- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- Notebooks
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Search
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Extend Datadog
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API-based Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Service Level Objectives
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Event Management
- Incident Response
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- End User Device Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Storage Management
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Setting Up ClickHouse
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Session Replay
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Code Coverage
- PR Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Developer Integrations
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- AI Guard
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Configuration
- Sources
- Processors
- Destinations
- Packs
- Akamai CDN
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs
- AWS Application Load Balancer Logs
- AWS CloudTrail
- AWS Elastic Load Balancer Logs
- AWS Network Load Balancer Logs
- Cisco ASA
- Cloudflare
- F5
- Fastly
- Fortinet Firewall
- HAProxy Ingress
- Istio Proxy
- Juniper SRX Firewall Traffic Logs
- Netskope
- NGINX
- Okta
- Palo Alto Firewall
- Windows XML
- ZScaler ZIA DNS
- Zscaler ZIA Firewall
- Zscaler ZIA Tunnel
- Zscaler ZIA Web Logs
- Search Syntax
- Scaling and Performance
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Guides and Resources
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
- Account Management
- Data Security
- Help
- feature_flags_client
Git Hooks
This product is not supported for your selected Datadog site. ().
Overview
A Git hook is a program executed before a user commits code to a repository or pushes code to a remote location. A Git hook is generally used to run verifications and enforce requirements on the code before it is pushed to the remote branch.
Datadog Code Security provides a Git hook to check for Static Code Analysis (SAST) violations or secrets before code is pushed or committed. The Code Security Git hook checks the code from the latest commit and the default branch and flags any errors it detects.
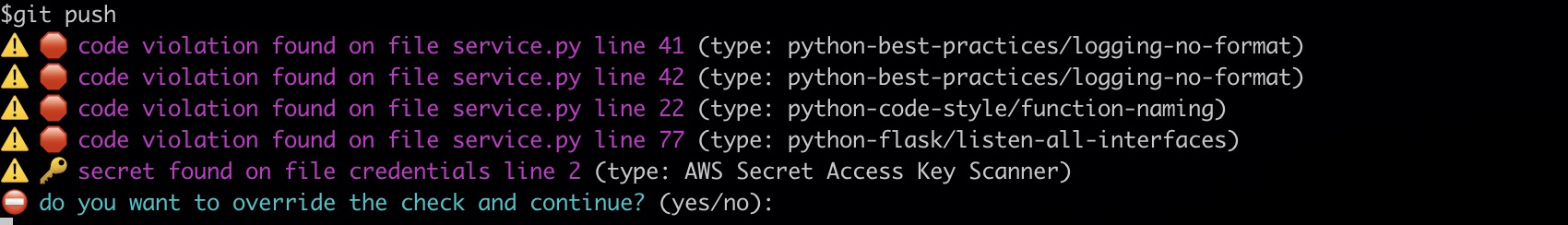
The Datadog Git hook warns developers before they push any code containing coding errors, vulnerabilities, or secrets. When you commit code with an error, a prompt like the following appears in the user terminal:
Setup
- Download the
datadog-git-hookprogram from the release page or the Datadog Static Analyzer releases. - Install the program on your computer.
- Add a
.git/hooks/pre-pushfile in the repository with the script below. Note: The script assumes thedatadog-static-analyzer-git-hookbinary is in/usr/local/bin/datadog-static-analyzer-git-hook.
#!/bin/sh
# Get the repo root path
repo_path=$(git rev-parse --show-toplevel)
# Make sure the user can provide some input
exec < /dev/tty
/usr/local/bin/datadog-static-analyzer-git-hook -r $repo_path --static-analysis --secrets --confirmation --default-branch <default-branch>
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
echo "datadog-static-analyzer check passed"
exit 0
else
echo "datadog-static-analyzer check failed"
exit 1
fi
The program accepts the following parameters:
--confirmation: Ask the user for confirmation to override the Git hook check--default-branch: Specify the name of the default branch.--static-analysis: Enable Static Code Analysis.--secrets: Enable secrets detection (in preview - please reach out to Datadog Support).--output <file>: Export the findings found in the commit into a SARIF file.