- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- Notebooks
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Search
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Extend Datadog
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API-based Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Service Level Objectives
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Event Management
- Incident Response
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- End User Device Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Storage Management
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Session Replay
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Code Coverage
- PR Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Developer Integrations
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- AI Guard
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Configuration
- Sources
- Processors
- Destinations
- Packs
- Akamai CDN
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs
- AWS Application Load Balancer Logs
- AWS CloudTrail
- AWS Elastic Load Balancer Logs
- AWS Network Load Balancer Logs
- Cisco ASA
- Cloudflare
- F5
- Fastly
- Fortinet Firewall
- HAProxy Ingress
- Istio Proxy
- Juniper SRX Firewall Traffic Logs
- Netskope
- NGINX
- Okta
- Palo Alto Firewall
- Windows XML
- ZScaler ZIA DNS
- Zscaler ZIA Firewall
- Zscaler ZIA Tunnel
- Zscaler ZIA Web Logs
- Search Syntax
- Scaling and Performance
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Guides and Resources
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
OCSF Processor
Overview
Cloud SIEM provides out-of-the-box Open Cybersecurity Framework (OCSF) support (with editable settings) for certain integrations. You can also add custom mappings with the OCSF processor to normalize your security logs according to the OCSF framework.
This document explains how to set up the OCSF processor, which is configured in Log Management pipelines.
To use the OCSF processor, you need to:
- Create a log pipeline that filters for the logs you want to remap to OCSF.
- Within each pipeline, create a sub-pipeline for each OCSF target event class.
- Add processors for pre-processing, if needed.
- Add and configure the OCSF processor in that log pipeline.
Use an OCSF processor
Create a log pipeline
Create separate log pipelines for each log source you want to remap to OCSF. For example, if you want to remap your Windows, AWS CloudTrail, and Okta logs to OCSF, you must:
- Create a pipeline for your Windows logs, a pipeline for AWS CloudTrail logs, and a pipeline for Okta logs.
- Within each of those pipelines, create sub-pipelines for every target class.
To create a log pipeline:
- Navigate to Log Pipelines.
- Click New Pipeline.
- Enter a query to filter for logs you want to send to the OCSF processor.
- Enter a name for the pipeline.
- (Optional) Add tags and a description to indicate the purpose of the pipeline. Pipeline tags do not affect logs, but can be used to filter and search pipelines within the Pipelines page.
- Click Create.
Create sub-pipelines
Within the pipeline that filters for logs by source (for example, Okta), create a sub-pipeline for each OCSF target class. For example, if you want to normalize all your Okta Authentication and Detection Findings logs to OCSF, create the following in your Okta pipeline:
- A sub-pipeline for the OCSF class Authentication, where you filter for all Okta authentication events and logs
- A sub-pipeline for the OCSF class Detection Finding, where you filter all Okta detection events logs
To create a sub-pipeline:
- Click the down arrow next to the pipeline you created for the source.
- Click Add Nested Pipeline.
- Enter a query to filter for logs you want to send to the OCSF processor. For example, if you want to filter for Okta detection events, use the query:
[@eventType:(security.threat.detected OR user.risk.*)]. - Enter a name for the sub pipeline, such as
Okta OCSF sub-pipeline for class Detection Finding [2004]. - (Optional) Add tags and a description to indicate the purpose of the pipeline. Pipeline tags do not affect logs, but can be used to filter and search pipelines within the Pipelines page.
- Click Create.
Add processors for pre-processing logs
In Log Management pipelines, the order of pipelines matter. If you have to pre-process your logs before they get remapped to OCSF, the pre-processing must occur before the OCSF processor. For example, if the logs you want to remap to OCSF have an attribute that is encoded in base64, you must decode the attribute in a different pipeline and processor, before remapping it using the OCSF processor.
Depending on your use case, you can add processors to reformat your logs in the sub-pipeline for a target class or in a separate pipeline. For example:
- If pre-processing logs is required for several target classes, add processors to reformat your logs in a separate pipeline before the logs are sent to the OCSF processor.
- If pre-processing logs is only required for one target class, add processors to reformat logs in the sub-pipeline for that target class.
See Processors for more information on the processors you can use to reformat your logs if needed.
Configure the OCSF processor
Add an OCSF processor
- Click the down arrow next to the pipeline for you log source.
- Click Add Processor.
- Select OCSF Processor.
- Enter a name for the processor, such as
Okta auth logs. - Select the OCSF schema version and class you want to use in the dropdown menus.
- (Optional) Select the profile in the dropdown menu.
Define mapping
Class attribute configuration
The OCSF Processor remaps attributes, including enumerated (ENUM) attributes. After you select the OCSF schema version and class, the Define Mapping (OCSF Schema Class Attributes) section shows attributes that you can configure. You can filter and search for specific attributes or choose to see only required, recommended, or optional attributes. If you do not see an attribute that you want to configure, you can manually add it.
ENUM attributes are configured in the ENUM attribute configuration section.
- For each target attribute, in the Source attribute column, enter the attribute name from the source log that corresponds to the OSCF attribute.
- You must fill out the Source attribute for all required fields.
- You can add multiple fields for Source attribute. For example, Okta’s
user.system.startlogs have either theeventTypeorlegacyEventTypefield. You can map both fields to the same OCSF field. - You can also map a field to itself. For example, if you pre-processed a log to decode a base64 value and also added that value to the correct OCSF attribute, you can map that field to itself. In the below image, is remapped to itself because the source attribute entered is the same as the target attribute.
- Notes:
- Required root-level attributes cannot be deleted.
- (Optional) Click Add Field if you want to add additional attributes to be mapped. If you want to explore the attributes you can add, click OCSF Schema Documentation next to the Schema configuration header.
- Enter the path to the attribute, such as
actor.user.name, and select the attribute from the dropdown menu.- Note: If the attribute is not in the dropdown menu, you can manually enter the path to the attribute to add it. The attribute must be in the OCSF Schema documentation.
- Click add.
- If you see the error
Invalid OCSF attribute, check the OCSF documentation to make sure you have the correct path. - If you see the error
ENUM attribute, you have to enter the attribute in the ENUM attribute configuration section.
- If you see the error
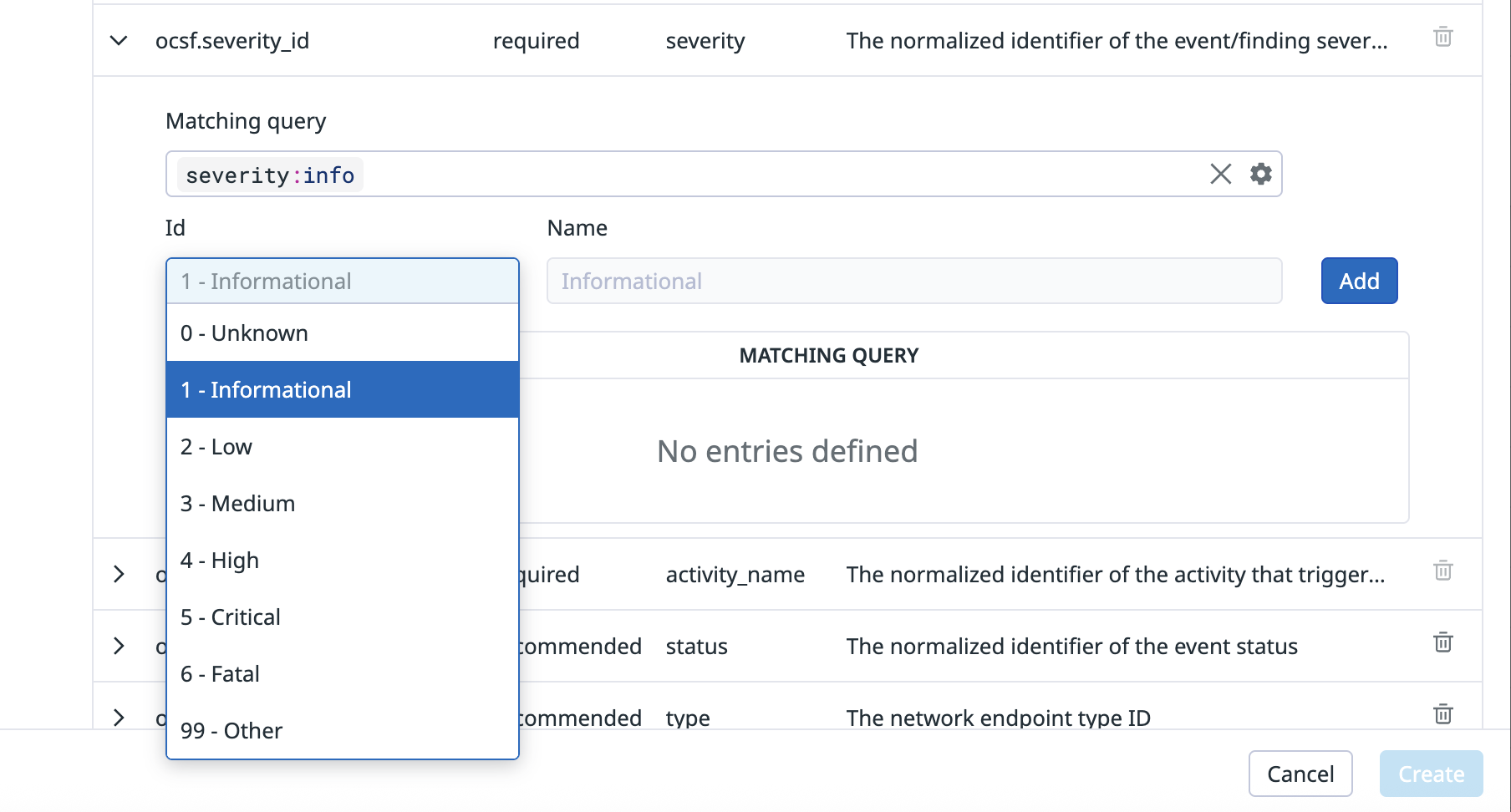
ENUM attribute configuration
Enumeration (ENUM) attributes are defined as specific numerical values. For example, the severity_id in the Authentication [3002] class is an enum attribute where numbers from 0 to 6, and 99 each represent a severity level. The values of a source log’s severity field must be mapped to the OCSF severity_id’s values listed in Authentication [3002].
Some enum attributes have a sibling string attribute associated with the enum attribute. For example, severity_id:1 has the sibling string attribute severity:Informational. The sibling string attribute is automatically populated for the target attribute when the enum value is selected.
An example of mapping severity values:
| Log value | OCSF severity ID | OCSF severity |
|---|---|---|
INFO | 1 | Informational |
WARN | 3 | Medium |
ERROR | 4 | High |
In the ENUM Attribute Configuration section of the processor, you define the source log attribute that corresponds to the different attribute IDs. Some attributes are pre-populated based on the class selected.
- Click the down arrow next to the enum attribute that you want to configure.
- In the Matching query field, enter the log attribute that corresponds to this OSCF attribute, such as
severity:info. - In the ID dropdown menu, select the number that corresponds to the log attribute’s value.
- (Optional) Enter a name for the sibling string attribute. See Enum attributes for more information.
- Click Add.
- If you added the enum value
Other (99), you must enter the fallback values in the Other fallback value(s) field. - Repeat steps 1 to 6 until all required enum attributes are filled out.
- (Optional) Click Add Field if you want to manually add enum attributes to be mapped.
- Enter the path to the attribute, such as
ocsf.actor.user.name. - Click add.
- If you get an error, see Errors when manually adding an attribute for more information.
- Enter the path to the attribute, such as
- Click Create to add the processor.
Errors when manually adding an attribute
Value is already added
If you see the error This value has already been added, the attribute you are trying to add has already been added.
Unrecognized ENUM attribute, add as class attribute
If you see the error Unrecognized ENUM attribute, add as a class attribute, you are trying to add a class attribute in the ENUM attribute configuration section. To resolve the issue, add the class attribute in the Define mapping (class attribute) section.
Unrecognized class attribute, add as ENUM attribute
If you see the error Unrecognized class attribute, add as an ENUM attribute, you are trying to add an ENUM attribute in the class attribute configuration section. To resolve the issue, add the ENUM attribute in the ENUM attribute configuration section.
Invalid OCSF attribute
If you see the error Invalid OCSF attribute, check the OCSF Schema to ensure that you are adding an attribute in the schema.
Further reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: