- 重要な情報
- はじめに
- Datadog
- Datadog サイト
- DevSecOps
- AWS Lambda のサーバーレス
- エージェント
- インテグレーション
- コンテナ
- ダッシュボード
- アラート設定
- ログ管理
- トレーシング
- プロファイラー
- タグ
- API
- Service Catalog
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Synthetic モニタリング
- Incident Management
- Database Monitoring
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Learning Center
- Support
- 用語集
- Standard Attributes
- ガイド
- インテグレーション
- エージェント
- OpenTelemetry
- 開発者
- 認可
- DogStatsD
- カスタムチェック
- インテグレーション
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Recommended Monitor
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- サービスのチェック
- IDE インテグレーション
- コミュニティ
- ガイド
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- モバイルアプリケーション
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- アプリ内
- Service Management
- インフラストラクチャー
- アプリケーションパフォーマンス
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- データベース モニタリング
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Digital Experience
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility (CI/CDの可視化)
- CD Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- セキュリティ
- セキュリティの概要
- Cloud SIEM
- クラウド セキュリティ マネジメント
- Application Security Management
- AI Observability
- ログ管理
- Observability Pipelines(観測データの制御)
- ログ管理
- 管理
Amazon RDS
概要
Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) は、クラウドでリレーショナルデータベースのセットアップ、運用、スケーリングに使用される Web サービスです。このインテグレーションを有効にすると、Datadog にすべての RDS メトリクスを表示できます。
注: 環境変数 DD_SITE がコード の外のリージョンに設定されていることを確認するか、または次のようにコードで変数を設定します。
DD_SITE = os.getenv("DD_SITE", default="")
RDS インスタンスを監視するには、Standard、Enhanced、Native の 3 つのオプションがあります。コンフィギュレーションを選択する前に、メトリクスのリスト全体を確認してください。各メトリクスには対応するコンフィギュレーションのラベルが付いているためです。さらに、以下の情報を確認して、各コンフィギュレーションの要件とプリセットダッシュボードの詳細を確認してください。
標準インテグレーションの場合、AWS インテグレーションページの Metric Collection タブで RDS を有効にする必要があります。これにより、ご使用の CloudWatch インテグレーションで利用可能な回数だけ、インスタンスに関するメトリクスを受信できます。すべての RDS エンジンタイプに対応しています。
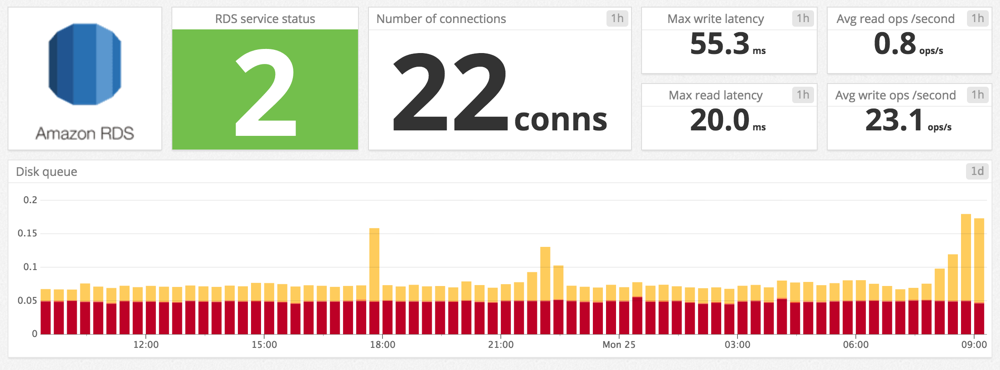
このインテグレーションのプリセットダッシュボードには、接続、レプリケーションラグ、読み取り操作とレイテンシー、コンピューター、RAM、書き込み操作とレイテンシー、ディスクメトリクスのメトリクス情報が含まれています。
拡張インテグレーションの場合、構成を追加する必要があります。また、MySQL、Aurora、MariaDB、SQL Server、Oracle、PostgreSQL エンジンで使用できます。メトリクスを追加することができますが、追加したメトリクスを Datadog に送信するには、AWS Lambda が必要です。粒度が高く、追加のサービスが必要になると AWS の追加料金が発生します。
このインテグレーションのプリセットダッシュボードには、負荷、アップタイム、CPU 使用率、タスク、メモリ、SWAP、ネットワーク受信、ネットワーク送信、プロセスごとに使用される CPU、プロセスごとに使用されるメモリ、ディスク操作、使用されるファイルシステム (pct)、 実行中のタスク、システム CPU 使用率のメトリクス情報が含まれています。
ネイティブデータベースインテグレーションはオプションです。MySQL、Aurora、MariaDB、SQL Server、PostgreSQL の各エンジンタイプで使用できます。RDS とネイティブインテグレーションの両方からメトリクスを取得して照合するには、RDS インスタンスに割り当てる識別子に基づいて、ネイティブインテグレーションで dbinstanceidentifier タグを使用します。RDS インスタンスには自動的にタグが割り当てられます。
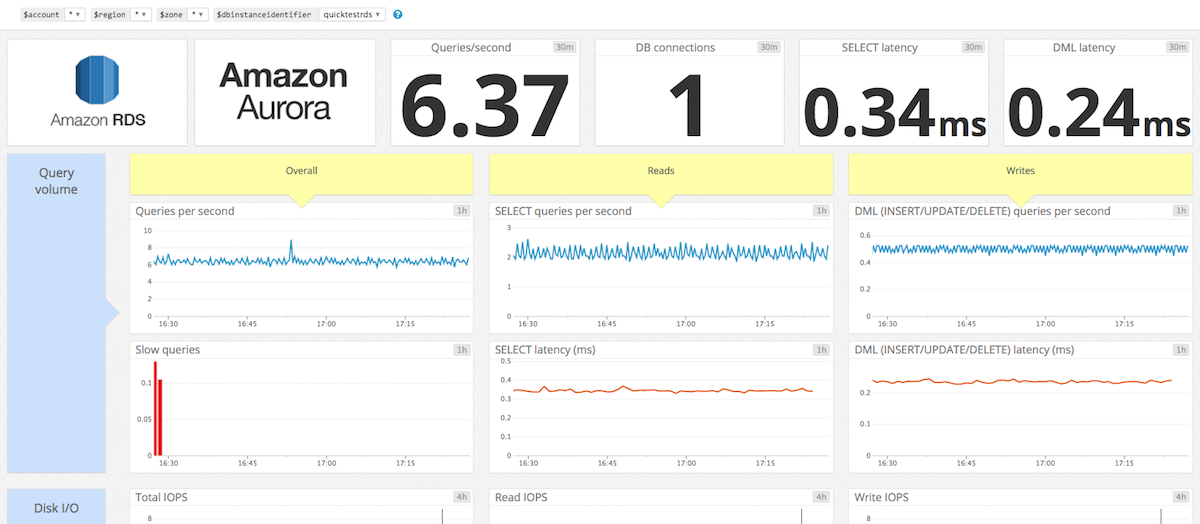
このコンフィギュレーションで使用できるプリセットダッシュボードは、MySQL、Aurora、PostgreSQL の 3 つです。各ダッシュボードには、クエリボリューム、ディスク I/O、接続、レプリケーション、AWS リソースのメトリクスが含まれています。
注: これらのダッシュボードには、AWS CloudWatch と個々のデータベースエンジン自体の両方からのメトリクスが表示されます。すべてのインテグレーションメトリクスに対して、インテグレーション (MySQL、Aurora、PostgreSQL) の 1 つを有効にします。
セットアップ
インストール
標準 RDS インテグレーションの場合、最初に Amazon Web Services インテグレーション をセットアップします。
インスタンスの作成中または作成後に RDS インスタンスの拡張モニタリングを有効にするには、Instance Actions の下にある Modify を選択します。監視の詳細度には 15 を選択することをお勧めします。
次の手順では、KMS と Lambda Management Console を使用して、RDS Enhanced Monitoring Lambda 関数でのみ使用できる Datadog API キーの暗号化バージョンを作成します。Log Forwarder などの別の Lambda 関数ですでに暗号化された API キーをお持ちの場合は、他のオプションについて Lambda 関数の README を参照してください。
KMS キーの作成
- KMS のホーム (https://console.aws.amazon.com/kms/home) を開きます。
- Customer managed keys に進みます。
- Create Key を選択します。
- キーのエイリアス (例:
lambda-datadog-key) を入力します。注: 「aws」で始まるエイリアスは使用できません。「aws」で始まるエイリアスは、ご使用のアカウントで AWS 管理の CMK を表すために Amazon Web Services によって予約されています。 - 適切な管理者を追加して、このキーを管理できるユーザーを指定します。
- ロールを追加する必要はありません。
- KMS キーを保存します。
Lambda 関数の作成
- Lambda マネジメントコンソールから、新しい Lambda 関数を作成します。Lambda 関数は、作成した KMS キーと同じリージョンにある必要があります。
Serverless Application Repositoryを選択し、Datadog-RDS-Enhancedを検索して選択します。- アプリケーションに一意の名前を付けます。
- 前のセクションで作成したキーの ID を
KMSKeyIdパラメーターに貼り付け、デプロイします。 - アプリケーションがデプロイされたら、新しく作成された Lambda 関数を開きます (「Resource」の下にある関数をクリック)。
Configurationタブをクリックし、Environment variablesセクションに移動します。環境変数kmsEncryptedKeysのvalueフィールドに、以下のように完全な JSON 形式で Datadog API キー を追加します:{"api_key":"<YOUR_API_KEY>"}Encryption configurationセクションを開き、Enable helpers for encryption in transitを選択します。KMS key to encrypt at restセクションで、Use a customer master keyを選択し、先に作成したものと同じ KMS キーを入力します。- 先ほど入力した JSON blob の横にある Encrypt ボタンを押し、ポップアップで、先ほど作成したものと同じ KMS キーを選択します。
- Save を押します。
RDSOSMetricsCloudWatch ロググループをソースとして使用して新しいトリガーを作成します。- フィルターに名前を付け、オプションでフィルターパターンを指定して、Save を押します。
Lambda 関数のテストボタンをクリックすると、次のエラーが発生する可能性があります。
{
"stackTrace": [
[
"/var/task/lambda_function.py",
109,
"lambda_handler",
"event = json.loads(gzip.GzipFile(fileobj=StringIO(event['awslogs']['data'].decode('base64'))).read())"
]
],
"errorType": "KeyError",
"errorMessage": "'awslogs'"
}
これは無視してかまいません。Test ボタンはこのセットアップでは機能しません。
AWS コンソールに移動し、RDS セクションを開いて、監視するインスタンスを見つけます。
エンドポイント URL をメモします (例: mysqlrds.blah.us-east1.rds.amazonaws.com:3306)。これは Agent の構成に使用されます。
DB Instance identifierもメモします (例 mysqlrds)。これはグラフやダッシュボードの作成に使用されます。
コンフィギュレーション
AWS インテグレーションページで、
Metric Collectionタブの下にあるRDSが有効になっていることを確認します。Amazon RDS のメトリクスを収集するには、次のアクセス許可を Datadog IAM ポリシーに追加します。詳細については、AWS ウェブサイト上の RDS ポリシーを参照してください。
AWS アクセス許可 説明 rds:DescribeDBInstancesタグを追加するための RDS インスタンスを記述します。 rds:ListTagsForResourceRDS インスタンスにカスタムタグを追加します。 rds:DescribeEventsRDS データベースに関連するイベントを追加します。 Datadog - Amazon RDS インテグレーションをインストールします。
AWS インテグレーションページで、
Metric Collectionタブの下にあるRDSが有効になっていることを確認します。Amazon RDS のメトリクスを収集するには、次のアクセス許可を Datadog IAM ポリシーに追加します。詳細については、AWS ウェブサイト上の RDS ポリシーを参照してください。
AWS アクセス許可 説明 rds:DescribeDBInstancesタグを追加するための RDS インスタンスを記述します。 rds:ListTagsForResourceRDS インスタンスにカスタムタグを追加します。 rds:DescribeEventsRDS データベースに関連するイベントを追加します。 Datadog - Amazon RDS インテグレーションをインストールします。
conf.d ディレクトリ内の適切な yaml ファイルを編集することで Agent を構成し、RDS インスタンスに接続します。その後、Agent を再起動します。
RDS Aurora の場合は、使用しているデータベース用の YAML ファイルを編集します。
MySQL または MariaDB を使用している場合は、mysql.yaml を編集します。
init_config:
instances:
# AWS コンソールからのエンドポイント URL
- server: 'mysqlrds.blah.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com'
user: '<USERNAME>'
pass: '<PASSWORD>'
port: 3306
tags:
- 'dbinstanceidentifier:<INSTANCE_NAME>'
PostgreSQL を使用している場合は、postgres.yaml を編集します。
init_config:
instances:
- host: 'postgresqlrds.blah.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com'
port: 5432
username: '<USERNAME>'
password: '<PASSWORD>'
dbname: '<DB_NAME>'
tags:
- 'dbinstanceidentifier:<DB_INSTANCE_NAME>'
Microsoft SQL Server を使用している場合は、sqlserver.yaml を編集します。
init_config:
instances:
- host: 'sqlserverrds.blah.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com,1433'
username: '<USERNAME>'
password: '<PASSWORD>'
tags:
- 'dbinstanceidentifier:<DB_INSTANCE_NAME>'
検証
Agent の status サブコマンドを実行し、Checks セクションでこれに似た値を探します。
Checks
======
[...]
mysql
-----
- instance #0 [OK]
- Collected 8 metrics & 0 events
使用方法
数分経つと、RDS メトリクスと MySQL、Aurora、MariaDB、SQL Server、Oracle、PostgreSQL の各メトリクスが Datadog のメトリクスエクスプローラー、ダッシュボード、アラートからアクセスできようになります。
下記に RDS と MySQL 双方のインテグレーションから取得した複数のメトリクスを表示する Aurora ダッシュボードの例を示します。インスタンス quicktestrds で双方のインテグレーションから取得したメトリクスを dbinstanceidentifier タグを使用して一つにまとめています。
ログの収集
ログの有効化
MySQL、MariaDB、および Postgres のログを Amazon CloudWatch に転送することができます。Amazon CloudWatch で Amazon Aurora MySQL、Amazon RDS for MySQL、MariaDB のログを監視の指示に従って、RDS のログを CloudWatch に送信します。
ログを Datadog に送信する方法
- Datadog ログコレクション AWS Lambda 関数をまだセットアップしていない場合は、セットアップします。
- Lambda 関数をインストールしたら、RDS ログを含む CloudWatch ロググループにトリガーを手動で追加します。対応する CloudWatch ロググループを選択し、フィルター名 (オプション) を追加して、トリガーを追加します。
完了したら、Datadog Log セクションに移動し、ログを確認します。
収集データ
データベースエンジンから収集されたメトリクスのほかに、以下の RDS メトリクスも受信します。
メトリクス
| aws.rds.active_transactions (gauge) | The average rate of current transactions executing on a DB instance. Only available for Aurora MySQL DBs. Shown as transaction |
| aws.rds.aurora_binlog_replica_lag (gauge) | The amount of time a replica DB cluster running on Aurora with MySQL compatibility lags behind the source DB cluster. Only available for Aurora MySQL DBs. Shown as second |
| aws.rds.aurora_replica_lag (gauge) | The average lag when replicating updates from the primary instance. Only available for Aurora DBs. Shown as millisecond |
| aws.rds.aurora_replica_lag_maximum (gauge) | The maximum amount of lag between the primary instance and each Aurora instance in the DB cluster. Only available for Aurora DBs. Shown as millisecond |
| aws.rds.aurora_replica_lag_minimum (gauge) | The minimum amount of lag between the primary instance and each Aurora instance in the DB cluster. Only available for Aurora DBs. Shown as millisecond |
| aws.rds.backup_retention_period_storage_used (gauge) | The amount of backup storage used for storing continuous backups at the current time. Only available for Aurora DBs. Shown as byte |
| aws.rds.bin_log_disk_usage (gauge) | Amount of disk space occupied by binary logs on the master. Only available for non-Aurora DBs. Shown as byte |
| aws.rds.blocked_transactions (count) | The average rate of transactions in the database that are blocked. Only available for Aurora MySQL DBs. Shown as transaction |
| aws.rds.buffer_cache_hit_ratio (gauge) | The percentage of requests that are served by the Buffer cache. Only available for Aurora DBs. Shown as percent |
| aws.rds.burst_balance (gauge) | The percent of General Purpose SSD (gp2) burst-bucket I/O credits available. Only available for non-Aurora DBs. Shown as percent |
| aws.rds.commit_latency (gauge) | The amount of latency for committed transactions. Only available for Aurora DBs. Shown as millisecond |
| aws.rds.commit_throughput (rate) | The average rate of committed transactions. Only available for Aurora DBs. Shown as transaction |
| aws.rds.cpucredit_balance (gauge) | [T2 instances] Number of CPU credits that an instance has accumulated. Available for Aurora DBs. |
| aws.rds.cpucredit_usage (gauge) | [T2 instances] Number of CPU credits consumed. Available for Aurora DBs. |
| aws.rds.cpusurplus_credit_balance (gauge) | The number of surplus credits that have been spent by an unlimited instance when its CPUCreditBalance value is zero. |
| aws.rds.cpusurplus_credits_charged (gauge) | The number of spent surplus credits that are not paid down by earned CPU credits, and which thus incur an additional charge. |
| aws.rds.cpuutilization (gauge) | Percentage of CPU utilization. Recommended metric for standard monitoring. Available for Aurora DBs. Shown as percent |
| aws.rds.cpuutilization.guest (gauge) | The percentage of CPU in use by guest programs. (Enhanced) Shown as percent |
| aws.rds.cpuutilization.idle (gauge) | The percentage of CPU that is idle. (Enhanced) Shown as percent |
| aws.rds.cpuutilization.irq (gauge) | The percentage of CPU in use by software interrupts. (Enhanced) Shown as percent |
| aws.rds.cpuutilization.kern (gauge) | The percentage of CPU in use by the kernel. (Enhanced, SQL Server Only) Shown as percent |
| aws.rds.cpuutilization.maximum (gauge) | Maximum percentage of CPU utilization. Shown as percent |
| aws.rds.cpuutilization.nice (gauge) | The percentage of CPU in use by programs running at lowest priority. (Enhanced) Shown as percent |
| aws.rds.cpuutilization.steal (gauge) | The percentage of CPU in use by other virtual machines. (Enhanced) Shown as percent |
| aws.rds.cpuutilization.system (gauge) | The percentage of CPU in use by the kernel. (Enhanced) Shown as percent |
| aws.rds.cpuutilization.total (gauge) | The total percentage of the CPU in use. This value excludes the nice value. Recommended metric for enhanced monitoring. (Enhanced) Shown as percent |
| aws.rds.cpuutilization.user (gauge) | The percentage of CPU in use by user programs. (Enhanced) Shown as percent |
| aws.rds.cpuutilization.wait (gauge) | The percentage of CPU unused while waiting for I/O access. (Enhanced) Shown as percent |
| aws.rds.database_connections (gauge) | Number of database connections in use. Available for Aurora DBs. Shown as connection |
| aws.rds.dbload (gauge) | The number of active sessions for the DB engine (Performance Insights must be enabled). Shown as session |
| aws.rds.dbload_cpu (gauge) | The number of active sessions where the wait event type is CPU (Performance Insights must be enabled). Shown as session |
| aws.rds.dbload_non_cpu (gauge) | The number of active sessions where the wait event type is not CPU (Performance Insights must be enabled). Shown as session |
| aws.rds.dbload_relative_to_num_vcpus (gauge) | The ratio of the DB load to the number of virtual CPUs for the database. Shown as percent |
| aws.rds.ddllatency (gauge) | The amount of latency for DDL requests (create/alter/drop). Only available for Aurora MySQL DBs. Shown as millisecond |
| aws.rds.ddlthroughput (rate) | The average rate of DDL requests per second. Only available for Aurora MySQL DBs. Shown as request |
| aws.rds.deadlocks (count) | The average number of deadlocks in the database per second. Only available for Aurora DBs. Shown as lock |
| aws.rds.delete_latency (gauge) | The average latency for delete queries. Only available for Aurora MySQL DBs. Shown as millisecond |
| aws.rds.delete_throughput (rate) | The average rate of delete queries. Only available for Aurora MySQL DBs. Shown as query |
| aws.rds.disk_queue_depth (gauge) | Number of outstanding IOs (read/write requests) waiting to access the disk. Available for Aurora DBs. Shown as request |
| aws.rds.diskio.avgQueueLen (gauge) | The number of requests waiting in the I/O device’s queue. This metric is not available for Amazon Aurora. (Enhanced) Shown as request |
| aws.rds.diskio.avgReqSz (gauge) | The average request size. This metric is not available for Amazon Aurora. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.diskio.await (gauge) | The number of milliseconds required to respond to requests including queue time and service time. This metric is not available for Amazon Aurora. (Enhanced) Shown as millisecond |
| aws.rds.diskio.readIOsPS (rate) | The rate of read operations. (Enhanced) Shown as operation |
| aws.rds.diskio.readKb (gauge) | The total amount of data read. This metric is not available for Amazon Aurora. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.diskio.readKbPS (rate) | The rate that data is read. This metric is not available for Amazon Aurora. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.diskio.readLatency (gauge) | The elapsed time between the submission of a read I/O request and its completion, in milliseconds. (Enhanced, Aurora Only) Shown as millisecond |
| aws.rds.diskio.readThroughput (rate) | The amount of network throughput used by requests to the DB cluster, in bytes per second. (Enhanced, Aurora Only) Shown as byte |
| aws.rds.diskio.rrqmPS (rate) | The rate of merged read requests queue. This metric is not available for Amazon Aurora. (Enhanced) Shown as request |
| aws.rds.diskio.tps (rate) | The rate of I/O transactions. This metric is not available for Amazon Aurora. (Enhanced) Shown as transaction |
| aws.rds.diskio.util (gauge) | The percentage of CPU time during which requests were issued. The percentage of CPU time during which requests were issued. (Enhanced) Shown as percent |
| aws.rds.diskio.writeIOsPS (rate) | The rate of write operations. (Enhanced) Shown as operation |
| aws.rds.diskio.writeKb (gauge) | The total amount of data written. This metric is not available for Amazon Aurora. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.diskio.writeKbPS (rate) | The rate that data is written. This metric is not available for Amazon Aurora. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.diskio.writeLatency (gauge) | The average elapsed time between the submission of a write I/O request and its completion, in milliseconds. (Enhanced, Aurora Only) Shown as millisecond |
| aws.rds.diskio.writeThroughput (rate) | The amount of network throughput used by responses from the DB cluster, in bytes per second. (Enhanced, Aurora Only) Shown as byte |
| aws.rds.diskio.wrqmPS (rate) | The rate of merged write requests queue. This metric is not available for Amazon Aurora. (Enhanced) Shown as request |
| aws.rds.dmllatency (gauge) | The average latency for inserts and updates and deletes. Only available for Aurora MySQL DBs. Shown as millisecond |
| aws.rds.dmlthroughput (rate) | The average rate of inserts and updates and deletes. Only available for Aurora MySQL DBs. Shown as operation |
| aws.rds.engine_uptime (gauge) | The amount of time that the DB instance has been active. Only available for Aurora DBs. Shown as second |
| aws.rds.failed_sqlserver_agent_jobs_count (count) | The number of failed SQL Server Agent jobs during the last minute. Shown as minute |
| aws.rds.filesystem.maxFiles (gauge) | The maximum number of files that can be created for the file system. (Enhanced) Shown as file |
| aws.rds.filesystem.total (gauge) | The total amount of disk space available for the file system. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.filesystem.used (gauge) | The amount of disk space used by files in the file system. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.filesystem.usedFilePercent (gauge) | The percentage of available files in use. (Enhanced) Shown as percent |
| aws.rds.filesystem.usedFiles (gauge) | The number of files in the file system. (Enhanced) Shown as file |
| aws.rds.filesystem.usedPercent (gauge) | The percentage of the file-system disk space in use. (Enhanced) Shown as percent |
| aws.rds.free_local_storage (gauge) | The amount of local storage that is free on an instance. Only available for Aurora DBs. Shown as byte |
| aws.rds.free_storage_space (gauge) | Amount of available storage space. Shown as byte |
| aws.rds.freeable_memory (gauge) | Amount of available random access memory. Shown as byte |
| aws.rds.insert_latency (gauge) | The amount of latency for insert queries. Only available for Aurora MySQL DBs. Shown as millisecond |
| aws.rds.insert_throughput (rate) | The average rate of insert queries. Only available for Aurora MySQL DBs. Shown as query |
| aws.rds.load.1 (gauge) | The number of processes requesting CPU time over the last minute. (Enhanced) Shown as process |
| aws.rds.load.15 (gauge) | The number of processes requesting CPU time over the last 15 minutes. (Enhanced) Shown as process |
| aws.rds.load.5 (gauge) | The number of processes requesting CPU time over the last 5 minutes. (Enhanced) Shown as process |
| aws.rds.login_failures (count) | The average number of failed login attempts per second. Only available for Aurora MySQL DBs. Shown as operation |
| aws.rds.maximum_used_transaction_ids (count) | The maximum transaction ID that has been used. Only available for Aurora PostgreSQL DBs. |
| aws.rds.memory.active (gauge) | The amount of assigned memory. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.memory.buffers (gauge) | The amount of memory used for buffering I/O requests prior to writing to the storage device. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.memory.cached (gauge) | The amount of memory used for caching file system-based I/O. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.memory.commitLimitKb (gauge) | The maximum possible value for the commitTotKb metric. This value is the sum of the current pagefile size plus the physical memory available for pageable contents–excluding RAM that is assigned to non-pageable areas. (Enhanced, SQL Server Only) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.memory.commitPeakKb (gauge) | The largest value of the commitTotKb metric since the operating system was last started. (Enhanced, SQL Server Only) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.memory.commitTotKb (gauge) | The amount of pagefile-backed virtual address space in use, that is, the current commit charge. This value is composed of main memory (RAM) and disk (pagefiles). (Enhanced, SQL Server Only) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.memory.dirty (gauge) | The amount of memory pages in RAM that have been modified but not written to their related data block in storage. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.memory.free (gauge) | The amount of unassigned memory. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.memory.hugePagesFree (gauge) | The number of free huge pages. (Enhanced) Shown as page |
| aws.rds.memory.hugePagesRsvd (gauge) | The number of committed huge pages. (Enhanced) Shown as page |
| aws.rds.memory.hugePagesSize (gauge) | The size for each huge pages unit. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.memory.hugePagesSurp (gauge) | The number of available surplus huge pages over the total. (Enhanced) Shown as page |
| aws.rds.memory.hugePagesTotal (gauge) | The total number of huge pages for the system. (Enhanced) Shown as page |
| aws.rds.memory.inactive (gauge) | The amount of inactive memory (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.memory.kernNonpagedKb (gauge) | The amount of memory in the non-paged kernel pool. (Enhanced, SQL Server Only) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.memory.kernPagedKb (gauge) | The amount of memory in the paged kernel pool. (Enhanced, SQL Server Only) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.memory.kernTotKb (gauge) | The sum of the memory in the paged and non-paged kernel pools. (Enhanced, SQL Server Only) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.memory.mapped (gauge) | The total amount of file-system contents that is memory mapped inside a process address space. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.memory.pageSize (gauge) | The size of a page. (Enhanced, SQL Server Only) Shown as byte |
| aws.rds.memory.pageTables (gauge) | The amount of memory used by page tables. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.memory.physAvailKb (gauge) | The amount of available physical memory. (Enhanced, SQL Server Only) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.memory.physTotKb (gauge) | The amount of physical memory. (Enhanced, SQL Server Only) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.memory.slab (gauge) | The amount of reusable kernel data structures. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.memory.sqlServerTotKb (gauge) | The amount of memory committed to Microsoft SQL Server. (Enhanced, SQL Server Only) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.memory.sysCacheKb (gauge) | The amount of system cache memory. (Enhanced, SQL Server Only) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.memory.total (gauge) | The total amount of memory. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.memory.writeback (gauge) | The amount of dirty pages in RAM that are still being written to the backing storage. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.network.rdBytesPS (gauge) | The number of bytes received per second. (Enhanced, SQL Server Only) Shown as byte |
| aws.rds.network.rx (gauge) | The number of packets received. (Enhanced) Shown as packet |
| aws.rds.network.tx (gauge) | The number of packets uploaded. (Enhanced) Shown as packet |
| aws.rds.network.wrBytesPS (gauge) | The number of bytes sent per second. (Enhanced, SQL Server Only) Shown as byte |
| aws.rds.network_receive_throughput (rate) | Incoming (Receive) network traffic on the DB instance. Available for Aurora DBs. Shown as byte |
| aws.rds.network_throughput (rate) | The rate of network throughput sent and received from clients by each instance in the DB cluster. Only available for Aurora DBs. Shown as byte |
| aws.rds.network_transmit_throughput (rate) | Outgoing (Transmit) network traffic on the DB instance. Available for Aurora DBs. Shown as byte |
| aws.rds.oldest_replication_slot_lag (gauge) | The lagging size of the replica lagging the most in terms of WAL data received. Only available for Aurora PostgreSQL DBs. Shown as byte |
| aws.rds.process.cpuUsedPc (gauge) | The percentage of CPU used by the process. (Enhanced) Shown as percent |
| aws.rds.process.memUsedPc (gauge) | The percentage of total memory used by the process. (Enhanced, SQL Server Only) Shown as percent |
| aws.rds.process.memoryUsedPc (gauge) | The percentage of memory used by the process. (Enhanced) Shown as percent |
| aws.rds.process.parentID (gauge) | The process identifier for the parent proces of the process. (Enhanced) |
| aws.rds.process.pid (gauge) | The identifier of the process. This value is not present for processes that are owned by Amazon RDS. (Enhanced, SQL Server Only) |
| aws.rds.process.ppid (gauge) | The process identifier for the parent of this process. This value is only present for child processes. (Enhanced, SQL Server Only) |
| aws.rds.process.rss (gauge) | The amount of RAM allocated to the process. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.process.tgid (gauge) | The thread group identifier which is a number representing the process ID to which a thread belongs. This identifier is used to group threads from the same process. (Enhanced) |
| aws.rds.process.tid (gauge) | The thread identifier. This value is only present for threads. The owning process can be identified by using the pid value. (Enhanced, SQL Server Only) |
| aws.rds.process.virtKb (gauge) | The amount of virtual address space the process is using. Use of virtual address space does not necessarily imply corresponding use of either disk or main memory pages. (Enhanced, SQL Server Only) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.process.vss (gauge) | The amount of virtual memory allocated to the process. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.process.workingSetKb (gauge) | The amount of memory in the private working set plus the amount of memory that is in use by the process and can be shared with other processes. (Enhanced, SQL Server Only) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.process.workingSetPrivKb (gauge) | The amount of memory that is in use by a process, but can’t be shared with other processes. (Enhanced, SQL Server Only) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.process.workingSetShareableKb (gauge) | The amount of memory that is in use by a process and can be shared with other processes. (Enhanced, SQL Server Only) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.queries (rate) | The average rate of queries. Only available for Aurora MySQL DBs. Shown as query |
| aws.rds.rdsto_aurora_postgre_sqlreplica_lag (gauge) | The amount of lag in seconds when replicating updates from the primary RDS PostgreSQL instance to other nodes in the cluster. Only available for Aurora PostgreSQL DBs. Shown as second |
| aws.rds.read_iops (rate) | Average number of disk read I/O operations. Shown as operation |
| aws.rds.read_latency (gauge) | Average amount of time taken per disk read I/O operation. Shown as second |
| aws.rds.read_throughput (rate) | Average number of bytes read from disk. Shown as byte |
| aws.rds.replica_lag (gauge) | Amount of time a Read Replica DB Instance lags behind the source DB Instance. Shown as second |
| aws.rds.replication_slot_disk_usage (gauge) | The disk space used by replication slot files. Available for Aurora PostgreSQL DBs. Shown as byte |
| aws.rds.result_set_cache_hit_ratio (gauge) | The percentage of requests that are served by the Resultset cache. Only available for Aurora MySQL DBs. Shown as percent |
| aws.rds.select_latency (gauge) | The average latency for select queries. Only available for Aurora MySQL DBs. Shown as millisecond |
| aws.rds.select_throughput (rate) | The average rate of select queries. Only available for Aurora MySQL DBs. Shown as query |
| aws.rds.snapshot_storage_used (gauge) | The amount of backup storage used for storing manual snapshots beyond the backup retention period. Only available for Aurora DBs. Shown as byte |
| aws.rds.swap.cached (gauge) | The amount of swap memory used as cache memory. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.swap.free (gauge) | The total amount of swap memory free. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.swap.in (gauge) | The amount of memory swapped in from disk. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.swap.out (gauge) | The amount of memory swapped out from disk. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.swap.total (gauge) | The total amount of swap memory available. (Enhanced) Shown as kibibyte |
| aws.rds.swap_usage (gauge) | Amount of swap space used on the DB instance. Shown as byte |
| aws.rds.tasks.blocked (gauge) | The number of tasks that are blocked. (Enhanced) Shown as task |
| aws.rds.tasks.running (gauge) | The number of tasks that are running. (Enhanced) Shown as task |
| aws.rds.tasks.sleeping (gauge) | The number of tasks that are sleeping. (Enhanced) Shown as task |
| aws.rds.tasks.stopped (gauge) | The number of tasks that are stopped. (Enhanced) Shown as task |
| aws.rds.tasks.total (gauge) | The total number of tasks. (Enhanced) Shown as task |
| aws.rds.tasks.zombie (gauge) | The number of child tasks that are inactive with an active parent task. (Enhanced) Shown as task |
| aws.rds.total_backup_storage_billed (gauge) | The sum of BackupRetentionPeriodStorageUsed and SnapshotStorageUsed minus an amount of free backup storage which equals the size of the cluster volume for one day. Only available for Aurora DBs. Shown as byte |
| aws.rds.total_storage_space (gauge) | Total amount of storage available on an instance. Shown as byte |
| aws.rds.transaction_logs_disk_usage (gauge) | Amount of disk space occupied by transaction logs. Only available for Aurora PostgreSQL DBs. Shown as byte |
| aws.rds.transaction_logs_generation (gauge) | The size of transaction logs generated per second. Shown as byte |
| aws.rds.update_latency (gauge) | The average latency for update queries. Only available for Aurora MySQL DBs. Shown as millisecond |
| aws.rds.update_throughput (rate) | The average rate of update queries. Only available for Aurora MySQL DBs. Shown as query |
| aws.rds.uptime (gauge) | RDS instance uptime. (Enhanced) Shown as second |
| aws.rds.virtual_cpus (gauge) | The number of virtual CPUs for the DB instance. (Enhanced) Shown as cpu |
| aws.rds.volume_bytes_used (gauge) | The amount of storage in bytes used by your Aurora database. Only available for Aurora DBs. Shown as byte |
| aws.rds.volume_read_iops (count) | The number of billed read I/O operations from a cluster volume, reported at 5-minute intervals. Only available for Aurora DBs. Shown as operation |
| aws.rds.volume_write_iops (count) | The average number of write disk I/O operations to the cluster volume reported at 5-minute intervals. Only available for Aurora DBs. Shown as operation |
| aws.rds.write_iops (rate) | Average number of disk write I/O operations per second. Shown as operation |
| aws.rds.write_latency (gauge) | Average amount of time taken per disk write I/O operation. Shown as second |
| aws.rds.write_throughput (rate) | Average number of bytes written. Shown as byte |
Each of the metrics retrieved from AWS is assigned the same tags that appear in the AWS console, including but not limited to host name, security-groups, and more.
AWS から取得される各メトリクスには、ホスト名やセキュリティ グループなど、AWS コンソールに表示されるのと同じタグが割り当てられます。
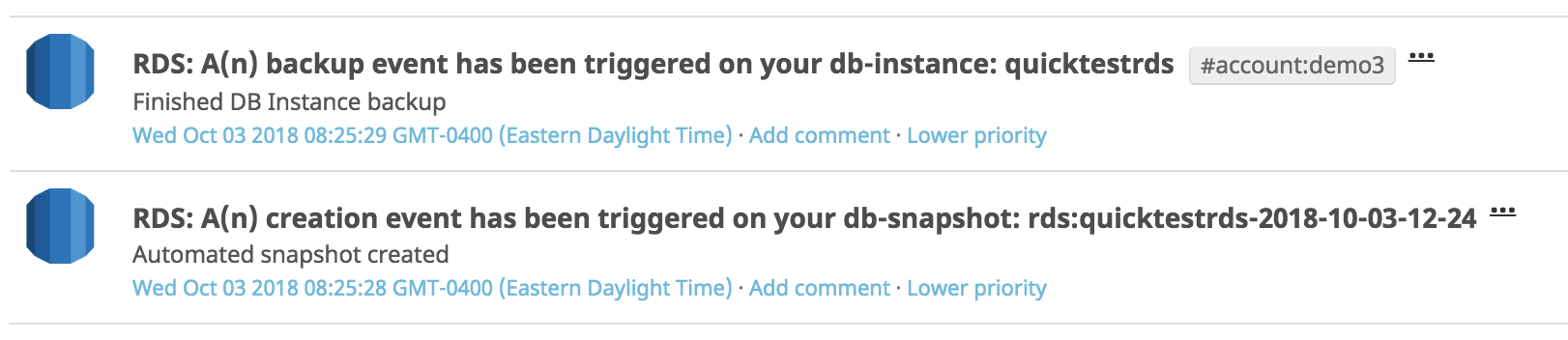
イベント
Amazon RDS インテグレーションには、DB インスタンス、セキュリティグループ、スナップショット、およびパラメーターグループに関連するイベントが含まれます。以下はイベントの例です。
サービスのチェック
aws.rds.read_replica_status
読み取りレプリケーションのステータスを監視します。このチェックは、以下のいずれかのステータスを返します。
- OK - レプリケート中または接続中
- CRITICAL - エラーまたは途中終了
- WARNING - 停止
- UNKNOWN - その他
すぐに使える監視
Amazon RDS インテグレーションは、パフォーマンスを監視し最適化するために、すぐに使える監視機能を提供します。
- Amazon RDS ダッシュボード: すぐに使える Amazon RDS ダッシュボードを使用して、RDS インスタンスの包括的な概要を得ることができます。
- 推奨モニター: Amazon RDS の推奨モニターを有効にすると、問題をプロアクティブに検出し、タイムリーなアラートを受信することができます。
トラブルシューティング
ご不明な点は、Datadog のサポートチームまでお問合せください。