- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Agent
- Integrations
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Monitors
- Logs
- APM Tracing
- Profiler
- Tags
- API
- Service Catalog
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Synthetic Monitoring
- Incident Management
- Database Monitoring
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Test Impact Analysis
- Code Analysis
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- OpenTelemetry
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Recommended Monitor
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Datadog Mobile App
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Infrastructure
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Service Catalog
- API Catalog
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Product Analytics
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Optimization
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Log Management
- Administration
Kotlin Multiplatform Advanced Configuration
Overview
If you have not set up the SDK yet, follow the in-app setup instructions or refer to the Kotlin Multiplatform RUM setup documentation.
Enrich user sessions
Kotlin Multiplatform RUM automatically tracks attributes such as user activity, screens, errors, and network requests. See the RUM Data Collection documentation to learn about the RUM events and default attributes. You can further enrich user session information and gain finer control over the attributes collected by tracking custom events.
Custom Views
In addition to tracking views automatically, you can also track specific distinct views (such as activities and fragments) manually. Stop tracking when the view is no longer visible.
// to start view
GlobalRumMonitor.get().startView(viewKey, viewName, viewAttributes)
// to stop view
GlobalRumMonitor.get().stopView(viewKey, viewAttributes)
Add your own performance timing
In addition to RUM’s default attributes, you can measure where your application is spending its time by using the addTiming API. The timing measure is relative to the start of the current RUM view. For example, you can time how long it takes for your hero image to appear:
fun onHeroImageLoaded() {
GlobalRumMonitor.get().addTiming("hero_image")
}
Once the timing is sent, the timing is accessible as @view.custom_timings.<timing_name>. For example: @view.custom_timings.hero_image. You must create a measure before graphing it in RUM analytics or in dashboards.
Custom Actions
In addition to tracking actions automatically, you can also track specific custom user actions (such as taps, clicks, and scrolls) with RumMonitor#addAction. For continuous action tracking (for example, tracking a user scrolling a list), use RumMonitor#startAction and RumMonitor#stopAction.
The action type should be one of the following: “custom”, “click”, “tap”, “scroll”, “swipe”, “back”.
fun onUserInteraction() {
GlobalRumMonitor.get().addAction(actionType, name, actionAttributes)
}
Custom Resources
In addition to tracking resources automatically, you can also track specific custom resources (such as network requests and third-party provider APIs) with methods (such as GET and POST) while loading the resource with RumMonitor#startResource. Stop tracking with RumMonitor#stopResource when it is fully loaded, or RumMonitor#stopResourceWithError if an error occurs while loading the resource.
fun loadResource() {
GlobalRumMonitor.get().startResource(resourceKey, method, url, resourceAttributes)
try {
// do load the resource
GlobalRumMonitor.get().stopResource(resourceKey, resourceKind, additionalAttributes)
} catch (e: Exception) {
GlobalRumMonitor.get().stopResourceWithError(resourceKey, message, origin, e)
}
}
Note: stopResource / stopResourceWithError methods accepting NSURLConnection and NSError are also available from iOS source set.
Custom Errors
To track specific errors, notify the monitor when an error occurs with the message, source, exception, and additional attributes. Refer to the Attributes collected documentation.
GlobalRumMonitor.get().addError(message, source, throwable, attributes)
Note: addError method accepting NSError is also available from iOS source set.
Add user properties
You can use the addUserExtraInfo API to append extra user properties to previously set properties.
Datadog.addUserExtraInfo(extraInfo)
Event and data management
The Kotlin Multiplatform SDK first stores events. It only uploads these events when the intake specification conditions are met.
Clear all data
You have the option of deleting all unsent data stored by the SDK with the clearAllData API.
Datadog.clearAllData()
Stop data collection
You can use the stopInstance API to stop the SDK instance from collecting and uploading data further.
Datadog.stopInstance()
Set remote log threshold
You can define the minimum log level (priority) to send events to Datadog in a logger instance. If the log priority is below the one you set at this threshold, it does not get sent. The default value is to allow all.
val logger = Logger.Builder()
.setRemoteLogThreshold(LogLevel.INFO)
.build()
Track custom global attributes
In addition to the default RUM attributes captured by the RUM Kotlin Multiplatform SDK automatically, you can choose to add additional contextual information, such as custom attributes, to your RUM events to enrich your observability within Datadog. Custom attributes allow you to filter and group information about observed user behavior (such as cart value, merchant tier, or ad campaign) with code-level information (such as backend services, session timeline, error logs, and network health).
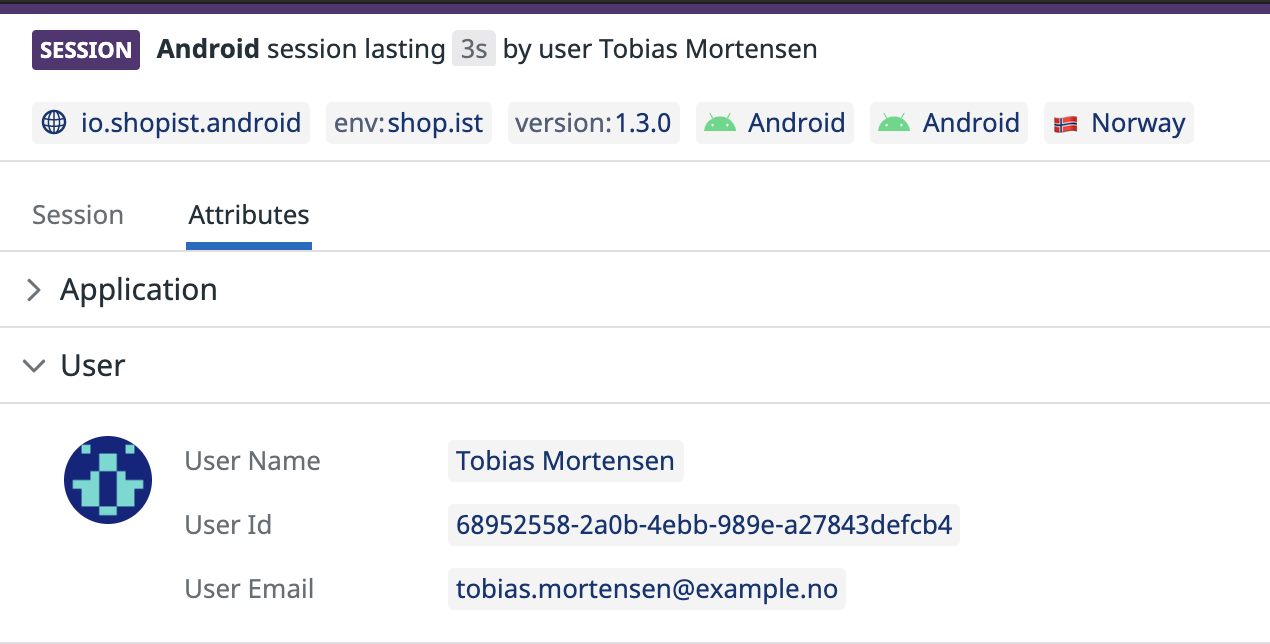
Track user sessions
Adding user information to your RUM sessions helps you to:
- Follow the journey of a given user
- Know which users are the most impacted by errors
- Monitor performance for your most important users
The following attributes are optional, but you should provide at least one of them:
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| usr.id | String | Unique user identifier. |
| usr.name | String | User friendly name, displayed by default in the RUM UI. |
| usr.email | String | User email, displayed in the RUM UI if the user name is not present. It is also used to fetch Gravatars. |
To identify user sessions, use the setUserInfo API, for example:
Datadog.setUserInfo('1234', 'John Doe', 'john@doe.com')
Track attributes
// Adds an attribute to all future RUM events
GlobalRumMonitor.get().addAttribute(key, value)
// Removes an attribute to all future RUM events
GlobalRumMonitor.get().removeAttribute(key)
Track background events
You can track events such as crashes and network requests when your application is in the background (for example, no active view is available).
Add the following snippet during RUM configuration:
.trackBackgroundEvents(true)
Tracking background events may lead to additional sessions, which can impact billing. For questions, contact Datadog support.
Initialization parameters
You can use the following methods in Configuration.Builder when creating the Datadog configuration to initialize the library:
useSite(DatadogSite)- Switches target data to EU, US1, US3, US5, US1_FED, and AP1 sites.
setBatchSize([SMALL|MEDIUM|LARGE])- Defines the individual batch size for requests sent to Datadog.
setUploadFrequency([FREQUENT|AVERAGE|RARE])- Defines the frequency for requests made to Datadog endpoints (if requests are available).
setBatchProcessingLevel(LOW|MEDIUM|HIGH)- Defines the number of batches sent in each upload cycle.
trackCrashes(Boolean)- Allows you to control whether JVM/iOS crashes are tracked or not. The default value is
true.
You can use the following methods in RumConfiguration.Builder when creating the RUM configuration to enable RUM features:
Common configuration methods
trackLongTasks(durationThreshold)- Enables tracking tasks taking longer than
durationThresholdon the main thread as long tasks in Datadog. See Automatically track long tasks for more information. setVitalsUpdateFrequency([FREQUENT|AVERAGE|RARE|NEVER])- Sets the preferred frequency for collecting mobile vitals.
setSessionSampleRate(<sampleRate>)- Sets the RUM sessions sample rate. (A value of 0 means no RUM events are sent. A value of 100 means all sessions are kept.)
setSessionListener(RumSessionListener)- Sets a listener to be notified on when a new RUM Session starts.
setTelemetrySampleRate- The sampling rate for the SDK internal telemetry utilized by Datadog. This must be a value between
0and100. By default, this is set to20. setViewEventMapper- Sets the ViewEventMapper for the RUM ViewEvent. You can use this interface implementation to modify the ViewEvent attributes before serialization.
setResourceEventMapper- Sets the EventMapper for the RUM ResourceEvent. You can use this interface implementation to modify the ResourceEvent attributes before serialization.
setActionEventMapper- Sets the EventMapper for the RUM ActionEvent. You can use this interface implementation to modify the ActionEvent attributes before serialization.
setErrorEventMapper- Sets the EventMapper for the RUM ErrorEvent. you can use this interface implementation to modify the ErrorEvent attributes before serialization.
setLongTaskEventMapper- Sets the EventMapper for the RUM LongTaskEvent. You can use this interface implementation to modify the LongTaskEvent attributes before serialization.
trackBackgroundEvents- Enable/disable tracking RUM events when no activity is happening in the foreground. By default, background events are not tracked. Enabling this feature might increase the number of sessions tracked, and therefore your billing.
trackFrustrations- Enable/disable tracking of frustration signals.
Android configuration methods
These methods can be accessed only from Android source set.
trackNonFatalAnrs(Boolean)- Enables tracking non-fatal ANRs. This is enabled by default on Android API 29 and below, and disabled by default on Android API 30 and above.
trackUserInteractions(Array<ViewAttributesProvider>)- Enables tracking user interactions (such as tap, scroll, or swipe). The parameter also allows you to add custom attributes to the RUM Action events based on the widget with which the user interacted.
useViewTrackingStrategy(strategy)- Defines the strategy used to track views. See Automatically track views for more information.
iOS configuration methods
trackUiKitViews(UIKitRUMViewsPredicate)- Enable automatic tracking of
UIViewControllers as RUM views. See Automatically track views for more information. trackUiKitActions(UIKitRUMActionsPredicate)- Enable automatic tracking of
UITouchevents as RUM actions. The predicate implementation should return RUM action parameters if the given interaction should be accepted, ornullto ignore it. By default, all touches are accepted. setAppHangThreshold(Long)- Enables app hangs monitoring with the given threshold (in milliseconds). See Add app hang reporting for more information.
Automatically track views
Android
To automatically track your views (such as activities and fragments), provide a tracking strategy at initialization. Depending on your application’s architecture, you can choose one of the following strategies:
ActivityViewTrackingStrategy- Every activity in your application is considered a distinct view.
FragmentViewTrackingStrategy- Every fragment in your application is considered a distinct view.
MixedViewTrackingStrategy- Every activity or fragment in your application is considered a distinct view.
NavigationViewTrackingStrategy- Recommended for Android Jetpack Navigation library users. Each Navigation destination is considered a distinct view.
For instance, to set each fragment as a distinct view, use the following configuration in your setup:
// in common source set
val rumConfig = RumConfiguration.Builder(applicationId)
.apply {
platformSpecificSetup(this)
}
.build()
internal expect fun platformSpecificSetup(
rumConfigurationBuilder: RumConfiguration.Builder
)
// in Android source set
internal actual fun platformSpecificSetup(
rumConfigurationBuilder: RumConfiguration.Builder
) {
rumConfigurationBuilder.useViewTrackingStrategy(
FragmentViewTrackingStrategy(...)
)
}
For ActivityViewTrackingStrategy, FragmentViewTrackingStrategy, or MixedViewTrackingStrategy, you can filter which Fragment or Activity is tracked as a RUM View by providing a ComponentPredicate implementation in the constructor:
val strategy = ActivityViewTrackingStrategy(
trackExtras = true,
componentPredicate = object : ComponentPredicate<Activity> {
override fun accept(component: Activity): Boolean {
return true
}
override fun getViewName(component: Activity): String? = null
})
Note: By default, the library is using ActivityViewTrackingStrategy. If you decide not to provide a view tracking strategy, you must manually send the views by calling the startView and stopView methods yourself.
iOS
To automatically track views (UIViewControllers), use the trackUiKitViews method when enabling RUM. By default, views are named with the view controller’s class name. To customize it, provide your own implementation of the uiKitViewsPredicate that conforms to UIKitRUMViewsPredicate interface.
Inside the createView(viewController: UIViewController) implementation, your app should decide if a given UIViewController instance should start the RUM view (return value) or not (return null). The returned RUMView value must specify the name and may provide additional attributes for the created RUM view.
For instance, you can configure the predicate to use explicit type check for each view controller in your app:
class YourCustomPredicate: UIKitRUMViewsPredicate {
override fun createView(viewController: UIViewController): RUMView? {
return when (viewController) {
is HomeViewController -> RUMView("Home)
is DetailsViewController -> RUMView("Details")
else -> null
}
}
}
You can even come up with a more dynamic solution depending on your app’s architecture.
Note: By default, UIKit view tracking is not enabled.
Automatically track long tasks
Long running operations performed on the main thread can impact the visual performance and reactivity of your application. To track these operations, define the duration threshold above which a task is considered too long.
val rumConfig = RumConfiguration.Builder(applicationId)
// …
.trackLongTasks(durationThreshold)
.build()
For example, to replace the default 100 ms duration, set a custom threshold in your configuration.
val rumConfig = RumConfiguration.Builder(applicationId)
// …
.trackLongTasks(250L) // track tasks longer than 250ms as long tasks
.build()
Modify or drop RUM events
To modify some attributes in your RUM events, or to drop some of the events entirely before batching, provide an implementation of EventMapper<T> when initializing the RUM Kotlin Multiplatform SDK:
val rumConfig = RumConfiguration.Builder(applicationId)
// ...
.setErrorEventMapper(rumErrorEventMapper)
.setActionEventMapper(rumActionEventMapper)
.setResourceEventMapper(rumResourceEventMapper)
.setViewEventMapper(rumViewEventMapper)
.setLongTaskEventMapper(rumLongTaskEventMapper)
.build()
When implementing the EventMapper<T> interface, only some attributes are modifiable for each event type:
| Event type | Attribute key | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ViewEvent | view.referrer | URL that linked to the initial view of the page. |
view.url | URL of the view. | |
view.name | Name of the view. | |
| ActionEvent | action.target.name | Target name. |
view.referrer | URL that linked to the initial view of the page. | |
view.url | URL of the view. | |
view.name | Name of the view. | |
| ErrorEvent | error.message | Error message. |
error.stack | Stacktrace of the error. | |
error.resource.url | URL of the resource. | |
view.referrer | URL that linked to the initial view of the page. | |
view.url | URL of the view. | |
view.name | Name of the view. | |
| ResourceEvent | resource.url | URL of the resource. |
view.referrer | URL that linked to the initial view of the page. | |
view.url | URL of the view. | |
view.name | Name of the view. | |
| LongTaskEvent | view.referrer | URL that linked to the initial view of the page. |
view.url | URL of the view. | |
view.name | Name of the view. |
Note: If you return null from the EventMapper<T> implementation, the event is dropped.
Retrieve the RUM session ID
Retrieving the RUM session ID can be helpful for troubleshooting. For example, you can attach the session ID to support requests, emails, or bug reports so that your support team can later find the user session in Datadog.
You can access the RUM session ID at runtime without waiting for the sessionStarted event:
GlobalRumMonitor.get().getCurrentSessionId { sessionId ->
currentSessionId = sessionId
}
Further Reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: