- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- Notebooks
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Search
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Extend Datadog
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API-based Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Service Level Objectives
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Event Management
- Incident Response
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- End User Device Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Storage Management
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Session Replay
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Code Coverage
- PR Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Developer Integrations
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- AI Guard
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Configuration
- Sources
- Processors
- Destinations
- Packs
- Akamai CDN
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs
- AWS Application Load Balancer Logs
- AWS CloudTrail
- AWS Elastic Load Balancer Logs
- AWS Network Load Balancer Logs
- Cisco ASA
- Cloudflare
- F5
- Fastly
- Fortinet Firewall
- HAProxy Ingress
- Istio Proxy
- Juniper SRX Firewall Traffic Logs
- Netskope
- NGINX
- Okta
- Palo Alto Firewall
- Windows XML
- ZScaler ZIA DNS
- Zscaler ZIA Firewall
- Zscaler ZIA Tunnel
- Zscaler ZIA Web Logs
- Search Syntax
- Scaling and Performance
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Guides and Resources
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
Runtime Code Analysis (IAST)
This product is not supported for your selected Datadog site. ().
Overview
Datadog Runtime Code Analysis (IAST) identifies code-level vulnerabilities in your services, using an Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST) approach to find vulnerabilities within your application code based on your Datadog application instrumentation.
IAST enables Datadog to identify vulnerabilities using legitimate application traffic instead of relying on external tests that could require extra configuration or periodic scheduling. It also monitors your code’s interactions with other components of your stack, such as libraries and infrastructure, providing an up-to-date view of your attack surface area.
For a list of supported services, see the Library Compatibility Requirements. IAST detection rules support the following languages:
| Severity | Detection Rule | Code | Java | .NET | Node.js | Python |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Critical | NoSQL Injection | NOSQL_MONGODB_INJECTION | FALSE | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE |
| Critical | SQL Injection | SQL_INJECTION | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| Critical | Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) | SSRF | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| Critical | Code Injection | CODE_INJECTION | FALSE | FALSE | TRUE | FALSE |
| Critical | Command Injection | COMMAND_INJECTION | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| High | LDAP Injection | LDAP_INJECTION | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE |
| High | Email HTML Injection | EMAIL_HTML_INJECTION | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE |
| High | Hardcoded Secrets | HARDCODED_SECRET | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE |
| High | Hardcoded Passwords | HARDCODED_PASSWORD | FALSE | FALSE | TRUE | FALSE |
| High | Path Traversal | PATH_TRAVERSAL | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| High | Trust Boundary Violation | TRUST_BOUNDARY_VIOLATION | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE |
| High | Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) | XSS | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE |
| High | Untrusted Deserialization | UNTRUSTED_DESERIALIZATION | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
| High | Unvalidated Redirect | UNVALIDATED_REDIRECT | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE |
| High | XPath Injection | XPATH_INJECTION | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE |
| High | Header Injection | HEADER_INJECTION | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| High | Directory Listing Leak | DIRECTORY_LISTING_LEAK | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
| High | Default HTML Escape Invalid | DEFAULT_HTML_ESCAPE_INVALID | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
| High | Verb Tampering | VERB_TAMPERING | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
| Medium | No SameSite Cookie | NO_SAMESITE_COOKIE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| Medium | Insecure Cookie | INSECURE_COOKIE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| Medium | No HttpOnly Cookie | NO_HTTPONLY_COOKIE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| Medium | Weak Hashing | WEAK_HASH | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| Medium | Weak Cipher | WEAK_CIPHER | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| Medium | Stacktrace Leak | STACKTRACE_LEAK | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE |
| Medium | Reflection Injection | REFLECTION_INJECTION | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE |
| Medium | Insecure Authentication Protocol | INSECURE_AUTH_PROTOCOL | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE |
| Medium | Hardcoded Key | HARDCODED_KEY | FALSE | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE |
| Medium | Insecure JSP Layout | INSECURE_JSP_LAYOUT | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
| Low | HSTS Header Missing | HSTS_HEADER_MISSING | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE |
| Low | X-Content-Type-Options Header Missing | XCONTENTTYPE_HEADER_MISSING | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | FALSE |
| Low | Weak Randomness | WEAK_RANDOMNESS | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| Low | Admin Console Active | ADMIN_CONSOLE_ACTIVE | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
| Low | Session Timeout | SESSION_TIMEOUT | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
| Low | Session Rewriting | SESSION_REWRITING | TRUE | FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
How IAST detects vulnerabilities
Datadog Runtime Code Analysis (IAST) utilizes the same tracing libraries as Datadog APM, enabling it to monitor live application traffic and detect code-level vulnerabilities in real time. It follows this process:
- Tracking data sources:: IAST observes data entering your application from external sources such as request URLs, bodies, or headers. These inputs are tagged and monitored throughout their lifecycle.
- Analyzing data flow: The Datadog tracing library tracks how the input data moves through the application—even if it’s transformed, split, or combined. This allows IAST to understand if and how the original input reaches sensitive parts of the code.
- Identifying vulnerable points: IAST detects code locations where user-controlled inputs are used in potentially insecure ways—for example, in SQL queries, dynamic code execution, or HTML rendering.
- Confirming the vulnerability: A vulnerability is only reported when IAST can confirm that tainted input reaches a vulnerable point in the code. This approach minimizes false positives and ensures that findings are actionable.
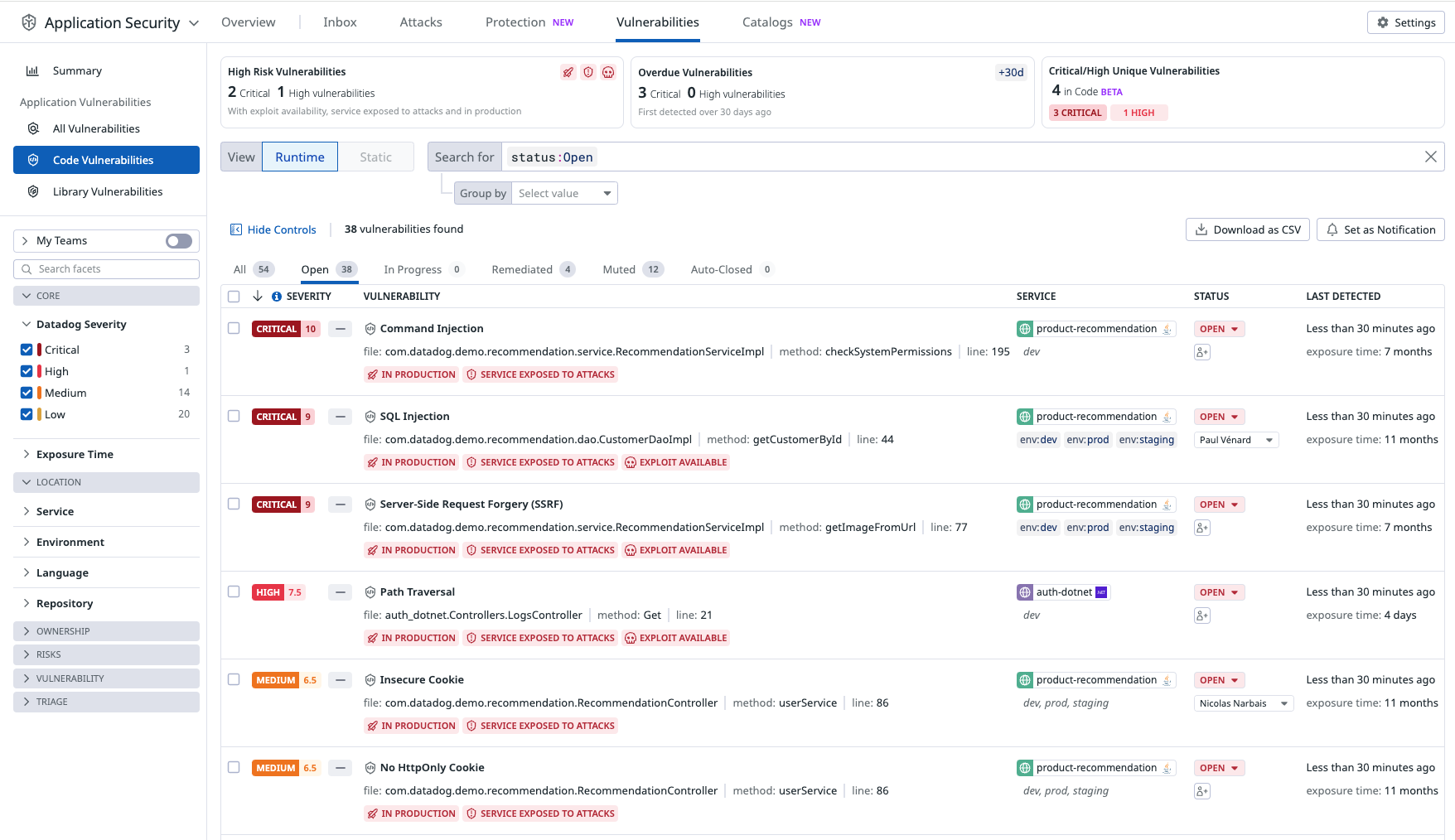
Explore and manage code vulnerabilities
The Vulnerability Explorer uses real-time threat data to help you understand vulnerabilities endangering your system. Vulnerabilities are ordered by severity.
To triage vulnerabilities, each vulnerability contains a brief description of the issue, including:
- Impacted services.
- Vulnerability type.
- First detection.
- The exact file and line number where the vulnerability was found.
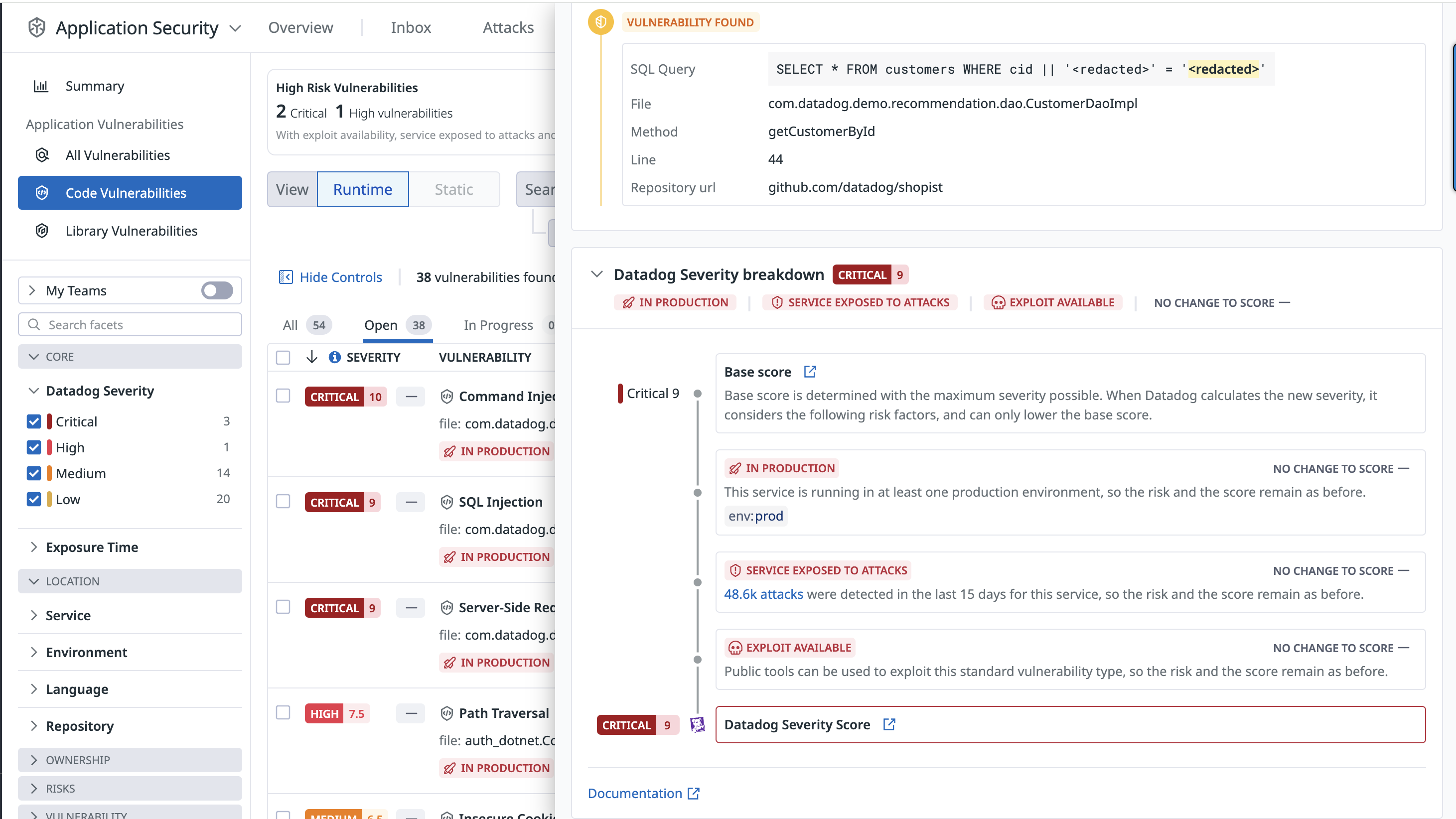
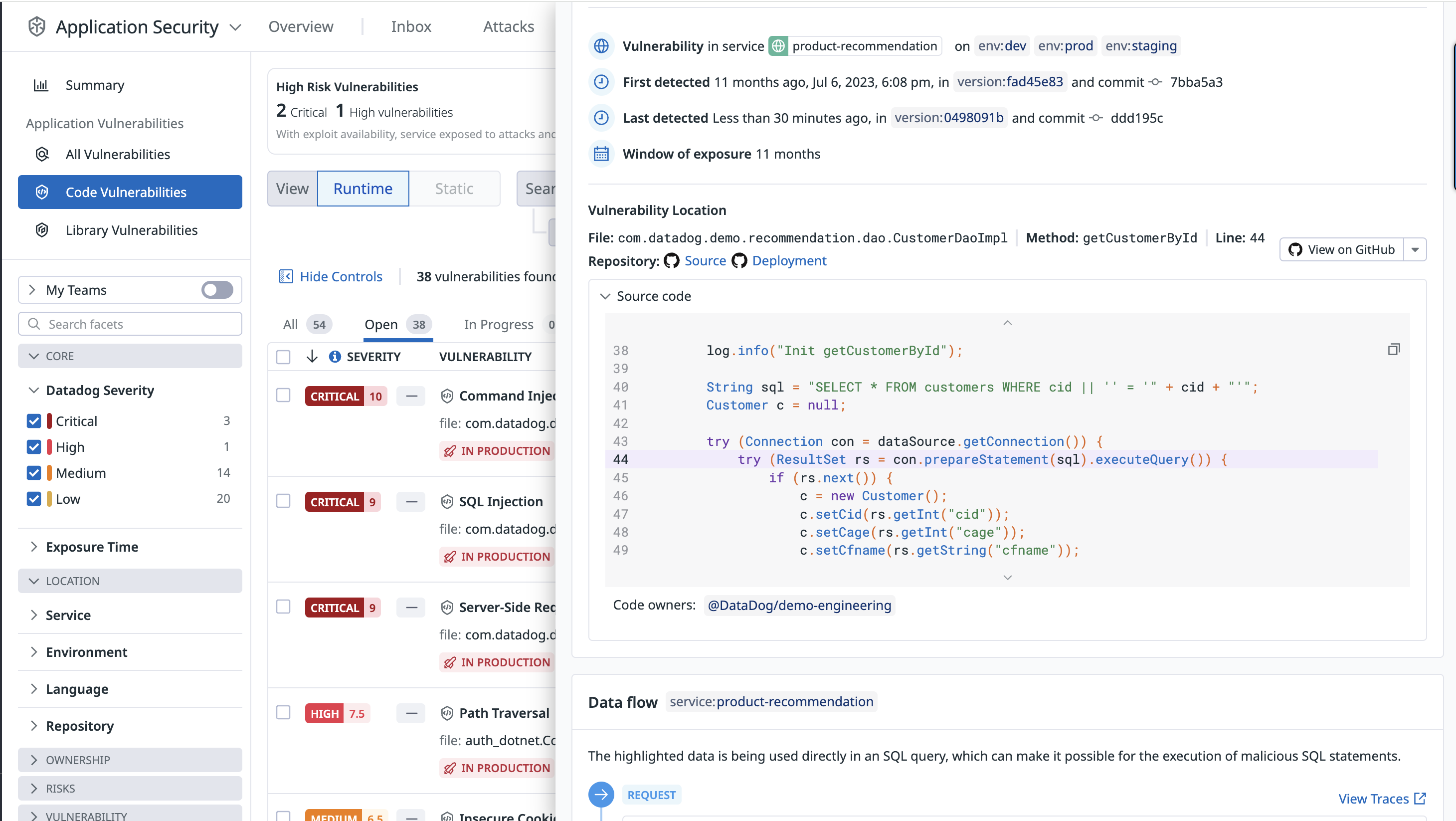
Each vulnerability detail includes a risk score (see screenshot below) and a severity rating: critical, high, medium, or low.
The risk score is tailored to the specific runtime context, including factors such as where the vulnerability is deployed and whether the service is targeted by active attacks.
Remediate a code vulnerability
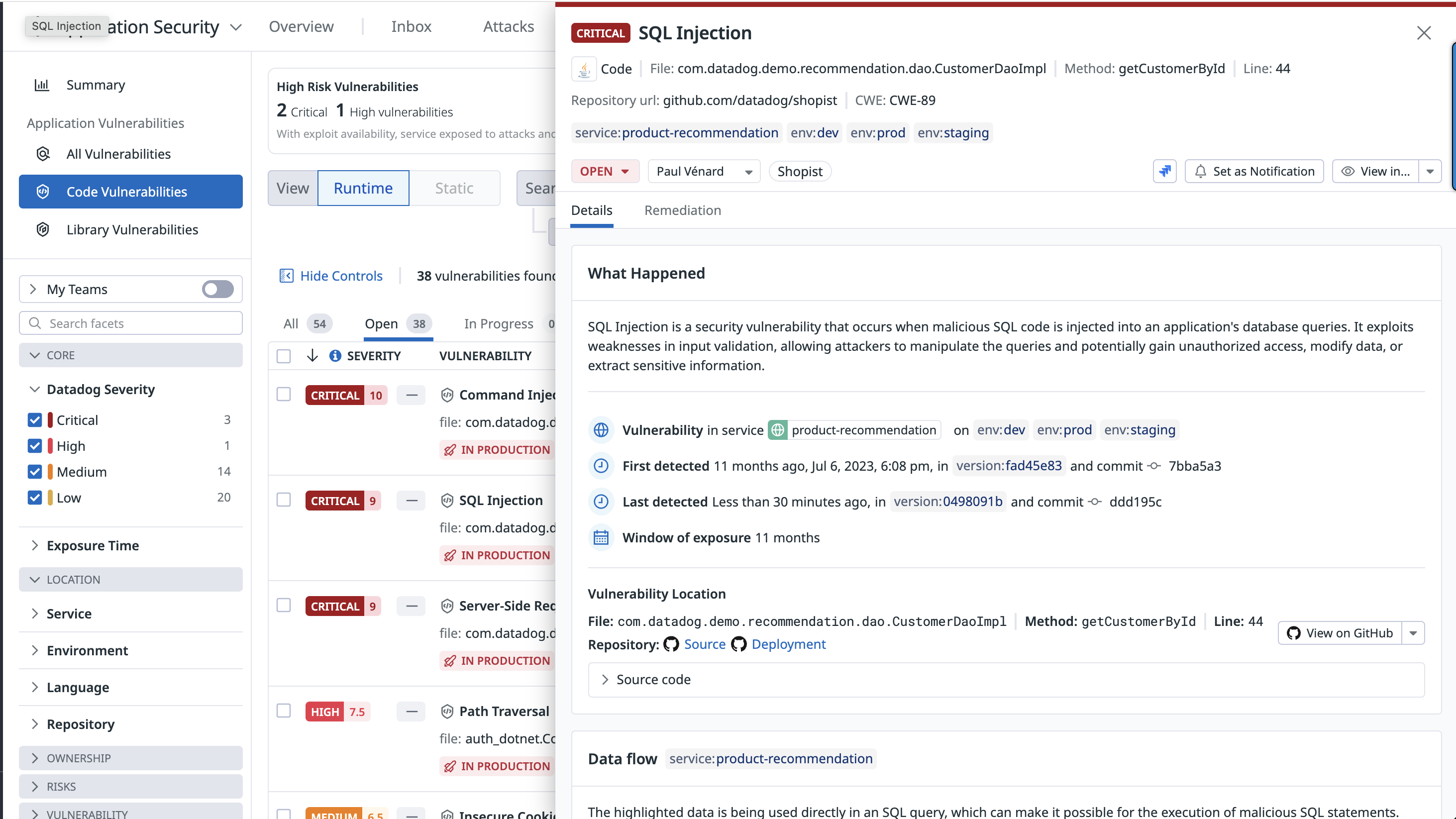
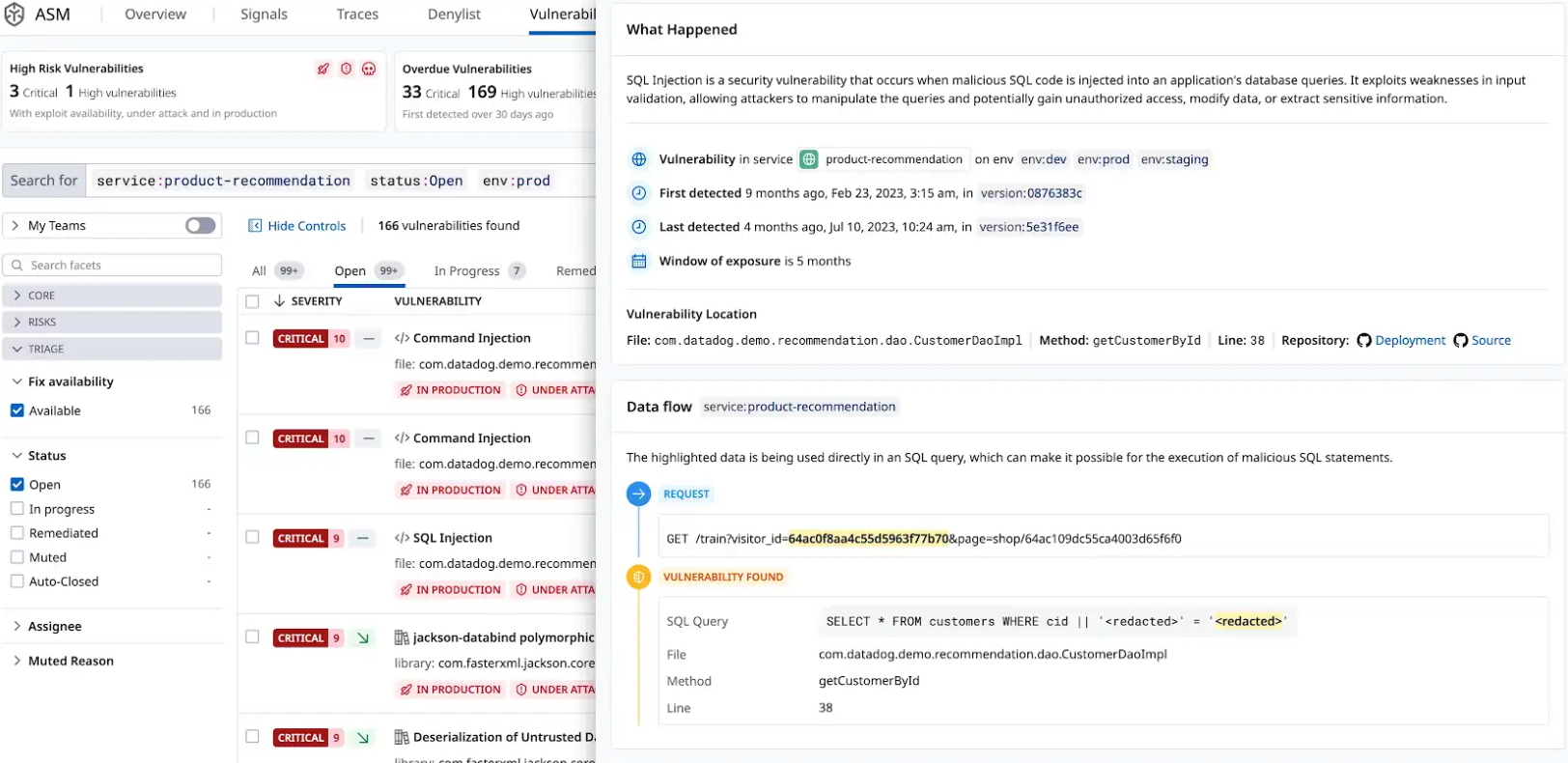
Datadog Code Security automatically provides the information teams need to identify where a vulnerability is in an application, from the affected filename down to the exact method and line number.
When the GitHub integration is enabled, Code Security shows the first impacted version of a service, the commit that introduced the vulnerability, and a snippet of the vulnerable code. This information gives teams insight into where and when a vulnerability occurred and helps to prioritize their work.
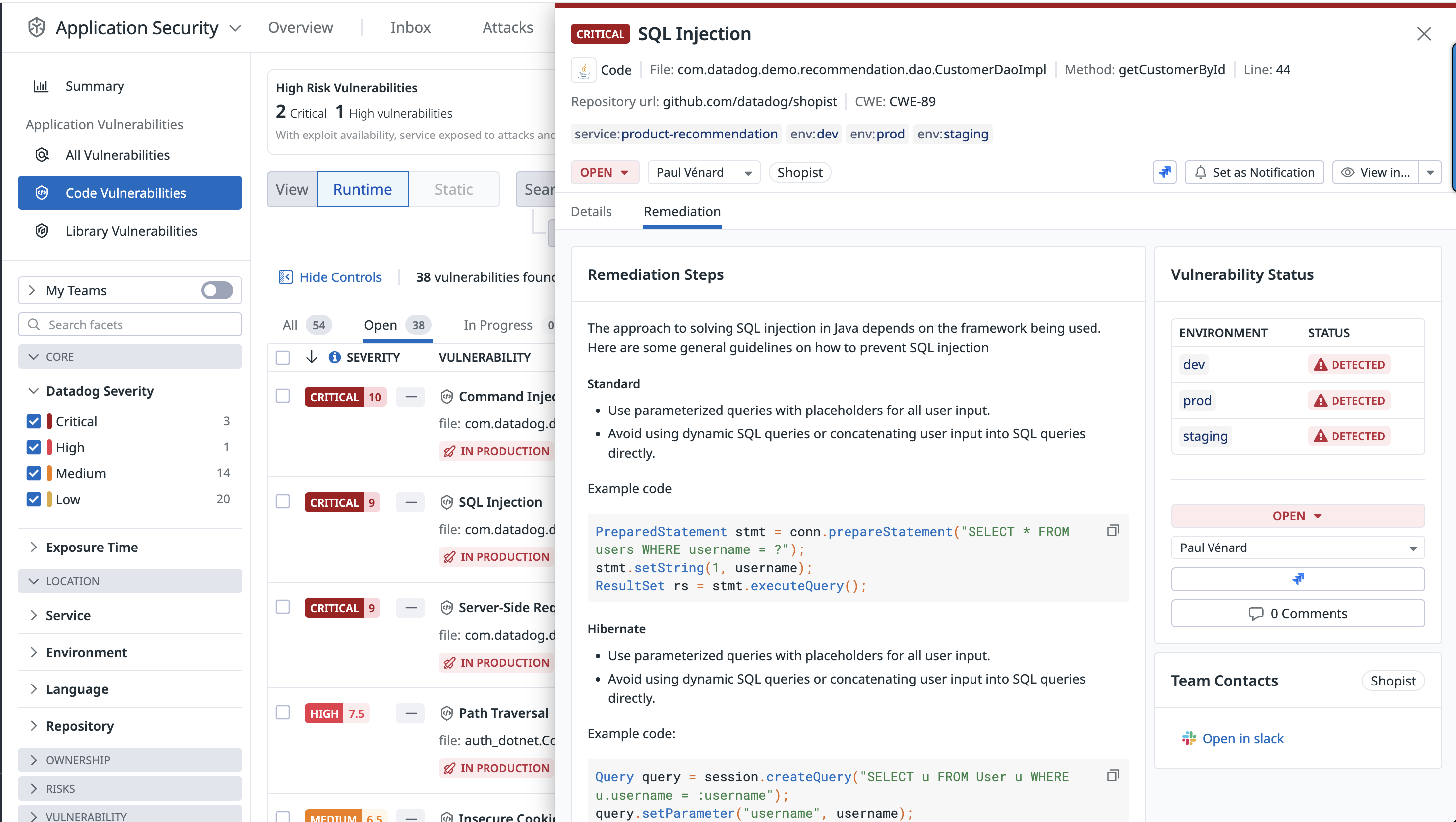
Detailed remediation steps are provided for each detected vulnerability.
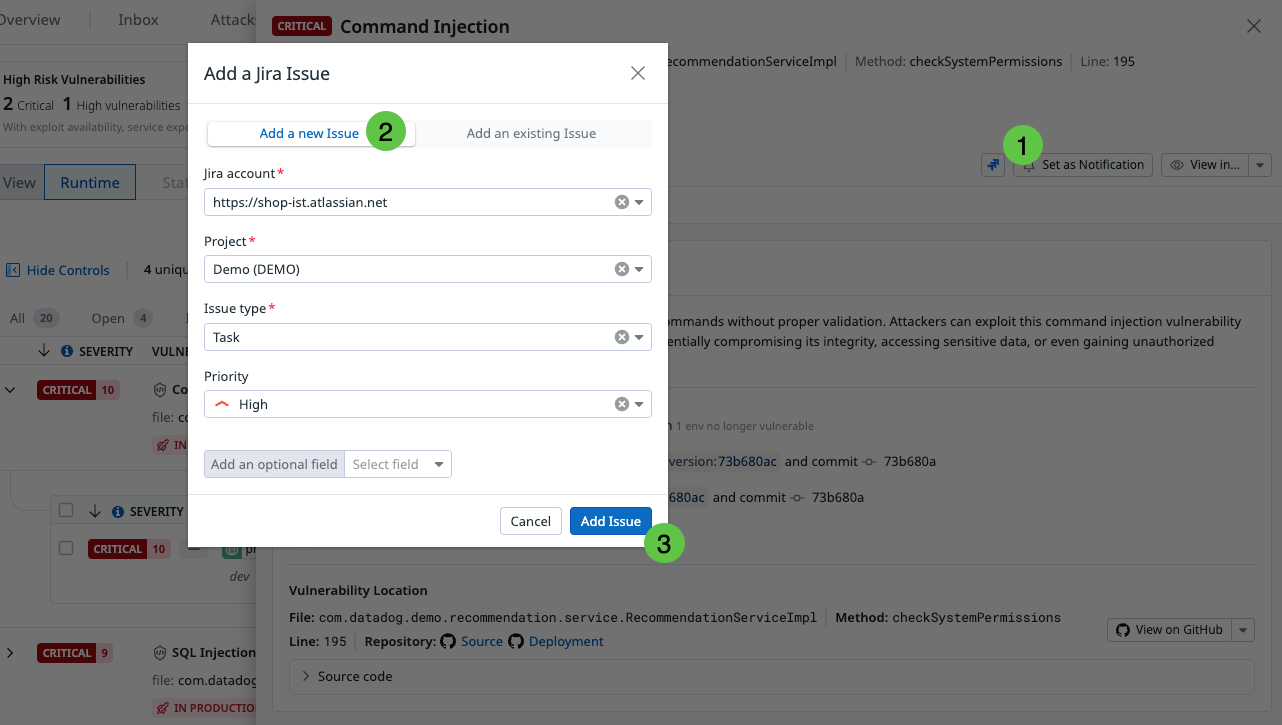
Recommendations enable you to change the status of a vulnerability, assign it to a team member for review, and create a Jira issue for tracking.
Note: To create Jira issues for vulnerabilities, you must configure the Jira integration, and have the manage_integrations permission. For detailed instructions, see the Jira integration documentation, as well as the Role Based Access Control documentation.
Vulnerability lifecycle
Datadog automatically manages the lifecycle of vulnerabilities detected by IAST to ensure findings remain accurate and relevant over time.
Automatic closure: Vulnerabilities detected by IAST are automatically closed by Datadog when they haven’t been observed for 14 days since their last detection.
Service version updates: If a new version of the service is deployed in the environment where the vulnerability was originally detected, the vulnerability is automatically closed 24 hours after it is no longer seen in that new version.
Reopening logic: If a vulnerability that was previously closed is detected again within the following 15 months, Datadog automatically reopens it.
Enable Runtime Code Analysis (IAST)
To enable IAST, configure the Datadog Tracing Library. Detailed instructions for both methods can be found in the Security > Code Security > Settings section.
If you need additional help, contact Datadog support.
Disable Code Security
For information on disabling IAST, see Disabling Code Security.
Further reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: