションフィルターに “@trace_type:stepfunctions” を追加し、望むリテンション率を設定します。デバッグのために、Datadog ではリテンション率を 100% に設定することを推奨しています。デバッグが終わったらフィルターを無効にできます。
トレースにいくつかのステップスパンがない
- Lambda、DynamoDB、StepFunction、その他ほとんどの AWS サービスのアクションはサポートされています。
Wait、Choice、Success、Fail、Pass、Inline MapState、Parallelはサポート対象で、Distributed MapStateは限定的にサポートされています。
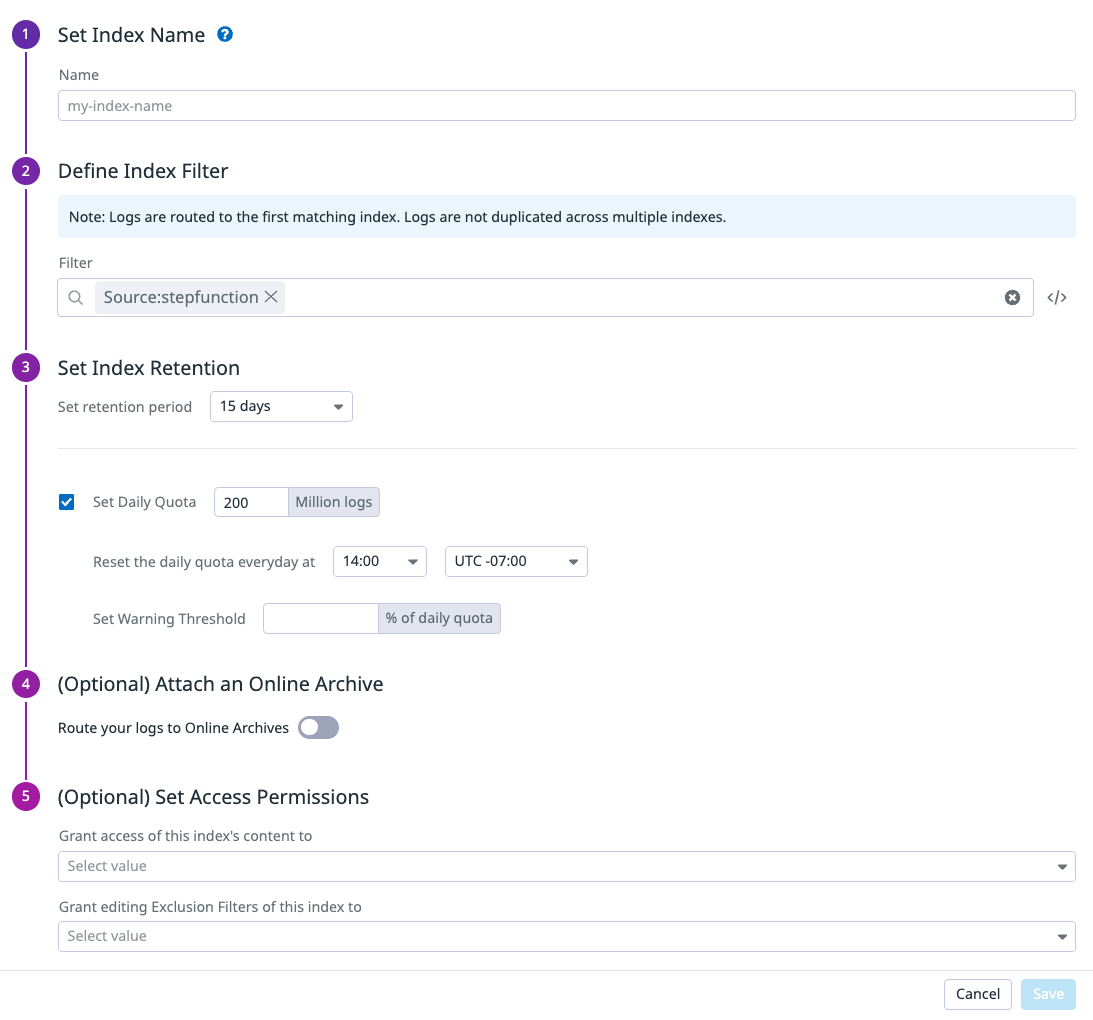
履歴ログを検索する
過去ログを検索できるようにするには、転送されたログに一時的なインデックスを追加します。Datadog で Logs の Indexes タブを開き、右上の New Index ボタンをクリックします。
名前を決め、インデックスフィルターを Source:stepfunction に設定し、他はデフォルト値のままにして保存します。
組織が低い上限を持つ既存のすべてを網羅するインデックスを持っている場合、新しいインデックスを一番上に配置します。
注: トレースの取得には必ずしもログのインデックス化は必要ではありませんし、追加コストが発生する可能性があります。特定の問題をトラブルシュートする場合、ログを一時的にインデックスへ送信してデバッグし、その後でインデックスを削除する方法もあります。詳細は Indexes を参照してください。
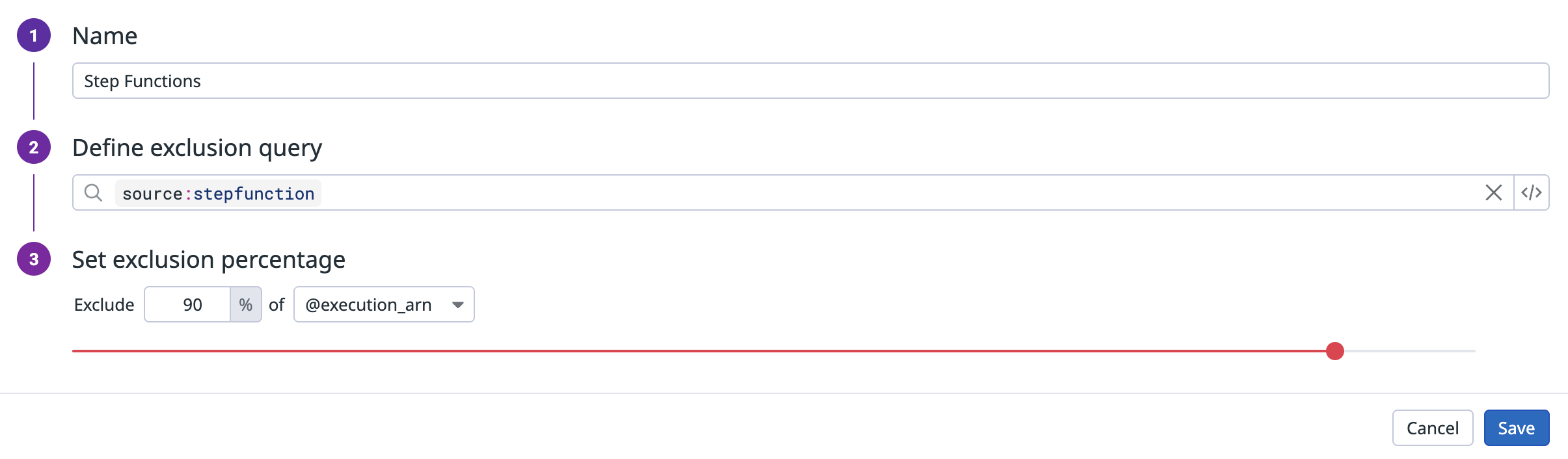
実行内のログが不足している
除外フィルターを使い、特定の execution_arn を含むログの一定割合を除外できます。除外フィルターを使用してもトレーシングには影響ありません。
以下の例では、フィルターが @execution_arn を 90% 除外します。
Datadog Lambda Forwarder をカスタマイズしてデプロイする場合
Datadog Lambda Forwarder を独自にカスタマイズしてデプロイしている場合、Step Functions のトレースを有効にするためのデバッグに役立つヒントを以下に示します。
- Forwarder で環境変数
DD_FETCH_STEP_FUNCTIONS_TAGSをtrueに設定してください。 - Datadog バックエンドで Step Functions トレースを生成するには、Datadog-Forwarder のレイヤーバージョンが 31 より上である必要があります。このバージョンでは、
DD_TRACE_ENABLEDを含むステートマシンタグを取得できます。 - v3.121.0 以降では、Forwarder レベルで
DD_STEP_FUNCTIONS_TRACE_ENABLEDタグを設定し、その Forwarder を使用するすべての Step Functions に対してトレーシングを有効にできます。 - Forwarder の IAM ロールには
tags:getResourcesの権限が必要です。 - ステートマシンの CloudWatch ロググループに、Datadog Forwarder へのサブスクリプションフィルターを設定してください。
- ログが Datadog バックエンドに到達しているかを確認するには、Log Explorer ページを開き、
source:stepfunctionをLive検索のタイムフレームで検索します (Datadog のログ受け取りに入っているすべてのログが表示されます)。ログが一切見当たらない場合は、Datadog Forwarder 上に誤った/無効な API キーなどのエラーログがないか確認してください。環境変数DD_LOG_LEVELにDEBUGを設定することで、Forwarder の問題をデバッグできます。もし Step Functions のログが表示されたら、それらのログにdd_trace_enable:trueタグ (すべてのタグは正規化されます) が含まれていることを確認し、数分後にはログに関連付けられた Step Function トレースが表示されるはずです。