- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- APM Terms and Concepts
- Application Instrumentation
- APM Metrics Collection
- Trace Pipeline Configuration
- Correlate Traces with Other Telemetry
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origins for Spans
- Service Observability
- Endpoint Observability
- Dynamic Instrumentation
- Live Debugger
- Error Tracking
- Data Security
- Guides
- Troubleshooting
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Log Management
- Administration
Detection Rules
Detection rules define conditional logic that is applied to all ingested logs and cloud configurations. When at least one case defined in a rule is matched over a given period of time, a security signal is generated. You can view these signals in the Signals Explorer.
Out-of-the-box detection rules
Datadog provides out-of-the-box detection rules to flag attacker techniques and potential misconfigurations. When new detection rules are released, they are automatically imported into your account, your App and API Protection library, and the Agent, depending on your configuration.
Out-of-the box rules are available for the following security products:
- Cloud SIEM uses log detection to analyze ingested logs in real-time.
- Cloud Security:
- Cloud Security Misconfigurations uses cloud configuration and infrastructure configuration detection rules to scan the state of your cloud environment.
- Workload Protection uses the Datadog Agent and detection rules to actively monitor and evaluate system activity.
- Cloud Security Identity Risks uses detection rules to detect IAM-based risks in your cloud infrastructure.
- App and API Protection (AAP) leverages Datadog APM, the Datadog Agent, and detection rules to detect threats in your application environment.
Beta detection rules
Datadog’s Security Research team continually adds new OOTB security detection rules. While the aim is to deliver high quality detections with the release of integrations or other new features, the performance of the detection at scale often needs to be observed before making the rule generally available. This gives Datadog’s Security Research the time to either refine or deprecate detection opportunities that do not meet our standards.
Custom detection rules
There may be situations where you need to customize a rule based on your environment or workload. For example, if you’re using AAP, you may want to customize a detection rule that detects users performing sensitive actions from a geolocation where your business doesn’t operate.
To create custom rules, you can clone the default rules and edit the copies, or create your own rules from scratch.
Search and filter detection rules
To view out-of-the-box and custom detection rules in Datadog, navigate to the Security Settings page. Rules are listed on separate pages for each product (App and API Protection, Cloud Security, and Cloud SIEM).
To search and filter the rules, use the search box and facets to query by value. For example, to only show rules for a given rule type, hover over the rule type and select only. You can also filter by facets such as source and severity when investigating and triaging incoming issues.
Create detection rules
To create a custom detection rule, click the New Rule button in the upper-right corner of the Detection Rules page. You can also clone an existing default or custom rule and use it as a template.
For detailed instructions, see the following articles:
Manage detection rules
Enable or disable rules
To enable or disable a rule, toggle the switch to the right of the rule name.
You can also bulk enable or disable rules:
- Click Select Rules.
- Select the rules you want to enable or disable.
- Click the Edit Rules dropdown menu.
- Select Enable Rules or Disable Rules.
Edit a rule
For out-of-the-box detection rules, you can only add or edit a suppression query. To update the query, adjust triggers, or manage notifications, you can clone the default rule and use it as a template for a custom rule. You can then disable the default rule.
- To edit a default rule, click the vertical three-dot menu for the rule and select Edit default rule.
- To edit a custom rule, click the vertical three-dot menu for the rule and select Edit rule.
Clone a rule
To clone a rule, click the vertical three-dot menu for the rule and select Clone rule.
Cloning a rule is helpful if you wish to duplicate an existing rule and lightly modify settings to cover other areas of detection. For example, you could duplicate a log detection rule and modify it from Threshold to Anomaly to add a new dimension to threat detection using the same queries and triggers.
Delete a rule
To delete a custom rule, click the vertical three-dot menu for the rule and select Delete rule.
Note: You can only delete custom rules. To remove a default rule, you must disable it.
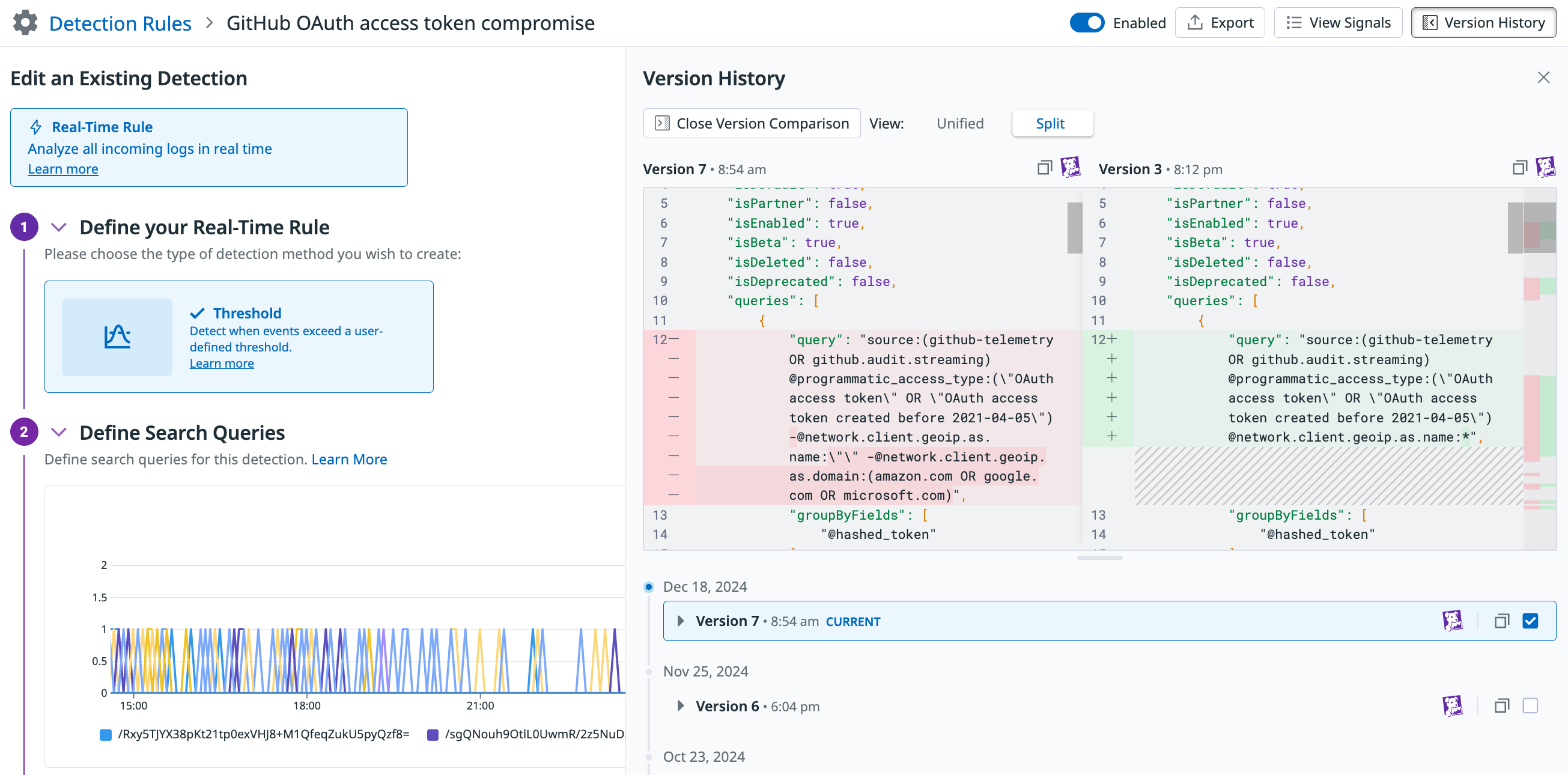
See the version history for a rule
Use Rule Version History to:
- See past versions of a detection rule and understand the changes over time.
- See who made the changes for improved collaboration.
- Compare versions with diffs to analyze the modifications and impact of the changes.
To see the version history of a rule:
- Navigate to the Security Settings page. In the left navigation panel:
- For AAP: Click App and API Protection and then click Detection Rules.
- For Cloud Security: Click Cloud Security and then click Threat Detection Rules.
- For Cloud SIEM: Click Cloud SIEM and then click Detection Rules.
- Click on the rule you are interested in.
- In the rule editor, click Version History to see past changes.
- Click a specific version to see what changes were made.
- Click Open Version Comparison to see what changed between versions.
- Select the two versions you want to compare.
- Data highlighted in red indicates data that was modified or removed.
- Data highlighted in green indicates data that was added.
- Click Unified if you want to see the comparison in the same panel.
Restrict edit permissions
By default, all users have view and edit access to the detection rules. To use granular access controls to limit the roles that may edit a single rule:
- Click the vertical three-dot menu for the rule and select Permissions.
- Click Restrict Access. The dialog box updates to show that members of your organization have Viewer access by default. Use that dropdown menu to select one or more roles, teams, or users that may edit the security rule.
- Use the dropdown menu to select one or more roles, teams, or users that may edit the security rule.
- Click Add.
- Click Save.
Note: To maintain your edit access to the rule, Datadog requires you to include at least one role that you are a member of before saving.
To restore access to a rule:
- Click the vertical three-dot menu for the rule and select Permissions.
- Click Restore Full Access.
- Click Save.
View generated signals
To view the security signals for a rule in the Signals Explorer, click the vertical three-dot menu and select View generated signals. This is useful when correlating signals across multiple sources by rule, or when completing an audit of rules.
Export a rule as JSON
To export a copy of a rule as JSON, click the vertical three-dot menu for the rule and select Export as JSON.
Rule deprecation
Regular audits of all detection rules are performed to maintain high fidelity signal quality. Deprecated rules are replaced with an improved rule.
The rule deprecation process is as follows:
- There is a warning with the deprecation date on the rule. In the UI, the warning is shown in the:
- Signal side panel’s Rule Details > Playbook section
- Misconfigurations side panel (Cloud Security Misconfigurations only)
- Rule editor for that specific rule
- Once the rule is deprecated, there is a 15 month period before the rule is deleted. This is due to the signal retention period of 15 months. During this time, you can re-enable the rule by cloning the rule in the UI.
- Once the rule is deleted, you can no longer clone and re-enable it.
Further reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: