- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- Notebooks
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Search
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Extend Datadog
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API-based Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Service Level Objectives
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Event Management
- Incident Response
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- End User Device Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Storage Management
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Setting Up ClickHouse
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Session Replay
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Code Coverage
- PR Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Developer Integrations
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- AI Guard
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Configuration
- Sources
- Processors
- Destinations
- Packs
- Akamai CDN
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs
- AWS Application Load Balancer Logs
- AWS CloudTrail
- AWS Elastic Load Balancer Logs
- AWS Network Load Balancer Logs
- Cisco ASA
- Cloudflare
- F5
- Fastly
- Fortinet Firewall
- HAProxy Ingress
- Istio Proxy
- Juniper SRX Firewall Traffic Logs
- Netskope
- NGINX
- Okta
- Palo Alto Firewall
- Windows XML
- ZScaler ZIA DNS
- Zscaler ZIA Firewall
- Zscaler ZIA Tunnel
- Zscaler ZIA Web Logs
- Search Syntax
- Scaling and Performance
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Guides and Resources
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
- feature_flags_client
Getting Started with Private Locations
Overview
Private locations allow you to monitor internal-facing applications or private URLs that aren’t accessible from the public internet.
You can also use private locations to:
- Create custom locations in mission-critical areas of your business.
- Verify the application performance in your internal testing environment before you release new features to production with Synthetic tests in your CI/CD pipelines.
- Compare the application performance from inside and outside your internal network.
- Authenticate Synthetic Monitoring tests using Kerberos SSO for internal Windows-based sites and APIs.
Private locations are Docker containers or Windows services that you can install anywhere inside your private network. Retrieve the docker image on Google Container Registry or download the Windows installer.*
Note: Private locations on Docker containers are supported only on the amd64 architecture. If you have any questions about arm64 support, contact Datadog support.
* Use and operation of this software is governed by the End User License Agreement available here.
Once you’ve created and installed your private location, you can assign Synthetic tests to your private location just like you would with a managed location.
Your private locations test results display identically to your managed location test results.
Create your private location
In the Datadog site, hover over Digital Experience and select Settings > Private Locations.
Click Add Private Location.
Fill out your private location details. Only
NameandAPI keyfields are mandatory.Click Save Location and Generate Configuration File to generate the configuration file associated with your private location on your worker.
Depending on where you installed your private location, you may need to input additional parameters to your configuration file:
- If you are using a proxy, input the URL as
http://<YOUR_USER>:<YOUR_PWD>@<YOUR_IP>:<YOUR_PORT>. - If you want to block reserved IPs, toggle Block reserved IPs and enter the IP ranges.
For more information, see Private Locations Configuration Options and Run Synthetic Tests from Private Locations.
- If you are using a proxy, input the URL as
Copy and paste your private location configuration file to your working directory.
Note: The configuration file contains secrets for private location authentication, test configuration decryption, and test result encryption. Datadog does not store the secrets, so store them locally before leaving the Private Locations creation form. You need to be able to reference the secrets again in order to add more workers to your private location.
When you are ready, click View Installation Instructions.
Follow the installation instructions based on the environment you want to run the Private Location worker in.
If you are using Docker, launch your worker as a standalone container using the Docker
runcommand and your configuration file:docker run --rm -v $PWD/worker-config-<LOCATION_ID>.json:/etc/datadog/synthetics-check-runner.json datadog/synthetics-private-location-workerThis command starts a Docker container and prepares your private location to run tests. Datadog recommends running the container in detached mode with proper restart policy.
You can use another container runtime such as Podman. For more information, see the Private Locations documentation.If you are using Windows, run the Synthetics Private Location Installer with a GUI or run the
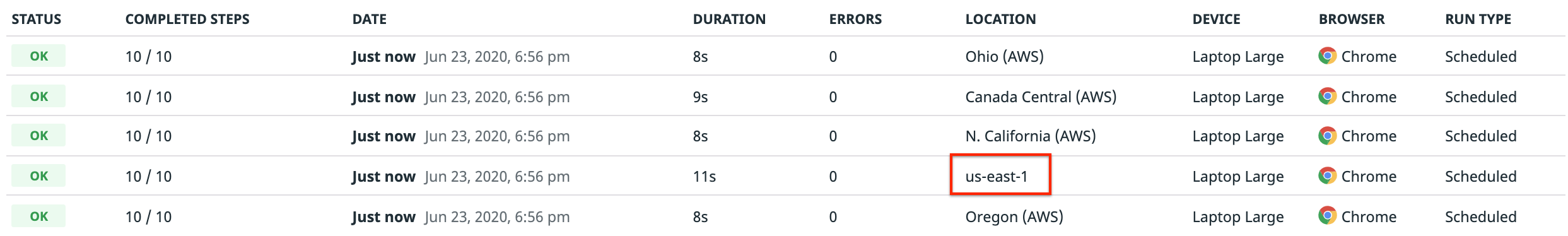
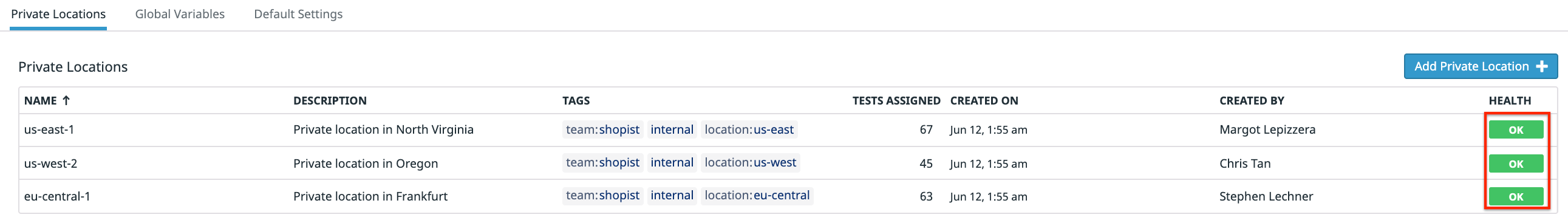
msiexeccommand on the command line inside the directory where you downloaded the installer:msiexec /i datadog-synthetics-worker-1.65.0.amd64.msiIf your private location reports correctly to Datadog, an
OKhealth status displays under Private Location Status and on the Private Locations list in the Settings page:Additionally, you can see private location logs in your terminal:
2022-02-28 16:20:03 [info]: Fetching 10 messages from queue - 10 slots available 2022-02-28 16:20:03 [info]: Fetching 10 messages from queue - 10 slots available 2022-02-28 16:20:04 [info]: Fetching 10 messages from queue - 10 slots availableOnce you’re done testing your internal endpoint, click OK.
Run Synthetic tests with your private location
Use your new private location just like a managed location in your Synthetic tests.
Create an API test, multistep API test, or browser test on any internal endpoint or application you want to monitor.
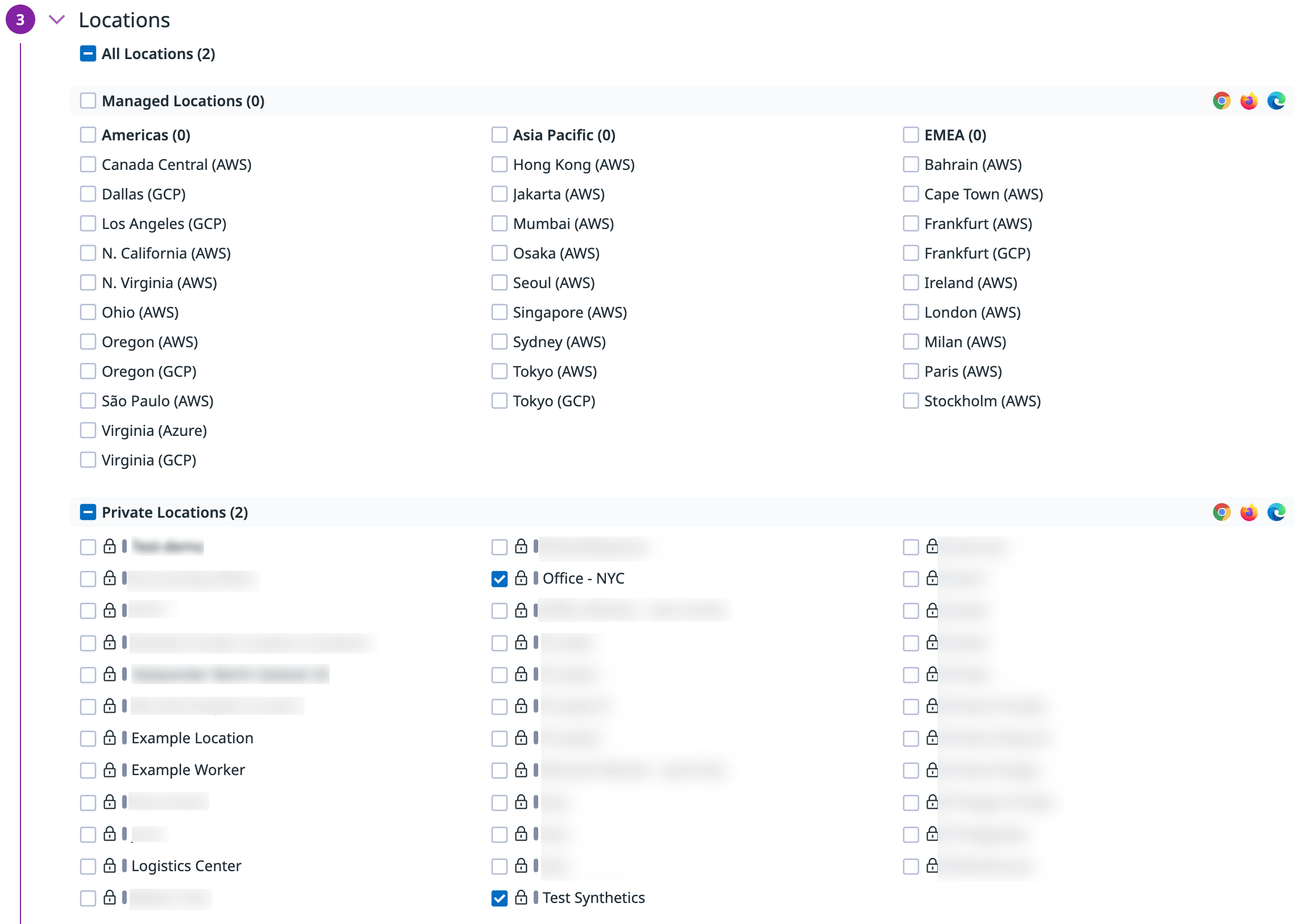
Under Private Locations, select your new private location:
Continue filling out your test!
Further Reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: