- Esenciales
- Empezando
- Datadog
- Sitio web de Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Serverless para Lambda AWS
- Agent
- Integraciones
- Contenedores
- Dashboards
- Monitores
- Logs
- Rastreo de APM
- Generador de perfiles
- Etiquetas (tags)
- API
- Catálogo de servicios
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Monitorización Synthetic
- Gestión de incidencias
- Monitorización de bases de datos
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Análisis de código
- Centro de aprendizaje
- Compatibilidad
- Glosario
- Atributos estándar
- Guías
- Agent
- Uso básico del Agent
- Arquitectura
- IoT
- Plataformas compatibles
- Recopilación de logs
- Configuración
- Configuración remota
- Automatización de flotas
- Solucionar problemas
- Detección de nombres de host en contenedores
- Modo de depuración
- Flare del Agent
- Estado del check del Agent
- Problemas de NTP
- Problemas de permisos
- Problemas de integraciones
- Problemas del sitio
- Problemas de Autodiscovery
- Problemas de contenedores de Windows
- Configuración del tiempo de ejecución del Agent
- Consumo elevado de memoria o CPU
- Guías
- Seguridad de datos
- Integraciones
- OpenTelemetry
- Desarrolladores
- Autorización
- DogStatsD
- Checks personalizados
- Integraciones
- Crear una integración basada en el Agent
- Crear una integración API
- Crear un pipeline de logs
- Referencia de activos de integración
- Crear una oferta de mercado
- Crear un cuadro
- Crear un dashboard de integración
- Crear un monitor recomendado
- Crear una regla de detección Cloud SIEM
- OAuth para integraciones
- Instalar la herramienta de desarrollo de integraciones del Agente
- Checks de servicio
- Complementos de IDE
- Comunidad
- Guías
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Aplicación móvil de Datadog
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- En la aplicación
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- Editor DDSQL
- Hojas
- Monitores y alertas
- Infraestructura
- Métricas
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Catálogo de servicios
- Catálogo de APIs
- Error Tracking
- Gestión de servicios
- Objetivos de nivel de servicio (SLOs)
- Gestión de incidentes
- De guardia
- Gestión de eventos
- Gestión de casos
- Workflow Automation
- App Builder
- Infraestructura
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Contenedores
- Serverless
- Monitorización de red
- Coste de la nube
- Rendimiento de las aplicaciones
- APM
- Términos y conceptos de APM
- Instrumentación de aplicación
- Recopilación de métricas de APM
- Configuración de pipelines de trazas
- Correlacionar trazas (traces) y otros datos de telemetría
- Trace Explorer
- Observabilidad del servicio
- Instrumentación dinámica
- Error Tracking
- Seguridad de los datos
- Guías
- Solucionar problemas
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Gastos generales de integración del Agent
- Arquitecturas de configuración
- Configuración de Postgres
- Configuración de MySQL
- Configuración de SQL Server
- Configuración de Oracle
- Configuración de MongoDB
- Conexión de DBM y trazas
- Datos recopilados
- Explorar hosts de bases de datos
- Explorar métricas de consultas
- Explorar ejemplos de consulta
- Solucionar problemas
- Guías
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Experiencia digital
- Real User Monitoring
- Monitorización del navegador
- Configuración
- Configuración avanzada
- Datos recopilados
- Monitorización del rendimiento de páginas
- Monitorización de signos vitales de rendimiento
- Monitorización del rendimiento de recursos
- Recopilación de errores del navegador
- Rastrear las acciones de los usuarios
- Señales de frustración
- Error Tracking
- Solucionar problemas
- Monitorización de móviles y TV
- Plataforma
- Session Replay
- Exploración de datos de RUM
- Feature Flag Tracking
- Error Tracking
- Guías
- Seguridad de los datos
- Monitorización del navegador
- Análisis de productos
- Pruebas y monitorización de Synthetics
- Continuous Testing
- Entrega de software
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Configuración
- Tests en contenedores
- Búsqueda y gestión
- Explorador
- Monitores
- Flujos de trabajo de desarrolladores
- Cobertura de código
- Instrumentar tests de navegador con RUM
- Instrumentar tests de Swift con RUM
- Detección temprana de defectos
- Reintentos automáticos de tests
- Correlacionar logs y tests
- Guías
- Solucionar problemas
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- Métricas de DORA
- Seguridad
- Información general de seguridad
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- Observabilidad de la IA
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Gestión de logs
- Administración
- Gestión de cuentas
- Seguridad de los datos
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- Ayuda
Basic Agent Usage for Linux
Esta página aún no está disponible en español. Estamos trabajando en su traducción.
Si tienes alguna pregunta o comentario sobre nuestro actual proyecto de traducción, no dudes en ponerte en contacto con nosotros.
Si tienes alguna pregunta o comentario sobre nuestro actual proyecto de traducción, no dudes en ponerte en contacto con nosotros.
Overview
This page outlines the basic features of the Datadog Agent for Linux environments. See the Supported Platforms documentation for the complete list of supported Linux distributions and versions.
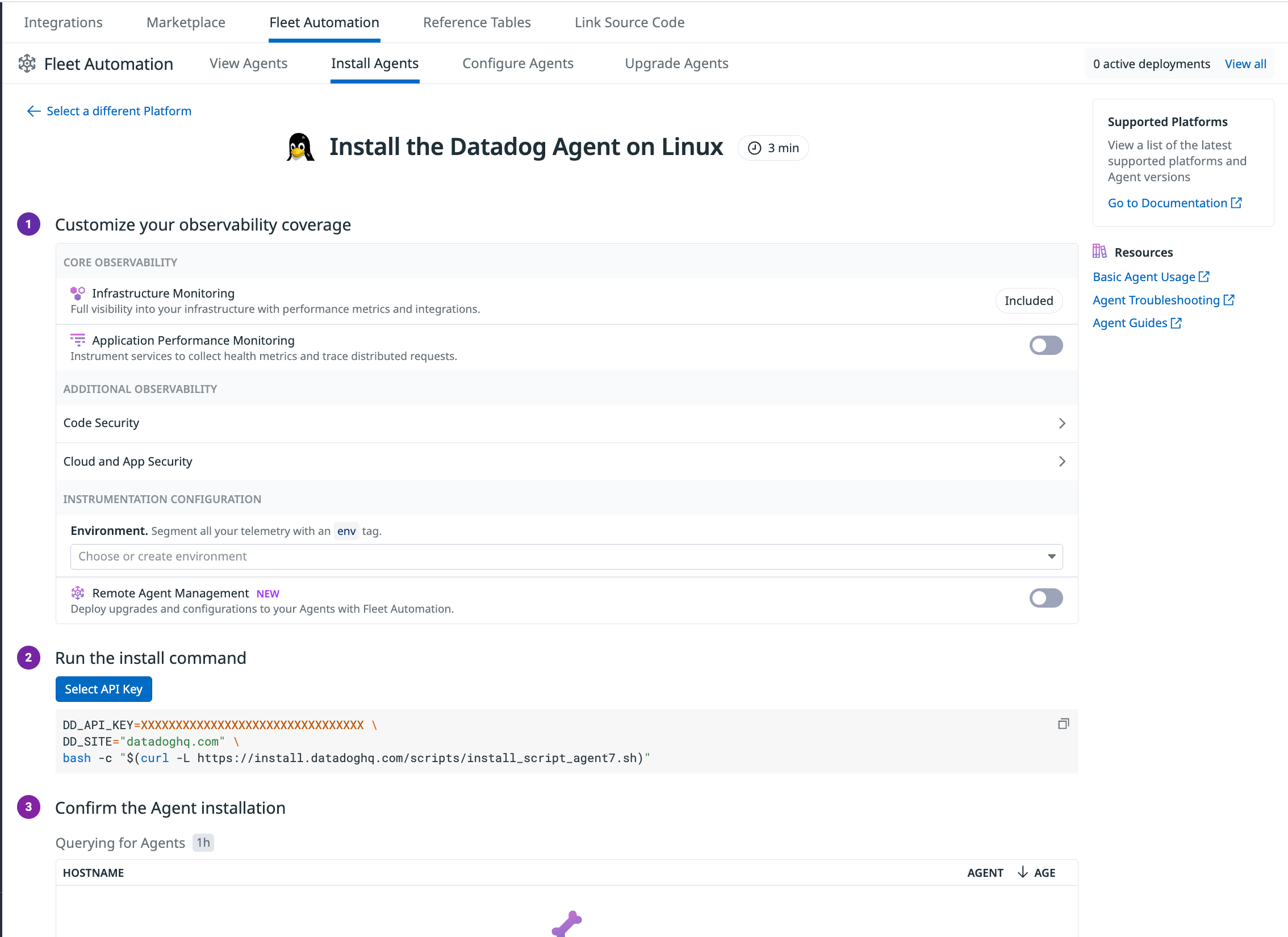
Install the Agent
To install the Agent on Linux, follow the in-app instructions in Fleet Automation, and run the generated script on your hosts.
Configure the Agent
The Datadog Agent configuration file is located in /etc/datadog-agent/datadog.yaml. This YAML file holds the host-wide connection details used to send data to Datadog including:
api_key: Your organization’s Datadog API keysite: Target Datadog region (for exampledatadoghq.com,datadoghq.eu,ddog-gov.com)proxy: HTTP/HTTPS proxy endpoints for outbound traffic (see Datadog Agent Proxy Configuration)- Default tags, log level, and Datadog configurations
A fully commented reference file, located in /etc/datadog-agent/datadog.yaml.example, lists every available option for comparison or to copy and paste. Alternatively, see the sample config_template.yaml file for all available configuration options.
Integration files
Configuration files for integrations live in /etc/datadog-agent/conf.d/. Each integration has its own sub-directory, <INTEGRATION>.d/, that contains:
conf.yaml: The active configuration controlling how the integration gathers metrics and logsconf.yaml.example: A sample illustrating supported keys and defaults
Commands
| Description | Command |
|---|---|
| Start Agent as a service | sudo systemctl start datadog-agent |
| Stop Agent running as a service | sudo systemctl stop datadog-agent |
| Restart Agent running as a service | sudo systemctl restart datadog-agent |
| Status of Agent service | sudo systemctl status datadog-agent |
| Status page of running Agent | sudo datadog-agent status |
| Send flare | sudo datadog-agent flare |
| Display command usage | sudo datadog-agent --help |
| Run a check | sudo -u dd-agent -- datadog-agent check <CHECK_NAME> |
Note: For upstart-based systems, such as CentOS/RHEL 6 or SUSE 11, swap systemctl <action> with <action>. For example, when starting an Agent as a service on a SUSE 11 system, use sudo start datadog-agent.
Uninstall the Agent
To uninstall the Agent, run the command for the appropriate Linux environment:
For CentOS, Rocky, AlmaLinux, Amazon Linux, Oracle Linux, and Red Hat
sudo yum remove datadog-agent
For Debian, Ubuntu
sudo apt-get remove datadog-agent -y
For SUSE
sudo zypper remove datadog-agent
The above commands remove the Agent, but do not remove:
- The
datadog.yamlconfiguration file - User-created files in the
/etc/datadog-agentconfiguration folder - User-created files in the
/opt/datadog-agentfolder - The
dd-agentuser - Datadog log files
To remove these elements, run this command after removing the Agent:
sudo userdel dd-agent \
&& sudo rm -rf /opt/datadog-agent/ \
&& sudo rm -rf /etc/datadog-agent/ \
&& sudo rm -rf /var/log/datadog/
To uninstall remaining Agent artifacts for Debian and Ubuntu run:
sudo apt-get remove --purge datadog-agent -y
Uninstall Single Step APM Instrumentation
If you installed the Agent with Single Step APM Instrumentation and want to uninstall it, you need to run additional commands to remove APM Instrumentation. Follow the steps for your specific environment.
Troubleshooting
For detailed steps, see Agent Troubleshooting.
Working with the embedded Agent
The Agent contains an embedded Python environment at /opt/datadog-agent/embedded/. Common binaries such as python and pip are contained within /opt/datadog-agent/embedded/bin/.
See the instructions on how to add packages to the embedded Agent for more information.
Further Reading
Más enlaces, artículos y documentación útiles: