- Principales informations
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- Tracing
- Conteneurs
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Site Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Intégrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- OpenTelemetry
- Profileur
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Intégrations
- Développeurs
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Application mobile
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Alertes
- Watchdog
- Métriques
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Conteneurs
- Processes
- Sans serveur
- Surveillance réseau
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Termes et concepts de l'APM
- Sending Traces to Datadog
- APM Metrics Collection
- Trace Pipeline Configuration
- Connect Traces with Other Telemetry
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origin for Spans
- Observabilité des services
- Endpoint Observability
- Dynamic Instrumentation
- Live Debugger
- Suivi des erreurs
- Sécurité des données
- Guides
- Dépannage
- Profileur en continu
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Configuration de Postgres
- Configuration de MySQL
- Configuration de SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Données collectées
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Explorer les métriques de requête
- Explorer des échantillons de requêtes
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Dépannage
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- RUM et Session Replay
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Visibility
- Code Coverage
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Securité
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Pipelines d'observabilité
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
Quality Evaluations
Ce produit n'est pas pris en charge par le site Datadog que vous avez sélectionné. ().
Cette page n'est pas encore disponible en français, sa traduction est en cours.
Si vous avez des questions ou des retours sur notre projet de traduction actuel, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter.
Si vous avez des questions ou des retours sur notre projet de traduction actuel, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter.
Quality evaluations help ensure your LLM-powered applications generate accurate, relevant, and safe responses. Managed evaluations automatically score model outputs on key quality dimensions and attach results to traces, helping you detect issues, monitor trends, and improve response quality over time.
Hallucination
This check identifies instances where the LLM makes a claim that disagrees with the provided input context.
| Evaluation Stage | Evaluation Method | Evaluation Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Evaluated on Output | Evaluated using LLM | Hallucination flags any output that disagrees with the context provided to the LLM. |
Instrumentation
You can use Prompt Tracking annotations to track your prompts and set them up for hallucination configuration. Annotate your LLM spans with the user query and context so hallucination detection can evaluate model outputs against the retrieved data.
from ddtrace.llmobs import LLMObs
from ddtrace.llmobs.types import Prompt
# if your llm call is auto-instrumented...
with LLMObs.annotation_context(
prompt=Prompt(
id="generate_answer_prompt",
template="Generate an answer to this question :{user_question}. Only answer based on the information from this article : {article}",
variables={"user_question": user_question, "article": article},
rag_query_variables=["user_question"],
rag_context_variables=["article"]
),
name="generate_answer"
):
oai_client.chat.completions.create(...) # autoinstrumented llm call
# if your llm call is manually instrumented ...
@llm(name="generate_answer")
def generate_answer():
...
LLMObs.annotate(
prompt=Prompt(
id="generate_answer_prompt",
template="Generate an answer to this question :{user_question}. Only answer based on the information from this article : {article}",
variables={"user_question": user_question, "article": article},
rag_query_variables=["user_question"],
rag_context_variables=["article"]
),
)variables dictionary should contain the key-value pairs your app uses to construct the LLM input prompt (for example, the messages for an OpenAI chat completion request). Use rag_query_variables and rag_context_variables to specify which variables represent the user query and which represent the retrieval context. A list of variables is allowed to account for cases where multiple variables make up the context (for example, multiple articles retrieved from a knowledge base).Hallucination detection does not run if either the rag query, the rag context, or the span output is empty.
Prompt Tracking is available on python starting from the 3.15 version, It also requires an ID for the prompt and the template set up to monitor and track your prompt versions. You can find more examples of prompt tracking and instrumentation in the SDK documentation.
Hallucination configuration
Hallucination detection is only available for OpenAI.
Hallucination detection makes a distinction between two types of hallucinations, which can be configured when Hallucination is enabled.| Configuration Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Contradiction | Claims made in the LLM-generated response that go directly against the provided context |
| Unsupported Claim | Claims made in the LLM-generated response that are not grounded in the context |
Contradictions are always detected, while Unsupported Claims can be optionally included. For sensitive use cases, we recommend including Unsupported Claims.
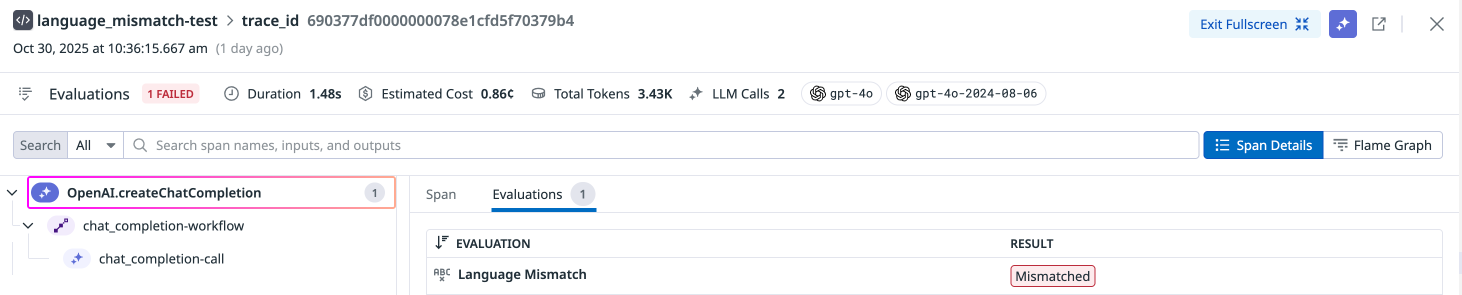
Language Mismatch
This check identifies instances where the LLM generates responses in a different language or dialect than the one used by the user, which can lead to confusion or miscommunication. This check ensures that the LLM’s responses are clear, relevant, and appropriate for the user’s linguistic preferences and needs.
Language mismatch is only supported for natural language prompts. Input and output pairs that mainly consist of structured data such as JSON, code snippets, or special characters are not flagged as a language mismatch.
Supported languages
Supported languages
Afrikaans, Albanian, Arabic, Armenian, Azerbaijani, Belarusian, Bengali, Norwegian Bokmal, Bosnian, Bulgarian, Chinese, Croatian, Czech, Danish, Dutch, English, Estonian, Finnish, French, Georgian, German, Greek, Gujarati, Hebrew, Hindi, Hungarian, Icelandic, Indonesian, Irish, Italian, Japanese, Kazakh, Korean, Latvian, Lithuanian, Macedonian, Malay, Marathi, Mongolian, Norwegian Nynorsk, Persian, Polish, Portuguese, Punjabi, Romanian, Russian, Serbian, Slovak, Slovene, Spanish, Swahili, Swedish, Tamil, Telugu, Thai, Turkish, Ukrainian, Urdu, Vietnamese, Yoruba, Zulu
| Evaluation Stage | Evaluation Method | Evaluation Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Evaluated on Input and Output | Evaluated using Open Source Model | Language Mismatch flags whether each prompt-response pair demonstrates that the LLM application answered the user’s question in the same language that the user used. |