- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- APM Terms and Concepts
- Application Instrumentation
- APM Metrics Collection
- Trace Pipeline Configuration
- Correlate Traces with Other Telemetry
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origins for Spans
- Service Observability
- Endpoint Observability
- Dynamic Instrumentation
- Live Debugger
- Error Tracking
- Data Security
- Guides
- Troubleshooting
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Log Management
- Administration
Using the .NET diagnostic tool for troubleshooting
If your application does not produce traces as expected after installing the .NET tracer, run the diagnostic tool dd-dotnet described on this page for basic troubleshooting. It can help you determine issues with your setup, such as missing environment variables, incomplete installation, or an unreachable Agent.
The diagnostic tool dd-dotnet is bundled with the tracing library starting with version 2.42.0. It is located in the tracing library’s installation folder, and automatically added to the system PATH to be invoked from anywhere.
Installing dd-trace
This section is for versions of the tracer older than 2.42.0.
Older versions of the tracer did not include the dd-dotnet tool. You can install the dd-trace tool instead. Its features and syntax are similar to dd-dotnet.
You can install dd-trace in one of the following ways:
Using the .NET SDK by running the command:
dotnet tool install -g dd-traceBy downloading the appropriate version:
- Win-x64: https://dtdg.co/dd-trace-dotnet-win-x64
- Linux-x64: https://dtdg.co/dd-trace-dotnet-linux-x64
- Linux-musl-x64 (Alpine): https://dtdg.co/dd-trace-dotnet-linux-musl-x64
Or by downloading from the github release page.
When invoking the commands in the next sections, make sure to replace dd-dotnet with dd-trace.
Process diagnostics
For most applications, use the process diagnostics to find the problem.
Ensure the application is running, and get the process ID (pid).
To get the pid of a Windows process, open Task Manager, open the Details tab, and look for the PID column. You can also run the command
tasklist /FI "IMAGENAME eq target.exe"wheretarget.exeis the name of the process.To get the pid of a process on Linux, run the command
ps aux | grep targetwheretargetis the name of the process (the pid is typically1when running in a Docker container).Pass the pid into the dd-dotnet tool:
dd-dotnet check process <pid>This runs basic configuration checks and displays recommendations if any issues are found.
Example output with no issues:
$ dd-dotnet check process 35888
Running checks on process 35888
Process name: SimpleApp
---- STARTING TRACER SETUP CHECKS -----
Target process is running with .NET Core
1. Checking Modules Needed so the Tracer Loads:
[SUCCESS]: The native library version 2.42.0.0 is loaded into the process.
[SUCCESS]: The tracer version 2.42.0.0 is loaded into the process.
2. Checking DD_DOTNET_TRACER_HOME and related configuration value:
[SUCCESS]: DD_DOTNET_TRACER_HOME is set to 'C:\git\dd-trace-dotnet-2\shared\bin\monitoring-home\win-x64\..' and the
directory was found correctly.
3. Checking CORECLR_PROFILER_PATH and related configuration value:
[SUCCESS]: The environment variable CORECLR_PROFILER_PATH_32 is set to the correct value of
C:\git\dd-trace-dotnet-2\shared\bin\monitoring-home\win-x86\Datadog.Trace.ClrProfiler.Native.dll.
[SUCCESS]: The environment variable CORECLR_PROFILER_PATH_64 is set to the correct value of
C:\git\dd-trace-dotnet-2\shared\bin\monitoring-home\win-x64\Datadog.Trace.ClrProfiler.Native.dll.
4. Checking CORECLR_PROFILER and related configuration value:
[SUCCESS]: The environment variable CORECLR_PROFILER is set to the correct value of
{846F5F1C-F9AE-4B07-969E-05C26BC060D8}.
5. Checking CORECLR_ENABLE_PROFILING and related configuration value:
[SUCCESS]: The environment variable CORECLR_ENABLE_PROFILING is set to the correct value of 1.
---- CONFIGURATION CHECKS -----
1. Checking if tracing is disabled using DD_TRACE_ENABLED.
[INFO]: DD_TRACE_ENABLED is not set, the default value is true.
2. Checking if profiling is enabled using DD_PROFILING_ENABLED.
[INFO]: DD_PROFILING_ENABLED is not set, the continuous profiler is disabled.
---- DATADOG AGENT CHECKS -----
Detected agent url: http://127.0.0.1:8126/. Note: this url may be incorrect if you configured the application through a
configuration file.
Connecting to Agent at endpoint http://127.0.0.1:8126/ using HTTP
Detected agent version 7.48.0
[SUCCESS]: No issue found with the target process.
Example output with issues:
$ dd-dotnet check process 4464
Running checks on process 4464
Process name: SimpleApp
---- STARTING TRACER SETUP CHECKS -----
Target process is running with .NET Core
1. Checking Modules Needed so the Tracer Loads:
[WARNING]: The native loader library is not loaded into the process
[WARNING]: The native tracer library is not loaded into the process
[WARNING]: Tracer is not loaded into the process
2. Checking DD_DOTNET_TRACER_HOME and related configuration value:
[WARNING]: DD_DOTNET_TRACER_HOME is set to 'C:\Program Files\Datadog\.NET Tracer\' but the directory does not exist.
3. Checking CORECLR_PROFILER_PATH and related configuration value:
[FAILURE]: The environment variable CORECLR_PROFILER_PATH_32 is set to C:\Program Files\Datadog\.NET
Tracer\win-x86\Datadog.Trace.ClrProfiler.Native.dll but the file is missing or you don't have sufficient permission.
[FAILURE]: The environment variable CORECLR_PROFILER_PATH_64 is set to C:\Program Files\Datadog\.NET
Tracer\win-x64\Datadog.Trace.ClrProfiler.Native.dll but the file is missing or you don't have sufficient permission.
4. Checking CORECLR_PROFILER and related configuration value:
[SUCCESS]: The environment variable CORECLR_PROFILER is set to the correct value of
{846F5F1C-F9AE-4B07-969E-05C26BC060D8}.
5. Checking CORECLR_ENABLE_PROFILING and related configuration value:
[FAILURE]: The environment variable CORECLR_ENABLE_PROFILING should be set to '1' (current value: not set)
6. Checking if process tracing configuration matches Installer or Bundler:
Installer/MSI related documentation:
https://docs.datadoghq.com/tracing/trace_collection/dd_libraries/dotnet-core/?tab=windows#install-the-tracer
[FAILURE]: Unable to find Datadog .NET Tracer program, make sure the tracer has been properly installed with the MSI.
[WARNING]: The registry key SOFTWARE\Classes\CLSID\{846F5F1C-F9AE-4B07-969E-05C26BC060D8}\InprocServer32 is missing. If
using the MSI, make sure the installation was completed correctly try to repair/reinstall it.
[WARNING]: The registry key SOFTWARE\Classes\Wow6432Node\CLSID\{846F5F1C-F9AE-4B07-969E-05C26BC060D8}\InprocServer32 is
missing. If using the MSI, make sure the installation was completed correctly try to repair/reinstall it.
IIS diagnostics
For an IIS application, you can get more thorough diagnostics by using the following command, where <FULL SITE NAME> is the name of the site in IIS followed by the name of the application:
dd-dotnet check iis "<FULL SITE NAME>"
Because application pools are started lazily in IIS, make sure that the site has received at least one request before you run the command.
Remember to enclose the name in quotation marks if it has spaces in it.
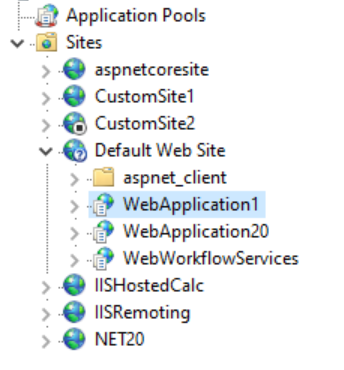
For example, the full site name for the application shown below is Default Web Site/WebApplication1:
The command to run IIS diagnostics on this application is:
dd-dotnet check iis "Default Web Site/WebApplication1"
To instrument the root application of the site, run:
dd-dotnet check iis "Default Web Site"
The check iis command includes process diagnostics, so it runs basic configuration checks and displays recommendations if any issues are found.
Example output without issues:
$ dd-dotnet check iis "Default Web Site/WebFormsTestApp"
Fetching IIS application "Default Web Site/WebFormsTestApp".
Inspecting worker process 39852
---- STARTING TRACER SETUP CHECKS -----
Target process is running with .NET Framework
1. Checking Modules Needed so the Tracer Loads:
[SUCCESS]: The native library version 2.42.0.0 is loaded into the process.
[SUCCESS]: The tracer version 2.42.0.0 is loaded into the process.
2. Checking DD_DOTNET_TRACER_HOME and related configuration value:
[SUCCESS]: DD_DOTNET_TRACER_HOME is set to 'C:\Program Files\Datadog\.NET Tracer\' and the directory was found
correctly.
3. Checking COR_PROFILER_PATH and related configuration value:
[SUCCESS]: The environment variable COR_PROFILER_PATH_32 is set to the correct value of C:\Program Files\Datadog\.NET
Tracer\win-x86\Datadog.Trace.ClrProfiler.Native.dll.
[SUCCESS]: The environment variable COR_PROFILER_PATH_64 is set to the correct value of C:\Program Files\Datadog\.NET
Tracer\win-x64\Datadog.Trace.ClrProfiler.Native.dll.
4. Checking COR_PROFILER and related configuration value:
[SUCCESS]: The environment variable COR_PROFILER is set to the correct value of {846F5F1C-F9AE-4B07-969E-05C26BC060D8}.
5. Checking COR_ENABLE_PROFILING and related configuration value:
[SUCCESS]: The environment variable COR_ENABLE_PROFILING is set to the correct value of 1.
---- CONFIGURATION CHECKS -----
1. Checking if tracing is disabled using DD_TRACE_ENABLED.
[INFO]: DD_TRACE_ENABLED is not set, the default value is true.
2. Checking if profiling is enabled using DD_PROFILING_ENABLED.
[INFO]: DD_PROFILING_ENABLED is not set, the continuous profiler is disabled.
---- DATADOG AGENT CHECKS -----
Detected agent url: http://127.0.0.1:8126/. Note: this url may be incorrect if you configured the application through a
configuration file.
Connecting to Agent at endpoint http://127.0.0.1:8126/ using HTTP
Detected agent version 7.48.0
Found Datadog.Trace version 2.42.0.0 in the GAC
[SUCCESS]: No issue found with the IIS site.
Example output with issues:
$ dd-dotnet check iis "Default Web Site/WebFormsTestApp"
Fetching IIS application "Default Web Site/WebFormsTestApp".
Inspecting worker process 35152
---- STARTING TRACER SETUP CHECKS -----
Target process is running with .NET Framework
1. Checking Modules Needed so the Tracer Loads:
[SUCCESS]: The native library version 2.42.0.0 is loaded into the process.
[SUCCESS]: The tracer version 2.42.0.0 is loaded into the process.
2. Checking DD_DOTNET_TRACER_HOME and related configuration value:
[SUCCESS]: DD_DOTNET_TRACER_HOME is set to 'C:\Program Files\Datadog\.NET Tracer\' and the directory was found
correctly.
3. Checking COR_PROFILER_PATH and related configuration value:
[SUCCESS]: The environment variable COR_PROFILER_PATH_32 is set to the correct value of C:\Program Files\Datadog\.NET
Tracer\win-x86\Datadog.Trace.ClrProfiler.Native.dll.
[SUCCESS]: The environment variable COR_PROFILER_PATH_64 is set to the correct value of C:\Program Files\Datadog\.NET
Tracer\win-x64\Datadog.Trace.ClrProfiler.Native.dll.
4. Checking COR_PROFILER and related configuration value:
[SUCCESS]: The environment variable COR_PROFILER is set to the correct value of {846F5F1C-F9AE-4B07-969E-05C26BC060D8}.
5. Checking COR_ENABLE_PROFILING and related configuration value:
[SUCCESS]: The environment variable COR_ENABLE_PROFILING is set to the correct value of 1.
---- CONFIGURATION CHECKS -----
1. Checking if tracing is disabled using DD_TRACE_ENABLED.
[INFO]: DD_TRACE_ENABLED is not set, the default value is true.
2. Checking if profiling is enabled using DD_PROFILING_ENABLED.
[INFO]: DD_PROFILING_ENABLED is not set, the continuous profiler is disabled.
---- DATADOG AGENT CHECKS -----
Detected agent url: http://127.0.0.1:8126/. Note: this url may be incorrect if you configured the application through a
configuration file.
Connecting to Agent at endpoint http://127.0.0.1:8126/ using HTTP
Detected agent version 7.48.0
[FAILURE]: The Datadog.Trace assembly could not be found in the GAC. Make sure the tracer has been properly installed
with the MSI.
Agent connectivity diagnostics
If you don’t want to run checks for a specific application but just want to test the connection to the Agent, run:
dd-dotnet check agent <url>
This command sends a request to the Agent and looks for errors. If the optional url parameter is omitted, then the location of the Agent is determined from the environment variables. The supported protocols are http:// or unix:// (for domain sockets).
Example output without issues:
$ dd-dotnet check agent
No Agent URL provided, using environment variables
Connecting to Agent at endpoint http://127.0.0.1:8126/ using HTTP
Detected agent version 7.48.0
[SUCCESS]: Connected successfully to the Agent.
Example output with issues:
$ dd-dotnet check agent
No Agent URL provided, using environment variables
Connecting to Agent at endpoint http://127.0.0.1:8126/ using HTTP
[FAILURE]: Error connecting to Agent at http://127.0.0.1:8126/: System.Net.Http.HttpRequestException: No connection
could be made because the target machine actively refused it. (127.0.0.1:8126)
Read Connection Errors for more information about Agent connectivity issues.