- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- Notebooks
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Search
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Extend Datadog
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API-based Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Service Level Objectives
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Event Management
- Incident Response
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- End User Device Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Storage Management
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Setting Up ClickHouse
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Session Replay
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Code Coverage
- PR Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Developer Integrations
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- AI Guard
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Configuration
- Sources
- Processors
- Destinations
- Packs
- Akamai CDN
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs
- AWS Application Load Balancer Logs
- AWS CloudTrail
- AWS Elastic Load Balancer Logs
- AWS Network Load Balancer Logs
- Cisco ASA
- Cloudflare
- F5
- Fastly
- Fortinet Firewall
- HAProxy Ingress
- Istio Proxy
- Juniper SRX Firewall Traffic Logs
- Netskope
- NGINX
- Okta
- Palo Alto Firewall
- Windows XML
- ZScaler ZIA DNS
- Zscaler ZIA Firewall
- Zscaler ZIA Tunnel
- Zscaler ZIA Web Logs
- Search Syntax
- Scaling and Performance
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Guides and Resources
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
Container Image Scanning in CI/CD
Overview
Cloud Security enables you to scan container images for vulnerabilities during CI/CD, before images are deployed to production. By integrating vulnerability scanning directly into your pipelines, you can detect and remediate security issues early in the development lifecycle.
To support CI/CD-based container image scanning, Datadog provides the Datadog Security CLI. The CLI is designed to be run directly inside your CI jobs, giving you full control over when and how scans are executed as part of your pipelines.
Note: For vulnerability management in production environments, see Cloud Security Vulnerabilities.
Get started
To get started with container image scanning in CI/CD:
- Configure Datadog credentials
- Install the Datadog Security CLI in your CI/CD pipeline
- View scan results on the Cloud Security Vulnerabilities page
- Optionally, run local scans during development for faster iteration
Configure Datadog credentials
To upload scan results to Datadog, configure the following environment variables in your CI pipeline:
| Name | Description | Required | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
DD_API_KEY | Your Datadog API key. This key is created by your Datadog organization and should be stored as a secret. | Yes | |
DD_APP_KEY | Your Datadog application key. This key, created by your Datadog organization, should include the appsec_vm_read scope and be stored as a secret. | Yes | |
DD_SITE | The Datadog site to send information to. Your Datadog site is | No | datadoghq.com |
Store your API and application keys as secrets in your CI/CD platform to protect sensitive credentials.
Install the Datadog Security CLI
Join the Preview
The Datadog Security CLI is in Preview and available to install from Datadog package repositories.
You can install Datadog Security CLI on Debian/Ubuntu, Red Hat/CentOS, and macOS systems. Container image scanning works with all major CI/CD platforms, including:
- GitHub Actions
- GitLab CI/CD
- Azure DevOps
- Other CI providers that can execute shell scripts
The customizable script approach gives you full control over when and how scans are executed in your pipelines. Choose your installation method below.
Install from package repository
# Import Datadog APT signing key
DD_APT_KEY_URL="https://keys.datadoghq.com/DATADOG_APT_KEY_CURRENT.public"
curl -fsSL "$DD_APT_KEY_URL" | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/datadog-archive-keyring.gpg
# Add Datadog repository
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/datadog-archive-keyring.gpg] https://apt.datadoghq.com/ stable datadog-security-cli" \
| sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/datadog-security-cli.list
# Update package list and install
sudo apt update
sudo apt install datadog-security-cli
Install from package repository
# Import Datadog RPM signing key
sudo rpm --import https://keys.datadoghq.com/DATADOG_RPM_KEY_CURRENT.public
# Add Datadog repository
sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/datadog-security-cli.repo > /dev/null <<'EOF'
[datadog-security-cli]
name=Datadog Security CLI
baseurl=https://yum.datadoghq.com/stable/datadog-security-cli/\$basearch/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://keys.datadoghq.com/DATADOG_RPM_KEY_CURRENT.public
repo_gpgcheck=1
EOF
# Install the CLI
sudo yum install datadog-security-cli
Install with Homebrew
# Install via Homebrew
brew install --cask datadog-security-cli
Run your first scan
After installing the Datadog Security CLI, configure your Datadog credentials and scan a container image:
# Configure Datadog credentials
export DD_API_KEY=<your_api_key>
export DD_APP_KEY=<your_app_key>
export DD_SITE=
# Scan your container image
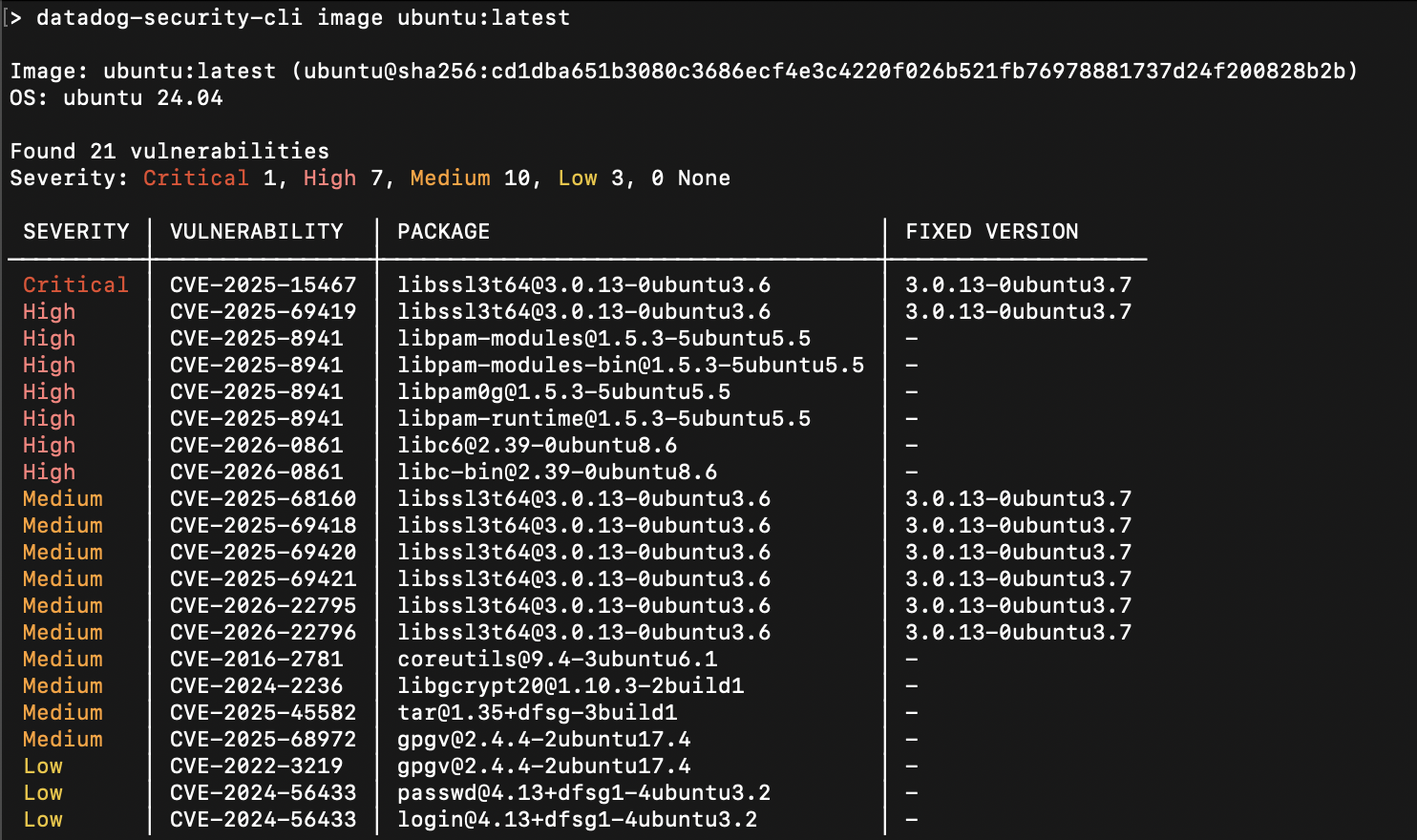
datadog-security-cli image myimage:tag
The CLI outputs scan results directly to your terminal, showing:
- Image information (name, digest, operating system)
- Total number of vulnerabilities found
- Severity breakdown (Critical, High, Medium, Low)
- Detailed table of vulnerabilities with CVE IDs, affected packages, and available fixes
View scan results
After running your first scan, results appear on the Cloud Security Vulnerabilities page within minutes. You can:
- Filter by resource type: View vulnerabilities specific to container images scanned in CI/CD
- Prioritize by severity: Focus on critical and high-severity vulnerabilities first
- Track remediation: Assign vulnerabilities to team members and track resolution
- Set up notifications: Get alerted when new critical vulnerabilities are detected
Run local scans during development
For faster iteration before committing to CI, install the Datadog Security CLI locally using the same installation methods described in the installation section above.
Scan locally without persisting results
When testing locally, scan images without uploading results to Datadog using the --no-persist flag:
# Scan locally without sending results to Datadog
datadog-security-cli image myapp:latest --no-persist
This is useful for:
- Testing the CLI functionality without affecting your Datadog data
- Validating container images during local development
- Iterating quickly on image builds before committing to CI
Scan options
The Datadog Security CLI supports various options to customize your container image scans:
Configure severity thresholds
# Fail the build if critical vulnerabilities are found
datadog-security-cli image myapp:latest --fail-on critical
# Fail on high or critical vulnerabilities
datadog-security-cli image myapp:latest --fail-on high
Output formats
# Output results in JSON format
datadog-security-cli image myapp:latest --output json
Troubleshooting
Authentication errors
If you encounter authentication errors:
- Verify your
DD_API_KEYandDD_APP_KEYare correctly set. - Ensure the application key has the
appsec_vm_readscope. - Check that your
DD_SITEmatches your Datadog organization’s site.
Image not found errors
If the CLI cannot find your image:
- Verify the image exists locally:
docker images. - Use the full image name, including registry (if applicable).
- Ensure the image is built before scanning.
Network connectivity issues
If scans fail due to network issues:
- Verify your CI environment can reach the Datadog site.
- Check for proxy or firewall restrictions.
- Ensure outbound HTTPS connections are allowed.
For additional help, see the Cloud Security troubleshooting guide or contact Datadog support.
Further reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: