- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- Notebooks
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Search
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API-based Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Service Level Objectives
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Event Management
- Incident Response
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- End User Device Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Storage Management
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Session Replay
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Code Coverage
- PR Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- AI Guard
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Configuration
- Sources
- Processors
- Destinations
- Packs
- Akamai CDN
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs
- AWS Application Load Balancer Logs
- AWS CloudTrail
- AWS Elastic Load Balancer Logs
- AWS Network Load Balancer Logs
- Cisco ASA
- Cloudflare
- F5
- Fastly
- Fortinet Firewall
- HAProxy Ingress
- Istio Proxy
- Juniper SRX Firewall Traffic Logs
- Netskope
- NGINX
- Okta
- Palo Alto Firewall
- Windows XML
- ZScaler ZIA DNS
- Zscaler ZIA Firewall
- Zscaler ZIA Tunnel
- Zscaler ZIA Web Logs
- Search Syntax
- Scaling and Performance
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Guides and Resources
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
Attacker Clustering
This product is not supported for your selected Datadog site. ().
Overview
Attacker Clustering improves distributed attack blocking. Datadog App and API Protection (AAP) identifies security signal traffic attacker patterns and to help you mitigate distributed attacks more efficiently.
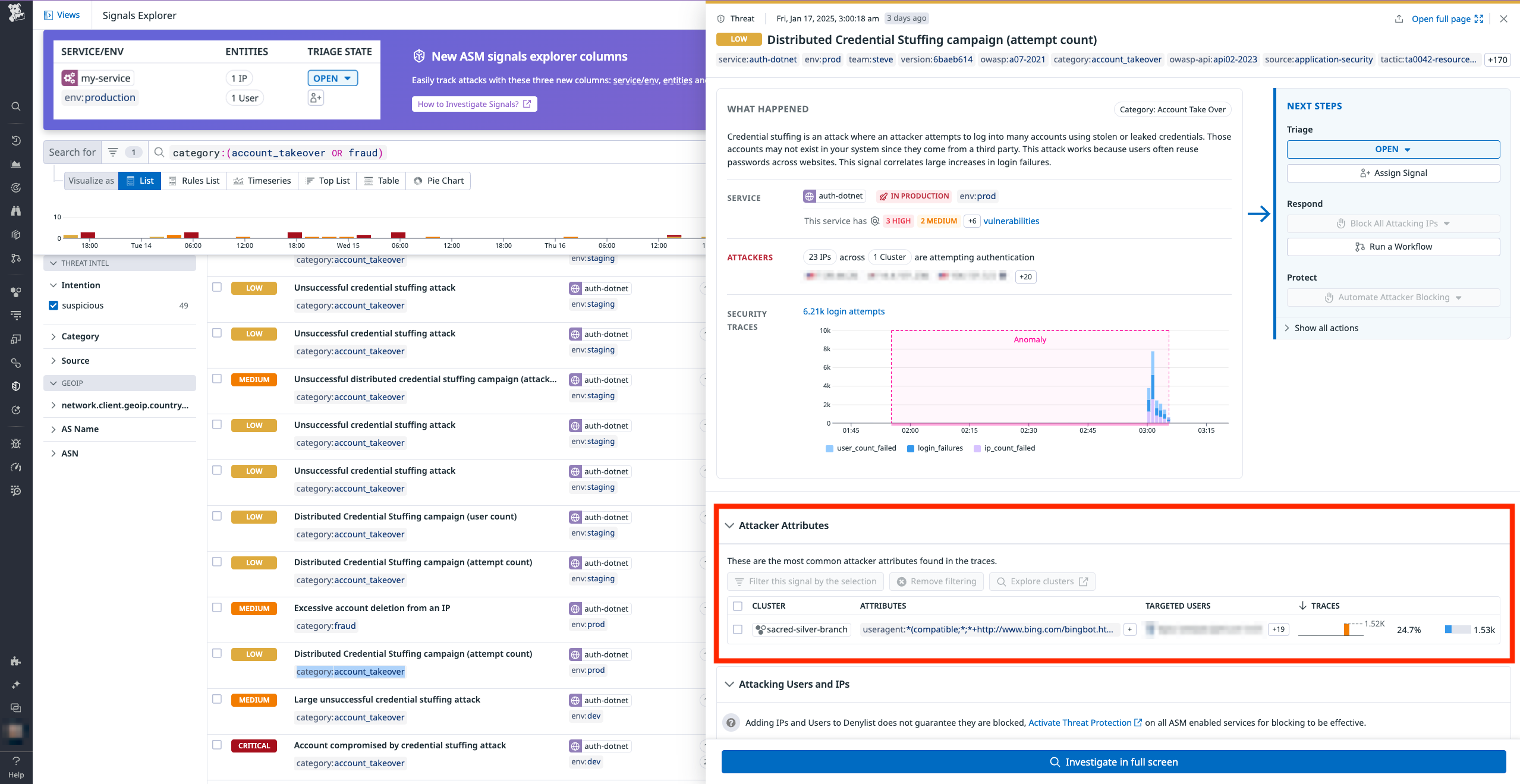
Attacker clustering highlights a set of common attributes shared by a significant portion of traffic and suggests blocking based on those attributes.
Blocking on attacker attributes means you keep your application or API protected even as the attacker rotates between IPs.
What signals are used for attacker clusters?
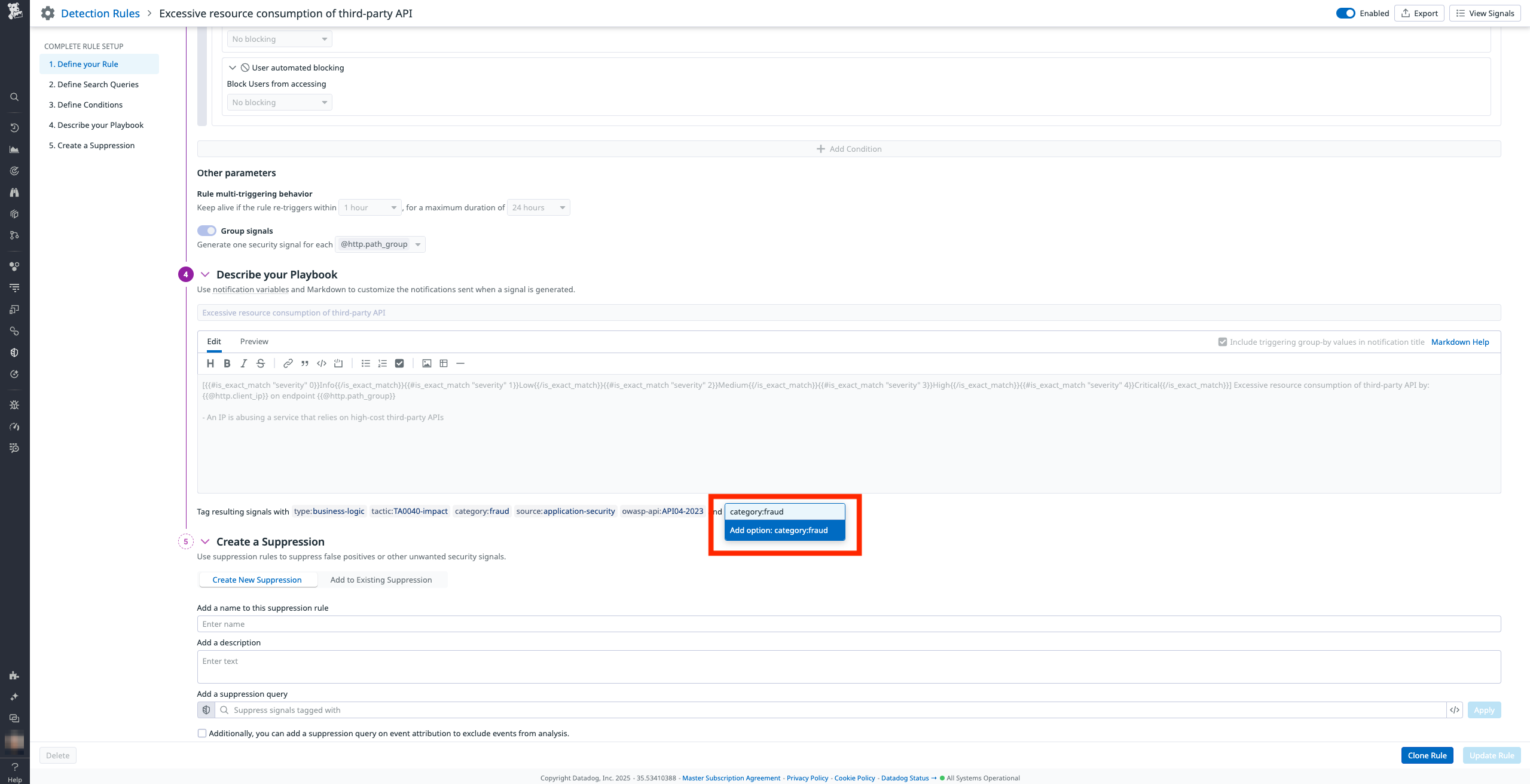
The attacker clustering is computed for every AAP security signal emitted from a detection rule tagged with category:account_takeover or category:fraud
Out of the box, attacker clustering is computed for the AAP detection rules that detect API abuse, credential stuffing, or brute force attacks.
If you want the attacker clustering executed on custom detection rules, add these tags in the detection rule editor (see screenshot below).
Attacker clustering attributes
Attacker clustering is computed using the following request attributes:
- Browser name
- Browser version
- OS name
- OS version
- User agent header
- HTTP request headers (for example,
accept-encoding,content-type) - Datadog attacker fingerprinting
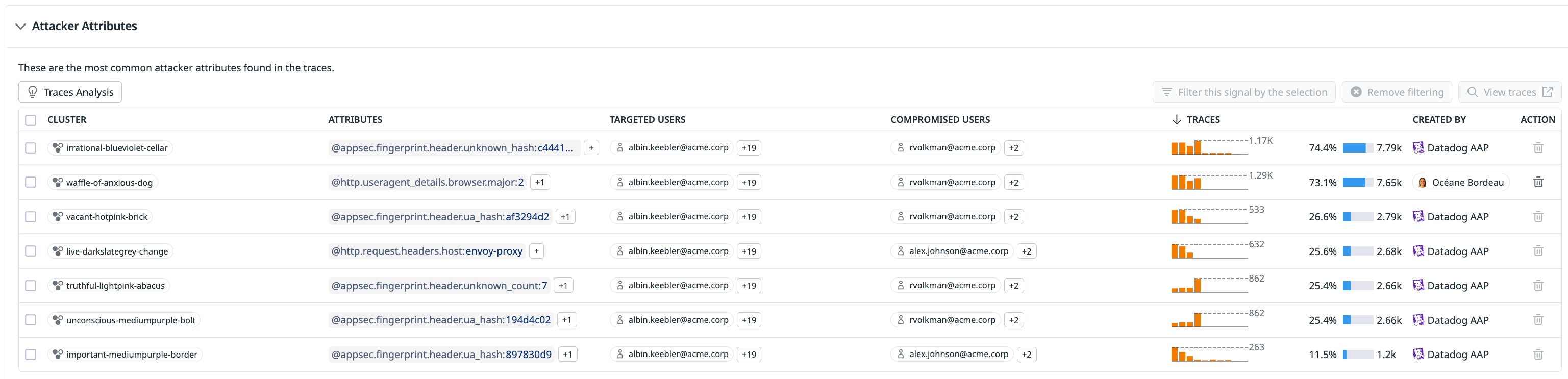
When the attacker attributes are identified, they are displayed on the signal side panel and Signals page. Attacker attributes can be a combination of the attributes listed above.
Custom HTTP request headers
If you want to use custom HTTP request headers for attacker clustering, they must be added under the path @http.request.headers in your traces. You can add custom headers to your traces by configuring the tracer with the DD_TRACE_REQUEST_HEADER_TAGS environment variable. For more information about this configuration, see Configure the Datadog Tracing Library.
Attacker clustering mechanism
The clustering algorithm analyzes the frequency of attributes in the attack traffic. It selects attributes that appear frequently while also filtering out typical traffic noise. This process results in attributes that can be blocked to stop or slow the attacker.
The algorithm tracks the changes in the attack traffic by identifying emerging trends as the attacker changes tactics (for example, changing headers, tool, etc.). The attacker cluster is updated with the latest traffic trends.
Traffic associated with threat intelligence is also considered in the clustering mechanism. The more an attribute is correlated with Threat Intelligence, the higher the chance to create an attacker cluster around this attribute.
The attacker clustering attributes selected are then shown as regular expressions that can be used to block with AAP’s In-App WAF or to filter out traffic in AAP Traces explorer for investigation.
Custom attacker clustering
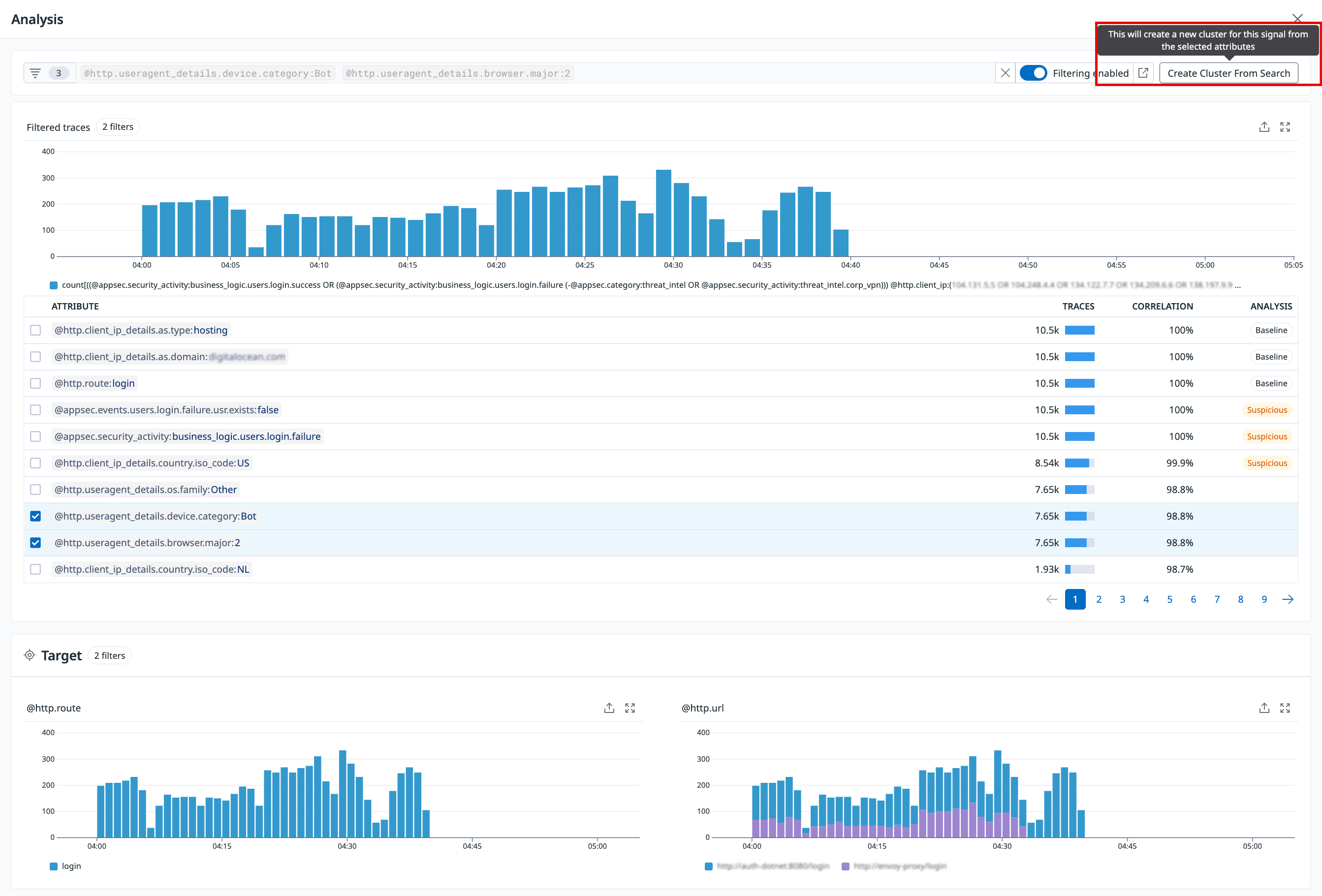
If the automatic attacker clustering detection fails to identify the appropriate attributes, you can manually create attacker clusters by selecting attributes from the trace analysis side panel.
To create a custom attacker cluster:
- Open the trace analysis panel from a security signal.
- Select the specific attributes that correspond to the attacker’s patterns.
- Create a cluster based on your selected attributes.
This manual approach allows you to create more targeted blocking rules when the automatic detection doesn’t capture the right patterns.
Further reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: