Overview
Session Replay provides privacy controls to help ensure organizations of any scale do not expose sensitive or personal data. Data is stored on Datadog-managed cloud instances and encrypted at rest.
Default privacy options for Session Replay protect end user privacy and prevent sensitive organizational information from being collected.
By enabling Mobile Session Replay, you can automatically mask sensitive elements from being recorded through the RUM Mobile SDK. When data is masked, that data is not collected in its original form by Datadog's SDKs and thus is not sent to the backend.
Fine-grained masking
Using the masking modes below, you can override the default setup on a per-application basis. Masking is fine-grained, which means you can override masking for text and inputs, images, and touches individually to create a custom configuration that suits your needs.
Text and input masking
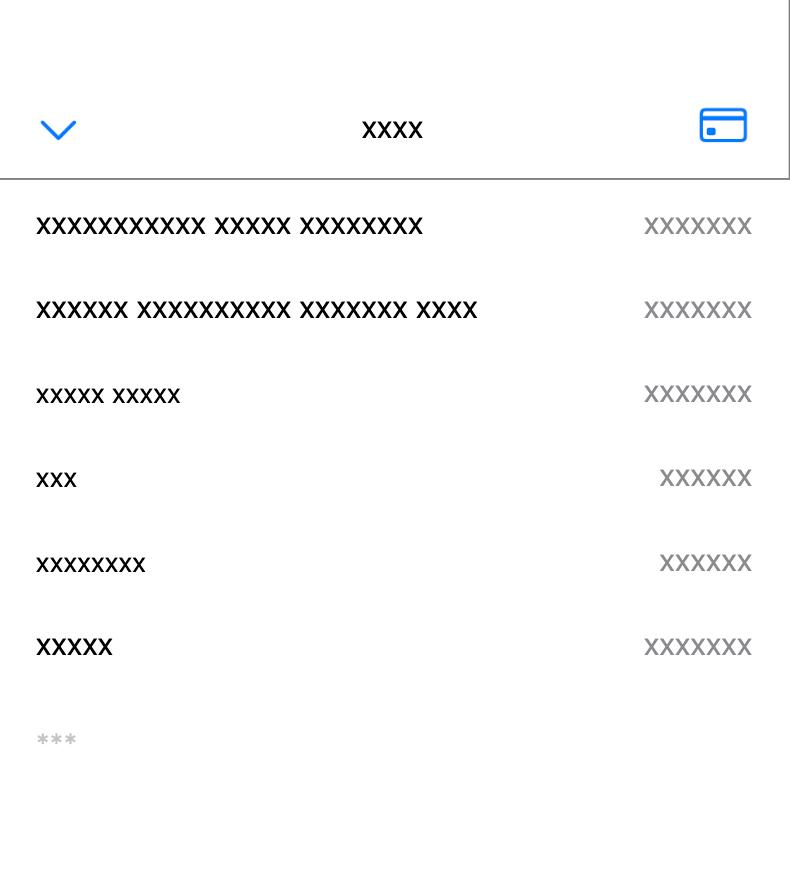
By default, the mask_all setting is enabled for all data. With this setting enabled, all text and input content on screen is masked, as shown below.
Mask sensitive inputs
With the mask_sensitive_inputs setting enabled, all text and inputs are shown except those considered sensitive (passwords, emails, and phone numbers).
application.kt
val sessionReplayConfig = SessionReplayConfiguration.Builder([sampleRate])
.setTextAndInputPrivacy(TextAndInputPrivacy.MASK_SENSITIVE_INPUTS)
.build()
SessionReplay.enable(sessionReplayConfig)
AppDelegate.swift
let sessionReplayConfig = SessionReplay.Configuration(
replaySampleRate: sampleRate,
textAndInputPrivacyLevel: .maskSensitiveInputs,
imagePrivacyLevel: imagePrivacyLevel,
touchPrivacyLevel: touchPrivacyLevel
)
SessionReplay.enable(with: sessionReplayConfig)
App.tsx
import {
SessionReplay,
SessionReplayConfiguration,
TextAndInputPrivacyLevel,
} from "@datadog/mobile-react-native-session-replay";
const config: SessionReplayConfiguration = {
replaySampleRate: sampleRate,
textAndInputPrivacyLevel: TextAndInputPrivacyLevel.MASK_SENSITIVE_INPUTS,
}
SessionReplay.enable(config)
final configuration = DatadogConfiguration(
// ...
)..enableSessionReplay(
DatadogSessionReplayConfiguration(
textAndInputPrivacyLevel: TextAndInputPrivacyLevel.maskSensitiveInputs,
replaySampleRate: replay,
),
);
Mask all inputs
With the mask_all_inputs setting enabled, all inputs fields are masked in the replay.
application.kt
val sessionReplayConfig = SessionReplayConfiguration.Builder([sampleRate])
.setTextAndInputPrivacy(TextAndInputPrivacy.MASK_ALL_INPUTS)
.build()
SessionReplay.enable(sessionReplayConfig)
AppDelegate.swift
let sessionReplayConfig = SessionReplay.Configuration(
replaySampleRate: sampleRate,
textAndInputPrivacyLevel: .maskAllInputs,
imagePrivacyLevel: imagePrivacyLevel,
touchPrivacyLevel: touchPrivacyLevel
)
SessionReplay.enable(with: sessionReplayConfig)
App.tsx
import {
SessionReplay,
SessionReplayConfiguration,
TextAndInputPrivacyLevel,
} from "@datadog/mobile-react-native-session-replay";
const config: SessionReplayConfiguration = {
replaySampleRate: sampleRate,
textAndInputPrivacyLevel: TextAndInputPrivacyLevel.MASK_ALL_INPUTS,
}
SessionReplay.enable(config)
final configuration = DatadogConfiguration(
// ...
)..enableSessionReplay(
DatadogSessionReplayConfiguration(
textAndInputPrivacyLevel: TextAndInputPrivacyLevel.maskAllInputs,
replaySampleRate: replay,
),
);
Mask all
With the mask_all setting enabled, all text and input fields are masked in the replay.
application.kt
val sessionReplayConfig = SessionReplayConfiguration.Builder([sampleRate])
.setTextAndInputPrivacy(TextAndInputPrivacy.MASK_ALL)
.build()
SessionReplay.enable(sessionReplayConfig)
AppDelegate.swift
let sessionReplayConfig = SessionReplay.Configuration(
replaySampleRate: sampleRate,
textAndInputPrivacyLevel: .maskAll,
imagePrivacyLevel: imagePrivacyLevel,
touchPrivacyLevel: touchPrivacyLevel
)
SessionReplay.enable(with: sessionReplayConfig)
App.tsx
import {
SessionReplay,
SessionReplayConfiguration,
TextAndInputPrivacyLevel,
} from "@datadog/mobile-react-native-session-replay";
const config: SessionReplayConfiguration = {
replaySampleRate: sampleRate,
textAndInputPrivacyLevel: TextAndInputPrivacyLevel.MASK_ALL,
}
SessionReplay.enable(config)
final configuration = DatadogConfiguration(
// ...
)..enableSessionReplay(
DatadogSessionReplayConfiguration(
textAndInputPrivacyLevel: TextAndInputPrivacyLevel.maskAll,
replaySampleRate: replay,
),
);
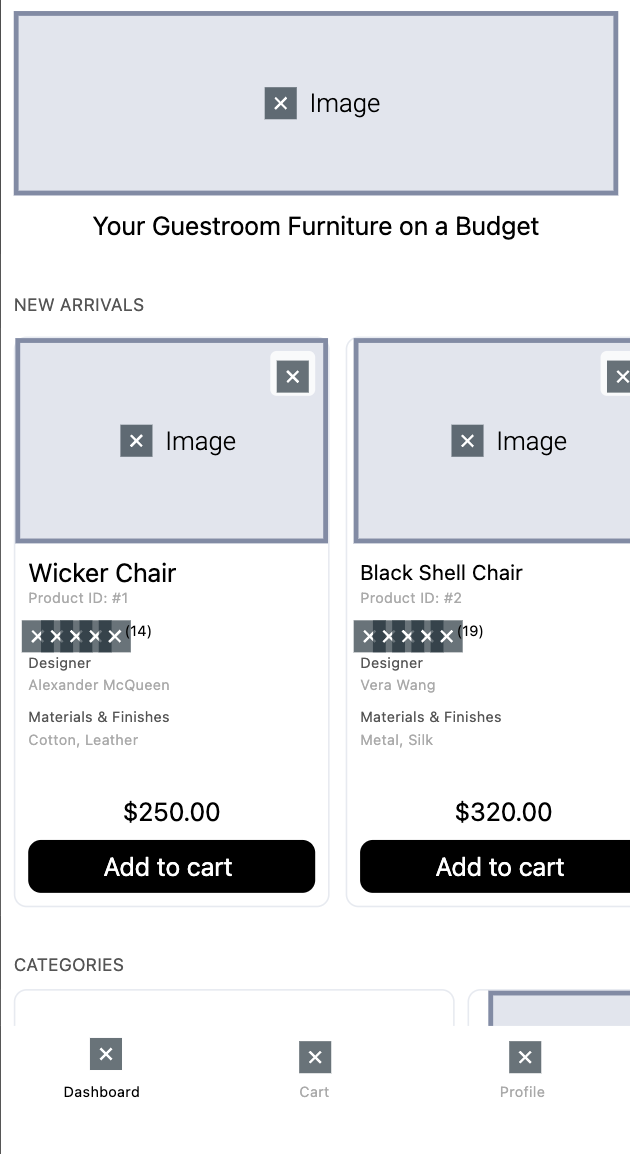
Image masking
By default, the mask_all setting is enabled for all images. With this setting enabled, all images on screen are masked.
For performance reasons, large images (those exceeding 1000x1000 total pixels) are masked in Flutter, and will display "Large Image" in the Session Replay player.
Mask all images
With the mask_all setting enabled, all images are replaced by placeholders labeled 'Image' in the replay.
application.kt
val sessionReplayConfig = SessionReplayConfiguration.Builder([sampleRate])
.setImagePrivacy(ImagePrivacy.MASK_ALL)
.build()
SessionReplay.enable(sessionReplayConfig)
AppDelegate.swift
let sessionReplayConfig = SessionReplay.Configuration(
replaySampleRate: sampleRate,
textAndInputPrivacyLevel: textAndInputPrivacyLevel,
imagePrivacyLevel: .maskAll,
touchPrivacyLevel: touchPrivacyLevel
)
SessionReplay.enable(with: sessionReplayConfig)
App.tsx
import {
SessionReplay,
SessionReplayConfiguration,
ImagePrivacyLevel,
} from "@datadog/mobile-react-native-session-replay";
const config: SessionReplayConfiguration = {
replaySampleRate: sampleRate,
imagePrivacyLevel: ImagePrivacyLevel.MASK_ALL,
}
SessionReplay.enable(config)
final configuration = DatadogConfiguration(
// ...
)..enableSessionReplay(
DatadogSessionReplayConfiguration(
imagePrivacyLevel: ImagePrivacyLevel.maskAll,
replaySampleRate: replay,
),
);
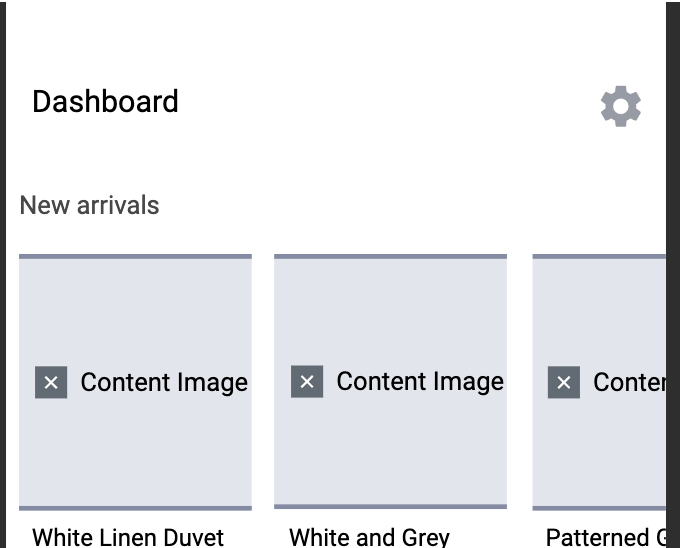
Mask content images
You can manage content masking while still allowing system or bundled images to be visible.
Use the maskNonBundledOnly setting to replace non-bundled images with a "Content Image" placeholder in the replay.
- In UIKit, the SDK can determine whether an image is bundled and can mask it accordingly.
- In SwiftUI, this determination isn't possible. Instead, the SDK uses a heuristic: if an image exceeds 100×100 points, it is assumed to be non-bundled and is masked.
Select the mask_large_only setting, which replaces images with dimensions that exceed 100x100dp with a "Content Image" placeholder.
Note: These dimensions refer to the drawable resource, not the view's size.
application.kt
val sessionReplayConfig = SessionReplayConfiguration.Builder([sampleRate])
.setImagePrivacy(ImagePrivacy.MASK_LARGE_ONLY)
.build()
SessionReplay.enable(sessionReplayConfig)
AppDelegate.swift
let sessionReplayConfig = SessionReplay.Configuration(
replaySampleRate: sampleRate,
textAndInputPrivacyLevel: textAndInputPrivacyLevel,
imagePrivacyLevel: .maskNonBundledOnly,
touchPrivacyLevel: touchPrivacyLevel
)
SessionReplay.enable(with: sessionReplayConfig)
App.tsx
import {
SessionReplay,
SessionReplayConfiguration,
ImagePrivacyLevel,
} from "@datadog/mobile-react-native-session-replay";
const config: SessionReplayConfiguration = {
replaySampleRate: sampleRate,
imagePrivacyLevel: ImagePrivacyLevel.MASK_NON_BUNDLED_ONLY,
}
SessionReplay.enable(config)
Bundled images are those that use AssetImage as their image provider.
final configuration = DatadogConfiguration(
// ...
)..enableSessionReplay(
DatadogSessionReplayConfiguration(
imagePrivacyLevel: ImagePrivacyLevel.maskNonAssetsOnly,
replaySampleRate: replay,
),
);
Show all images
With the mask_none setting enabled, all images are shown in the replay.
application.kt
val sessionReplayConfig = SessionReplayConfiguration.Builder([sampleRate])
.setImagePrivacy(ImagePrivacy.MASK_NONE)
.build()
SessionReplay.enable(sessionReplayConfig)
AppDelegate.swift
let sessionReplayConfig = SessionReplay.Configuration(
replaySampleRate: sampleRate,
textAndInputPrivacyLevel: textAndInputPrivacyLevel,
imagePrivacyLevel: .maskNone,
touchPrivacyLevel: touchPrivacyLevel
)
SessionReplay.enable(with: sessionReplayConfig)
App.tsx
import {
SessionReplay,
SessionReplayConfiguration,
ImagePrivacyLevel,
} from "@datadog/mobile-react-native-session-replay";
const config: SessionReplayConfiguration = {
replaySampleRate: sampleRate,
imagePrivacyLevel: ImagePrivacyLevel.MASK_NONE,
}
SessionReplay.enable(config)
Touch masking
By default, the hide setting is enabled for all touches. With this setting enabled, all touches on screen are hidden.
Hide all touches
With the hide setting enabled, all touches that occur during the replay are hidden. This is the default setting.
application.kt
val sessionReplayConfig = SessionReplayConfiguration.Builder([sampleRate])
.setTouchPrivacy(TouchPrivacy.HIDE)
.build()
SessionReplay.enable(sessionReplayConfig)
AppDelegate.swift
let sessionReplayConfig = SessionReplay.Configuration(
replaySampleRate: sampleRate,
textAndInputPrivacyLevel: textAndInputPrivacyLevel,
imagePrivacyLevel: imagePrivacyLevel,
touchPrivacyLevel: .hide
)
SessionReplay.enable(with: sessionReplayConfig)
App.tsx
import {
SessionReplay,
SessionReplayConfiguration,
TouchPrivacyLevel,
} from "@datadog/mobile-react-native-session-replay";
const config: SessionReplayConfiguration = {
replaySampleRate: sampleRate,
touchPrivacyLevel: TouchPrivacyLevel.HIDE,
}
SessionReplay.enable(config)
final configuration = DatadogConfiguration(
// ...
)..enableSessionReplay(
DatadogSessionReplayConfiguration(
imagePrivacyLevel: ImagePrivacyLevel.maskNone,
replaySampleRate: replay,
),
);
Show all touches
With the show setting enabled, all touches that occur during the replay are shown.
application.kt
val sessionReplayConfig = SessionReplayConfiguration.Builder([sampleRate])
.setTouchPrivacy(TouchPrivacy.SHOW)
.build()
SessionReplay.enable(sessionReplayConfig)
AppDelegate.swift
let sessionReplayConfig = SessionReplay.Configuration(
replaySampleRate: sampleRate,
textAndInputPrivacyLevel: textAndInputPrivacyLevel,
imagePrivacyLevel: imagePrivacyLevel,
touchPrivacyLevel: .show
)
SessionReplay.enable(with: sessionReplayConfig)
App.tsx
import {
SessionReplay,
SessionReplayConfiguration,
TouchPrivacyLevel,
} from "@datadog/mobile-react-native-session-replay";
const config: SessionReplayConfiguration = {
replaySampleRate: sampleRate,
touchPrivacyLevel: TouchPrivacyLevel.SHOW,
}
SessionReplay.enable(config)
Bundled images are those that use AssetImage as their image provider.
final configuration = DatadogConfiguration(
// ...
)..enableSessionReplay(
DatadogSessionReplayConfiguration(
touchPrivacyLevel: TouchPrivacyLevel.show,
replaySampleRate: replay,
),
);
Privacy overrides
The sections above describe the global masking levels that apply to the entire application. However, it is also possible to override these settings at the view level. The same privacy levels as above are available for text and inputs, images, touches, and an additional setting to completely hide a specific view.
To ensure overrides are recognized properly, they should be applied as early as possible in the view lifecycle. This prevents scenarios where Session Replay might process a view before applying the overrides.
Privacy overrides affect views and their descendants. This means that even if an override is applied to a view where it might have no immediate effect (for example, applying an image override to a text input), the override still applies to all child views.
Overrides operate using a "nearest parent" principle: if a view has an override, it uses that setting. Otherwise, it inherits the privacy level from the closest parent in the hierarchy with an override. If no parent has an override, the view defaults to the application's general masking level.
Text and input override
To override text and input privacy in Android classic view, use setSessionReplayTextAndInputPrivacy on a view instance and pass a value from the TextAndInputPrivacy enum. Passing null removes the override.
application.kt
// Set a text and input override on your view
myView.setSessionReplayTextAndInputPrivacy(TextAndInputPrivacy.MASK_SENSITIVE_INPUTS)
// Remove a text and input override from your view
myView.setSessionReplayTextAndInputPrivacy(null)
To override text and input privacy in Jetpack Compose, use Modifier.sessionReplayTextAndInputPrivacy on the modifier of a composable and pass a value from the TextAndInputPrivacy enum.
application.kt
// Set a text and input override on your view
Text(modifier = Modifier
.padding(16.dp)
.sessionReplayTextAndInputPrivacy(textAndInputPrivacy = TextAndInputPrivacy.MASK_SENSITIVE_INPUTS),
text = "Datadog"
)
To override text and input privacy in UIKit views, use dd.sessionReplayOverrides.textAndInputPrivacy on a view instance and set a value from the TextAndInputPrivacyLevel enum. Setting it to nil removes the override.
AppDelegate.swift
// Set a text and input override on your view
myView.dd.sessionReplayOverrides.textAndInputPrivacy = .maskSensitiveInputs
// Remove a text and input override from your view
myView.dd.sessionReplayOverrides.textAndInputPrivacy = nil
To override text and input privacy in SwiftUI, wrap your content with SessionReplayPrivacyView and configure the textAndInputPrivacy parameter. You can combine this with other privacy settings in the same view for better performance.
ContentView.swift
struct ContentView: View {
@State private var username = ""
@State private var password = ""
var body: some View {
// Set a text and input override on your SwiftUI content
SessionReplayPrivacyView(textAndInputPrivacy: .maskAllInputs) {
VStack {
Text("User Profile")
TextField("Enter name", text: $username)
SecureField("Password", text: $password)
}
}
}
}
To override text and input privacy in Flutter, use the SessionReplayPrivacy widget to override the privacy settings for an entire widget tree. Setting any value to null keeps the privacy values unchanged from values provided higher up the widget tree.
class MyWidget: StatelessWidget {
Widget build() {
return SessionReplayPrivacy(
textAndInputPrivacyLevel: TextAndInputPrivacyLevel.maskAllInputs,
child: TextField(
decoration: InputDecoration(
labelText: 'Simple Text Field',
),
),
);
}
}
Image override
To override image privacy in Android classic view, use setSessionReplayImagePrivacy on a view instance and pass a value from the ImagePrivacy enum. Passing null removes the override.
application.kt
// Set an image override on your view
myView.setSessionReplayImagePrivacy(ImagePrivacy.MASK_ALL)
// Remove an image override from your view
myView.setSessionReplayImagePrivacy(null)
To override image privacy in Jetpack Compose, use Modifier.sessionReplayImagePrivacy on the modifier of a composable and pass a value from the ImagePrivacy enum.
application.kt
// Set a image privacy override on your image
Image(modifier = Modifier
.padding(16.dp)
.sessionReplayImagePrivacy(imagePrivacy = ImagePrivacy.MASK_ALL),
painter = painterResource(id = R.drawable.ic_datadog),
contentDescription = null
)
To override image privacy in UIKit views, use dd.sessionReplayOverrides.imagePrivacy on a view instance and set a value from the ImagePrivacyLevel enum. Setting it to nil removes the override.
AppDelegate.swift
// Set an image override on your view
myView.dd.sessionReplayOverrides.imagePrivacy = .maskAll
// Remove an image override from your view
myView.dd.sessionReplayOverrides.imagePrivacy = nil
To override image privacy in SwiftUI, wrap your content with SessionReplayPrivacyView and configure the imagePrivacy parameter.
ContentView.swift
struct ProfileView: View {
let profileImageURL = URL(string: "https://example.com/profile.jpg")
var body: some View {
// Set an image privacy override on your SwiftUI content
SessionReplayPrivacyView(imagePrivacy: .maskAll) {
VStack {
Image("userAvatar")
.resizable()
.frame(width: 60, height: 60)
.clipShape(Circle())
AsyncImage(url: profileImageURL) { image in
image.resizable()
} placeholder: {
ProgressView()
}
.frame(width: 100, height: 100)
}
}
}
}
To override image privacy in Flutter, use the SessionReplayPrivacy widget to override the privacy settings for an entire widget tree. Setting any value to null keeps the privacy values unchanged from values provided higher up the widget tree.
class MyWidget: StatelessWidget {
Widget build() {
return SessionReplayPrivacy(
imagePrivacyLevel: ImagePrivacyLevel.maskAll,
child: Image.asset('assets/my_image.png'),
);
}
}
Touch override
To override touch privacy in Android classic view, use setSessionReplayTouchPrivacy on a view instance and pass a value from the TouchPrivacy enum. Passing null removes the override.
application.kt
// Set a touch override on your view
view.setSessionReplayTouchPrivacy(TouchPrivacy.HIDE)
// Remove a touch override from your view
view.setSessionReplayTouchPrivacy(null)
To override touch privacy in Jetpack Compose, use Modifier.sessionReplayTouchPrivacy on the modifier of a composable and pass a value from the TouchPrivacy enum.
application.kt
// Set a touch privacy override on your view
Column(modifier = Modifier
.padding(16.dp)
.sessionReplayTouchPrivacy(touchPrivacy = TouchPrivacy.HIDE)){
// Content
}
To override touch privacy in UIKit views, use dd.sessionReplayOverrides.touchPrivacy on a view instance and set a value from the TouchPrivacyLevel enum. Setting it to nil removes the override.
AppDelegate.swift
// Set a touch override on your view
myView.dd.sessionReplayOverrides.touchPrivacy = .hide
// Remove a touch override from your view
myView.dd.sessionReplayOverrides.touchPrivacy = nil
To override touch privacy in SwiftUI, wrap your content with SessionReplayPrivacyView and configure the touchPrivacy parameter.
ContentView.swift
struct SettingsView: View {
@State private var sliderValue = 0.5
var body: some View {
// Set a touch privacy override on your SwiftUI content
SessionReplayPrivacyView(touchPrivacy: .hide) {
VStack(spacing: 20) {
Button("Some Action") {
// Handle action
}
.padding()
.background(Color.blue)
.foregroundColor(.white)
.cornerRadius(8)
Slider(value: $sliderValue, in: 0...1) {
Text("Some Value")
}
}
.padding()
}
}
}
To override touch privacy in Flutter, use the SessionReplayPrivacy widget to override the privacy settings for an entire widget tree. Setting any value to null keeps the privacy values unchanged from values provided higher up the widget tree.
Enabling touch privacy affects the entire widget tree, and cannot be toggled back to "show" in children.
class MyWidget: StatelessWidget {
Widget build() {
return SessionReplayPrivacy(
touchPrivacyLevel: TouchPrivacyLevel.hide,
child: PinPadWidget(),
);
}
}
Hidden elements override
For sensitive elements that need to be completely hidden, use the hidden setting.
When an element is hidden, it is replaced by a placeholder labeled as "Hidden" in the replay, and its subviews are not recorded.
Note: Marking a view as hidden does not prevent touch interactions from being recorded on that element. To hide touch interactions as well, use the touch override in addition to marking the element as hidden.
Use setSessionReplayHidden(hide = true) to hide the element. Setting hide to false removes the override.
application.kt
// Mark a view as hidden
myView.setSessionReplayHidden(hide = true)
// Remove the override from the view
myView.setSessionReplayHidden(hide = false)
Use Modifier.sessionReplayHide to hide the element in Jetpack Compose.
application.kt
// Mark a Column as hidden
Column(modifier = Modifier
.padding(16.dp)
.sessionReplayHide(hide = true)){
// Content
}
In UIKit views, use dd.sessionReplayOverrides.hide to hide the element:
AppDelegate.swift
// Mark a view as hidden
myView.dd.sessionReplayOverrides.hide = true
// Remove the override from the view
myView.dd.sessionReplayOverrides.hide = false
In SwiftUI, wrap your content with SessionReplayPrivacyView and set the hide parameter to true:
ContentView.swift
struct PaymentView: View {
@State private var cardNumber = ""
@State private var cvv = ""
var body: some View {
// Mark SwiftUI content as hidden
SessionReplayPrivacyView(hide: true) {
VStack(spacing: 16) {
Text("Payment Information")
.font(.headline)
TextField("Card Number", text: $cardNumber)
.textFieldStyle(RoundedBorderTextFieldStyle())
SecureField("CVV", text: $cvv)
.textFieldStyle(RoundedBorderTextFieldStyle())
Text("Card ending in 1234")
.foregroundColor(.secondary)
}
.padding()
}
}
}
Note: Setting the hidden override to nil or false has the same effect—it disables the override.
Combining privacy settings in SwiftUI
Combine multiple privacy settings in one SessionReplayPrivacyView for different configurations. Datadog recommends combining options in a single view rather than nesting multiple instances to avoid adding unnecessary view layers.
ContentView.swift
struct UserProfileView: View {
@State private var userBio = ""
@State private var cardNumber = ""
var body: some View {
VStack(spacing: 30) {
// Preferred: Combine multiple privacy settings in one view
SessionReplayPrivacyView(
textAndInputPrivacy: .maskSensitiveInputs,
imagePrivacy: .maskNonBundledOnly,
touchPrivacy: .show
) {
VStack(spacing: 20) {
// User profile section
HStack {
AsyncImage(url: URL(string: "https://example.com/profile.jpg")) { image in
image.resizable()
} placeholder: {
Circle().fill(Color.gray.opacity(0.3))
}
.frame(width: 60, height: 60)
.clipShape(Circle())
VStack(alignment: .leading) {
Text("John Doe")
.font(.headline)
TextField("Enter bio", text: $userBio)
.textFieldStyle(RoundedBorderTextFieldStyle())
}
}
Button("Save Profile") {
// Save action
print("Profile saved")
}
.padding()
.background(Color.blue)
.foregroundColor(.white)
.cornerRadius(8)
}
.padding()
}
// For completely different privacy requirements, use separate `SessionReplayPrivacyView` instances
SessionReplayPrivacyView(hide: true) {
VStack(spacing: 16) {
Text("Credit Card Information")
.font(.headline)
TextField("Card Number", text: $cardNumber)
.textFieldStyle(RoundedBorderTextFieldStyle())
}
.padding()
.background(Color.gray.opacity(0.1))
.cornerRadius(8)
}
}
.padding()
}
}
Note: Each SessionReplayPrivacyView introduces an additional native view layer. For optimal performance, prefer combining privacy settings instead of nesting multiple privacy views when possible.
To hide a widget tree in Flutter, use the SessionReplayPrivacy widget to override the privacy settings for an entire widget tree.
Hiding a widget tree affects the entire widget tree, and cannot be toggled back to false in children, as Session Replay stops processing widget trees that are marked with hide.
class MyWidget: StatelessWidget {
Widget build() {
return SessionReplayPrivacy(
hide: true,
child: PinPadWidget(),
);
}
}
Privacy overrides are fully supported in React Native starting from version 2.8.0 of the Datadog React Native SDK. Although the underlying functionality is shared with native Android and iOS platforms, the integration in React Native is designed to align with common React patterns.
Behavior consistency
React Native's implementation is built on the same foundation as the native Android and iOS SDKs. As a result, you can rely on the privacy features behaving the same way across all three platforms.
Usage with SessionReplayView
The SDK provides a set of React components under the SessionReplayView namespace, which are used to configure privacy settings within your React Native application.
To use them, import SessionReplayView as follows:
App.tsx
import { SessionReplayView } from "@datadog/mobile-react-native-session-replay";
This import provides access to four privacy-focused components.
Each of these components behaves like a regular React Native View, meaning they can be used anywhere you would typically use a View, with the addition of privacy-related behavior.
| Component | Description | Properties |
|---|---|---|
SessionReplayView.Privacy | Adds support for customizing text, image, and touch privacy settings for its children. |
|
SessionReplayView.MaskAll | Applies the most restrictive privacy settings (MaskAll or platform equivalent) to all children. |
|
SessionReplayView.MaskNone | Applies the least restrictive settings (MaskNone or platform equivalent). All child components are visible. | (No additional properties) |
SessionReplayView.Hide | Completely hides all child components from session replay. | (No additional properties) |
Integration approaches
There are two ways to apply privacy overrides in React Native:
- Wrap specific components with a privacy-focused
SessionReplayViewto target only certain elements, or - Replace an entire
<View>with aSessionReplayViewto apply privacy settings to a whole section of your UI.
This flexibility lets you control which parts of your app are masked or visible in session replays.
Use SessionReplayView components to wrap specific parts of your UI where you want to override privacy settings.
For example, going from:
App.tsx
const App = () => {
return (
<View>
{/* content */}
<TextInput placeholder="First Name" value="Data" />
<TextInput placeholder="Last Name" value="Dog" />
{/* content */}
</View>
);
}
To:
App.tsx
const App = () => {
return (
<View>
{/* content */}
<SessionReplayView.MaskAll showTouch={true}>
<TextInput placeholder="First Name" value="Data" />
<TextInput placeholder="Last Name" value="Dog" />
</SessionReplayView.MaskAll>
{/* content */}
</View>
);
}
Replace an existing <View> with a SessionReplayView component directly. This is ideal when a view already encapsulates the section of the UI that needs modified privacy behavior.
For example, instead of:
App.tsx
const App = () => {
return (
<View>
{/* content */}
</View>
);
}
You can use:
App.tsx
const App = () => {
return (
<SessionReplayView.MaskNone>
{/* content */}
</SessionReplayView.MaskNone>
);
}
Combining privacy components
You can freely combine the SessionReplayView components to apply different privacy settings to distinct sections of your UI. This is especially useful when you need a mix of hidden elements, masked input fields, and visible content within the same screen.
For example:
App.tsx
import { ImagePrivacyLevel, SessionReplayView, TextAndInputPrivacyLevel, TouchPrivacyLevel } from "@datadog/mobile-react-native-session-replay";
const App = () => {
return (
<SessionReplayView.Privacy
textAndInputPrivacy={TextAndInputPrivacyLevel.MASK_SENSITIVE_INPUTS}
imagePrivacy={ImagePrivacyLevel.MASK_NONE}
touchPrivacy={TouchPrivacyLevel.SHOW}>
{/* content */}
<SessionReplayView.MaskAll showTouch={true}>
{/* content */}
<SessionReplayView.MaskNone>
{/* content */}
</SessionReplayView.MaskNone>
{/* content */}
</SessionReplayView.MaskAll>
{/* content */}
<SessionReplayView.Hide>
{/* content */}
</SessionReplayView.Hide>
</SessionReplayView.Privacy>
);
}
Notes on WebViews
- Privacy overrides, aside from the
hiddenandtouchoptions, are not supported for WebViews. You can primarily manage their privacy using the browser SDK privacy settings. - When a WebView is marked as
hidden, it is replaced by a placeholder in the replay. However, the WebView itself continues to collect and send data. To avoid this, it is recommended to use browser SDK privacy settings for managing WebView privacy, as they provide more targeted control.
How and what data is masked
This section describes how the Datadog recorder handles masking based on data type and how that data is defined.
Text masking strategies
Depending on how you've configured your privacy settings, the type of text, and sensitivity of data, Datadog's masking rules apply different strategies to different types of text fields.
| Text masking strategy | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| No mask | The text is revealed in the session replay | "Hello world" → "Hello world" |
| Space-preserving mask | Each visible character is replaced with a lowercase "x" | "Hello world" → "xxxxx xxxxx" |
| Fixed-length mask | The entire text field is replaced with a constant of three asterisks (***) | "Hello world" → "***" |
With the above text strategies in mind, you have a few different options if you want to override the default privacy rule of mask in your configuration.
The following chart shows how Datadog applies different text masking strategies, using the rules you set up in your configuration, to the below text types.
| Type | Allow all | Mask all | Mask user input |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitive text | Fixed-length mask | Fixed-length mask | Fixed-length mask |
| Input and option text | No mask | Fixed-length mask | Fixed-length mask |
| Static text | No mask | Space-preserving mask | No mask |
| Hint text | No mask | Fixed-length mask | No mask |
Text masking definitions
Find below a description of how Datadog's recorder treats each text type.
Sensitive text
Sensitive text includes passwords, e-mails, and phone numbers marked in a platform-specific way, and other forms of sensitivity in text available to each platform.
Sensitive text can be detected in:
- Edit Text
- Address information
Sensitive text can be detected in:
- Text Field
- Text View
- Address information
- Credit card numbers
- One-time codes
Sensitive text can be detected in the following components.
| Component | Platform(s) |
|---|---|
| Text Field | iOS |
| Text View | iOS |
| Edit Text | Android |
| Address information | iOS, Android |
| Credit card numbers | iOS |
| One-time codes | iOS |
TextInputType.name | TextInputType.phone | TextInputType.emailAddress | TextInputType.streetAddress | TextInputType.twitter | TextInputType.visiblePassword |
Input and option text
Input and option text is text entered by the user with a keyboard or other text-input device, or a custom (non-generic) value in selection elements.
This includes the below.
- User-entered text in:
- Text Field
- Text View
- User-selected options in:
- Value Picker
- Segment
- Notable exclusions:
- Placeholder (hint) texts in Text Field and Text View (not entered by the user)
- Non-editable texts in Text View
- Month, day, and year labels in Date Picker (generic values)
- User-entered text in:
- Edit Text
- User-selected options in:
- Value Picker
- Drop Down List
- Notable exclusions:
- Placeholder (hint) texts in Edit Text (not entered by the user)
- Month, day, and year labels in Date Picker (generic values)
- User-entered text in:
- Text Field (iOS)
- Text View (iOS)
- Edit Text (Android)
- User-selected options in:
- Value Picker (iOS + Android)
- Segment (iOS)
- Drop Down List (Android)
- Notable exclusions:
- Placeholder (hint) texts in Text Field, Text View and Edit Text (not entered by the user)
- Non-editable texts in Text View (iOS).
- Month, day, and year labels in Date Picker (generic values)
- User-entered text in EditableText, which is used in:
- TextField
- CupertinoTextField
- many custom TextField implementations
- Notable exclusions:
- Placeholder (hint) texts in Text Field and Text View (not entered by the user)
- Text in Text Decorations (not entered by the user)
- Month, day, and year labels in Date Picker (generic values)
Static text
Static text is any text that is not directly entered by the user. This includes the below.
All texts in:
- Texts in non-editable Text View
- Month, day, and year labels in the date and time picker
- Values updated in response to gesture interaction with input elements, such as the current value of the Slider
- Other controls, not considered as "user input elements", such as Labels, Tab Bar, and Navigation Bar
- Checkbox and Radio Button titles
- Month, day, and year labels in the date and time picker
- Values updated in response to gesture interaction with input elements, such as the current value of the Slider
- Other controls, not considered as "user input elements", such as Tabs
- Checkbox and Radio Button titles (Android)
- Texts in non-editable Text View (iOS)
- Month, day and year labels in the date and time picker
- Values updated in response to gesture interaction with input elements, such as the current value of the Slider
- Other controls, not considered as "user input elements", such as Labels, Tab Bar, and Navigation Bar (iOS), or Tabs (Android)
- Checkbox and Radio Button titles
- Month, day and year labels in the date and time picker
- Values updated in response to gesture interaction with input elements, such as the current value of the Slider
- Other controls, not considered as "user input elements", such as Text, Tab Bar, and Bottom Navigation Bar
Hint text
Hint text is static text in editable text elements or option selectors that is displayed when no value is given. This includes:
- Placeholders in Text Field
- Placeholders in Text View
- Hints in Edit Text
- Prompts in Drop Down lists
- Placeholders in Text Field (iOS), Text View (iOS)
- Hints in Edit Text (Android)
- Prompts in Drop Down lists (Android)
- InputDecoration elements in TextView
- Placeholder text in CupertinoTextField
Appearance masking
The following chart shows how we apply different appearance masking strategies, using the rules you set up in your configuration, to the below text types.
| Type | Allow all | Mask all | Mask user input |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revealing attributes | |||
| Other attributes |
Revealing attributes
Revealing attributes are attributes that can reveal or suggest the value of input elements and can be used to infer a user's input or selection.
This includes:
Shapes
- Background of selected option in Segment
- Circle surrounding the selected date in a Date Picker
- Thumb of a Slider
Text attributes
- The color of a label rendering the selected date in Date Picker
- The position of the first and last option in Value Picker
Shapes
- Selection mark in Checkbox
- Thumb of a Slider
Text attributes
- The position of the first and last option in Value Picker
Shapes
| Type | Platform(s) |
|---|---|
| Background of selected option in Segment | iOS |
| Circle surrounding the selected date in Date Picker | iOS |
| Selection mark in Checkbox | Android |
| Thumb of a Slider | iOS, Android |
Text attributes
| Type | Platform(s) |
|---|---|
| The color of a label rendering the selected date in Date Picker | iOS |
| The position of the first and last option in Value Picker | iOS, Android |
Shapes
- Background of selected option in Segment
- Circle surrounding the selected date in a Date Picker
- Thumb of a Slider
Text attributes
- The color of a label rendering the selected date in Date Picker
- The position of the first and last option in Value Picker
Touch interactions
The following chart shows how we apply different touch interaction strategies, using the rules you set up in your configuration, to the below text types. While any interaction that happens on an on-screen keyboard is masked, interactions with other elements are not masked.
| Type | Allow all | Mask all | Mask user input |
|---|---|---|---|
| Other attributes | |||
| On-screen keyboard |
Image masking
The following chart shows how we apply different image masking strategies:
| Type | Mask None | Mask Large Only Mask Non Bundled Only Mark Large Only (Android) / Mask Non Bundled Only (iOS) | Mask All |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content Image | Shown | Masked | Masked |
| System Image | Shown | Shown | Masked |