- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- Notebooks
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Search
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API-based Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Service Level Objectives
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Event Management
- Incident Response
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- End User Device Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Storage Management
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Session Replay
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Code Coverage
- PR Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- AI Guard
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Configuration
- Sources
- Processors
- Destinations
- Packs
- Akamai CDN
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs
- AWS Application Load Balancer Logs
- AWS CloudTrail
- AWS Elastic Load Balancer Logs
- AWS Network Load Balancer Logs
- Cisco ASA
- Cloudflare
- F5
- Fastly
- Fortinet Firewall
- HAProxy Ingress
- Istio Proxy
- Juniper SRX Firewall Traffic Logs
- Netskope
- NGINX
- Okta
- Palo Alto Firewall
- Windows XML
- ZScaler ZIA DNS
- Zscaler ZIA Firewall
- Zscaler ZIA Tunnel
- Zscaler ZIA Web Logs
- Search Syntax
- Scaling and Performance
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Guides and Resources
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
Azure App Service - Windows Code
Overview
The Datadog extension for Azure App Service provides monitoring capabilities in addition to the Datadog-Azure integration, which provides metrics and logs.
- Full distributed APM tracing using automatic instrumentation.
- Customized APM service and trace views showing relevant Azure App Service metrics and metadata.
- Support for manual APM instrumentation to customize spans.
Trace_IDinjection into application logs.- Support for submitting custom metrics using DogStatsD.
The extension supports the following:
- App Service Web Apps: Supported for .NET, Java, and Node.js runtimes on Basic, Standard, and Premium plans.
- Azure Functions: Supported only for the .NET runtime on Basic, Standard, and Premium plans.
For all other Azure Functions configurations, you must use the Serverless Compatibility Layer.
Interested in support for other App Service resource types or runtimes? Sign up to be notified when a Preview becomes available.
Supported runtimes
The Datadog .NET, Java, and Node.js APM extensions support the following runtimes:
| Framework | Supported runtimes |
|---|---|
| .NET | ASPNET:V3.5, ASPNET:V4.8, dotnet:8, dotnet:9 |
| Java | JAVA:8, JAVA:11, JAVA:17, JAVA:21, TOMCAT:9.0-java8, TOMCAT:9.0-java11, TOMCAT:9.0-java17, TOMCAT:9.0-java21, TOMCAT:10.1-java8, TOMCAT:10.1-java11, TOMCAT:10.1-java17, TOMCAT:10.1-java21, TOMCAT:11.0-java8, TOMCAT:11.0-java11, TOMCAT:11.0-java17, TOMCAT:11.0-java21 |
| Node.js | NODE:20LTS, NODE:22LTS |
Extension-specific notes
Datadog’s automatic instrumentation relies on the .NET CLR Profiling API. This API allows only one subscriber (for example, Datadog’s .NET Tracer with Profiler enabled). To ensure maximum visibility, run only one APM solution within your application environment.
Additionally, if you are using the Azure Native integration, you can use the Datadog resource in Azure to add the extension to your .NET apps. For instructions, see the App Service extension section of Datadog’s Azure Native integration guide.
Support for Java Web Apps is in Preview for extension v2.4+.
There are no billing implications for tracing Java Web Apps during this period.
Installation
Datadog recommends doing regular updates to the latest version of the extension to ensure optimal performance, stability, and availability of features. Note that both the initial install and subsequent updates require your web app to be fully stopped in order to install/update successfully.
If you haven’t already, set up the Datadog-Azure integration. You can verify that your Azure integration is configured correctly by ensuring that you see the azure.app_services.count or azure.functions.count metrics in Datadog.
This step is critical for metric/trace correlation and functional trace panel views and improves the overall experience of using Datadog with Azure App Services.
Locally
Install the Datadog CLI
npm install -g @datadog/datadog-ci @datadog/datadog-ci-plugin-aas
Install the Azure CLI and authenticate with az login.
Then, run the following command to set up the sidecar container:
export DD_API_KEY=<DATADOG_API_KEY>
export DD_SITE=<DATADOG_SITE>
datadog-ci aas instrument -s <subscription-id> -g <resource-group-name> -n <app-service-name>
Set your Datadog site to . Defaults to datadoghq.com.
The Datadog CLI will automatically infer the runtime of your app and install the corresponding application. If this fails for whatever reason, you can override this behavior by specifying a runtime with the --windows-runtime flag.
Additional flags, like --service and --env, can be used to set the service and environment tags. For a full list of options, run datadog-ci aas instrument --help.
Azure Cloud Shell
To use the Datadog CLI in Azure Cloud Shell, open a cloud shell, set your API key and site in the DD_API_KEY and DD_SITE environment variables, and use npx to run the CLI directly:
export DD_API_KEY=<DATADOG_API_KEY>
export DD_SITE=<DATADOG_SITE>
npx @datadog/datadog-ci aas instrument -s <subscription-id> -g <resource-group-name> -n <app-service-name>
The Datadog Terraform module for Windows Web Apps wraps the azurerm_windows_web_app resource and automatically configures your Web App for Datadog Serverless Monitoring by adding required environment variables and the Windows Web App extension for your runtime.
If you don’t already have Terraform set up, install Terraform, create a new directory, and make a file called main.tf.
Then, add the following to your Terraform configuration, updating it as necessary based on your needs:
variable "datadog_api_key" {
description = "Your Datadog API key"
type = string
sensitive = true
}
provider "azurerm" {
features {}
subscription_id = "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000" // Replace with your subscription ID
}
resource "azurerm_service_plan" "my_asp" {
name = "my-app-service-plan" // Replace with your app service plan name
resource_group_name = "my-resource-group" // Replace with your resource group
os_type = "Windows"
location = "eastus"
sku_name = "P1v2"
}
module "my_web_app" {
source = "DataDog/web-app-datadog/azurerm//modules/windows"
version = "~> 1.0"
name = "my-web-app" // Replace with your web app name
resource_group_name = "my-resource-group" // Replace with your resource group
service_plan_id = azurerm_service_plan.my_asp.id
location = "eastus"
datadog_api_key = var.datadog_api_key
datadog_service = "my-service" // Replace with your service name
datadog_env = "prod" // Replace with your environment (e.g. prod, staging)
datadog_version = "0.0.0" // Replace with your application version
site_config = {
application_stack = {
node_version = "~22" // change for your specific runtime
}
}
app_settings = {
DD_TRACE_ENABLED = "true" // Example setting
}
}
Finally, run terraform apply, and follow any prompts.
The Datadog Windows Web App module only deploys the Web App resource and extension, so you need to deploy your code separately.
Update your existing Web App to include the necessary Datadog App Settings and extension, as follows:
@secure()
param datadogApiKey string
resource webApp 'Microsoft.Web/sites@2025-03-01' = {
// ...
properties: {
// ...
siteConfig: {
// ...
appSettings: [
//... Your existing app settings
{ name: 'DD_API_KEY', value: datadogApiKey }
{ name: 'DD_SITE', value: 'datadoghq.com' } // Replace with your Datadog site
{ name: 'DD_SERVICE', value: 'my-service' } // Replace with your service name
{ name: 'DD_ENV', value: 'prod' } // Replace with your environment (e.g. prod, staging)
{ name: 'DD_VERSION', value: '0.0.0' } // Replace with your application version
// Add any additional options here
]
}
}
}
resource datadogExtension 'Microsoft.Web/sites/siteextensions@2025-03-01' = {
parent: webApp
// Uncomment the extension for your runtime:
// name: 'Datadog.AzureAppServices.Node.Apm'
// name: 'Datadog.AzureAppServices.DotNet'
// name: 'Datadog.AzureAppServices.Java.Apm'
}
Deploy your updated template:
az deployment group create --resource-group <RESOURCE GROUP> --template-file <TEMPLATE FILE>
Note: You will need to manually (or via a script) stop and start the app, otherwise automatic tracing will not work. For updates, you should ensure that the app is stopped before deploying the template, and started again after the deployment finishes.
See the Manual tab for descriptions of all environment variables.
Update your existing Web App to include the necessary Datadog App Settings and sidecar, as follows:
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2019-04-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"parameters": {
"webAppName": {
"type": "string"
},
// ...
"datadogApiKey": {
"type": "securestring"
}
},
"resources": {
"webApp": {
"type": "Microsoft.Web/sites",
"apiVersion": "2025-03-01",
"name": "[parameters('webAppName')]",
// ...
"properties": {
// ...
"siteConfig": {
// ...
"appSettings": [
//... Your existing app settings
{ "name": "DD_API_KEY", "value": "[parameters('datadogApiKey')]" },
{ "name": "DD_SITE", "value": "datadoghq.com" }, // Replace with your Datadog site
{ "name": "DD_SERVICE", "value": "my-service" }, // Replace with your service name
{ "name": "DD_ENV", "value": "prod" }, // Replace with your environment (e.g. prod, staging)
{ "name": "DD_VERSION", "value": "0.0.0" }, // Replace with your application version
// Add any additional options here
]
}
}
},
"datadogExtension": {
"type": "Microsoft.Web/sites/siteextensions",
"apiVersion": "2025-03-01",
// Uncomment the extension for your runtime:
// "name": "[concat(parameters('webAppName'), '/Datadog.AzureAppServices.Node.Apm')]"
// "name": "[concat(parameters('webAppName'), '/Datadog.AzureAppServices.DotNet')]"
// "name": "[concat(parameters('webAppName'), '/Datadog.AzureAppServices.Java.Apm')]"
}
}
}
Deploy your updated template:
az deployment group create --resource-group <RESOURCE GROUP> --template-file <TEMPLATE FILE>
Note: You will need to manually (or via a script) stop and start the app, otherwise automatic tracing will not work. For updates, you should ensure that the app is stopped before deploying the template, and started again after the deployment finishes.
See the Manual tab for descriptions of all environment variables.
In your Azure Portal, navigate to the dashboard for the Azure app you wish to instrument with Datadog.
Configure the following Application Settings:
Required environment variables
DD_API_KEY- Value: Your Datadog API key.
See Organization Settings > API Keys in Datadog. DD_SITE- Value: Your Datadog site
Your Datadog site. Defaults todatadoghq.com.
Unified Service Tagging
Datadog recommends tagging your application with the
env,service, andversiontags for unified service tagging.DD_SERVICE- Value: Your application’s service name.
DD_ENV- Value: Your application’s environment name.
There is no default value for this field. DD_VERSION- Value: Your application’s version.
There is no default value for this field.
Additional environment variables
DD_LOGS_INJECTION- Value:
true(recommended)
Enables trace-log correlation by injecting trace IDs into your application logs.
This allows you to correlate logs with traces in the Datadog UI.
Click Save. This restarts your application.
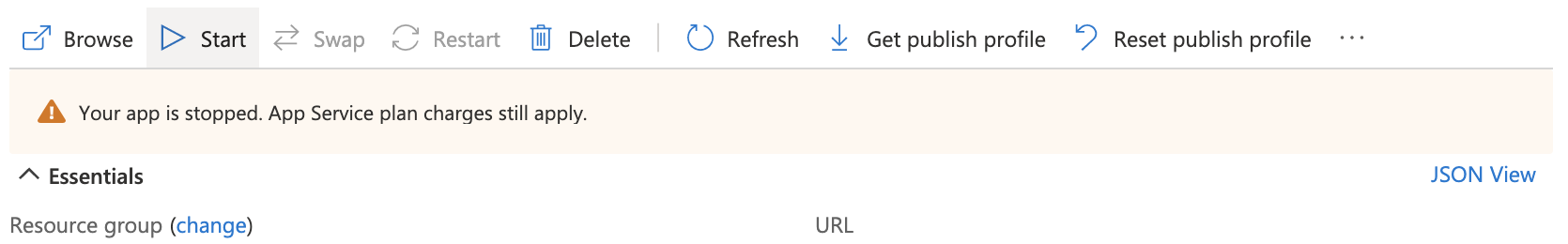
Stop your application by clicking Stop.
You must stop your application to successfully install Datadog.In your Azure Portal, navigate to the Extensions page and select the Datadog APM extension.
Accept the legal terms, click OK, and wait for the installation to complete.
This step requires that your application be in a stopped state.Start the main application, click Start:
Verify that the extension is installed and running by checking the Extensions page in your Azure Portal.
To avoid downtime, use deployment slots. You can create a workflow that uses the GitHub Action for Azure CLI. See the sample GitHub workflow.
Custom metrics
The Azure App Service extension includes an instance of DogStatsD, Datadog’s metrics aggregation service. This enables you to submit custom metrics, service checks, and events directly to Datadog from Azure Web Apps and Functions with the extension.
Writing custom metrics and checks in Azure App Service is similar to the process for doing so with an application on a host running the Datadog Agent. Unlike the standard DogStatsD config process, there is no need to set ports or a server name when initializing the DogStatsD configuration. There are ambient environment variables in Azure App Service that determine how the metrics are sent (requires v6.0.0+ of the DogStatsD client).
To submit custom metrics to Datadog from Azure App Service using the extension:
- Add the DogStatsD NuGet package to your Visual Studio project.
- Initialize DogStatsD and write custom metrics in your application.
- Deploy your code to Azure App Service.
- If you have not already, install the Datadog App Service extension.
To send metrics, use this code:
// Configure your DogStatsd client and configure any tags
if (!DogStatsd.Configure(new StatsdConfig() { ConstantTags = new[] { "app:sample.mvc.aspnetcore" } }))
{
// `Configure` returns false if the necessary environment variables are not present.
// These environment variables are present in Azure App Service, but
// need to be set in order to test your custom metrics: DD_API_KEY:{api_key}, DD_AGENT_HOST:localhost
// Ignore or log the error as it suits you
Console.WriteLine("Cannot initialize DogstatsD.");
}
// Send a metric
DogStatsd.Increment("sample.startup");
- Add the DogStatsD client to your project.
- Initialize DogStatsD and write custom metrics in your application.
- Deploy your code to a supported Azure web app.
- If you have not already, install the Datadog App Service extension.
To send metrics, use this code:
// Configure your DogStatsd client and configure any tags
StatsDClient client = new NonBlockingStatsDClientBuilder()
.constantTags("app:sample.service")
.build();
// Send a metric
client.Increment("sample.startup");
- Initialize DogStatsD and write custom metrics in your application.
- Deploy your code to a supported Azure Web App.
- If you have not already, install Datadog’s Azure App Service Node.js extension.
You do not need to install a Node.js DogStatsD client, as it is included in the Node.js tracer (
dd-trace) packaged in the Azure App Service extension.To send metrics, use this code:
const tracer = require('dd-trace');
tracer.init();
tracer.dogstatsd.increment('example_metric.increment', 1, { environment: 'dev' });
tracer.dogstatsd.decrement('example_metric.decrement', 1, { environment: 'dev' });
Datadog's Node.js tracer,
You do not need to add
dd-trace, is packaged in the Azure App Services extension. It is automatically appended to the NODE_PATH.You do not need to add
dd-trace as a dependency in package.json. Explicitly adding dd-trace as a dependency may override the version provided by the extension. For local testing, reference the release notes to find the appropriate version of the Node.js tracer for your version of the Azure App Service extension.Note: To send only custom metrics (while disabling tracing) set the following variables in your application’s config:
- Set
DD_TRACE_ENABLEDtofalse. - Set
DD_AAS_ENABLE_CUSTOM_METRICStotrue.
Learn more about custom metrics.
Logging
Application logging
You can send logs from your application in Azure App Service to Datadog in one of the following ways:
- Use the installation steps on this page to enable APM with the Datadog APM extension. Then enable Agentless logging.
- Use Agentless logging with the Serilog sink.
Both methods allow trace ID injection, making it possible to connect logs and traces in Datadog. To enable trace ID injection with the extension, add the application setting DD_LOGS_INJECTION:true.
Sending logs from your application in Azure App Service to Datadog requires streaming logs to Datadog directly from your app. Submitting logs with this method allows for trace ID injection, which makes it possible to connect logs and traces in Datadog.
Sending logs from your application in Azure App Service to Datadog requires streaming logs to Datadog directly from your app. Submitting logs with this method allows for trace ID injection, which makes it possible to connect logs and traces in Datadog.
Environment variables for logging
Configure these environment variables in your Azure App Service Application Settings for optimal log collection:
| Variable | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
DD_SERVICE | Your application’s service name | my-web-app |
DD_ENV | Your application’s environment | production, staging, development |
DD_LOGS_INJECTION | Enable trace-log correlation | true |
Logging best practices
- Enable trace correlation: Set
DD_LOGS_INJECTION=trueto correlate logs with traces - Set proper service names: Use
DD_SERVICEto ensure logs appear with the correct service name - Use structured logging: Implement structured logging in your application for better log parsing
Note: Trace ID injection occurs inside your application. Azure Resource logs are generated by Azure in the management plane, and therefore do not include the trace ID.
Code Example: Microsoft Native Logging
An example of how to set up logging in a .NET application using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging:
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
public class WeatherForecastController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly ILogger<WeatherForecastController> _logger;
public WeatherForecastController(ILogger<WeatherForecastController> logger)
{
_logger = logger;
}
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult Get()
{
_logger.LogInformation("Processing weather forecast request");
// Your business logic here
var forecast = GetWeatherForecast();
_logger.LogInformation("Weather forecast retrieved for user: {UserId}", userId);
return Ok(forecast);
}
}
Program.cs configuration
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Configure logging
builder.Logging.ClearProviders();
builder.Logging.AddConsole();
builder.Logging.AddDebug();
// Add structured logging with JSON format
builder.Logging.AddJsonConsole(options =>
{
options.JsonWriterOptions = new JsonWriterOptions
{
Indented = true
};
});
var app = builder.Build();
// ... rest of your application configuration
appsettings.json configuration
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning"
},
"Console": {
"FormatterName": "json",
"FormatterOptions": {
"IncludeScopes": true,
"TimestampFormat": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss "
}
}
}
}
This setup automatically includes trace correlation when DD_LOGS_INJECTION=true is set in your Azure App Service Application Settings.
See Stream logs directly to the Agent to configure application logging for Java in Azure App Service.
To configure application logging for Node.js in Azure App Service, see Agentless logging with Node.js.
Programmatic management
Datadog provides scripts to update or install the Azure App Service Extension using Powershell. Scripted extension management enables you to update extensions in bulk by resource group and designate the installation of specific versions of the site extension. You can also use scripts to programmatically add the extension in CI/CD pipelines, as well as discover and update extensions that are already installed.
Prerequisites
- The Azure CLI or Azure Cloud Shell.
- Azure App Service user-scope credentials. If you do not already have credentials, go to your Azure portal and access your Web App or Function App. Navigate to Deployment > Deployment Center to create or retrieve your user-scope credentials.
Installing the extension for the first time
The install script adds the latest version of the extension to an Azure Web App or Azure Function App. This occurs on a per-app basis, rather than at a resource group level.
Open the Azure CLI or Azure Cloud Shell.
Download the installation script using the following command:
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/DataDog/datadog-aas-extension/master/management-scripts/extension/install-latest-extension.ps1" -OutFile "install-latest-extension.ps1"Run the following command, passing in required and optional arguments as needed.
.\install-latest-extension.ps1 -Username <USERNAME> -Password <PASSWORD> -SubscriptionId <SUBSCRIPTION_ID> -ResourceGroup <RESOURCE_GROUP_NAME> -SiteName <SITE_NAME> -DDApiKey <DATADOG_API_KEY> -DDSite <DATADOG_SITE> -DDEnv <DATADOG_ENV> -DDService <DATADOG_SERVICE> -DDVersion <DATADOG_VERSION>
Note: The following arguments are required for the above command:
<USERNAME>: Your Azure user scope username.<PASSWORD>: Your Azure user scope password.<SUBSCRIPTION_ID>: Your Azure subscription ID.<RESOURCE_GROUP_NAME>: Your Azure resource group name.<SITE_NAME>: The name of your app.<DATADOG_API_KEY>: Your Datadog API key.
Also, set DATADOG_SITE to your Datadog site. DATADOG_SITE defaults to datadoghq.com. Your site is: .
Updating the extension for a resource group
The update script applies to an entire resource group. This script updates every Web App or Function App that has the extension installed. App Service apps that do not have the Datadog extension installed are not affected.
Open the Azure CLI or Azure Cloud Shell.
Download the update script using the following command:
$baseUri="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/DataDog/datadog-aas-extension/master/management-scripts/extension"; Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "$baseUri/update-all-site-extensions.ps1" -OutFile "update-all-site-extensions.ps1"; Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "$baseUri/install-latest-extension.ps1" -OutFile "install-latest-extension.ps1"Run the following command. All arguments are required.
.\update-all-site-extensions.ps1 -SubscriptionId <SUBSCRIPTION_ID> -ResourceGroup <RESOURCE_GROUP_NAME> -Username <USERNAME> -Password <PASSWORD>
Install a specific version of the extension
The Azure App Service UI does not support the ability to install a specific version of an extension. You may do this with the install or update script.
Install specific version on a single resource
To install a specific version on a single instance, follow the instructions for installing the extension for the first time and add the -ExtensionVersion parameter to the installation command.
.\install-latest-extension.ps1 -Username <USERNAME> -Password <PASSWORD> -SubscriptionId <SUBSCRIPTION_ID> -ResourceGroup <RESOURCE_GROUP_NAME> -SiteName <SITE_NAME> -DDApiKey <DATADOG_API_KEY> -ExtensionVersion <EXTENSION_VERSION>
Replace <EXTENSION_VERSION> with the version of the extension you wish to install. For instance, 1.4.0.
Install specific version on an entire resource group
To install a specific version for a resource group, follow the instructions for updating the extension for a resource group and add the -ExtensionVersion parameter to the installation command.
.\update-all-site-extensions.ps1 -SubscriptionId <SUBSCRIPTION_ID> -ResourceGroup <RESOURCE_GROUP_NAME> -Username <USERNAME> -Password <PASSWORD> -ExtensionVersion <EXTENSION_VERSION>
Replace <EXTENSION_VERSION> with the version of the extension you wish to install. For instance, 1.4.0.
ARM template
Many organizations use Azure Resource Management (ARM) templates to implement the practice of infrastructure-as-code. To build the App Service Extension into these templates, incorporate Datadog’s App Service Extension ARM template into your deployments to add the extension and configure it alongside your App Service resources.
Support for Java Web Apps is in Preview for extension v2.4+. Programmatic management is not available for Java Web Apps.
Interested in support for other App Service resource types or runtimes? Sign up to be notified when a Preview becomes available.
Interested in support for other App Service resource types or runtimes? Sign up to be notified when a Preview becomes available.
Deployment
To update your Datadog instrumentation with zero downtime, use deployment slots. You can create a workflow that uses GitHub Action for Azure CLI.
See the sample GitHub workflow.
Troubleshooting
If your apps are identified as being misconfigured in the Serverless View and/or you are missing corresponding metrics for your traces
It is likely that you do not have the Azure integration configured to monitor your application. Proper configuration improves your ability to correlate metrics, traces, and logs in the Datadog platform. Without the Azure integration configured, you are missing critical context for your traces. To fix this:
Go to the Azure integration tile.
Ensure you have installed the Azure integration for the Azure subscription where your application is running.
Ensure that any App Service plan filtering rules you have applied include the App Service plan where the app is running. If an App Service plan is not included, all apps and functions hosted on it are also not included. Tags on the app itself are not used for filtering by Datadog.
If APM traces are not appearing in Datadog
Verify you’ve set
DD_SITEandDD_API_KEYcorrectly.Do a full stop and start of your application.
If not resolved, try uninstalling the extension and re-installing (this also ensures you are running the latest version).
Note: To expedite the process of investigating application errors with the support team, set DD_TRACE_DEBUG:true and add the content of the Datadog logs directory (%AzureAppServiceHomeDirectory%\LogFiles\datadog) to your email.
Still need help? Contact Datadog support.
Further Reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: