- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- Notebooks
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Search
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API-based Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Service Level Objectives
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Event Management
- Incident Response
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- End User Device Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Storage Management
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Session Replay
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Code Coverage
- PR Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- AI Guard
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Configuration
- Sources
- Processors
- Destinations
- Packs
- Akamai CDN
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs
- AWS Application Load Balancer Logs
- AWS CloudTrail
- AWS Elastic Load Balancer Logs
- AWS Network Load Balancer Logs
- Cisco ASA
- Cloudflare
- F5
- Fastly
- Fortinet Firewall
- HAProxy Ingress
- Istio Proxy
- Juniper SRX Firewall Traffic Logs
- Netskope
- NGINX
- Okta
- Palo Alto Firewall
- Windows XML
- ZScaler ZIA DNS
- Zscaler ZIA Firewall
- Zscaler ZIA Tunnel
- Zscaler ZIA Web Logs
- Search Syntax
- Scaling and Performance
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Guides and Resources
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
Organization Settings
Overview
The Organization Settings section is available to Administrators by clicking Organization Settings from the account menu in the bottom of the left side navigation or by selecting Organization Settings from the header dropdown at the top of the Personal Settings page.
Organization Settings allow you to manage users, groups, RBAC, keys, and tokens. This page outlines every section and where in the documentation you can learn about specific tasks in Organization Settings.
Identity & Accounts
Users
Read the user management documentation to add, edit, and disable users.
Teams
Read the Teams documentation to manage teams for organizing your assets within Datadog.
Service accounts
Service accounts are non-interactive accounts that you can use to own application keys and other resources that are shared across your teams. Service account application keys can only be viewed once by the individual who created the key. You can use service accounts to access Datadog APIs without associating your application or script with a particular person.
Authentication
Login methods
The Login Methods tab shows password, Google, and SAML authentication settings. You can toggle each with the Enabled by Default dropdowns. In order to be “SAML Strict” or strict for any other type of login, disable the other login method types. You can allow per-user overrides in the User Management tab to allow users to login with another login method if needed.
Read the Configuring Login Methods documentation to authenticate users to log into your Datadog organization.
SAML settings
To learn how to configure SAML, read the Single sign on with SAML documentation.
SAML group mappings
When enabled, users logging in with SAML to your Datadog account are permanently stripped of their current roles and reassigned to new roles. The SAML assertion passed on from the Identity Provider and the mappings you create determine each user’s new roles.
Users who log in with SAML and do not have values that map to a Datadog role are permanently stripped of all roles. That user may no longer log in. To learn how to create and set mappings, read the Mapping SAML attributes documentation.
Access
API keys
This section allows you to view, copy, and revoke any API key in the list. Your API keys are unique to your organization. An API key is required by the Datadog Agent to submit metrics and events to Datadog. Read the API keys documentation for more information on creating, editing, and revoking keys.
Application keys
You can filter application keys by name, ID, or owner, or click the Only My Keys toggle to only view application keys you own. Read the Application keys documentation for more information on adding and removing keys.
Roles
To learn about default and custom roles in Datadog, read the Role Based Access Control documentation.
Remote Configuration
To learn how to remotely configure the behavior or Datadog components deployed in your infrastructure, read How Remote Configuration Works.
Client tokens
Client tokens are used to send events and logs from your user’s web and mobile applications. They are unique to your organization. Deleting a client token that is linked to a RUM Application causes your RUM Application to stop reporting. The process to create client tokens is similar to that for API and application keys.
Events API emails
If your application does not have an existing Datadog integration, and you don’t want to create a custom Agent check, you can send events with email. To learn how to set up events API emails, read the Events with email guide.
Synthetic tests
Learn how to access and control Synthetic Monitoring Settings.
Security
Safety Center
The Safety Center page contains security alerts, warnings, and recommendations to review in your organization.
Public sharing
The Public Sharing tab includes org-wide settings for sharing, along with lists of shared dashboards and graphs. You can enable sharing features granularly and configure additional security options, such as setting a maximum invite duration.
To apply sharing settings across all your orgs, reach out to Datadog Support.
Note: OrgAdmin permission is required to view and manage sharing settings and resources.
OAuth Apps
The OAuth Apps page allows you to view or manage OAuth applications in your organization.
Compliance
Audit trail
The Audit Trail tab in the Organization Settings page opens a new tab to the Audit Events Explorer.
Audit trail settings
The Audit Trail Settings tab allows you to set the retention period of audit trails and enable archiving to other cloud storage services.
General
Preferences
Organization name
To rename your organization, click the Edit button in the Preferences tab of Organization Settings, enter the new name, then click the Save button.
Note: Your organization name must not exceed 32 characters.
Datadog homepage
You can choose to set your organization homepage to a Dashboard List or an individual dashboard.
Out-of-contract retention periods for log indexes
Users with Org Management permission can enable the out-of-contract retention periods feature for log indexes. This feature is enabled on a per-org basis. This means that if a user enables the feature on a parent org, the feature is not automatically enabled for all child orgs.
When enabled, users with Modify Index permission can choose any of the 3-, 7-, 15-, 30-, 45-, and 60-day retention periods, even if it is not in the contract. This can be useful when troubleshooting a potential long standing issue or meeting compliance requirements for which customers need a higher retention period that is not part of the current contract.
Note: Using out-of-contract retention periods incur on-demand charges. If an out-of-contract retention period is often used, Datadog recommends that customers contact their account manager to have it added to their contract.
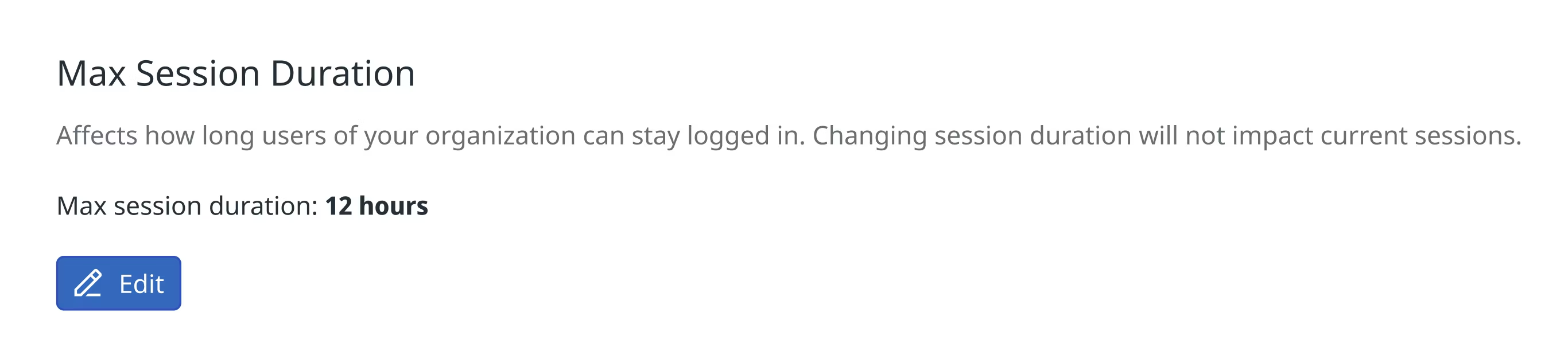
Max session duration configuration
Users with the Org Management permission can set a maximum session duration for their organization. The duration applies to all new web sessions created after you change it, for all users, regardless of their role in the organization. It doesn’t apply to Datadog mobile application sessions.
The session duration can be configured within the following limits:
- Minimum duration: 1 hour
- Maximum duration:
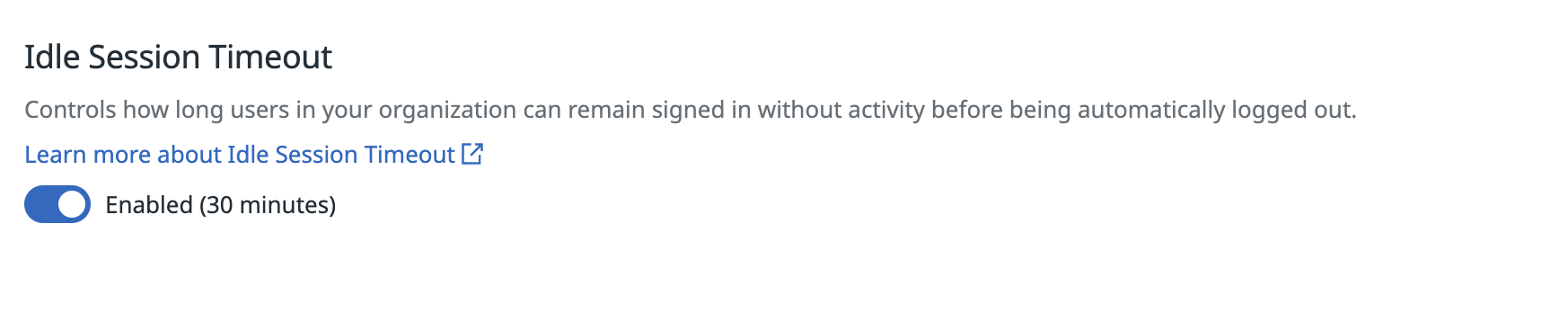
Idle time session duration configuration
Users with the Org Management permission can enable or disable the idle time session timeout for their organization. When enabled, users are automatically signed out after 30 minutes of inactivity. The setting applies to all new web sessions created after you change it, and for all users, regardless of their role in the organization. It doesn’t apply to Datadog mobile application sessions.
Further reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: