- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- Notebooks
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Search
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Extend Datadog
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API-based Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Service Level Objectives
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Event Management
- Incident Response
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- End User Device Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Storage Management
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Setting Up ClickHouse
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Session Replay
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Code Coverage
- PR Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Developer Integrations
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- AI Guard
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Configuration
- Sources
- Processors
- Destinations
- Packs
- Akamai CDN
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs
- AWS Application Load Balancer Logs
- AWS CloudTrail
- AWS Elastic Load Balancer Logs
- AWS Network Load Balancer Logs
- Cisco ASA
- Cloudflare
- F5
- Fastly
- Fortinet Firewall
- HAProxy Ingress
- Istio Proxy
- Juniper SRX Firewall Traffic Logs
- Netskope
- NGINX
- Okta
- Palo Alto Firewall
- Windows XML
- ZScaler ZIA DNS
- Zscaler ZIA Firewall
- Zscaler ZIA Tunnel
- Zscaler ZIA Web Logs
- Search Syntax
- Scaling and Performance
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Guides and Resources
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
- Account Management
- Data Security
- Help
- feature_flags_client
GuardDog
Supported OS
Integration version1.1.0
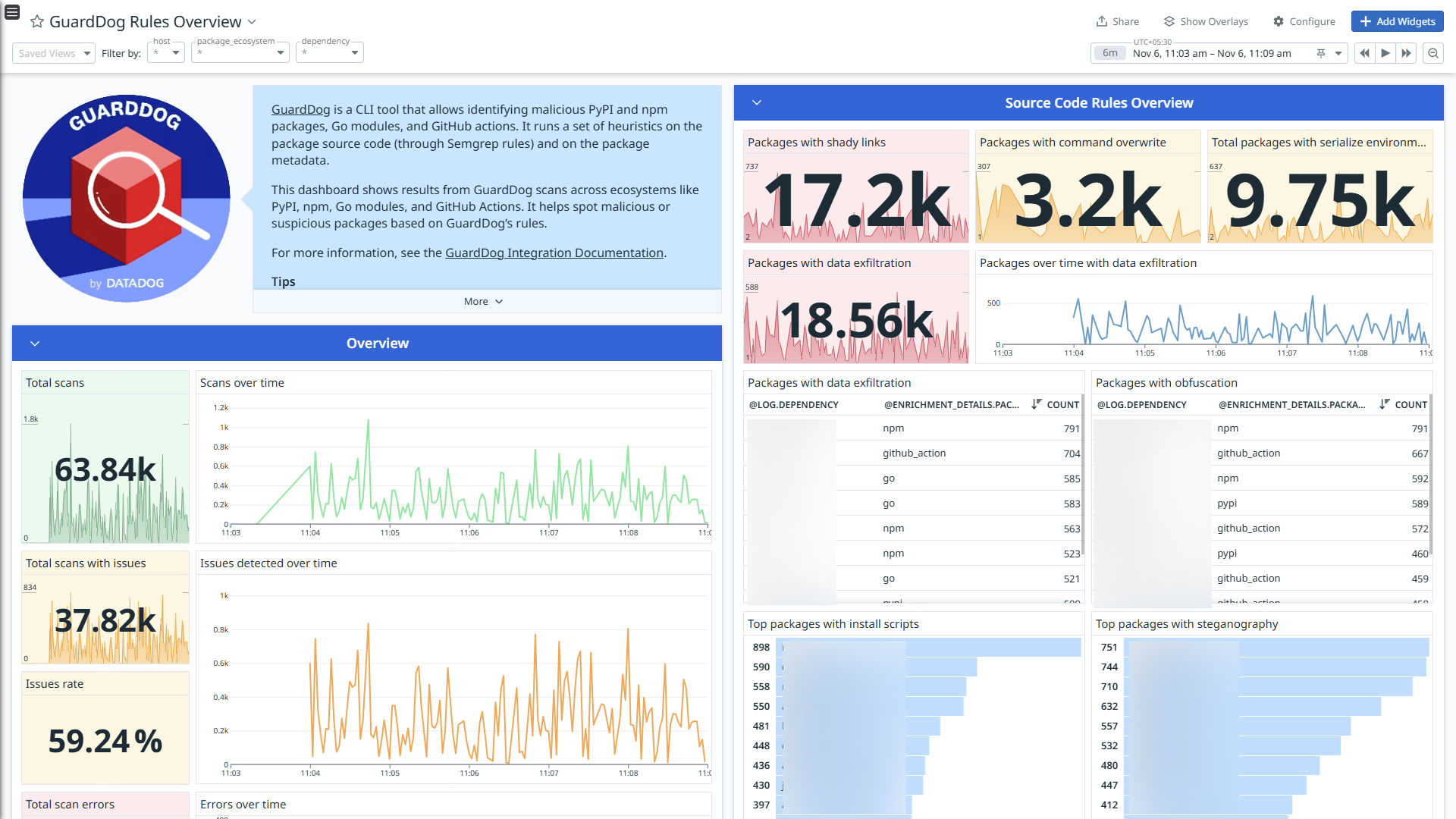
GuardDog Rules Overview
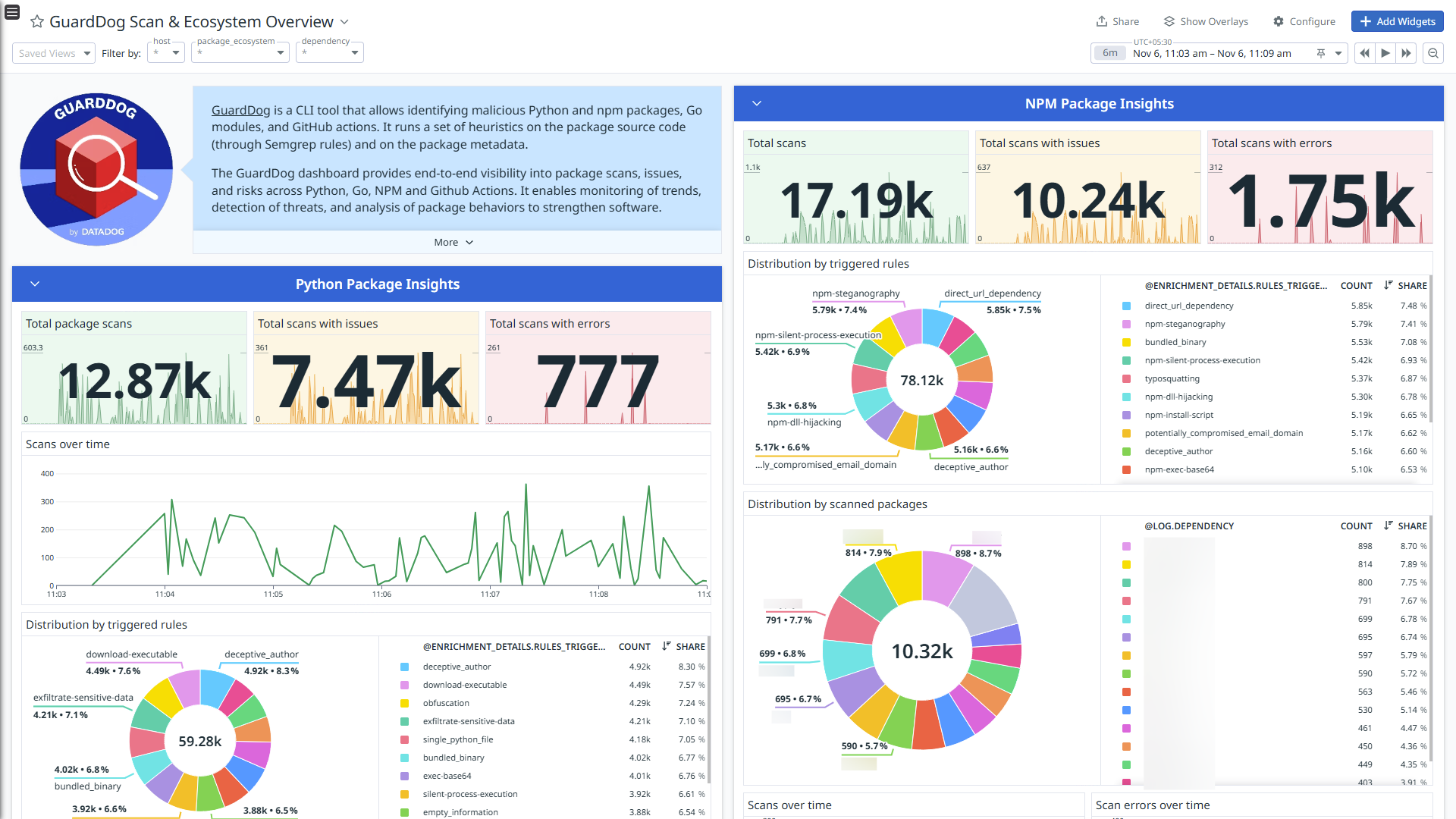
GuardDog Scan & Ecosystem Overview - 1
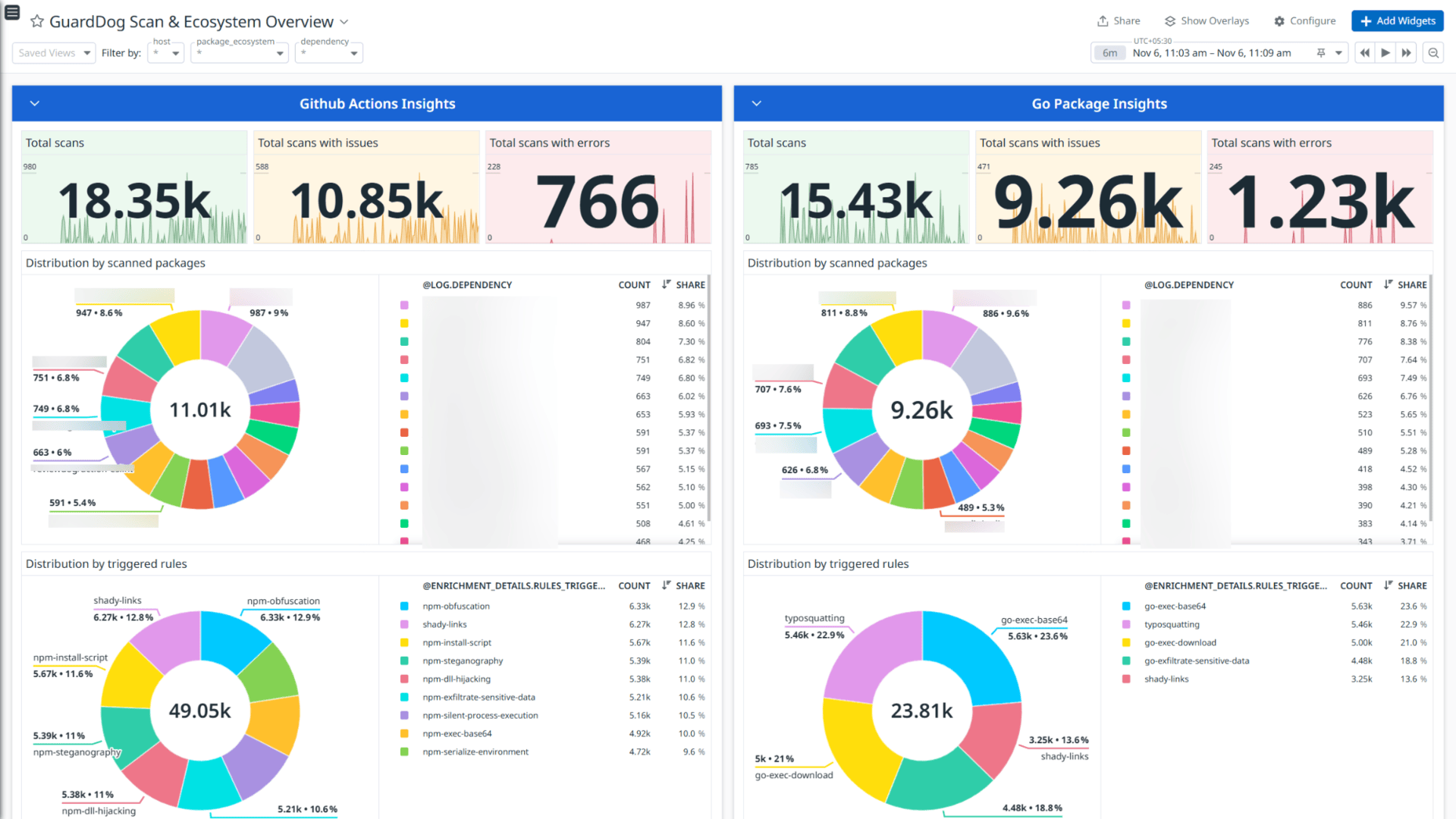
GuardDog Scan & Ecosystem Overview - 2
Overview
GuardDog is a CLI tool that allows you to identify malicious PyPI and npm packages, Go modules, and GitHub actions. It runs a set of heuristics on the package source code (through Semgrep rules) and on the package metadata.
This integration monitors configured dependency files using GuardDog scans and sends the scan output to Datadog for analysis, providing visual insights through out-of-the-box dashboards and the Log Explorer. It also helps monitor and respond to security threats with ready-to-use Cloud SIEM detection rules.
Note:
- Minimum Agent version: 7.74.0
Setup
Installation
The GuardDog check is already included with the Datadog Agent package, so no extra installation is required. You must also install the GuardDog package (see Install GuardDog under Configuration).
Configuration
Install GuardDog
Note: - GuardDog requires Python version 3.10 or higher. - The Datadog Agent must have access to the GuardDog executable path.
Install GuardDog using pip:
pip3 install guarddogRun this command to find the GuardDog executable path:
which guarddogThis path is required for the
guarddog_pathparameter in theguarddog.d/conf.yamlfile.
Log collection
Collecting logs is disabled by default in the Datadog Agent. Enable it in
datadog.yaml:logs_enabled: trueAdd this configuration block to your
guarddog.d/conf.yamlfile to start monitoring dependency files using GuardDog. See the sample guarddog.d/conf.yaml for available configuration options.logs: - type: integration service: guarddog source: guarddog init_config: ## @param guarddog_path - string - required ## Absolute path to the GuardDog file. Example: /usr/local/bin/guarddog # guarddog_path: <ABSOLUTE_PATH_OF_GUARDDOG> instances: ## @param package_ecosystem - string - required ## The type of package ecosystem. Supported values: pypi, npm, go and github_action # - package_ecosystem: <PACKAGE_ECOSYSTEM> ## @param dependency_file_path - string - required ## Absolute path to the dependency file you want to monitor. Example: /app/requirements.txt # dependency_file_path: <DEPENDENCY_FILE_PATH> ## @param min_collection_interval - number - required ## This changes the collection interval of the check. Default value is 86400 seconds(1 day). For more information, see: ## https://docs.datadoghq.com/developers/write_agent_check/#collection-interval # min_collection_interval: 86400Note:
- We recommend you do not change the
serviceandsourcevalues, as these parameters are integral to the pipeline’s operation. - To track more than one dependency file, add additional entries under
instances:instances: - package_ecosystem: pypi dependency_file_path: /app/requirements.txt min_collection_interval: 86400 - package_ecosystem: npm dependency_file_path: /app/package.json min_collection_interval: 86400 - package_ecosystem: go dependency_file_path: /app/go.mod min_collection_interval: 86400 - package_ecosystem: github_action dependency_file_path: /app/action.yml min_collection_interval: 86400
- We recommend you do not change the
Ensure the dd-agent user has read access to all dependency files you configure and traverse permission on every parent directory in the file path.
Validation
Run the Agent’s status subcommand and look for guarddog under the Checks section.
Data Collected
Logs
The GuardDog integration collects scan logs.
Metrics
The GuardDog integration does not include any metrics.
Events
The GuardDog integration does not include any events.
Troubleshooting
If you see a Permission denied error, run the following command to give the Datadog Agent permission for the GuardDog executable:
chmod o+rx /path/to/guarddog
If the issue persists, ensure that the parent directories in the path are accessible to the Datadog Agent. Run the following command to grant permissions to the parent directory:
chmod o+x /path/to/parent_directory
For any further assistance, contact Datadog support.
