- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- APM Terms and Concepts
- Application Instrumentation
- APM Metrics Collection
- Trace Pipeline Configuration
- Correlate Traces with Other Telemetry
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origins for Spans
- Service Observability
- Endpoint Observability
- Dynamic Instrumentation
- Live Debugger
- Error Tracking
- Data Security
- Guides
- Troubleshooting
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Log Management
- Administration
Build Apps
This product is not supported for your selected Datadog site. ().
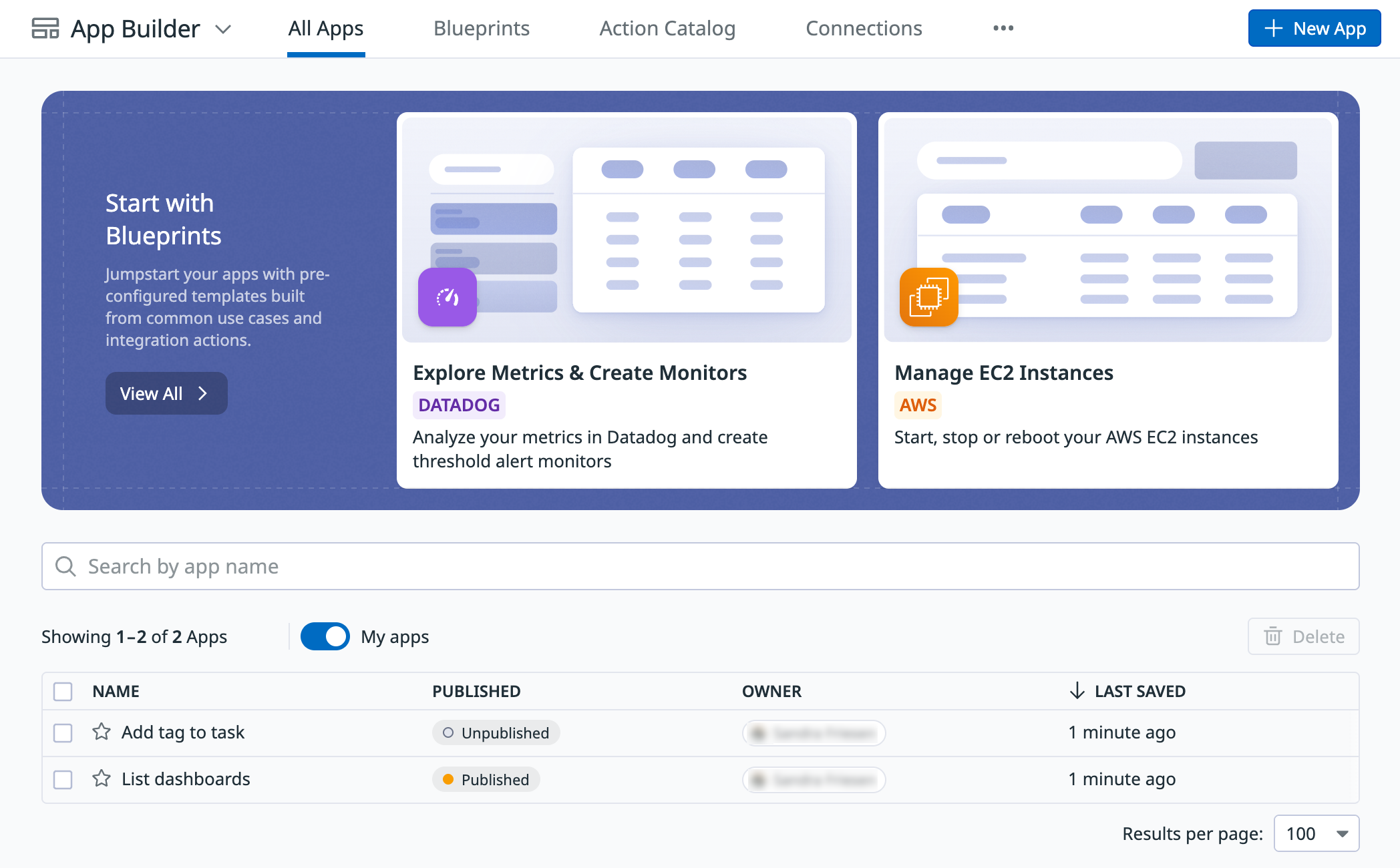
You can create an app or edit existing apps from the App Builder page. The page lists information about existing apps, including the following:
- Author
- Status
- Date that each app was last modified
- Whether the app is published
On the App Builder page, you can access and filter your apps. Hover over an app for options to edit, delete, view, or clone the app. You can also enable the My apps toggle to see only apps that you created:
Create an app
Build an app from a blueprint
Blueprints are helpful starter apps that cover common use cases. They come loaded with demo data that you can use to familiarize yourself with the app. Blueprints also showcase best practices for setting up app functionality and visual presentation.
- From App Builder, click the Blueprints tab.
- Find the blueprint that you want to use and click Preview.
- Click Use Blueprint to open the app blueprint.
- To change the app name and description, click the app name.
- Each blueprint template comes loaded with demo data. To customize the app, edit the Connection for each query.
- To save the app, click Save as New App.
- To preview the app, click Preview. Click Edit from the preview screen to return to the configuration view.
- After you finish modifying the app, Click Run to test it.
- When you’re ready to publish your app, click Publish. Publishing an app makes it available to your dashboards.
Create a custom app
- From App Builder, click New App.
- To change the app name and description, click the app name.
- To add a UI component to the app canvas, click the plus (
) to open the Components tab, then click the component or drag it onto the canvas.
- Use queries to populate or interact with your canvas.
- To save the app, click Save as New App.
- To preview the app, click Preview. Click Edit from the preview screen to return to the configuration view.
- After you finish modifying the app, Click Run to test it.
- When you’re ready to publish your app, click Publish. Publishing an app makes it available to your dashboards.
Customize your app
Apps are made up of UI components and queries which interact with each other to form the user experience and logic behind each app. The query list and editor appear on the left side of the page, while the app canvas and UI components make up the right side of the page.
Basic customization:
- To edit the Name, Description, or Canvas Color of your app, click the app name at the top left.
- Click the Preview button to preview your app. Preview mode allows you to view the app from the user’s perspective. Use preview mode to interact with the app UI and test your queries. When you’re done, click Edit to return to the app builder.
- To save your app, click Save.
- When you’re ready to publish your app, click Publish. Publishing an app makes it available to your dashboards.
App canvas and components
The app canvas represents the graphical interface that your users interact with. You can drag and drop components to move them around on the canvas. To see all available components, click the plus () to open the Components tab.
Each component features a list of corresponding configuration options that control how users interact with your app. For example, the Text Input component allows you to set a default value, placeholder text, and a label. The Button component includes a label and an event that triggers when the button is pressed. Components also feature an Appearance section that changes the way the components look and act. For example, you can disable a button or control its visibility.
To delete or duplicate a component, select the component and click the three dot ellipsis (…) to display the Delete or Duplicate options.
For a list of available UI components and their properties, see Components.
UI components can trigger reactions on an Event.
Queries populate your app with data from Datadog APIs or supported integrations. They take inputs from other queries or from UI components and return outputs for use in other queries or in UI components.
You can use JavaScript Expressions anywhere in App Builder to create custom interactions between the different parts of your app.
Tag an app
Tags display in a column on the app list.
To add a tag to an app:
- Open the App Properties tab in your app.
- Under Tags, use the drop-down to select an existing tag, or enter a new value and click Add option: [your text].
- Save your app.
The tag displays on the line for this app in the app list. You can click the tag in this list to copy it to your clipboard.
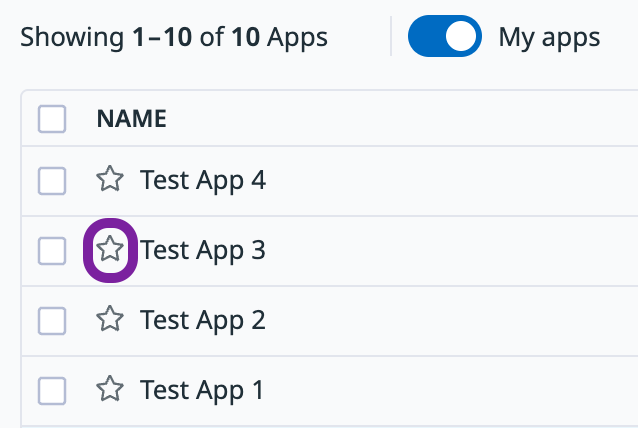
Favorite an app
To favorite an app and pin it to the top of your list of apps, click the star next to the name of the app in the app list:
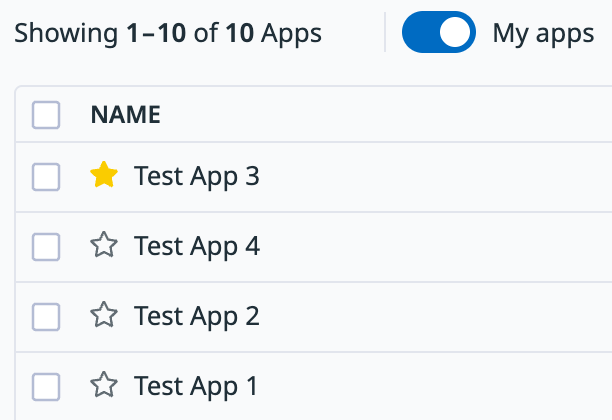
When you refresh the page, the starred app appears in a section at the top of your list of apps:
View app version history
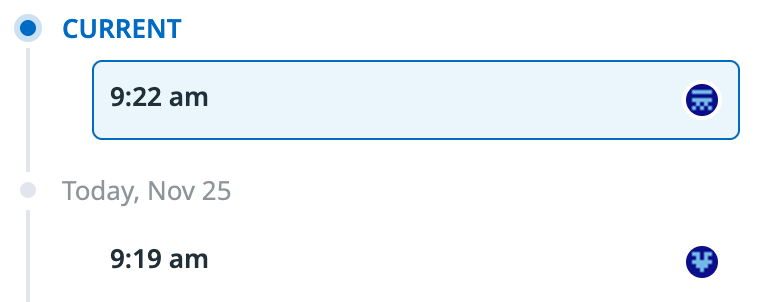
App Builder keeps a record of every saved version of your app.
To view the version history for your app, in the left-hand menu of your app, click the version history icon .
The UI displays up to 50 saved or published versions of your app, along with the icon of the user who saved or published the version:
You can perform the following operations:
- To view an app version, click the version in the list.
- To overwrite an existing app with a previous version, select the version, then click Restore Version in the upper right.
- To create a new app that is a copy of a version, select the version, then click Clone Version in the upper right.
Interact with an app in JSON
Edit an app
To edit an app with JSON, click the cog (Settings) icon and select Switch to JSON. The Switch to GUI option in the settings menu takes you back to the GUI editor.
Export an app
To copy an app layout across organizations or back it up, click the cog (Settings) icon and select Switch to JSON. This shows the JSON code for the entire app. Copy this JSON code and save it in a text editor. You can save intermediate states of your app during development and return to them if necessary.
To copy the app to another organization:
- Create an app.
- Click the cog (Settings) icon and select Switch to JSON.
- Replace the existing JSON with the JSON that you previously copied.
The Switch to GUI option in the settings menu takes you back to the GUI editor.
Further reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles:
Do you have questions or feedback? Join the #app-builder channel on the Datadog Community Slack.