- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- Notebooks
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Search
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Extend Datadog
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API-based Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Service Level Objectives
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Event Management
- Incident Response
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- End User Device Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Storage Management
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Setting Up ClickHouse
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Session Replay
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Code Coverage
- PR Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Developer Integrations
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- AI Guard
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Configuration
- Sources
- Processors
- Destinations
- Packs
- Akamai CDN
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs
- AWS Application Load Balancer Logs
- AWS CloudTrail
- AWS Elastic Load Balancer Logs
- AWS Network Load Balancer Logs
- Cisco ASA
- Cloudflare
- F5
- Fastly
- Fortinet Firewall
- HAProxy Ingress
- Istio Proxy
- Juniper SRX Firewall Traffic Logs
- Netskope
- NGINX
- Okta
- Palo Alto Firewall
- Windows XML
- ZScaler ZIA DNS
- Zscaler ZIA Firewall
- Zscaler ZIA Tunnel
- Zscaler ZIA Web Logs
- Search Syntax
- Scaling and Performance
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Guides and Resources
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
Create Policies and Custom Rules
This topic explains how to create custom Datadog Agent policies and detection rules for Workload Protection.
In addition to the out of the box (OOTB) default Agent and detection rules, you can write custom Agent and detection rules. Custom rules help to detect events Datadog is not detecting with its OOTB rules.
Agent rules are collected in policies. First, you create a policy, and then you add the default and custom rules you want applied by the policy.
When you create an Agent configuration policy it contains the default rules only. You can add custom rules to the policy to target specific infrastructure locations.
RBAC for custom rule management
Here are some important role and permissions to use for custom rules RBAC:
- The
security_monitoring_cws_agent_rules_actionspermission can be used to turn on and configure the Active Protection feature. Active Protection enables you to proactively block and terminate crypto mining threats identified by the Datadog Agent threat detection rules.- To use the
security_monitoring_cws_agent_rules_actionspermission, a user with the Datadog Admin role must create a role containing thesecurity_monitoring_cws_agent_rules_actionspermission and then add only those users that manage Active Protection to this role.
- To use the
- The Datadog Standard role enables users to create/update a custom rule by default, as long as the operation does not change the protection settings on the rule.
Policies
Rules are managed and applied using policies.
You can create and deploy different custom policies containing rules you want to apply to different sets of hosts in your infrastructure using tags.
Create a policy
- Go to Policies.
- Click New Policy. You can also open an existing policy, click Actions, and clone it.
- Enter a name for the policy and click Create. The new policy is created, but it is not enabled or deployed.
- Click the policy to open it.
- In New Rule, add custom Agent rules to the policy. For details, see Create the custom Agent and detection rules together.
- Click Edit next to Deployed on 0 agents.
- Add tags to the policy to target specific infrastructure.
- To deploy the policy, toggle the switch next to Policy is disabled and confirm.
Pin a Datadog-managed policy to its current version
Policy pinning is supported in Agent version 7.71.0 and later. Previous Agents will continue to receive the latest policy updates automatically.
When Datadog-managed policies are updated by Datadog, they are automatically deployed to your infrastructure.
To control when a new policy version is deployed to your infrastructure, you can pin the policy to its current version. Pinning a policy version prevents policy updates from being automatically rolled out when Datadog releases a new policy version.
To pin a policy, do the following:
- Go to Policies.
- Click a Datadog-managed policy.
- In Version, click the pin option. If your infrastructure is running Agents below version 7.71.0, an outdated agents warning appears. View and upgrade your Agent version in Fleet Automation.
- Click Pin. To unpin the policy version, click the pin option again.
Conflicting rules
When two policies deployed to the same host contain the same rule with a different status, the most severe aciton will be taken (Blocking > Monitoring > Disabled).
Apply tags
Tags are the target location where the policy is applied (environments, clusters, hosts, etc.). Add custom tags to policies to target the policy rules at certain portions of your infrastructure.
Tags identify two things: the Agents using the policy and the infrastructure where those Agents apply the policy. For example, if a policy has the tag cluster_name:mycluster the Agents in that cluster use the policy on the hosts in that cluster.
- Go to Agent Configuration.
- Open a policy and click Edit.
- Enter tags and click Apply. If the policy is enabled, the policy is applied to the tag targets.
When you add tags, Datadog displays how many agents the tags target as well the infrastructure running each agents. For example, Tags match 144 agents.
Custom detection rules summary
Custom detection rules depend on Agent rules. They are composed of existing, deployed Agent rules and additional expression parameters.
There are two use cases:
- Create a detection rule using an existing Agent rule: To create a threat detection rule that uses an existing Agent rule, you only need to create a threat detection rule that references the Agent rule and adds any additional expression parameters you need.
- Create a threat detection rule using a new Agent rule: To detect an event that the current Agent rules do not support, you need to create a custom Agent rule to detect that event, and then create a custom threat detection rule that uses the custom Agent rule.
For more information, see Workload Protection Detection Rules.
You can create custom rules using these methods:
- Simple: Use the Assisted rule creator to create the custom Agent and detection rules together.
- For steps on using the Assisted rule creator, see Create the custom Agent and detection rules together.
- Advanced: Create custom Agent and detection rules individually by defining their threat detection expressions.
- For steps on this method, see Create a custom agent rule and create a custom detection rule.
Create the custom Agent and detection rules together
When you create an Agent configuration policy it contains the default Agent rules only. You can add custom Agent rules to the policy to apply specific rules to specific Agents.
When you add an Agent configuration policy you can use the Assisted rule creator option to create the Agent and dependent detection rules together. This method ensures that the Agent rule is referenced in the detection rules. Using this tool is faster than creating the Agent and detection rules separately and then referencing the Agent rules in the detection rules.
As you define the rules using this tool, the threat expressions generated for these rules are displayed in the tool.
To use the Assisted rule creator:
- Go to Agent Configuration.
- Create or open a policy.
- In Add Agent Rule, select Assisted rule creator.
- Define the detection. To monitor your resource effectively, you have the following detection type options:
- To detect nonstandard and suspicious changes to files, select File integrity monitoring (FIM).
- To track and analyze system software processes for malicious behavior or policy violations, select Process activity monitoring.
- Enter the file/process names or paths to monitor.
- Specify more conditions. Enter any arguments to add to the threat rule expression. For example, the argument
foois added asprocess.argv in ["foo"]. - Set severity and notification lists.
- Select the severity for the signal generated when this threat is detected.
- Select notification lists to notify when a signal is generated.
- Add the rule name and description.
- Select Create N Rules.
- In Generate Rules, select Confirm. The rules are generated.
- Select Finish. The policy displays the new rules.
Create a custom Agent rule
You can create a custom Agent rule and deploy it as part of a new Agent policy. Later, when defining a custom detection rule, you reference the custom Agent rule and add expression parameters.
- Go to Agent Configuration.
- Create or open a policy.
- In Actions, select Manual rule creator.
- Add a name and description for the rule.
- In Expression, define the Agent expression using Datadog Security Language (SECL) syntax.
- Click Create Agent Rule. This automatically navigates you back to the policy page.
After you create a custom Agent rule, the change is saved along with other pending rule updates. To apply the change to your environment, deploy the updated custom policy to the Agent.
Remote Configuration
To perform remote configuration, you use the Datadog UI to apply policies to infrastructure. When you enable a policy, it is applied to the infrastructure identified by the policy’s tags.
- On the Agent Configuration page, hover over a policy and click Apply Tags & Deploy Policy. You can also open a policy and click Apply Tags & Deploy Policy.
- Add tags to identify the target infrastructure.
- Select Enabled.
- Click Apply. The policy is applied to all infrastructure targeted by the policy tags.
Manual deployment
To perform manual deployment, you create the policy and its rules in the Datadog UI, download it, and then upload it to the Agent(s) where you want it applied.
- On the Agent Configuration page, open a policy.
- In Actions, select Download Policy.
Next, use the following instructions to upload the policy file to each host.
Copy the default.policy file to the target host in the /etc/datadog-agent/runtime-security.d folder. The file must have read and write access for the root user on the host. This may require use of a utility such as SCP or FTP.
To apply the changes, restart the Datadog Agent.
Create a ConfigMap containing
default.policy, for example,kubectl create configmap jdefaultpol --from-file=default.policy.Add the ConfigMap (
jdefaultpol) tovalues.yamlwithdatadog.securityAgent.runtime.policies.configMap:securityAgent: # [...] runtime: # datadog.securityAgent.runtime.enabled # Set to true to enable Security Runtime Module enabled: true policies: # datadog.securityAgent.runtime.policies.configMap # Place custom policies here configMap: jdefaultpol # [...]Upgrade the Helm chart with
helm upgrade <RELEASENAME> -f values.yaml --set datadog.apiKey=<APIKEY> datadog/datadog.Note: If you need to make further changes to
default.policy, you can either usekubectl edit cm jdefaultpolor replace the configMap withkubectl create configmap jdefaultpol --from-file default.policy -o yaml --dry-run=client | kubectl replace -f -.
Enable and deploy policies
Enabled policies apply their rules to the infrastructure targets identified by their tags. Enabling a policy is the same as deploying it.
You can use Remote Configuration in the Datadog UI to automatically deploy the custom policy to the hosts designated by the policy tags (all hosts or a defined subset of hosts), or you can manually upload the policy to the Agent on each host.
To enable a policy using Remote Configuration in the Datadog UI, do the following:
- On Agent Configuration, hover over a policy and click Apply Tags & Deploy Policy. You can also open a policy and click Apply Tags & Deploy Policy.
- Add tags to identify the target infrastructure.
- Select Enabled.
- Click Apply. The policy is applied to all infrastructure targeted by the policy tags.
If you disable a policy, its rules are no longer applied to the infrastructure identified by its tags.
Custom Agent rules are deployed to the Agent in a custom policy separate from the default policies. The custom policy contains only custom Agent rules.
Create a custom detection rule
After you upload the new default policy file to the Agent, navigate to the Threat Detection Rules page.
- On Agent Configuration, select New Rule, and then select Manual rule creator.
- Select a rule type:
- In Detection rule types, select Workload Security.
- Select a detection method such as Threshold or New Value.
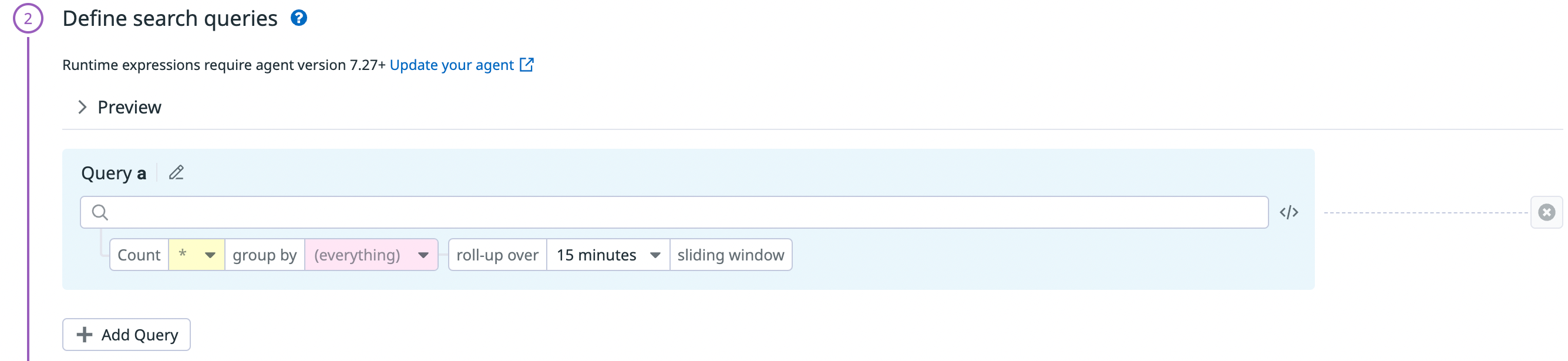
- Define search queries:
Configure a new Workload Protection rule. A rule can have multiple rule cases combined with Boolean logic, for example
(||, &&). You can also set the counter, group by, and roll-up window.Enter a query so that a trigger is only generated when a value is met. You can also enter suppression queries in the Suppression Rules, so that a trigger is not generated when the specified values are met.
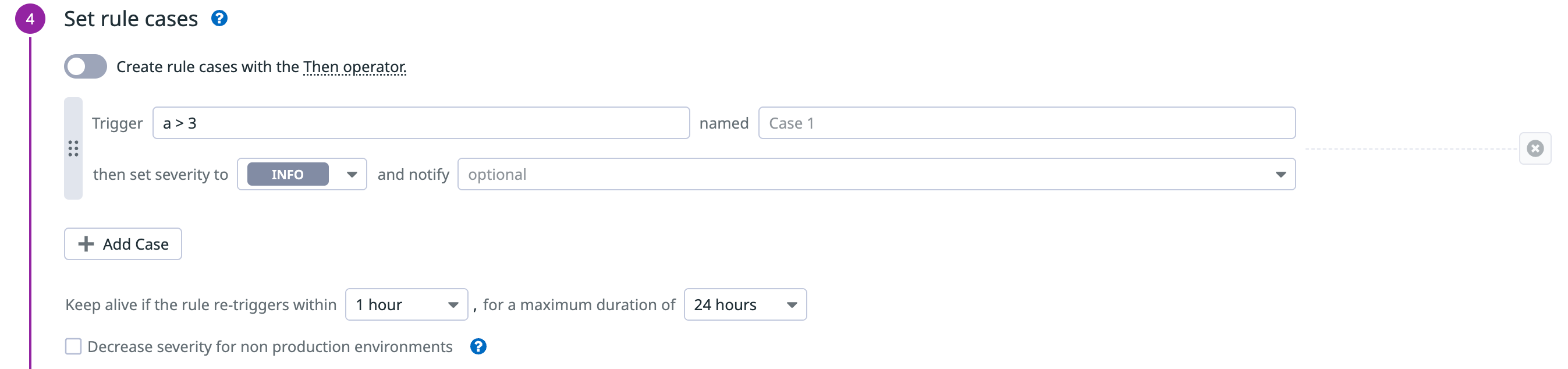
- Set rule cases:
Set a rule case for the trigger and severity.
Define the logic for when this rule triggers a security signal. For example,
a>0means a security signal triggers as long as the rule condition set in the search query is met at least once in the sliding time window.Select a severity to associate the rule with and select all relevant parties you want to notify.
- Say what’s happening:
- Name the rule and add the notification message in Markdown format. Use Notification variables to provide specific details about the signal by referencing its tags and event attributes. After the message, add multiple tags to give more context to the signals generated by your custom rule.
Datadog recommends including a remediation runbook in the body. As noted in the template, use substitution variables to dynamically generate contextualized content at runtime.
Disable default Agent rules
- To disable an Agent rule, navigate to the Agent Configuration page and select the policy using the rule.
- In the policy, open the rule.
- Next to the rule’s title, click Monitoring, and then select Disable Rule.
- Click Save Changes.
You can also disable a rule by setting the Then… section of a rule to Do Nothing.