- Principales informations
- Getting Started
- Datadog
- Site Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Agent
- Intégrations
- Conteneurs
- Dashboards
- Monitors
- Logs
- Tracing
- Profileur
- Tags
- API
- Service Catalog
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Incident Management
- Database Monitoring
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Intégrations
- OpenTelemetry
- Développeurs
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Checks custom
- Intégrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Recommended Monitor
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Checks de service
- IDE Plugins
- Communauté
- Guides
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Application mobile
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Alertes
- Infrastructure
- Métriques
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Service Catalog
- API Catalog
- Error Tracking
- Service Management
- Infrastructure
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Conteneurs
- Sans serveur
- Surveillance réseau
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Profileur en continu
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Configuration de Postgres
- Configuration de MySQL
- Configuration de SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Données collectées
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Explorer les métriques de requête
- Explorer des échantillons de requêtes
- Dépannage
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Digital Experience
- RUM et Session Replay
- Product Analytics
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Continuous Testing
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Exécuteur de tests intelligent
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Securité
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Pipelines d'observabilité
- Log Management
- Administration
Troubleshooting Serverless Monitoring for AWS Step Functions
Cette page n'est pas encore disponible en français, sa traduction est en cours.
Si vous avez des questions ou des retours sur notre projet de traduction actuel, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter.
Si vous avez des questions ou des retours sur notre projet de traduction actuel, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter.
I cannot see any traces
Verify that your Step Function is configured to send all logs
- Ensure that the
DD_TRACE_ENABLEDtag is set totrueon the Step Function in your AWS console. - In your AWS console, open your Step Function’s logging tab. Ensure that Log level is set to
ALL, and that Include execution data is selected. - Ensure that the CloudWatch log group (also found on the logging tab) has a subscription filter to the Datadog Lambda Forwarder in the same region.
Verify that logs are forwarded successfully to Datadog
- Check the Datadog Lambda Forwarder for error messages. Ensure that you have correctly set your API key and Datadog site.
- Enable
DEBUGlogs on the Datadog Lambda Forwarder by setting the environment variableDD_LOG_LEVELtodebug.
Verify that logs are searchable on Live Search and have DD_TRACE_ENABLED tag
In Datadog, go to Logs > Log Stream. Search for source:stepfunction. You may need to trigger the state machine a few times. If you need to upgrade Datadog Lambda Forwarder from an older version, check that after the upgrade, the Forwarder has the DD_FETCH_STEP_FUNCTIONS_TAGS tag set to true. If the upgraded Forwarder does not have the DD_FETCH_STEP_FUNCTIONS_TAGS tag, your Forwarder may not be upgraded correctly.
If the Forwarder and state machine tags are set up correctly with the previous steps, the logs are tagged with DD_TRACE_ENABLED:true.
Verify that your Step Function is using the latest version
- AWS may release updates to the Step Function API or introduce newer versions of the Step Function definitions. Older versions may result in unexpected log formatting or behavior.
- It’s also recommended that you are using the latest version of the Datadog Lambda Forwarder to avoid discrepancies in how logs are forwarded.
Caution when using custom log pipelines
- Custom log pipelines can offer flexibility in processing logs, but altering the log format too much can lead to issues downstream, such as logs not being parsed or recognized.
- Avoid making significant changes to the Step Function log structure that change the JSON format.
Lambda traces are not merging with Step Function traces
- Verify that you can see both Lambda traces and Step Function traces in Datadog.
- Verify that you are using the correct layer or tracer version according to the trace merging guide. Also ensure that the Lambda step is instrumented in your state machine definition.
- Execute your Step Function once and verify that the
TaskScheduledevent log of the Lambda step has the payload containing data from the Step Function context object. - If your Lambda has the
DD_TRACE_EXTRACTORenvironment variable set, its traces cannot be merged.
I can see the aws.stepfunctions root span but I cannot see any step spans
Please enable the Include execution data option on the state machine’s logging. After enabling this option, log execution input, data passed between states, and execution output is logged. The Datadog backend uses the logs to construct these step spans for you.
Traces are missing intermittently
When searching traces, select the Live Search option in the upper right corner. If Live Search shows your trace, add “@trace_type:stepfunctions” to the retention filter and set the desired retention rate. For debugging, Datadog recommends setting the retention rate to 100%. The filter can be disabled after debugging is done.
Some step spans are missing in the traces
- Actions from Lambda, DynamoDB, StepFunction, and most of the other AWS services are supported.
Wait,Choice,Success,Fail,Pass,Inline MapState, andParallelare supported, whileDistributed MapStatehas limited support.
Search historic logs
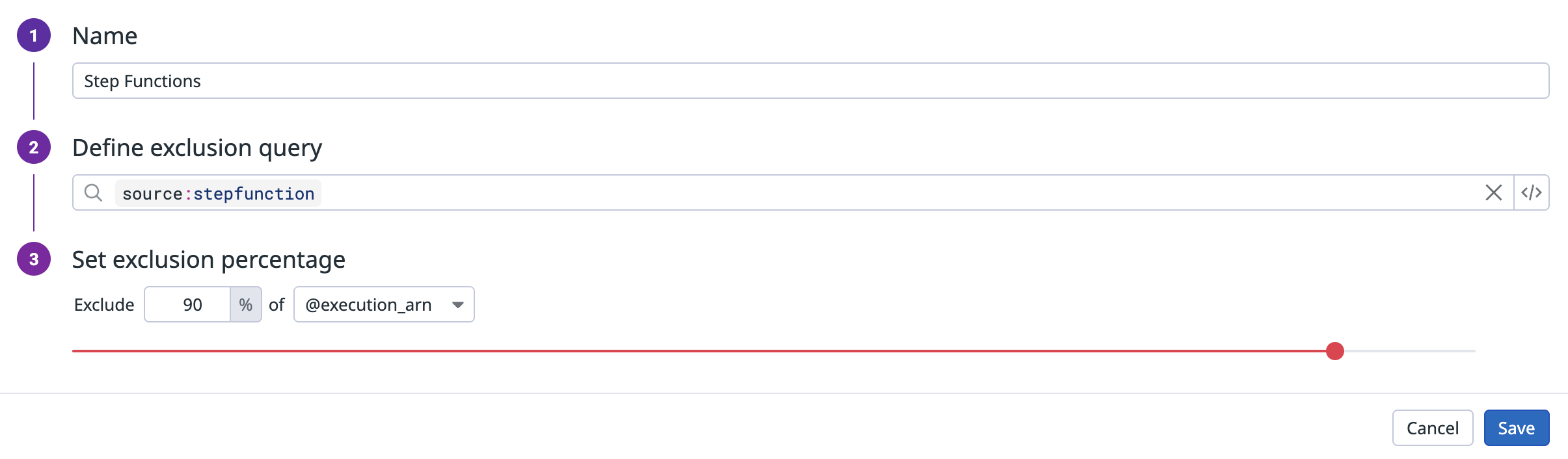
To enable searching historic logs, add a temporary index to the forwarded logs. In Datadog, open the Logs Indexes tab. Click the New Index button in the upper right.
Choose a name, set the index filter to Source:stepfunction, leave everything else with default values, and save.
If your organization has an existing all-encompassing index with a low limit, place your new index at the top.
Note: Indexing logs is not a requirement for getting traces and may incur additional cost. If you are troubleshooting a specific issue, you may wish to temporarily send logs to an index, debug, and delete the index afterwards. See Indexes for more information.
Missing logs within an execution
You can use exclusion filters to exclude a certain percentage of all logs with a particular execution_arn. Using exclusion filters does not impact tracing.
In the following example, the filter excludes logs for 90% of the @execution_arn.
Customized way to deploy Datadog Lambda Forwarder
If you are using your customized way to deploy Datadog Lambda Forwarder, here are some tips that can help you debug enabling Step Functions tracing:
- On the forwarder, set the environment variable
DD_FETCH_STEP_FUNCTIONS_TAGStotrue. - To enable Step Functions trace generation on the Datadog backend, the Datadog-Forwarder layer version must be greater than 31. This version is able to fetch state machine tags, including the required
DD_TRACE_ENABLEDtag. - You can also set the
DD_STEP_FUNCTIONS_TRACE_ENABLEDtag at the Forwarder-level to enable tracing for all Step Functions using that Forwarder on v3.121.0+. - The IAM role for the forwarder should have
tags:getResourcespermission. - Set up a subscription filter on your state machine CloudWatch log group to the Datadog forwarder.
- To verify if logs are reaching the Datadog backend, open the Log Explorer page and search
source:stepfunctionwith theLivesearch timeframe (which shows all logs going into Datadog’s logs intake). If you cannot see any logs, check if there are any error logs on the Datadog Forwarder such as wrong/invalid API key. Adding the environment variableDD_LOG_LEVELofDEBUGhelps you debug the Forwarder issue. If you see Step Functions logs, verify that the logs have thedd_trace_enable:truetag (all tags are normalized) and you should see Step Function traces associated with the log in a few minutes.