- 重要な情報
- はじめに
- 用語集
- Standard Attributes
- ガイド
- インテグレーション
- エージェント
- OpenTelemetry
- 開発者
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- DDSQL Reference
- モバイルアプリケーション
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft
- アプリ内
- ダッシュボード
- ノートブック
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Watchdog
- アラート設定
- メトリクス
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- インフラストラクチャー
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- ユニバーサル サービス モニタリング
- Hosts
- コンテナ
- Processes
- サーバーレス
- ネットワークモニタリング
- Cloud Cost
- アプリケーションパフォーマンス
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- データベース モニタリング
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- RUM & セッションリプレイ
- Synthetic モニタリング
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility (CI/CDの可視化)
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Visibility
- Code Coverage
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- セキュリティ
- セキュリティの概要
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- クラウド セキュリティ マネジメント
- Application Security Management
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- ログ管理
- Observability Pipelines(観測データの制御)
- ログ管理
- CloudPrem
- 管理
Amazon EventBridge
このページは日本語には対応しておりません。随時翻訳に取り組んでいます。
翻訳に関してご質問やご意見ございましたら、お気軽にご連絡ください。
翻訳に関してご質問やご意見ございましたら、お気軽にご連絡ください。
The Datadog for Government site does not support Amazon EventBridge.
Overview
Datadog’s integration with Amazon EventBridge offers the following features:
- Create custom event buses across your integrated AWS accounts
- Send Datadog alert notification events into the event buses of your choice
- Within AWS, set up triggers on your event buses with services like Kinesis, Lambda, and more
- Use the information within the alert event to execute auto-remediation pipelines and runbooks, run analytics queries, etc.
- This integration is not supported in GovCloud
Setup
If you haven’t already, set up the Amazon Web Services integration first.
Installation
- Ensure that the main AWS integration is installed for each AWS account that receives alert notifications.
- Ensure the following permissions exist in the permissions policy for Datadog AWS Role(s):
events:CreateEventBusandevents:PutPartnerEvents. - The Amazon EventBridge integration is automatically installed with the main AWS integration.
Note: You can also use the API or Terraform to set up an Amazon EventBridge source.
Configuration
events:CreateEventBus and events:PutPartnerEvents permissions are required to send alert notifications to your event buses. If you do not have these permissions set, read the Datadog IAM permissions documentation to enable permissions prior to further configuration.
- Navigate to the Datadog - Amazon EventBridge integration tile to see a list of AWS accounts integrated in Datadog where you can create Event Bridges.
- Within the AWS account of choice, create a new event bus by providing a name and selecting the region where you want it to exist.
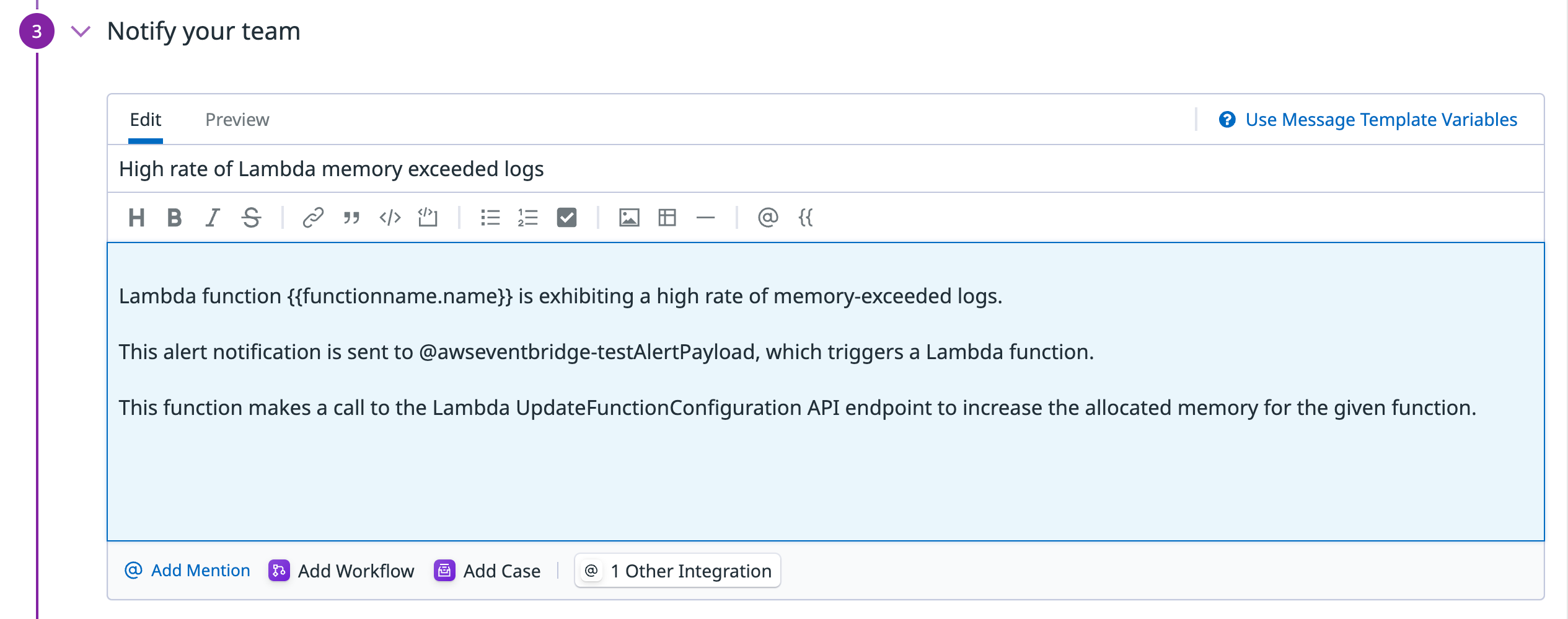
- Within Datadog alerts, use the
@awseventbridge-<MY_EVENT_BUS>syntax to send alert notifications to your event buses. - Within AWS, connect your event buses to targets such as Lambda, Kinesis, and many other services to create event-driven workflows. Note: Examples of Datadog use cases can be found on Datadog’s partner page in the AWS Console.
- After setting up an event bus in Datadog, navigate to the Amazon EventBridge console and select
Rulesin the navigation pane. - Select
Create Ruleand add a name and description for your rule. - Under Define Pattern, select
Event Pattern. SelectPredefined by serviceas the event matching pattern. For service provider, selectService partners. For service name, selectDatadog. This populates the event buses that are in Datadog. Add any additional information for your rule., then Save the rule. - To disconnect an event bus in Datadog, hover over the event bus of your choice and press the trash icon. Note: This action disconnects the event bus from AWS, but does not delete the event bus itself within AWS.
Note: EventBridge rules are not imported into Datadog unless the rule is active and has been triggered.
Automated actions
Set up new outbound notification channels for monitors and snapshots from Datadog with the Amazon EventBridge integration. With automated actions, you can configure your AWS resources to:
- Restart a process if process ends for live process monitoring
- Prompt EC2 reboots
- Prompt ECS Task (kick off another task when one task ends)
- Apply an Ansible Playbook (make any change on hosts)
- Run remote patches
- Run remote SSH scripts
- Run Windows Updates or install applications
The full list of resources you can target is available on the AWS website.
Data Collected
Metrics
| aws.events.dead_letter_invocations (count) | The number of times a rule’s target isn’t invoked in response to an event. |
| aws.events.events (count) | The number of partner events ingested by EventBridge. |
| aws.events.failed_invocations (count) | Measures the number of invocations that failed permanently. This does not include invocations that are retried or that succeeded after a retry attempt |
| aws.events.invocation_attempts (count) | Number of times EventBridge attempted invoking a target. |
| aws.events.invocations (count) | Measures the number of times a target is invoked for a rule in response to an event. This includes successful and failed invocations but does not include throttled or retried attempts until they fail permanently. |
| aws.events.invocations_created (count) | The total number of invocations created in response to each event. |
| aws.events.invocations_failed_to_be_sent_to_dlq (count) | The number of invocations that couldn’t be moved to a dead-letter queue. |
| aws.events.ingestion_to_invocation_complete_latency (gauge) | Time taken from event ingestion to completion of the first invocation attempt. |
| aws.events.ingestion_to_invocation_success_latency (gauge) | Time taken from event ingestion to successful target delivery. |
| aws.events.ingestion_to_invocation_start_latency (gauge) | Time to process events, measured from when an event is ingested by EventBridge to first invocation of a target. |
| aws.events.invocations_sent_to_dlq (count) | The number of invocations that are moved to a dead-letter queue. |
| aws.events.matched_events (count) | Measures the number of events that matched with any rule. |
| aws.events.put_events_approximate_call_count (count) | Approximate number of received PutEvents requests. |
| aws.events.put_events_approximate_failed_count (count) | Approximate number of failed PutEvents requests. |
| aws.events.put_events_approximate_success_count (count) | Approximate number of successful PutEvents requests. |
| aws.events.put_events_approximate_throttled_count (count) | Approximate number of PutEvents requests rejected due to throttling. |
| aws.events.put_events_entries_count (count) | The number of event entries contained in a PutEvents request. |
| aws.events.put_events_failed_entries_count (count) | The number of event entries contained in a PutEvents request that failed to be ingested. |
| aws.events.put_events_latency (gauge) | The time taken per PutEvents request. Shown as millisecond |
| aws.events.put_events_request_size (gauge) | The size of the PutEvents request. Shown as byte |
| aws.events.put_partner_events_approximate_call_count (count) | Approximate number of received PutPartnerEvents requests. |
| aws.events.put_partner_events_approximate_failed_count (count) | Approximate number of failed PutPartnerEvents requests. |
| aws.events.put_partner_events_approximate_success_count (count) | Approximate number of successful PutPartnerEvents requests. |
| aws.events.put_partner_events_approximate_throttled_count (count) | Approximate number of PutPartnerEvents requests rejected due to throttling. |
| aws.events.put_partner_events_entries_count (count) | The number of event entries contained in a PutPartnerEvents request. |
| aws.events.put_partner_events_failed_entries_count (count) | The number of event entries contained in a PutPartnerEvents request that failed to be ingested. |
| aws.events.put_partner_events_latency (gauge) | The time taken per PutPartnerEvents request. Shown as millisecond |
| aws.events.retry_invocation_attempts (count) | Number of times target invocation has been retried. |
| aws.events.successful_invocation_attempts (count) | Number of times target was successfully invoked. |
| aws.events.throttled_rules (count) | Measures the number of triggered rules that are being throttled. |
| aws.events.triggered_rules (count) | Measures the number of triggered rules that matched with any event. |
| aws.eventbridge.pipes.concurrency (gauge) | The number of concurrent executions of a pipe. |
| aws.eventbridge.pipes.duration (gauge) | Length of time the pipe execution took. Shown as millisecond |
| aws.eventbridge.pipes.event_count (count) | The number of events a pipe has processed. |
| aws.eventbridge.pipes.event_size (gauge) | The size of the payload of the event that invoked the pipe. Shown as byte |
| aws.eventbridge.pipes.execution_throttled (count) | How many executions of a pipe were throttled. |
| aws.eventbridge.pipes.execution_timeout (count) | How many executions of a pipe timed out before completing execution. |
| aws.eventbridge.pipes.execution_failed (count) | How many executions of a pipe failed. |
| aws.eventbridge.pipes.execution_partially_failed (count) | How many executions of a pipe partially failed. |
| aws.eventbridge.pipes.enrichment_stage_duration (gauge) | How long the enrichment stage took to complete. Shown as millisecond |
| aws.eventbridge.pipes.enrichment_stage_failed (count) | How many executions of a pipe’s enrichment stage failed. |
| aws.eventbridge.pipes.invocations (count) | Total number of invocations. |
| aws.eventbridge.pipes.target_stage_duration (gauge) | How long the target stage took to complete. Shown as millisecond |
| aws.eventbridge.pipes.target_stage_failed (count) | How many executions of a pipe’s target stage failed. |
| aws.eventbridge.pipes.target_stage_partially_failed (count) | How many executions of a pipe’s target stage partially failed. |
| aws.eventbridge.pipes.target_stage_skipped (count) | How many executions of a pipe’s target stage were skipped. |
| aws.scheduler.invocation_attempt_count (count) | Emitted for every invocation attempt. |
| aws.scheduler.target_error_count (count) | Emitted when the target returns an exception after EventBridge Scheduler calls the target API. |
| aws.scheduler.target_error_throttled_count (count) | Emitted when target invocation fails due to API throttling by the target. |
| aws.scheduler.invocation_throttle_count (count) | Emitted when EventBridge Scheduler throttles a target invocation because it exceeds your service quotas set by EventBridge Scheduler. |
| aws.scheduler.invocation_dropped_count (count) | Emitted when EventBridge Scheduler stops attempting to invoke the target after a schedule’s retry policy has been exhausted. |
| aws.scheduler.invocations_sent_to_dead_letter_count (count) | Emitted for every successful delivery to a schedule’s DLQ. |
| aws.scheduler.invocations_failed_to_be_sent_to_dead_letter_count (count) | Emitted when EventBridge Scheduler cannot deliver an event to the DLQ. |
| aws.scheduler.invocations_sent_to_dead_letter_count_truncated_message_size_exceeded (count) | Emitted when the payload of the event sent to the DLQ exceeds the maximum size allowed by Amazon SQS. |
Events
The Amazon EventBridge integration does not include any events.
Service Checks
The Amazon EventBridge integration does not include any service checks.
Troubleshooting
Need help? Contact Datadog support.
