- 重要な情報
- はじめに
- 用語集
- Standard Attributes
- ガイド
- インテグレーション
- エージェント
- OpenTelemetry
- 開発者
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- DDSQL Reference
- モバイルアプリケーション
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft
- アプリ内
- ダッシュボード
- ノートブック
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Watchdog
- アラート設定
- メトリクス
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- インフラストラクチャー
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- ユニバーサル サービス モニタリング
- Hosts
- コンテナ
- Processes
- サーバーレス
- ネットワークモニタリング
- Cloud Cost
- アプリケーションパフォーマンス
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- データベース モニタリング
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- RUM & セッションリプレイ
- Synthetic モニタリング
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility (CI/CDの可視化)
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Visibility
- Code Coverage
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- セキュリティ
- セキュリティの概要
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- クラウド セキュリティ マネジメント
- Application Security Management
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- ログ管理
- Observability Pipelines(観測データの制御)
- ログ管理
- CloudPrem
- 管理
Analysis Features
このページは日本語には対応しておりません。随時翻訳に取り組んでいます。
翻訳に関してご質問やご意見ございましたら、お気軽にご連絡ください。
翻訳に関してご質問やご意見ございましたら、お気軽にご連絡ください。
Notebooks Advanced Analysis is not available in the Datadog site ().
Advanced Data Sources
If you want to query data sources not yet available, use this form to submit your request.
Request AccessOverview
The analysis feature in Notebooks allows you to perform advanced analysis on your Datadog data. You can join multiple datasets, chain queries, and transform your data using either predefined transformations or SQL, while retaining the full capabilities that Notebooks provide.
Notebooks are collaborative text editors that allow you to embed Datadog graphs directly into your documents. While this is ideal for exploration and storytelling, deeper investigations might require more advanced control over data queries. The analysis features enable you to run queries that help you:
- Chain queries such as aggregating existing aggregated data or joining two sets of aggregating data.
- Join data across multiple log sources and other datasets.
- Perform advanced parsing, extract data, and add calculated fields at query time.
- Visualize transformed datasets with graphs.
Adding data to your notebook
To run complex queries in a notebook, first add a Data Source cell. There are two ways to do this:
From a notebook:
- Type
/datasourceand press Enter, or click the Data Source tile at the bottom of the page. - Type or select your desired data source from the drop down menu and press Enter.
Note: if there is a data source you want that is not available, request it here. - Enter your query. Reserved attributes from the filtered logs are automatically added as columns.
From the Log Explorer:
- Enter your query in the Log Explorer.
- Click Analyze in Notebooks.
- Check the Use as a computational data source box and select the notebook you want to use.
- A data source cell is added to the selected notebook with the same query you entered in the Log Explorer. By default, the columns shown in the Log Explorer are included in the data source cell.
Configuring a data source cell
After adding a data source cell to a notebook, you can continue modifying it to structure the data to suit your analysis needs.
Change the time frame for the data
By default, data source cells created from Notebooks use the notebook’s global time frame. Data source cells created from the Log Explorer use a local time fixed to the time frame at the time of export.
You can switch any data source cell between a local or global time frame using the toggle button in the top right corner of the cell.
Filter the data source
Regardless of how you create the data source cell, you can modify the query using the search bar. Any changes to the query automatically re-run the data source cell and any downstream cells, updating the preview of the data.
Add or modify a column
You can add or modify columns in your data source cell. There are two ways to adjust the columns:
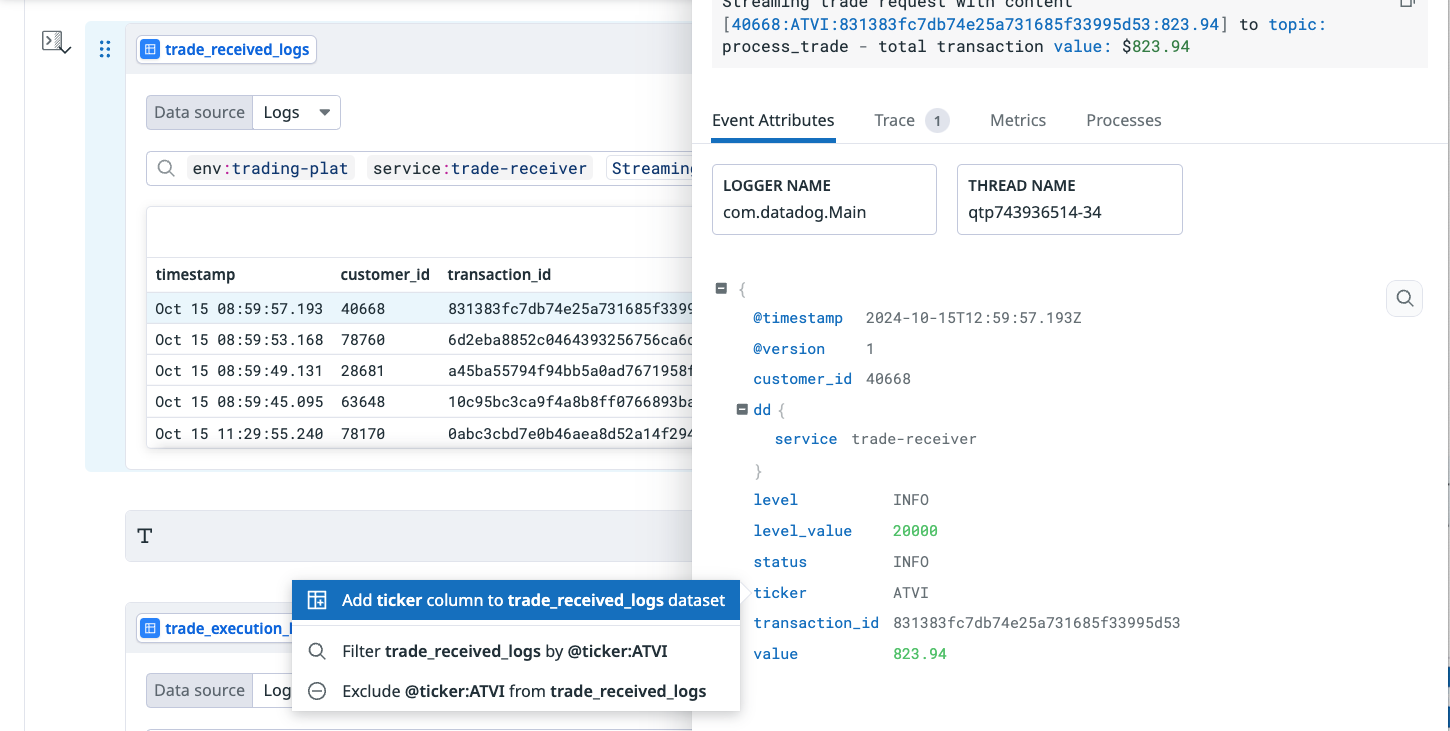
- In the preview section, click columns to search through available attributes for your data source.
- In the preview, click on a row to open the detail side panel. Click the attribute you want to add as a column, and from the pop up option, select Add “@your_column” to your “@your_datasource” dataset.
Calculated fields queries
You can take existing Log Explorer queries that include Calculated Fields and open them in Notebooks. To transfer these queries from the Log Explorer, click More and select Analyze in Notebooks. The Calculated Fields automatically convert into a Transformation cell.
You can also create Calculated Fields directly within a notebook to define a computed field from existing data sources. These fields can be reused in subsequent analysis:
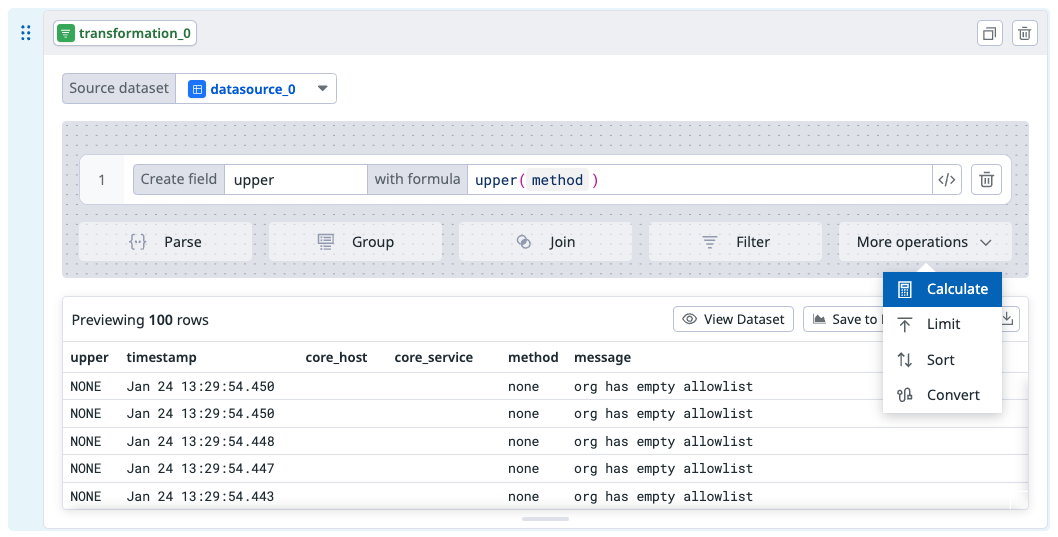
- Open a Workspace with a data source.
- Add a Transformation cell.
- Click More operations.
- Select Calculate.
Transforming and analyzing data
You can add various cell types to enhance your analysis capabilities. These cells enable you to include additional data sources, such as reference tables, RUM, or spans. Use SQL to join, transform, correlate, and visualize your data effectively. One of the key benefits of this approach is that cells that depend on other cells are automatically updated whenever a dependency changes, ensuring your analysis always reflects the most current data.
Transformation cell
Add a transformation cell to filter, group, join, or extract data defined in a data source cell.
- Type
/transformationand press Enter, or click on the transform dataset tile at the bottom of the page. - Select the data source you want to transform in the source dataset dropdown menu.
After adding the transformation cell, you can add any number of transformation operations inside the cell. Choose an operation from the list of supported transformations:
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| Parse | Enter grok syntax to extract data into a separate column. In the “from” dropdown menu, select the column the data is getting extracted from. |
| Group | Select what you want to group the data by in the dropdown menus. |
| Join | Select the type of join, the dataset to join against, and the fields to join on. |
| Filter | Add a filter query for the dataset. |
| Calculate | Add a name for the field and the function formula, using the calculated field formulas. |
| Limit | Enter the number of rows of the dataset you want to display. |
| Sort | Select the sort order and column to sort on. |
| Convert | Allows you to convert a column into a different type. Select the column and the column type to be converted. |
Analysis cell
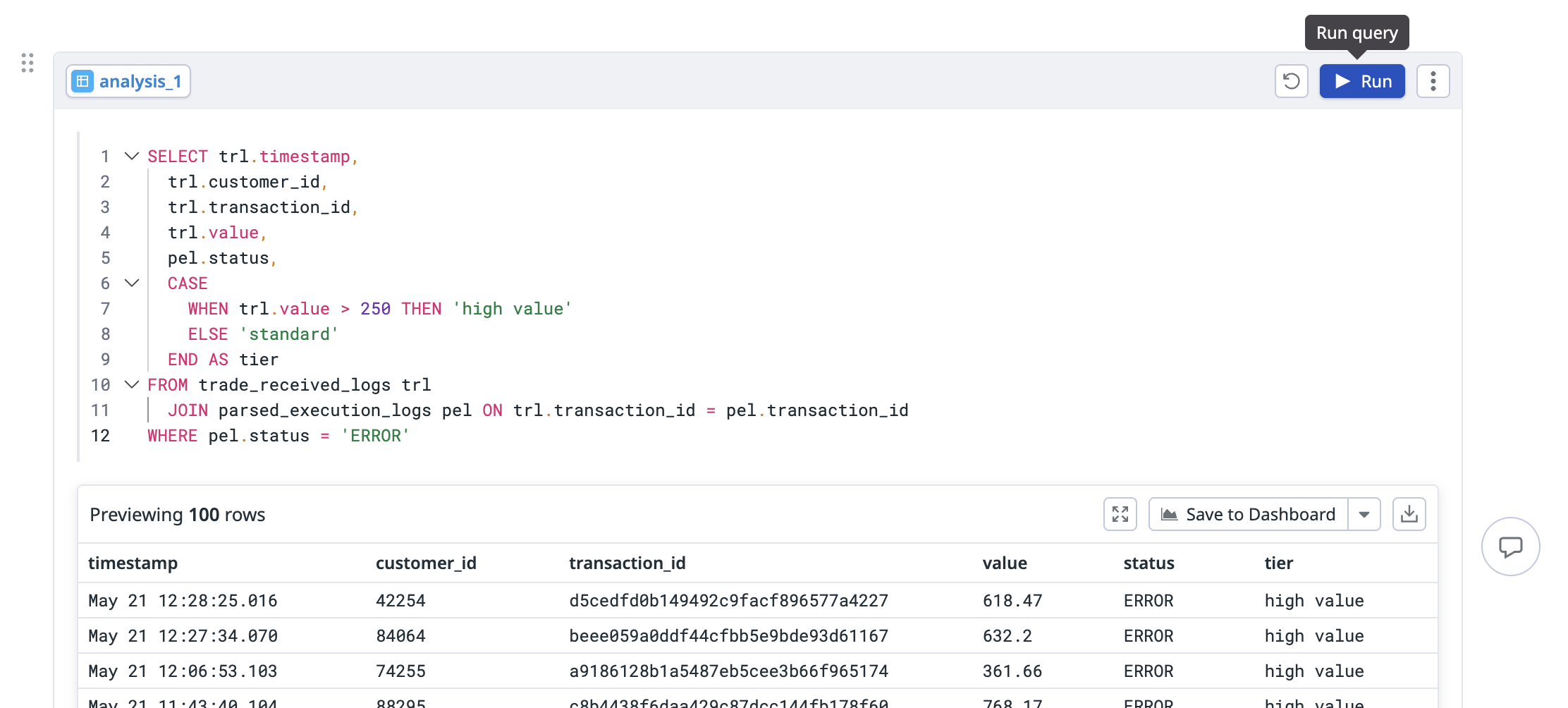
You can also transform your data using SQL by adding an analysis cell to your notebook.
- Type
/sqlor/analysisand press Enter, or click the SQL Query tile at the bottom of the page. - In the source dataset dropdown, select the data source you want to transform.
- Write your SQL query. For supported SQL syntax, see the DDSQL Reference.
- Click Run in the top-right corner of the analysis cell to execute your query.
Visualizing transformed data
You can graph the data you’ve transformed using analysis cells inside a notebook, customizing the visualization with filters, aggregations, and appearance settings.
To graph your data:
- Type
/graphand press Enter, or click the graph dataset tile at the bottom of the page. - Type or select your desired data source from the drop down menu and press Enter.
- Select your visualization type from the graph menu and press Enter.
Viewing and exporting data
For any analysis cell that includes a dataset preview, you can view the full 100-row preview by clicking the View dataset button.
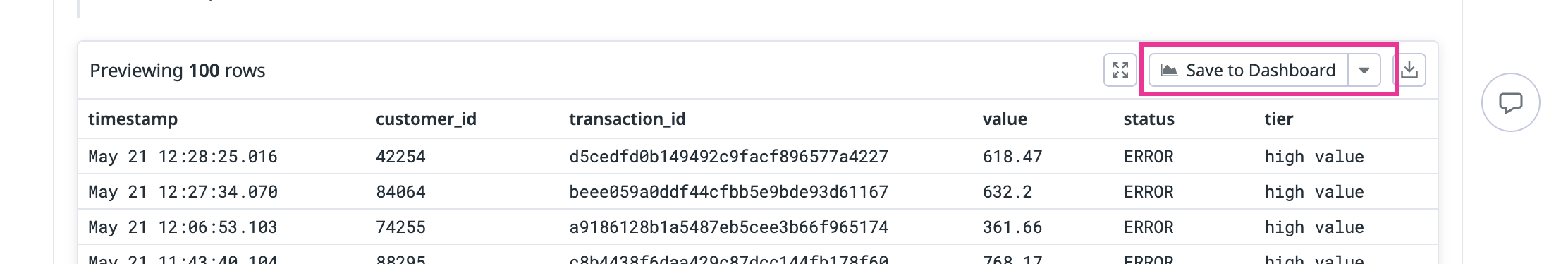
Export your query to a dashboard
You can save the results of any analysis cell to a dashboard by clicking Save to Dashboard and selecting an existing dashboard, or create a new one. Although this creates a sync between your notebook cell and the exported dashboard graph, changes to the query in your notebook do not automatically update the dashboard.
If you update the published cell or any upstream cells, a badge appears in the upper-right corner of the cell indicating unpublished changes. After you publish those changes, the updates sync to all dashboards where the query is used.
Note: By default, the dataset is tied to the global time frame of the dashboard, not to the time frame of the notebook. However, you have the ability to set a custom time frame on the dashboard widget.
Download dataset as a CSV
You can download data from cells for use in external tools or further processing outside of Datadog.
To download your dataset as a CSV file:
- Navigate to any analysis cell that contains a dataset.
- Click the download icon in the top-right corner of the cell.
- Select the number of rows you want to export (up to the maximum available).
- The CSV file automatically downloads to your computer.
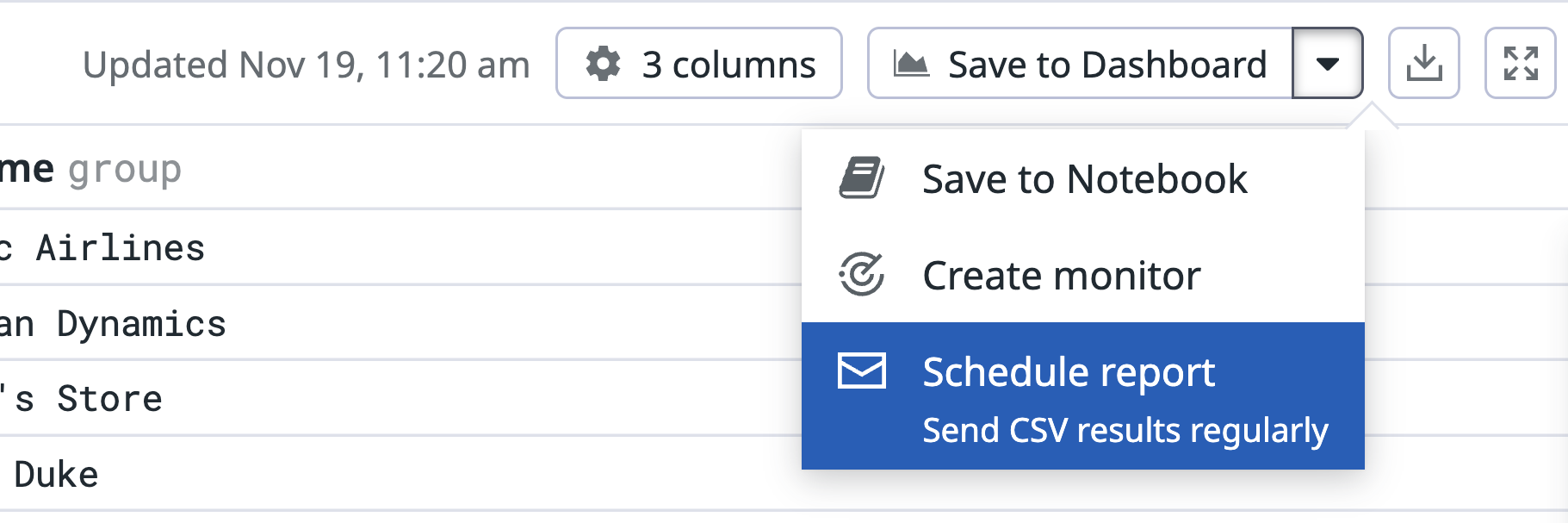
Schedule a CSV report
With scheduled reports, you can automatically receive query results from notebook analysis cells by email or Slack.
To schedule a report on an analysis cell:
Open the dropdown next to Save to Dashboard and select Schedule report.
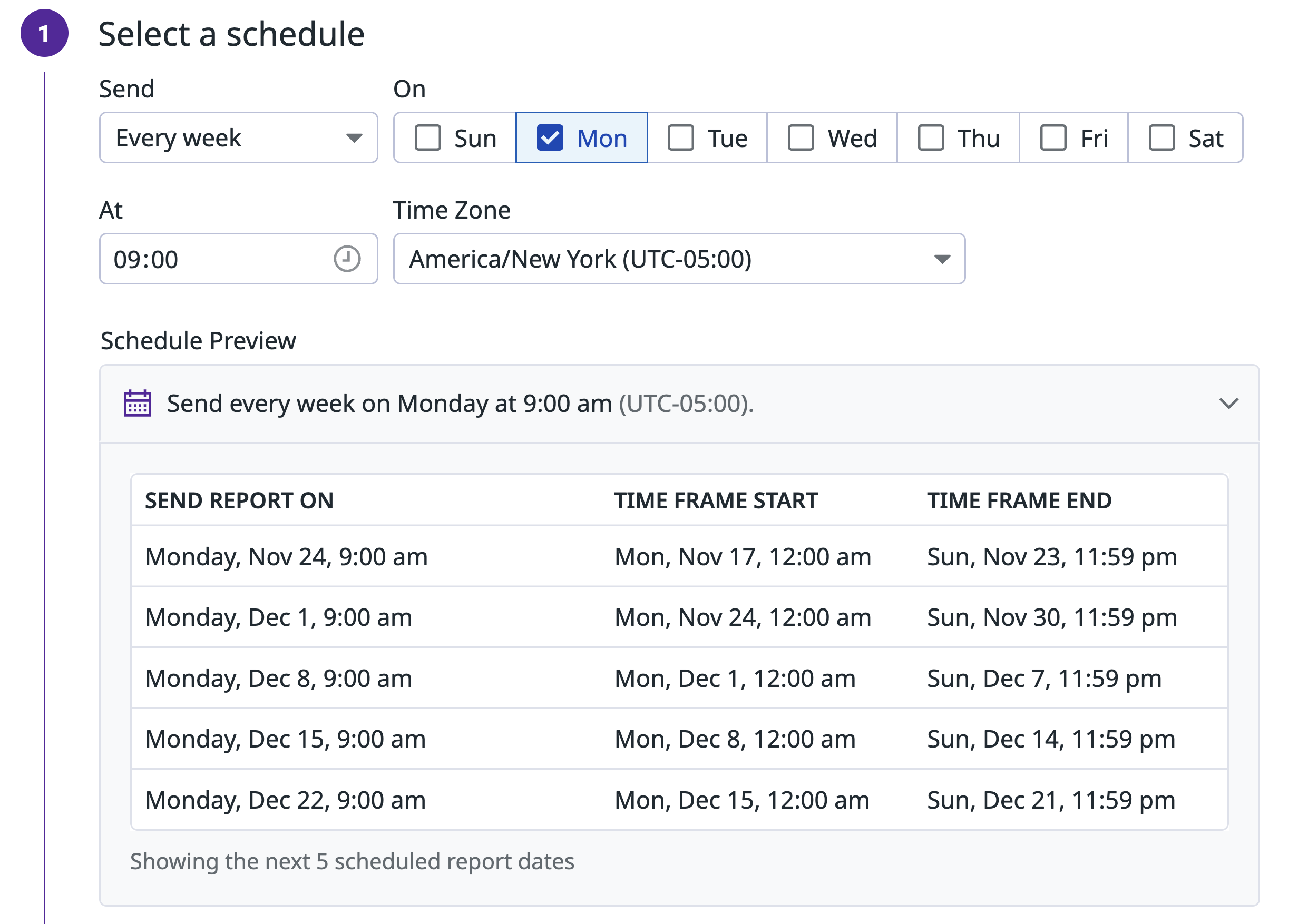
In the modal, select a schedule to configure when and how often the report is sent.
Enter a report name and select a time frame to define the data included in the report.
Note: If the analysis cell has not yet been published as a dataset, you can specify the name of the dataset created when the report is scheduled.
Add email recipients.
- The email associated with your Datadog account is included automatically. To remove it, hover over your email and click the trash icon.
- To preview the report before saving the schedule, click Send Test Email.
Note: Only Enterprise and Pro accounts can send reports to email addresses that aren’t associated with registered Datadog users.
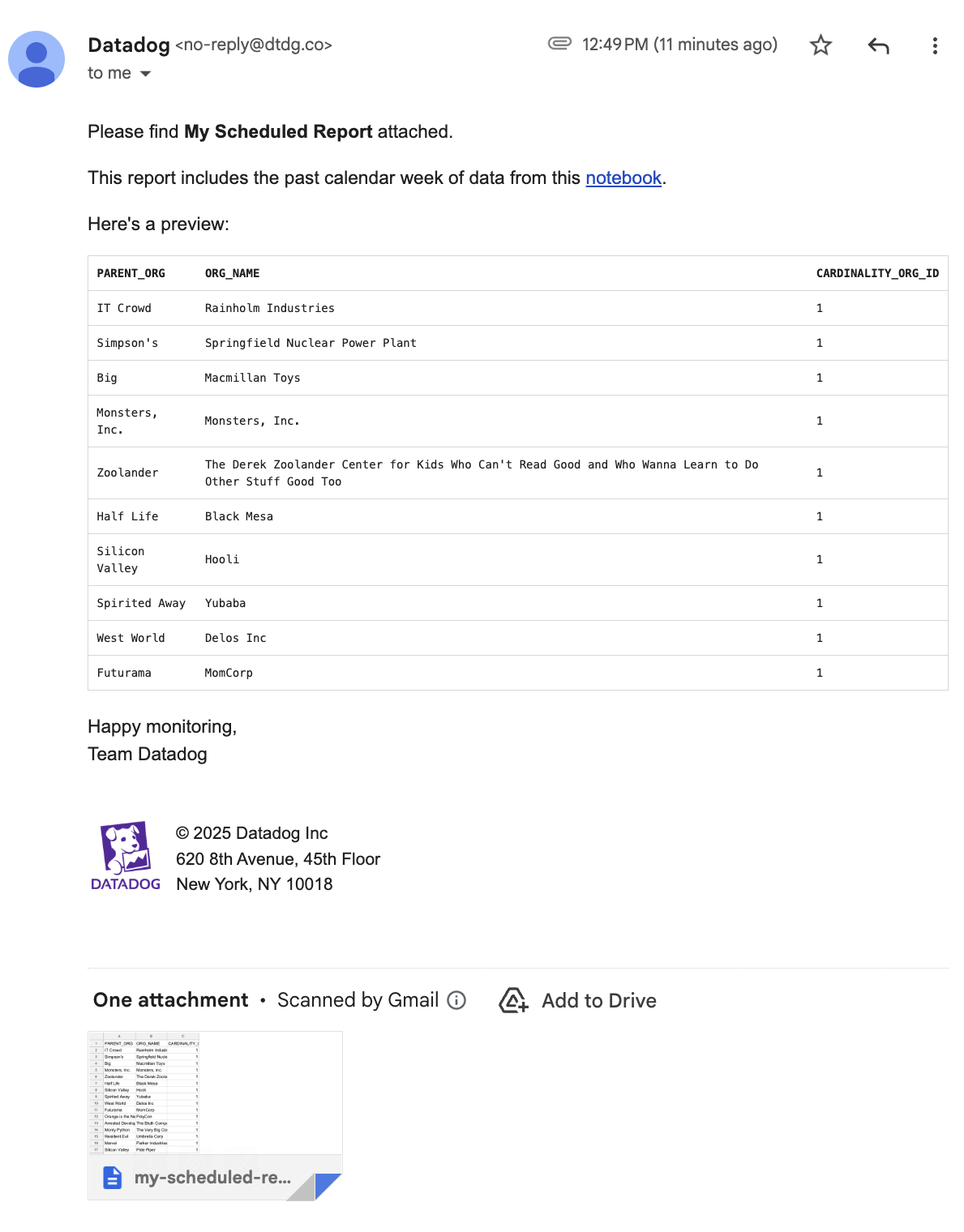
Example report email:
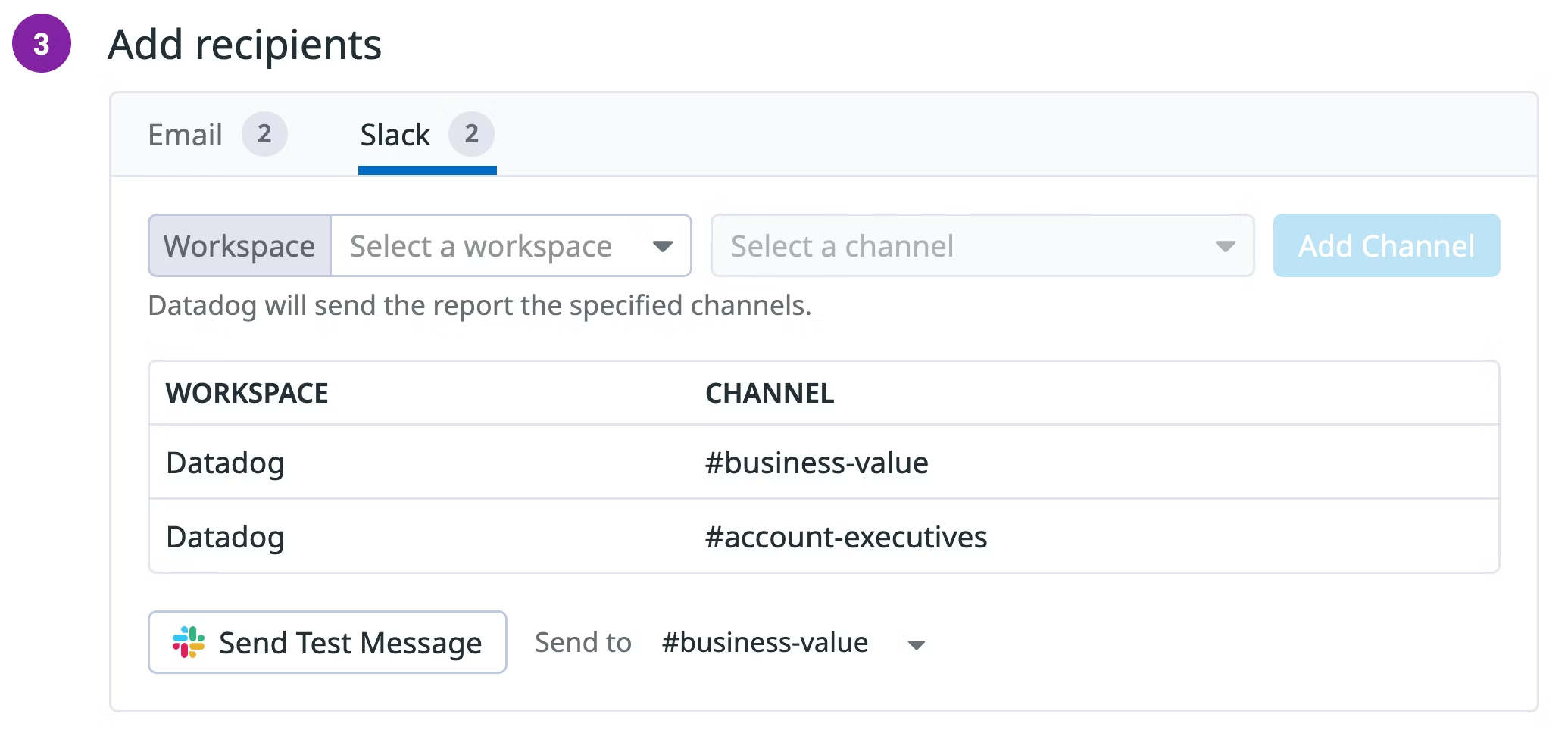
Add Slack recipients.
- Click on the Slack tab, then choose a workspace and channel.
- If no workspaces appear, verify that the Datadog Slack Integration is installed.
- Public channels are listed automatically. To send to a private channel, invite the Datadog Slack bot to your channel.
- To preview the message, add a channel and click Send Test Message.
- Click on the Slack tab, then choose a workspace and channel.
Save your schedule.
You can view, search, edit, and delete existing report schedules from the Reports tab:
Note: To schedule reports and view other users’ schedules, users need the CSV Report Schedules Write permission. To edit other users’ schedules, users need the CSV Report Schedules Manage permission. These permissions can be granted by a user with the Org Management permission.