- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- Notebooks
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Search
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API-based Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Service Level Objectives
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Event Management
- Incident Response
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- End User Device Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Storage Management
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Session Replay
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Code Coverage
- PR Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- AI Guard
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Configuration
- Sources
- Processors
- Destinations
- Packs
- Akamai CDN
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs
- AWS Application Load Balancer Logs
- AWS CloudTrail
- AWS Elastic Load Balancer Logs
- AWS Network Load Balancer Logs
- Cisco ASA
- Cloudflare
- F5
- Fastly
- Fortinet Firewall
- HAProxy Ingress
- Istio Proxy
- Juniper SRX Firewall Traffic Logs
- Netskope
- NGINX
- Okta
- Palo Alto Firewall
- Windows XML
- ZScaler ZIA DNS
- Zscaler ZIA Firewall
- Zscaler ZIA Tunnel
- Zscaler ZIA Web Logs
- Search Syntax
- Scaling and Performance
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Guides and Resources
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
Jetpack Compose Instrumentation
Overview
Jetpack Compose is a toolkit for building native UI in Android. If your application uses Jetpack Compose, you can instrument it manually or automatically with the Datadog Gradle Plugin. This enables Real User Monitoring (RUM) similar to what is available for Android classic Views.
The minimum supported Kotlin version is 1.9.23.
After initial setup, you can choose between automatic and manual instrumentation.
Setup
Step 1 - Declare “dd-sdk-android-compose” as a dependency
Add dd-sdk-android-compose as a dependency to each module you want to instrument. This includes the application module, any Jetpack Compose UI modules, or feature modules using Jetpack Compose.
The minimum version of dd-sdk-android-compose for Jetpack Compose instrumentation is 2.21.0.
dependencies {
implementation "com.datadoghq:dd-sdk-android-compose:x.x.x"
//(...)
}
dependencies {
implementation("com.datadoghq:dd-sdk-android-compose:x.x.x")
//(...)
}
Step 2 - Enable actions tracking option in RumConfiguration
After adding the dependency, enable Compose action tracking in your RumConfiguration. This step is required regardless of the instrumentation mode.
val rumConfig = RumConfiguration.Builder(applicationId)
//other configurations that you have already set
.enableComposeActionTracking()
.build()
Rum.enable(rumConfig)
RumConfiguration rumConfig = new RumConfiguration.Builder(applicationId)
//other configurations that you have already set
.enableComposeActionTracking()
.build();
Rum.enable(rumConfig);
Automatic Instrumentation
For full RUM coverage with minimal setup, you can automatically instrument your Jetpack Compose application.
As described in Step 1 of the Android setup section, declare the Datadog Gradle Plugin in your build script and apply it to each module you want to instrument.
The Datadog Gradle Plugin scans @Composable functions and adds Semantics tags to their modifiers. These tags allow Datadog RUM to track user interactions on Compose components with the correct target information. The plugin also detects NavHost usage and listens to Jetpack Compose navigation events.
Step 1 - Declare Datadog Gradle Plugin in your buildscript
The minimum version of Datadog Gradle Plugin for Jetpack Compose instrumentation is 1.17.0.
buildscript {
dependencies {
classpath "com.datadoghq:dd-sdk-android-gradle-plugin:x.x.x"
}
}
plugins {
id 'com.datadoghq.dd-sdk-android-gradle-plugin'
//(...)
}
buildscript {
dependencies {
classpath("com.datadoghq:dd-sdk-android-gradle-plugin:x.x.x")
}
}
plugins {
id("com.datadoghq.dd-sdk-android-gradle-plugin")
//(...)
}
Setup 2 - Select the instrumentation mode
In your module’s Gradle configuration, define the desired Compose instrumentation mode:
datadog {
// Other configurations that you may set before.
//(...)
// Jetpack Compose instrumentation mode option.
composeInstrumentation = "AUTO"
}
datadog {
// Other configurations that you may set before.
//(...)
// Jetpack Compose instrumentation mode option.
composeInstrumentation = InstrumentationMode.AUTO
}
Available instrumentation modes:
"AUTO": Instruments all@Composablefunctions."ANNOTATION": Only instruments@Composablefunctions annotated with@ComposeInstrumentation. You can define the scope of auto-instrumentation by using this annotation."DISABLE": Disables instrumentation completely.
InstrumentationMode.AUTO: Instruments all@Composablefunctions.InstrumentationMode.ANNOTATION: Only instruments@Composablefunctions annotated with@ComposeInstrumentation. You can define the scope of auto-instrumentation by using this annotation.InstrumentationMode.DISABLE: Disables instrumentation completely.
Note: If you don’t declare composeInstrumentation in datadog block, the auto-instrumentation is disabled by default.
How names are assigned with auto-instrumentation
When auto-instrumentation is enabled:
- The Compose navigation route is used as the view name.
- The name of the direct composable function that wraps an interactive element is used as the action target.
@Composable
fun AppScaffold(){
NavHost(navController = rememberNavController(), startDestination = "Home Screen"){
composable("Home Screen"){
HomeScreen()
}
}
}
@Composable
fun CustomButton(onClick: () -> Unit) {
Button(onClick = onClick){
Text("Welcome Button")
}
}
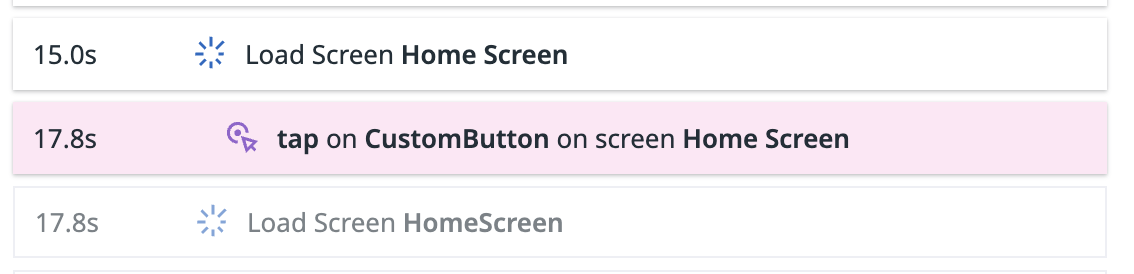
In the example above:
- “Home Screen” is used as the view name when
HomeScreen()is loaded. - “CustomButton” is used as the action target when the button is clicked.
Manual Instrumentation
If you need more customization or control over actions and views tracking, you can manually instrument your application(s).
Actions tracking
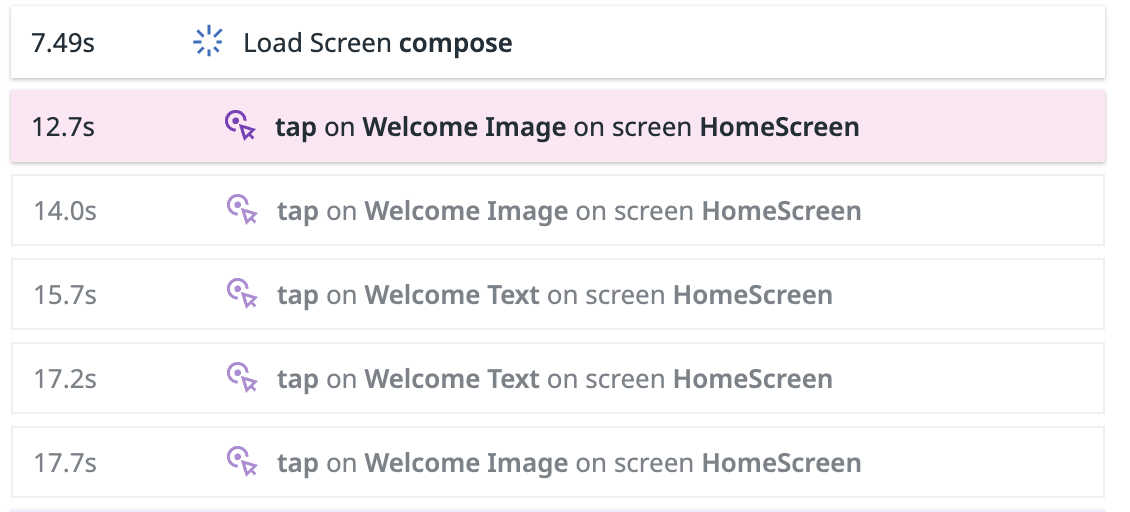
To track user interactions with specific Jetpack Compose components, apply the datadog modifier. The name argument defines the view name displayed in the RUM event list.
@Composable
fun HomeScreen(){
Column{
Image(modifier = Modifier.datadog(name = "Welcome Image").clickable{
// Action can be tracked if this image is clickable
},
// Other arguments
)
Text(modifier = Modifier.datadog(name = "Welcome Text").clickable{
// Action can be tracked if this text is clickable
},
// Other arguments
)
}
}
In the example above, the custom names are used for the interactive elements in Rum actions tracking.
Views tracking
To enable RUM view tracking based on Jetpack Compose navigation, call the NavigationViewTrackingEffect API and pass your app’s NavHostController.
@Composable
fun AppScaffold(){
val navController = rememberNavController()
NavigationViewTrackingEffect(
navController = navController,
trackArguments = true,
destinationPredicate = AcceptAllNavDestinations()
)
NavHost(navController = navController,
// other arguments
) {
// (...)
}
}
Further Reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: