- Esenciales
- Empezando
- Agent
- API
- Rastreo de APM
- Contenedores
- Dashboards
- Monitorización de bases de datos
- Datadog
- Sitio web de Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Gestión de incidencias
- Integraciones
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitores
- OpenTelemetry
- Generador de perfiles
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless para Lambda AWS
- Software Delivery
- Monitorización Synthetic
- Etiquetas (tags)
- Workflow Automation
- Centro de aprendizaje
- Compatibilidad
- Glosario
- Atributos estándar
- Guías
- Agent
- Arquitectura
- IoT
- Plataformas compatibles
- Recopilación de logs
- Configuración
- Automatización de flotas
- Solucionar problemas
- Detección de nombres de host en contenedores
- Modo de depuración
- Flare del Agent
- Estado del check del Agent
- Problemas de NTP
- Problemas de permisos
- Problemas de integraciones
- Problemas del sitio
- Problemas de Autodiscovery
- Problemas de contenedores de Windows
- Configuración del tiempo de ejecución del Agent
- Consumo elevado de memoria o CPU
- Guías
- Seguridad de datos
- Integraciones
- Desarrolladores
- Autorización
- DogStatsD
- Checks personalizados
- Integraciones
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Crear una integración basada en el Agent
- Crear una integración API
- Crear un pipeline de logs
- Referencia de activos de integración
- Crear una oferta de mercado
- Crear un dashboard de integración
- Create a Monitor Template
- Crear una regla de detección Cloud SIEM
- Instalar la herramienta de desarrollo de integraciones del Agente
- Checks de servicio
- Complementos de IDE
- Comunidad
- Guías
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Aplicación móvil de Datadog
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft
- En la aplicación
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- Editor DDSQL
- Reference Tables
- Hojas
- Monitores y alertas
- Watchdog
- Métricas
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Explorador
- Estados de problemas
- Detección de regresión
- Suspected Causes
- Error Grouping
- Bits AI Dev Agent
- Monitores
- Issue Correlation
- Identificar confirmaciones sospechosas
- Auto Assign
- Issue Team Ownership
- Rastrear errores del navegador y móviles
- Rastrear errores de backend
- Manage Data Collection
- Solucionar problemas
- Guides
- Change Tracking
- Gestión de servicios
- Objetivos de nivel de servicio (SLOs)
- Gestión de incidentes
- De guardia
- Status Pages
- Gestión de eventos
- Gestión de casos
- Actions & Remediations
- Infraestructura
- Cloudcraft
- Catálogo de recursos
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Contenedores
- Processes
- Serverless
- Monitorización de red
- Cloud Cost
- Rendimiento de las aplicaciones
- APM
- Términos y conceptos de APM
- Instrumentación de aplicación
- Recopilación de métricas de APM
- Configuración de pipelines de trazas
- Correlacionar trazas (traces) y otros datos de telemetría
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origin for Spans
- Observabilidad del servicio
- Endpoint Observability
- Instrumentación dinámica
- Live Debugger
- Error Tracking
- Seguridad de los datos
- Guías
- Solucionar problemas
- Límites de tasa del Agent
- Métricas de APM del Agent
- Uso de recursos del Agent
- Logs correlacionados
- Stacks tecnológicos de llamada en profundidad PHP 5
- Herramienta de diagnóstico de .NET
- Cuantificación de APM
- Go Compile-Time Instrumentation
- Logs de inicio del rastreador
- Logs de depuración del rastreador
- Errores de conexión
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Gastos generales de integración del Agent
- Arquitecturas de configuración
- Configuración de Postgres
- Configuración de MySQL
- Configuración de SQL Server
- Configuración de Oracle
- Configuración de MongoDB
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Conexión de DBM y trazas
- Datos recopilados
- Explorar hosts de bases de datos
- Explorar métricas de consultas
- Explorar ejemplos de consulta
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Solucionar problemas
- Guías
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Experiencia digital
- Real User Monitoring
- Pruebas y monitorización de Synthetics
- Continuous Testing
- Análisis de productos
- Entrega de software
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Visibility
- Configuración
- Network Settings
- Tests en contenedores
- Repositories
- Explorador
- Monitores
- Test Health
- Flaky Test Management
- Working with Flaky Tests
- Test Impact Analysis
- Flujos de trabajo de desarrolladores
- Cobertura de código
- Instrumentar tests de navegador con RUM
- Instrumentar tests de Swift con RUM
- Correlacionar logs y tests
- Guías
- Solucionar problemas
- Code Coverage
- Quality Gates
- Métricas de DORA
- Feature Flags
- Seguridad
- Información general de seguridad
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- Observabilidad de la IA
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Gestión de logs
- CloudPrem
- Administración
- Gestión de cuentas
- Seguridad de los datos
- Ayuda
Amazon ElastiCache
Información general
Consulta Monitorización de métricas de rendimiento de ElastiCache con Redis o Memcached para obtener información sobre métricas de rendimiento clave, cómo recopilarlas y cómo Coursera monitoriza ElastiCache utilizando Datadog.
Configuración
Si aún no lo has hecho, configura primero la integración de Amazon Web Services.
Instalación sin el Datadog Agent
En la página de la integración AWS, asegúrate de que
ElastiCacheestá habilitado en la pestañaMetric Collection.Añade los siguientes permisos a tu política IAM de Datadog para poder recopilar métricas de Amazon ElastiCache. Para obtener más información, consulta las políticas de ElastiCache en el sitio web de AWS.
AWS Permiso Descripción elasticache:DescribeCacheClustersEnumera y describe clústeres de caché, para añadir etiquetas (tags) y métricas adicionales. elasticache:ListTagsForResourceEnumera etiquetas personalizadas de un clúster, para añadir etiquetas personalizadas. elasticache:DescribeEventsAñade eventos de snapshots y mantenimientos. Instala la integración Datadog - Amazon ElastiCache.
Instalación con el Datadog Agent (recomendado)
Recopilación de métricas nativas con el Agent
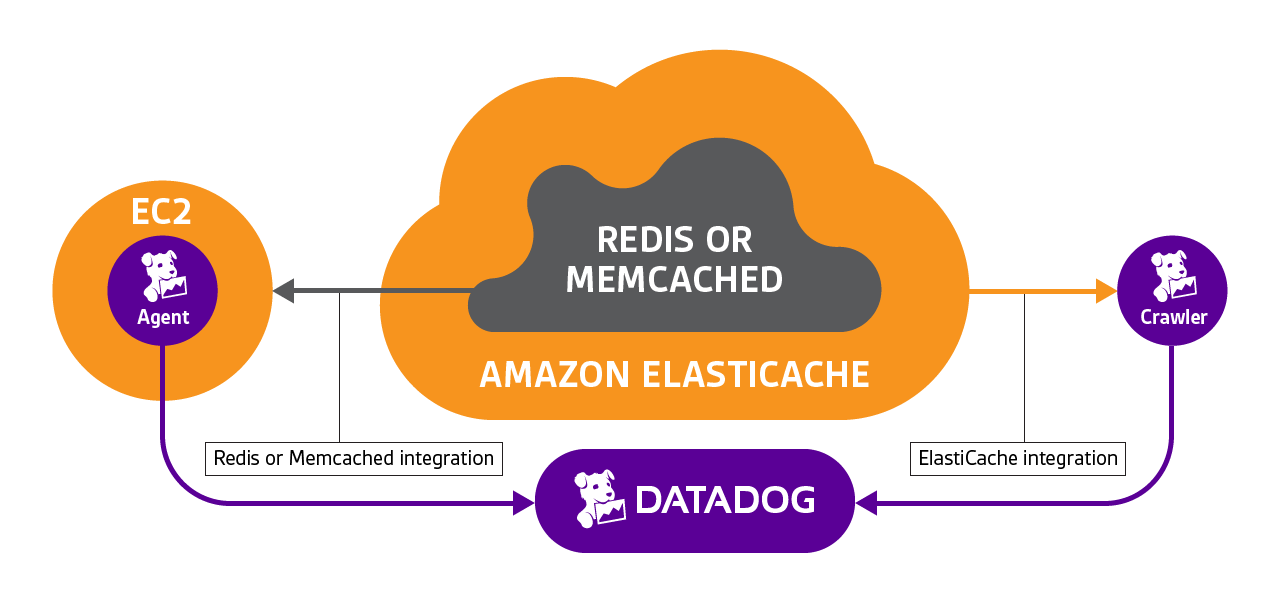
El siguiente diagrama muestra cómo Datadog recopila métricas directamente de CloudWatch con la integración ElastiCache nativa y cómo además puede recopilar métricas nativas directamente de tecnologías backend: Redis o Memcached. Al recopilar directamente del backend, tienes acceso a un mayor número de métricas importantes, a una mayor resolución.
Funcionamiento
Debido a que las métricas del Agent están vinculadas a la instancia EC2, donde se ejecuta el Agent, y no a la instancia ElastiCache real, es necesario utilizar la etiqueta cacheclusteridpara conectar todas las métricas. Una vez que el Agent esté configurado con las mismas etiquetas que la instancia ElastiCache, la combinación de las métricas Redis/Memcached con las métricas ElastiCache es realmente sencilla.
Paso a paso
Debido a que el Agent no se ejecuta en una instancia ElastiCache real, sino en una máquina remota, la clave para configurar correctamente esta integración es indicarle al Agent dónde recolectar las métricas.
Recopilación de la información de conexión para tu instancia ElastiCache
Primero ve a la consola de AWS, abre la sección ElastiCache y luego la pestaña Clústeres de caché para encontrar el clúster que quieres monitorizar. Deberías ver algo como lo siguiente:
Luego, haz clic en el enlace “nodo” para acceder a la URL de tu endpoint:
Anota la URL del endpoint (por ejemplo: replica-001.xxxx.use1.cache.amazonaws.com) y el cacheclusterid (por ejemplo: replica-001). Necesitas estos valores para configurar el Agent y para crear gráficos y dashboards.
Configuración del Agent
Las integraciones Redis/Memcached admiten el etiquetado de instancias de caché individuales. Originalmente diseñadas para permitir la monitorización de múltiples instancias en la misma máquina, estas etiquetas también se pueden utilizar para filtrar y agrupar métricas. El siguiente es un ejemplo de configuración de ElastiCache con Redis utilizando redisdb.yaml. Para obtener más información acerca de dónde se almacena este archivo en función de tu plataforma, consulta el directorio de configuración del Agent.
init_config:
instances:
# Endpoint URL from AWS console
- host: replica-001.xxxx.use1.cache.amazonaws.com
port: 6379
# Cache Cluster ID from AWS console
tags:
- cacheclusterid:replicaa-001
A continuación, reinicia el Agent: sudo /etc/init.d/datadog-agent restart (en Linux).
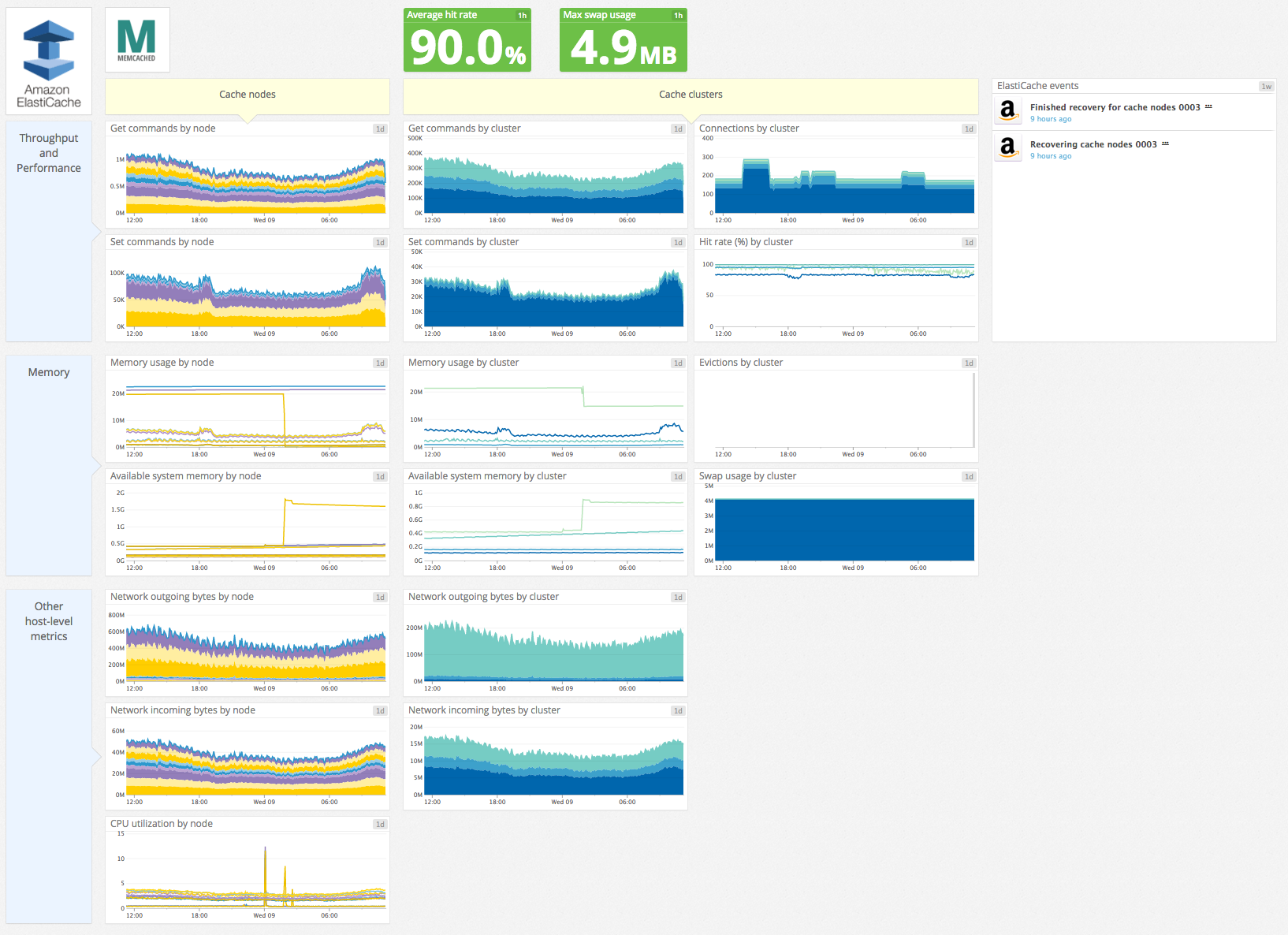
Visualizar métricas juntas
Después de unos minutos, se puede acceder a las métricas ElastiCache y a las métricas Redis o Memcached en Datadog para la creación de gráficos, la monitorización, etc.
A continuación se muestra un ejemplo de configuración de un gráfico para combinar las métricas de hits de caché de ElastiCache con las métricas de latencia nativas de Redis utilizando la misma etiqueta cacheclusterid replicaa-001.
Datos recopilados
Métricas
| aws.elasticache.active_defrag_hits (gauge) | Redis - Número de reasignaciones de valores por minuto realizadas por el proceso de desfragmentación activo. |
| aws.elasticache.bytes_read_into_memcached (count) | Memcached - Número de bytes leídos desde la red por el nodo caché. Se muestra como byte |
| aws.elasticache.bytes_used_for_cache (gauge) | Redis - Número total de bytes asignados por Redis. Se muestra como byte |
| aws.elasticache.bytes_used_for_cache_items (gauge) | Memcached - Número de bytes utilizados para almacenar los elementos de la caché. Se muestra como byte |
| aws.elasticache.bytes_used_for_hash (gauge) | Memcached - Número de bytes utilizados actualmente por las tablas hash. Se muestra como byte |
| aws.elasticache.bytes_written_out_from_memcached (count) | Memcached - Número de bytes escritos en la red por el nodo caché. Se muestra como byte |
| aws.elasticache.cache_hit_rate (gauge) | Redis - Indica la eficiencia de uso de la instancia Redis. Se muestra como porcentaje |
| aws.elasticache.cache_hits (count) | Redis - Número de búsquedas de claves realizadas con éxito. Se muestra como acierto |
| aws.elasticache.cache_misses (count) | Redis - Número de búsquedas de claves fallidas. Se muestra como fallido |
| aws.elasticache.cas_badval (count) | Memcached - Número de solicitudes de CAS (comprobación y definición) recibidas por la caché en las que el valor CAS no coincidió con el valor CAS almacenado. Se muestra como solicitud |
| aws.elasticache.cas_hits (count) | Memcached - Número de solicitudes de CAS recibidas por la caché en las que se encontró la clave solicitada y el valor de CAS coincidió. Se muestra como acierto |
| aws.elasticache.cas_misses (count) | Memcached - Número de solicitudes de CAS recibidas por la caché en las que no se encontró la clave solicitada. Se muestra como fallido |
| aws.elasticache.cluster_count (count) | Número de clústeres de Elasticache. |
| aws.elasticache.cmd_config_get (count) | Memcached - Número acumulado de solicitudes de configuración get. Se muestra como get |
| aws.elasticache.cmd_config_set (count) | Memcached - Número acumulado de solicitudes de configuración set. Se muestra como set |
| aws.elasticache.cmd_flush (count) | Memcached - Número de comandos flush recibidos por la caché. Se muestra como flush |
| aws.elasticache.cmd_get (count) | Memcached - Número de comandos get recibidos por la caché. Se muestra como get |
| aws.elasticache.cmd_set (count) | Memcached - Número de comandos set recibidos por la caché. Se muestra como set |
| aws.elasticache.cmd_touch (count) | Memcached - Número acumulado de solicitudes touch. Se muestra como solicitud |
| aws.elasticache.cpucredit_balance (gauge) | Número de créditos de CPU ganados, acumulados por una instancia desde su lanzamiento o inicio. Se muestra como unidad |
| aws.elasticache.cpucredit_usage (gauge) | Número de créditos de CPU utilizados por la instancia para la utilización de la CPU. Se muestra como unidad |
| aws.elasticache.cpuutilization (gauge) | Porcentaje de uso de la CPU para el servidor. Se muestra como porcentaje |
| aws.elasticache.curr_config (gauge) | Memcached - Número actual de configuraciones almacenadas. |
| aws.elasticache.curr_connections (gauge) | Redis - Número de conexiones de clientes, excluyendo las conexiones de réplicas de lectura. Memcached - Recuento del número de conexiones conectadas a la caché en un instante en el tiempo. Se muestra como conexión. |
| aws.elasticache.curr_items (gauge) | Redis - Número de elementos en la caché. Se obtiene a partir de la estadística del espacio de claves de Redis, sumando todas las claves del espacio de claves completo. Memcached - Recuento del número de elementos almacenados actualmente en la caché. Se muestra como elemento |
| aws.elasticache.database_memory_usage_percentage (gauge) | Redis - Porcentaje de memoria disponible para el clúster que está en uso. Se muestra como porcentaje |
| aws.elasticache.db_0average_ttl (gauge) | Redis - Expone avg_ttl del propietario de la base de datos (DB0) a partir de la estadística del espacio de claves del comando INFO de Redis. Se muestra como milisegundo |
| aws.elasticache.decr_hits (count) | Memcached - Número de solicitudes de decremento recibidas por la caché en las que se encontró la clave solicitada. Se muestra como acierto |
| aws.elasticache.decr_misses (count) | Memcached - Número de solicitudes de decremento recibidas por la caché en las que no se encontró la clave solicitada. Se muestra como fallido |
| aws.elasticache.delete_hits (count) | Memcached - Número de solicitudes de eliminación recibidas por la caché en las que se encontró la clave solicitada. Se muestra como acierto |
| aws.elasticache.delete_misses (count) | Memcached - Número de solicitudes de eliminación recibidas por la caché en las que no se encontró la clave solicitada. Se muestra como fallido |
| aws.elasticache.engine_cpuutilization (gauge) | Porcentaje de uso de la CPU para el proceso Redis. Se muestra como porcentaje |
| aws.elasticache.eval_based_cmds (count) | Redis - Número total de comandos para los comandos basados en eval. Se muestra como comando |
| aws.elasticache.eval_based_cmds_latency (gauge) | Redis - Latencia de los comandos basados en eval. Se muestra como microsegundo |
| aws.elasticache.evicted_unfetched (count) | Memcached - Número de elementos válidos desalojados de la caché de uso menos reciente (LRU) que nunca se tocaron después de definirse. Se muestra como elemento |
| aws.elasticache.evictions (count) | Redis - Número de claves desalojadas debido al límite máximo de memoria. Memcached - Número de elementos no caducados, desalojados por la caché para dejar espacio a nuevas escrituras. Se muestra como desalojo. |
| aws.elasticache.expired_unfetched (count) | Memcached - Número de elementos caducados recuperados de la caché de LRU que nunca se tocaron después de definirse. Se muestra como elemento |
| aws.elasticache.freeable_memory (gauge) | Cantidad de memoria libre disponible en el host. Se muestra como byte |
| aws.elasticache.geo_spatial_based_cmds (count) | Redis - Número total de comandos geoespaciales. Se muestra como comando |
| aws.elasticache.get_hits (count) | Memcached - Número de solicitudes get recibidas por la caché en las que se encontró la clave solicitada. Se muestra como acierto |
| aws.elasticache.get_misses (count) | Memcached - Número de solicitudes get recibidas por la caché en las que no se encontró la clave solicitada. Se muestra como fallido |
| aws.elasticache.get_type_cmds (count) | Redis - Número total de comandos de sólo lectura. Se obtiene de la estadística commandstats de Redis OSS sumando todos los comandos de sólo lectura (get, hget, scard, lrange, etc.) Se muestra como comando. |
| aws.elasticache.get_type_cmds_latency (gauge) | Redis - Latencia de los comandos de lectura. Se muestra como microsegundo |
| aws.elasticache.hash_based_cmds (count) | Redis - Número total de comandos basados en hash. Se obtiene de la estadística commandstats de Redis sumando todos los comandos que actúan sobre uno o más hashes. Se muestra como comando |
| aws.elasticache.hash_based_cmds_latency (gauge) | Redis - Latencia de los comandos basados en hash. Se muestra como microsegundo |
| aws.elasticache.hyper_log_log_based_cmds (count) | Redis - Número total de comandos basados en HyperLogLog. Se obtiene a partir de la estadística commandstats de Redis sumando todos los comandos de tipo pf (pfadd, pfcount, pfmerge). Se muestra como comando. |
| aws.elasticache.incr_hits (count) | Memcached - Número de solicitudes de incremento recibidas por la caché en las que se encontró la clave solicitada. Se muestra como acierto |
| aws.elasticache.incr_misses (count) | Memcached - Número de solicitudes de incremento recibidas por la caché en las que no se encontró la clave solicitada. Se muestra como fallido |
| aws.elasticache.is_master (gauge) | Redis - Devuelve 1 si el nodo es el principal, 0 en caso contrario. |
| aws.elasticache.key_based_cmds (count) | Redis - Número total de comandos basados en claves. Se obtiene a partir de la estadística commandstats de Redis sumando todos los comandos que actúan sobre una o varias claves. Se muestra como comando. |
| aws.elasticache.key_based_cmds_latency (gauge) | Redis - Latencia de los comandos basados en claves. Se muestra como microsegundo |
| aws.elasticache.list_based_cmds (count) | Redis - Número total de comandos basados en listas. Se obtiene de la estadística commandstats de Redis sumando todos los comandos que actúan sobre una o más listas. Se muestra como comando |
| aws.elasticache.master_link_health_status (gauge) | Redis - Un valor de 0 indica que los datos en el nodo primario de Elasticache no están sincronizados con Redis en EC2. Un valor de 1 indica que los datos están sincronizados. |
| aws.elasticache.memory_fragmentation_ratio (gauge) | Redis - Indica la eficiencia en la asignación de memoria del motor Redis. |
| aws.elasticache.network_bytes_in (count) | Número de bytes que el host ha leído de la red. Se muestra como byte |
| aws.elasticache.network_bytes_out (count) | Número de bytes que el host ha escrito en la red. Se muestra como byte |
| aws.elasticache.network_packets_in (count) | Número de paquetes recibidos en todas las interfaces de red por la instancia. Se muestra como paquete |
| aws.elasticache.network_packets_out (count) | Número de paquetes enviados en todas las interfaces de red por la instancia. Se muestra como paquete |
| aws.elasticache.new_connections (count) | Redis - Número total de conexiones aceptadas por el servidor durante este periodo. Memcached - Número de conexiones nuevas recibidas por la caché. Se obtiene a partir de la estadística memcached total_connections registrando el cambio en total_connections durante un periodo de tiempo. Siempre será al menos 1, debido a una conexión reservada para un ElastiCache. Se muestra como conexión |
| aws.elasticache.new_items (count) | Memcached - Número de nuevos elementos almacenados por la caché. Se obtiene a partir de la estadística memcached total_items registrando el cambio en total_items durante un periodo de tiempo. Se muestra como elemento |
| aws.elasticache.node_count (count) | Número de nodos Elasticache. Se muestra como nodo |
| aws.elasticache.reclaimed (count) | Redis - Número total de eventos de vencimiento de claves. Memcached - Número de elementos vencidos, desalojados por la caché para dejar espacio a nuevas escrituras. |
| aws.elasticache.replication_bytes (gauge) | Redis - Para elementos primarios con réplicas adjuntas, ReplicationBytes informa del número de bytes que el elemento primario está enviando a todas tus réplicas. Esta métrica es representativa de la carga de escritura en el grupo de replicación. Para réplicas y elementos primarios independientes, ReplicationBytes es siempre 0. Se muestra como byte |
| aws.elasticache.replication_lag (gauge) | Redis - Esta métrica sólo es aplicable a un nodo de caché que se ejecuta como réplica de lectura. Representa el retraso, en segundos, de la réplica al aplicar los cambios del clúster de caché primario. Se muestra como segundo |
| aws.elasticache.save_in_progress (gauge) | Redis - Esta métrica binaria devuelve 1 siempre que un proceso de almacenamiento en segundo plano (con o sin bifurcación) esté en curso, y 0 en caso contrario. Un proceso de almacenamiento en segundo plano se utiliza normalmente durante snapshots y sincronizaciones. Estas operaciones pueden degradar el rendimiento. Utilizando la métrica SaveInProgress, puedes diagnosticar si la degradación del rendimiento se debe a un proceso de almacenamiento en segundo plano. |
| aws.elasticache.set_based_cmds (count) | Redis - Número total de comandos basados en conjuntos. Se obtiene de la estadística commandstats de Redis sumando todos los comandos que actúan sobre uno o más conjuntos. Se muestra como comando |
| aws.elasticache.set_based_cmds_latency (gauge) | Redis - Latencia de los comandos basados en conjuntos. Se muestra como microsegundo |
| aws.elasticache.set_type_cmds (count) | Redis - Número total de tipos de comandos de escritura. Se obtiene de la estadística commandstats de Redis OSS sumando todos los tipos mutativos de comandos que operan con datos (set, hset, sadd, lpop, etc.) Se muestra como comando. |
| aws.elasticache.set_type_cmds_latency (gauge) | Redis - Latencia de los comandos de escritura. Se muestra como microsegundo |
| aws.elasticache.slabs_moved (count) | Memcached - Número total de páginas slab que se han movido. Se muestra como página |
| aws.elasticache.sorted_set_based_cmds (count) | Redis - Número total de comandos basados en conjuntos ordenados. Se obtiene a partir de la estadística commandstats de Redis sumando todos los comandos que actúan sobre uno o más conjuntos ordenados. Se muestra como comando |
| aws.elasticache.sorted_set_based_cmds_latency (gauge) | Redis - Latencia de los comandos basados en ordenamientos. Se muestra como microsegundo |
| aws.elasticache.stream_based_cmds (count) | Redis - Número total de comandos basados en flujos. Se muestra como comando |
| aws.elasticache.stream_based_cmds_latency (gauge) | Redis - Latencia de los comandos basados en flujos. Se muestra como microsegundo |
| aws.elasticache.string_based_cmds (count) | Redis - Número total de comandos basados en cadenas. Se obtiene a partir de la estadística commandstats de Redis sumando todos los comandos que actúan sobre una o más cadenas. Se muestra como comando |
| aws.elasticache.string_based_cmds_latency (gauge) | Redis - Latencia de los comandos basados en cadenas. Se muestra como microsegundo |
| aws.elasticache.swap_usage (gauge) | Cantidad de intercambio utilizada en el host. Se muestra como byte |
| aws.elasticache.touch_hits (count) | Memcached - Número de claves que se han tocado y a las se les ha dado un nuevo tiempo de vencimiento. Se muestra como acierto |
| aws.elasticache.touch_misses (count) | Memcached - Número de elementos que se han tocado, pero no se han encontrado. Se muestra como fallido |
| aws.elasticache.unused_memory (gauge) | Memcached - Cantidad de memoria no utilizada que la caché puede utilizar para almacenar elementos. Se obtiene a partir de las estadísticas memcached limit_maxbytes y bytes restando bytes de limit_maxbytes. Se muestra como byte. |
A cada una de las métricas recuperadas de AWS se le asignan las mismas etiquetas que aparecen en la consola de AWS, incluidos, entre otros, el nombre del host y los grupos de seguridad.
Nota: Las métricas para despliegues de ElastiCache Serverless se informan en el mismo espacio de nombres aws.elasticache. Estas métricas pueden distinguirse por etiquetas:
- Las métricas de ElastiCache existentes para cachés de diseño propio utilizan la etiqueta cacheclusterid para identificar una caché individual.
- Las métricas de caché serverless utilizan la etiqueta clusterid para identificar las cachés individuales
Eventos
La integración Amazon ElastiCache incluye eventos para clúster, grupos de seguridad de caché y grupos de parámetros de caché. Consulta los siguientes ejemplos de eventos:
Checks de servicio
La integración Amazon ElastiCache no incluye checks de servicios.
Solucionar problemas
¿Necesitas ayuda? Ponte en contacto con el servicio de asistencia de Datadog.