- Principales informations
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- Tracing
- Conteneurs
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Site Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Intégrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- OpenTelemetry
- Profileur
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Intégrations
- Développeurs
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Application mobile
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Alertes
- Watchdog
- Métriques
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Conteneurs
- Processes
- Sans serveur
- Surveillance réseau
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Termes et concepts de l'APM
- Sending Traces to Datadog
- APM Metrics Collection
- Trace Pipeline Configuration
- Connect Traces with Other Telemetry
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origin for Spans
- Observabilité des services
- Endpoint Observability
- Dynamic Instrumentation
- Live Debugger
- Suivi des erreurs
- Sécurité des données
- Guides
- Dépannage
- Profileur en continu
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Configuration de Postgres
- Configuration de MySQL
- Configuration de SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Données collectées
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Explorer les métriques de requête
- Explorer des échantillons de requêtes
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Dépannage
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- RUM et Session Replay
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Visibility
- Code Coverage
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Securité
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Pipelines d'observabilité
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
Google Cloud Metric Discrepancy
Cette page n'est pas encore disponible en français, sa traduction est en cours.
Si vous avez des questions ou des retours sur notre projet de traduction actuel, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter.
Si vous avez des questions ou des retours sur notre projet de traduction actuel, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter.
Overview
Use this guide to troubleshoot metric discrepancies between Google Cloud and Datadog.
Metric discrepancies
Datadog ingests the most granular raw values from Google Cloud. All aggregation seen in Datadog happens on the Datadog side. Datadog’s metrics intake imports the raw values from Google as gauges, and any further aggregation is performed within Datadog. The following steps reconcile the metric gcp.redis.stats.cpu_utilization between Google Cloud and Datadog.
Find the corresponding metric in Google Cloud.
For the Google Cloud integration, Datadog converts Google Cloud metrics into the format
gcp.Google_Cloud_SERVICE_NAME.METRIC_NAME. For the example metric, the Google Cloud service name is redis, and the metric name is stats/cpu_utilization. The full metric name isredis.googleapis.com/stats/cpu_utilization.Find the most granular dimensions.
These include all the Resource labels:
project_id,region,instance_id,node_id, and Metric labels:role,space,relationship. Refer to the Google Cloud documentation for other metrics.Resource type is associated with each metric under a Google Cloud service. Below are the supported resource types for redis service. The example metric’s resource type is
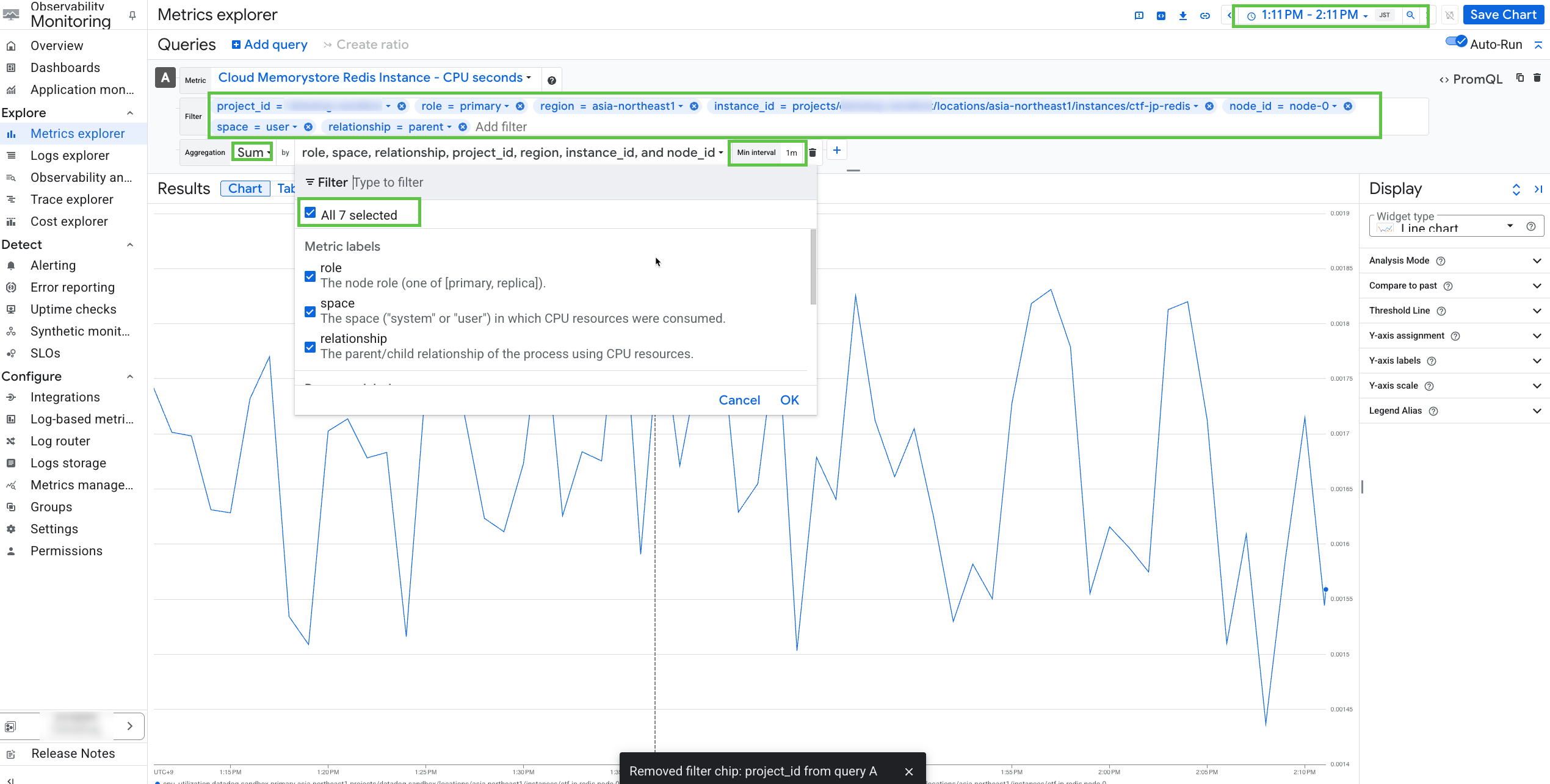
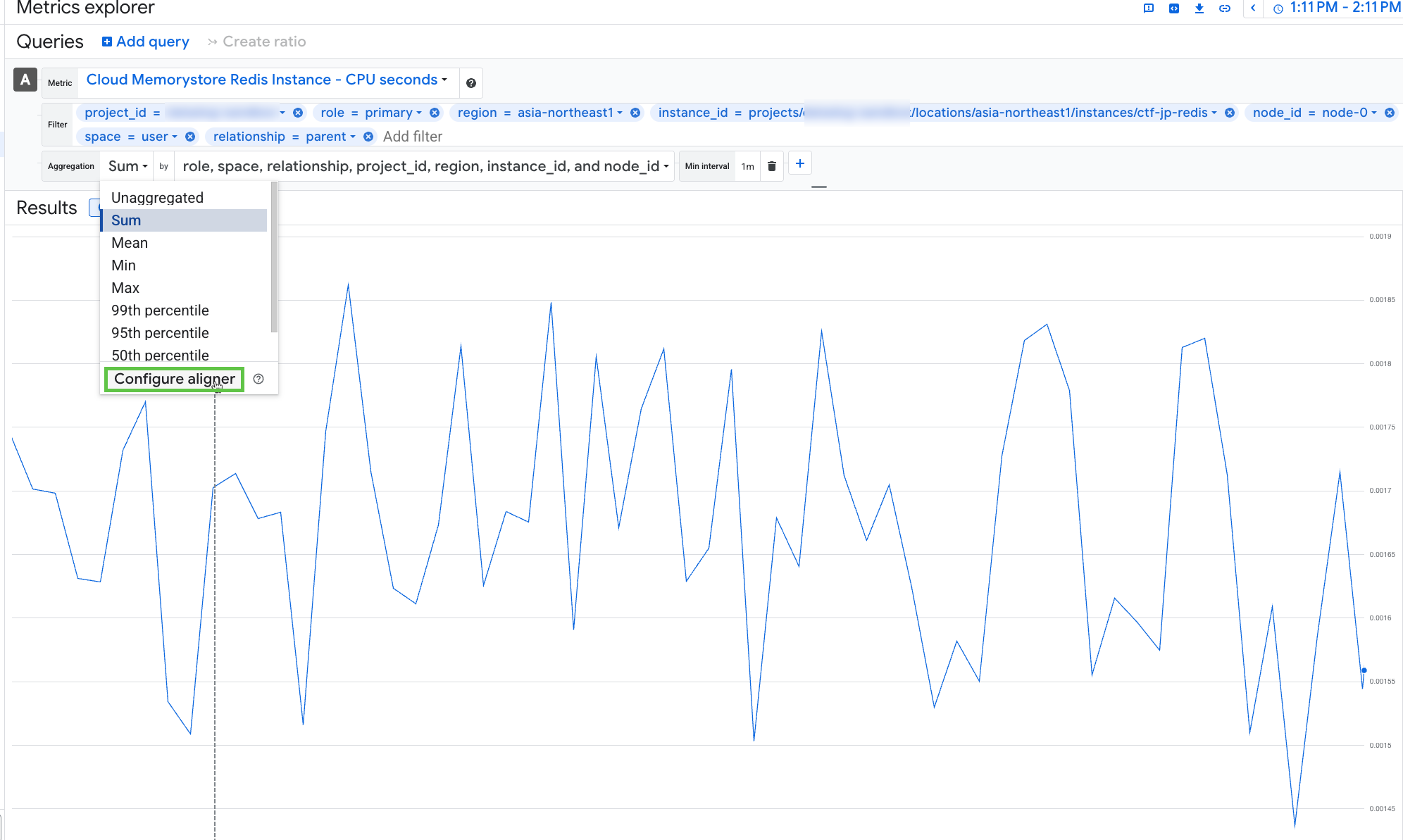
redis_instance.redis_instancehas Resource labels:project_id,region,instance_id,node_id.Graph the metric in the Google Cloud Metrics Explorer.
Search for
redis.googleapis.com/stats/cpu_utilization.- Time: 1 hour (ideally in UTC)
- Namespace: Cloud Memorystore Redis Instance
- Metric name: CPU Seconds
- Filter: (most granular dimensions) project_id, region, instance_id, node_id, role, space, relationship.
- Aggregation: Sum (should show the same values when using mean, min, max, sum, or none if using most granular dimensions)
- Min interval: 1m
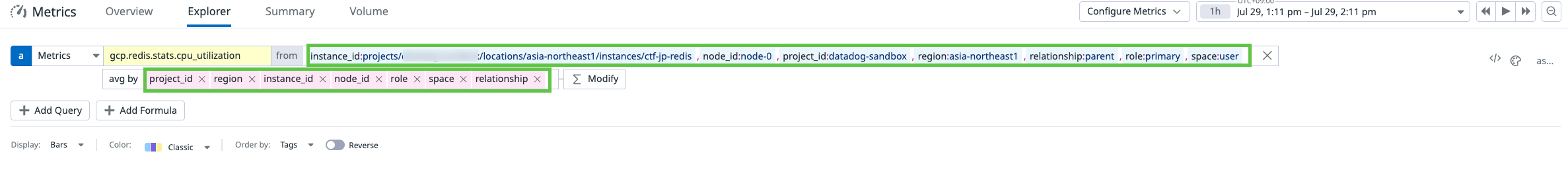
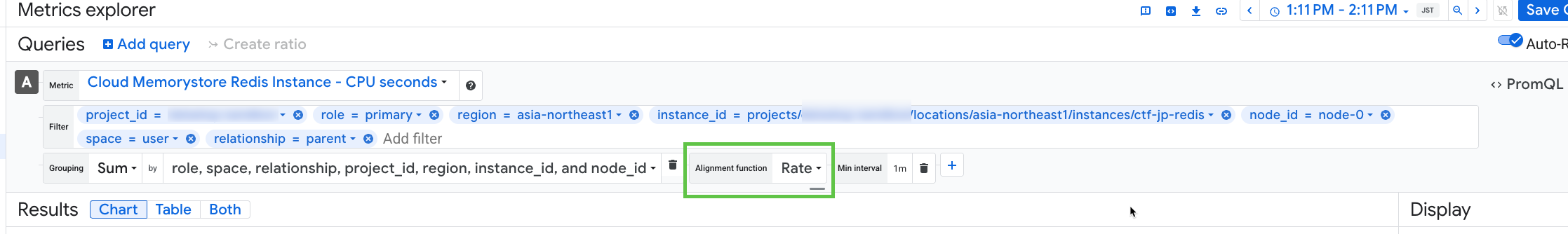
Graph the metric in the Datadog Metrics Explorer.
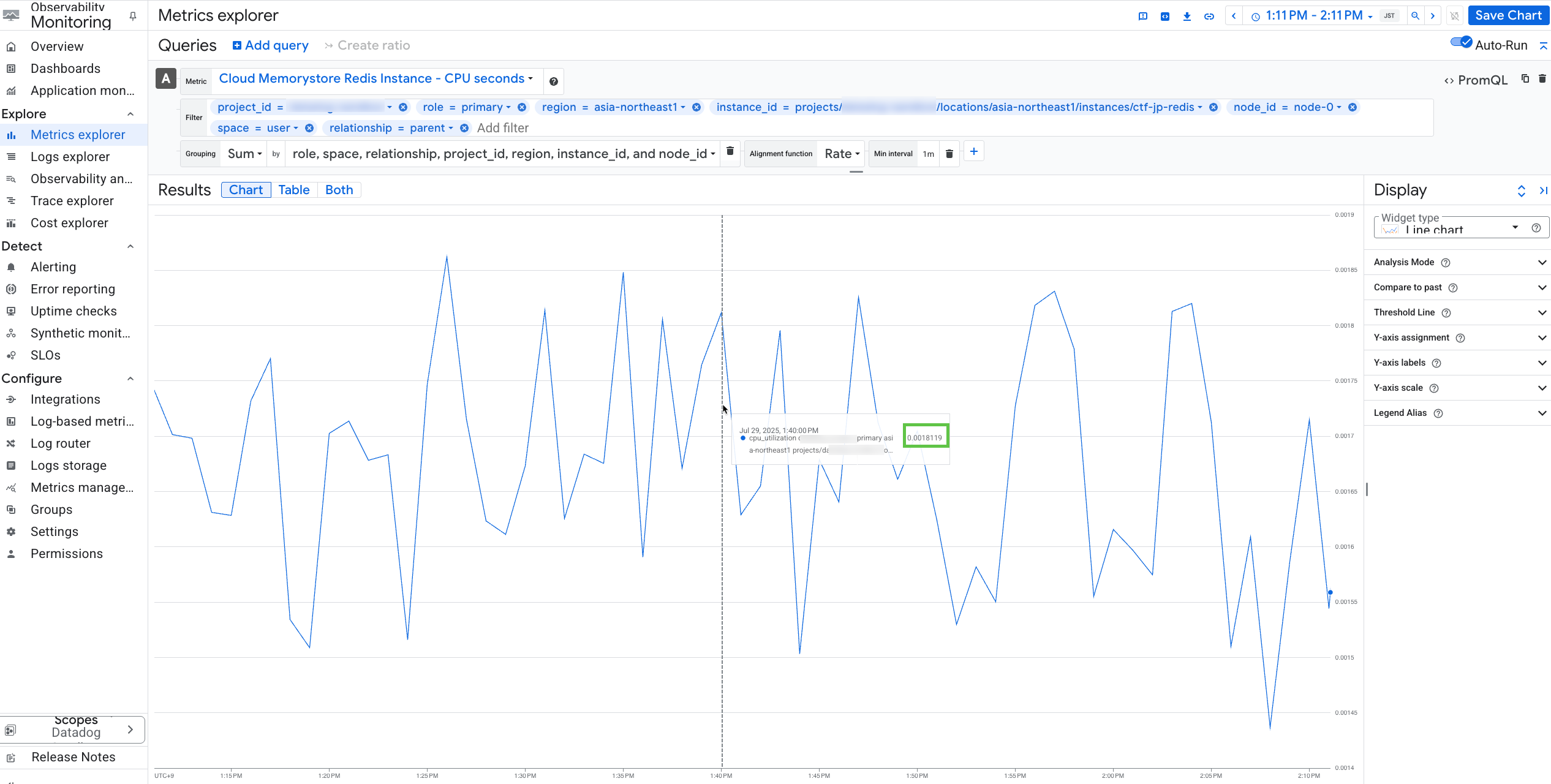
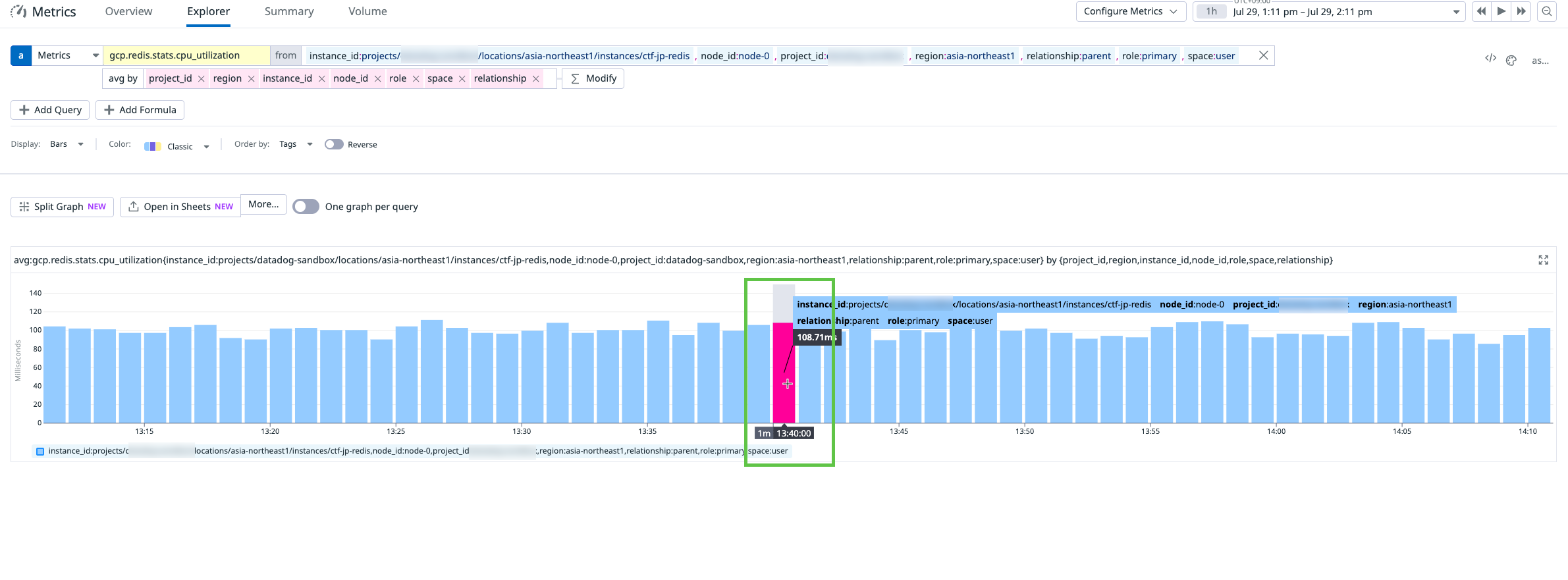
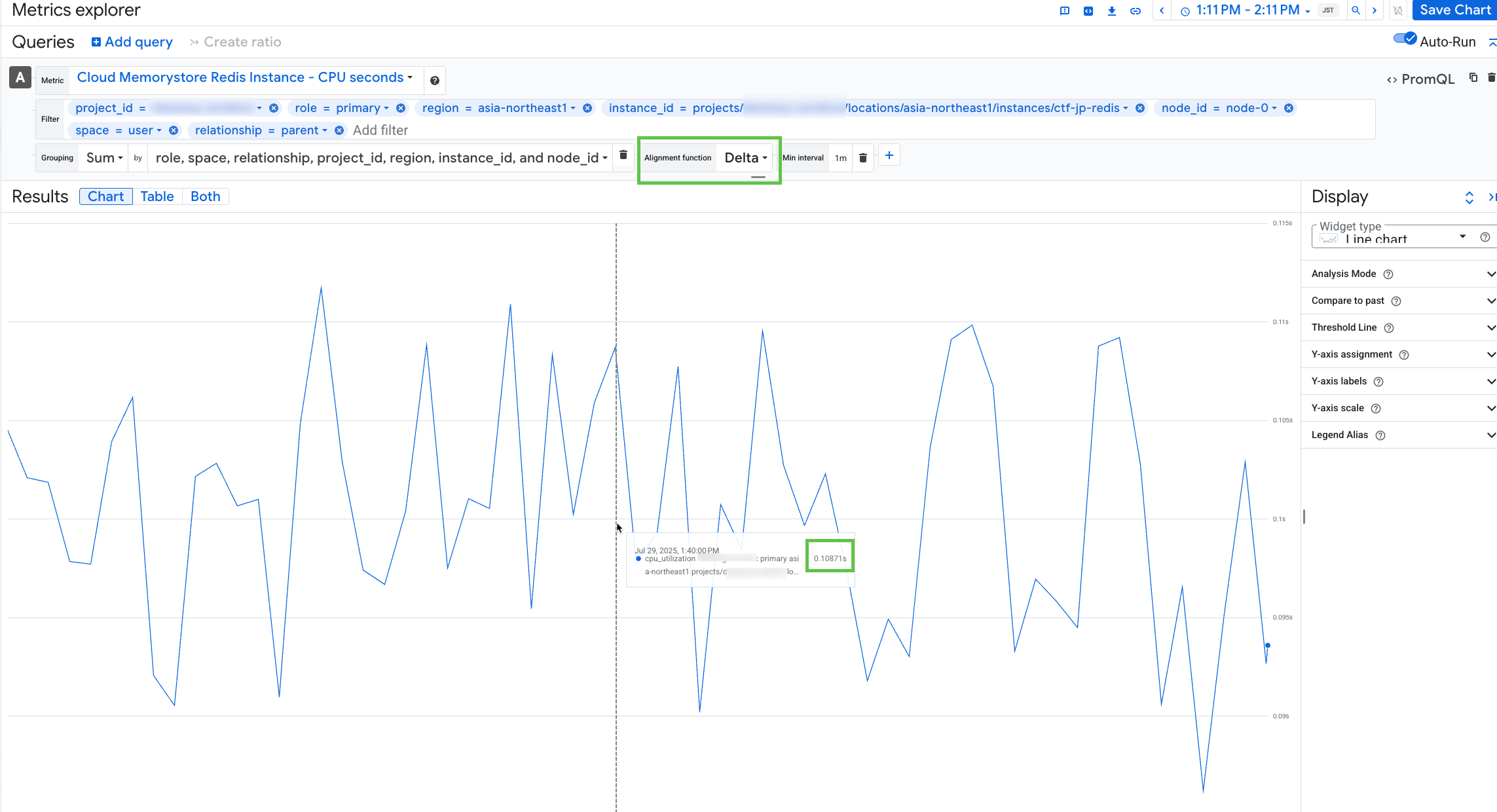
In most cases, after completing steps 1–4, you see the exact same values in both Google Cloud and Datadog. However, in our example, a discrepancy appears at 01:40:00 PM.
- Datadog: 108.71ms
- Google Cloud: 0.0018119s
Understand Google Cloud alignment functions.
This discrepancy occurs because by default, Google Cloud applies a rate alignment for this metric. For details, see the Google cloud alignment function documentation. Click on
configure alignerto see that the alignment function is automatically set to rate (0.108711 / 60 ≃ 0.0018119).Adjust the alignment function in Google Cloud.
Change the alignment function to
delta,min,max,sum, ormean. Assuming you are using the most granular dimensions, the value in Google Cloud should match the value in Datadog.
Further reading
Documentation, liens et articles supplémentaires utiles: