- 重要な情報
- はじめに
- 用語集
- Standard Attributes
- ガイド
- インテグレーション
- エージェント
- OpenTelemetry
- 開発者
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- DDSQL Reference
- モバイルアプリケーション
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft
- アプリ内
- ダッシュボード
- ノートブック
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Watchdog
- アラート設定
- メトリクス
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- インフラストラクチャー
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- ユニバーサル サービス モニタリング
- Hosts
- コンテナ
- Processes
- サーバーレス
- ネットワークモニタリング
- Cloud Cost
- アプリケーションパフォーマンス
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- データベース モニタリング
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- RUM & セッションリプレイ
- Synthetic モニタリング
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility (CI/CDの可視化)
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Visibility
- Code Coverage
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- セキュリティ
- セキュリティの概要
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- クラウド セキュリティ マネジメント
- Application Security Management
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- ログ管理
- Observability Pipelines(観測データの制御)
- ログ管理
- CloudPrem
- 管理
SQL Server
Supported OS
インテグレーションバージョン22.7.0
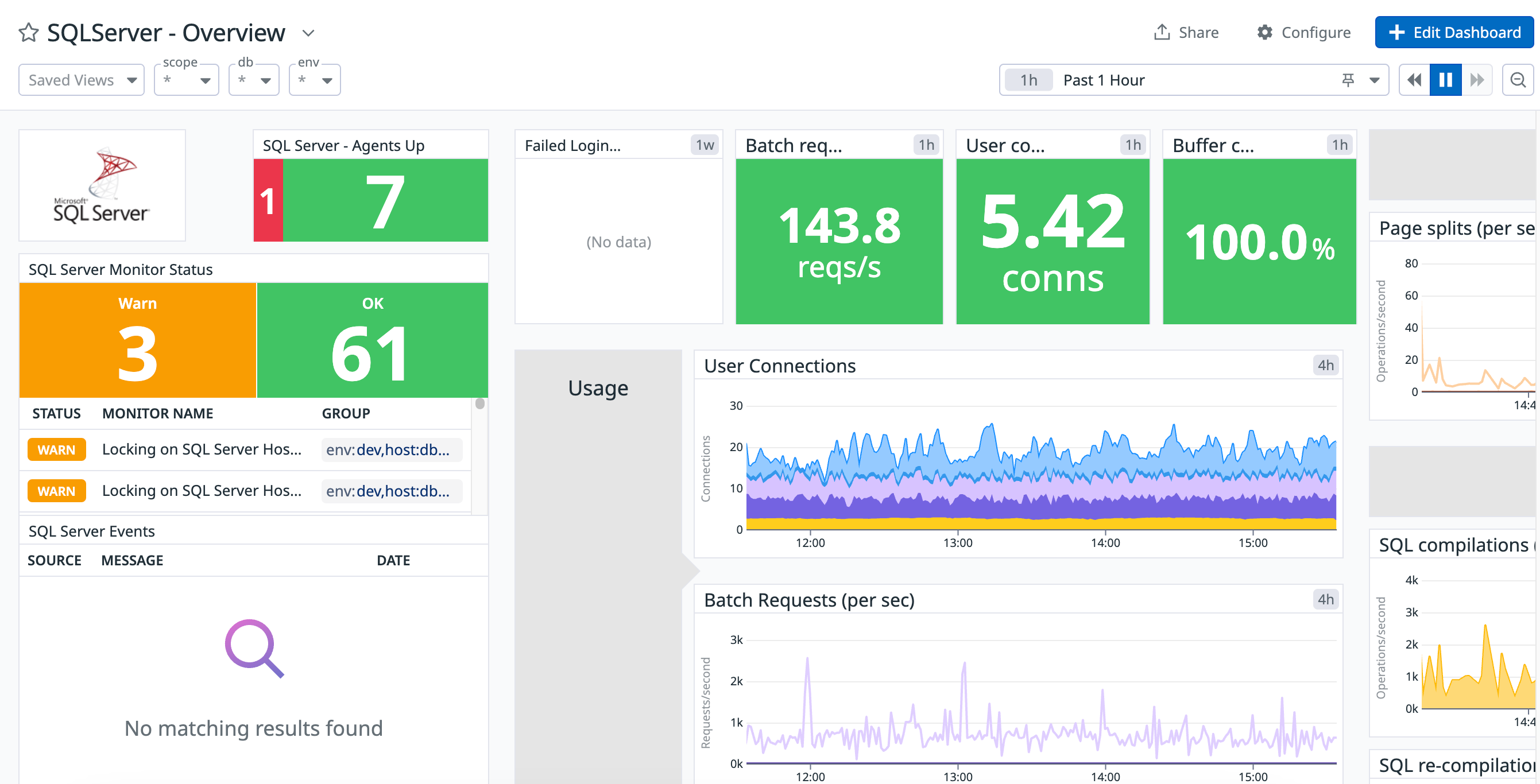
概要
SQL Server インテグレーションを使用して、SQL Server インスタンスのパフォーマンスを追跡できます。ユーザー接続の数、SQL のコンパイル率などのメトリクスを収集できます。
データベースモニタリング (DBM) を有効にすると、クエリのパフォーマンスとデータベースの健全性について詳細なインサイトを取得できます。標準のインテグレーションに加え、Datadog DBM では、クエリレベルのメトリクス、リアルタイムおよび過去のクエリスナップショット、待機イベントの分析情報、データベースの負荷、クエリ実行計画、ブロッキングを引き起こしているクエリについてのインサイトが提供されます。
SQL Server 2012、2014、2016、2017、2019、2022 がサポートされています。
セットアップ
このページでは、SQL Server Agent の標準インテグレーションについて説明します。SQL Server のデータベースモニタリング製品をお求めの場合は、Datadog データベースモニタリングをご覧ください。
インストール
SQL Server チェックは Datadog Agent パッケージに含まれています。SQL Server インスタンスに追加でインストールする必要はありません。
サーバーのプロパティで “SQL Server and Windows Authentication mode” を有効にして、SQL Server インスタンスが SQL Server 認証をサポートするよう、次のように指定します。
Server Properties -> Security -> SQL Server and Windows Authentication mode
前提条件
注: Database Monitoring for SQL Server をインストールするには、ドキュメントサイトでホスティングソリューションを選択し、手順を確認してください。
SQL Server チェックでサポートされる SQL Server のバージョンは Database Monitoring と同じです。現在サポートされているバージョンは、SQL Server のセットアップページのセルフホストの見出しを参照してください。
標準のインテグレーションを単体でインストールする場合のみ、このガイドの下記の手順に進んでください。
読み取り専用ログインを作成してサーバーに接続します。
CREATE LOGIN datadog WITH PASSWORD = '<PASSWORD>'; USE master; CREATE USER datadog FOR LOGIN datadog; GRANT SELECT on sys.dm_os_performance_counters to datadog; GRANT VIEW SERVER STATE to datadog;データベースごとにファイルサイズのメトリクスを収集するには、作成したユーザー (
datadog) にデータベースへの接続権限アクセスがあることを確認するために、以下を実行します。GRANT CONNECT ANY DATABASE to datadog;(AlwaysOn および
sys.master_filesメトリクスの場合に必要metrics) AlwaysOn およびsys.master_filesメトリクスを収集するには、以下の追加権限を付与します。GRANT VIEW ANY DEFINITION to datadog;
設定
ホスト
ホストで実行中の Agent に対してこのチェックを構成するには
Agent のコンフィギュレーションディレクトリのルートにある
conf.d/フォルダーのsqlserver.d/conf.yamlファイルを編集します。使用可能なすべてのコンフィギュレーションオプションについては、サンプル sqlserver.d/conf.yaml を参照してください。init_config: instances: - host: "<SQL_HOST>,<SQL_PORT>" username: datadog password: "<YOUR_PASSWORD>" connector: adodbapi adoprovider: MSOLEDBSQL19 # Replace with MSOLEDBSQL for versions 18 and previousポートオートディスカバリーを使用する場合は、
SQL_PORTに0を使用します。カスタムクエリを使用して独自のメトリクスを作成する方法など、すべてのオプションの詳細については、チェックコンフィギュレーションの例を参照してください。SQL Server の設定に基づき、サポートされているドライバー を使用してください。
注: また、以下のように指定することで、Windows 認証を使用し、ユーザー名/パスワードを指定しないこともできます:
connection_string: "Trusted_Connection=yes"Agent を再起動します。
Linux
Linux ホスト上で SQL Server インテグレーションを実行するには、以下のような追加の構成設定が必要です。
- ODBC SQL Server ドライバー (Microsoft ODBC ドライバーまたは FreeTDS ドライバー) をインストールします。
odbc.iniファイルとodbcinst.iniファイルを/opt/datadog-agent/embedded/etcフォルダーにコピーします。odbcコネクターを使用し、odbcinst.iniファイルで指定された正しいドライバーを指定するようにconf.yamlファイルを構成します。
ログ収集
Agent バージョン 6.0 以降で利用可能
Datadog Agent で、ログの収集はデフォルトで無効になっています。以下のように、
datadog.yamlファイルでこれを有効にします。logs_enabled: trueSQL Server のログの収集を開始するには、次の構成ブロックを
sqlserver.d/conf.yamlファイルに追加します。logs: - type: file encoding: utf-16-le path: "<LOG_FILE_PATH>" source: sqlserver service: "<SERVICE_NAME>"pathパラメーターとserviceパラメーターの値を環境に合わせて変更してください。使用可能なすべてのコンフィギュレーションオプションの詳細については、sqlserver.d/conf.yaml のサンプルを参照してください。Agent を再起動します。
コンテナ化
コンテナ環境の場合は、オートディスカバリーのインテグレーションテンプレートのガイドを参照して、次のパラメーターを適用してください。
メトリクスの収集
| パラメーター | 値 |
|---|---|
<INTEGRATION_NAME> | sqlserver |
<INIT_CONFIG> | 空白または {} |
<INSTANCE_CONFIG> | {"host": "%%host%%,%%port%%", "username": "datadog", "password": "<UNIQUEPASSWORD>", "connector": "odbc", "driver": "FreeTDS"} |
<UNIQUEPASSWORD> をラベルではなく環境変数として渡す方法について、詳細はオートディスカバリーテンプレート変数を参照してください。
ログ収集
Agent バージョン 6.0 以降で利用可能
Datadog Agent で、ログの収集はデフォルトで無効になっています。有効にする方法については、Kubernetes ログ収集を参照してください。
| パラメーター | 値 |
|---|---|
<LOG_CONFIG> | {"source": "sqlserver", "service": "sqlserver"} |
検証
Agent の status サブコマンドを実行し、Checks セクションの sqlserver を探します。
収集されるデータ
メトリクス
これらのメトリクスのほとんどは、SQL Server の sys.dm_os_performance_counters テーブルにあります。
イベント
SQL Server チェックには、イベントは含まれません。
サービス チェック
トラブルシューティング
ご不明な点は、Datadog のサポートチームまでお問い合わせください。
ARM aarch64 プロセッサで Agent を実行している場合、Agent バージョン 7.48.0 にバンドルされているこのチェックのバージョン 14.0.0 以降、既知の問題があります。Python の依存関係がロードに失敗し、Agent の status サブコマンドを実行すると以下のメッセージが表示されます。
Loading Errors
==============
sqlserver
---------
Core Check Loader:
Check sqlserver not found in Catalog
JMX Check Loader:
check is not a jmx check, or unable to determine if it's so
Python Check Loader:
unable to import module 'sqlserver': No module named 'sqlserver'
この問題は、チェックのバージョン 15.2.0 および Agent のバージョン 7.49.1 以降で修正されています。
