- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- APM Terms and Concepts
- Application Instrumentation
- APM Metrics Collection
- Trace Pipeline Configuration
- Correlate Traces with Other Telemetry
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origins for Spans
- Service Observability
- Endpoint Observability
- Dynamic Instrumentation
- Live Debugger
- Error Tracking
- Data Security
- Guides
- Troubleshooting
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Log Management
- Administration
Flutter Monitoring Setup
Overview
This page describes how to instrument your applications for both Real User Monitoring (RUM) and Error Tracking with the Flutter SDK. You can follow the steps below to instrument your applications for RUM (which includes Error Tracking) or Error Tracking if you have purchased it as a standalone product.
Setup
To start sending RUM or Error Tracking data from your Flutter application to Datadog:
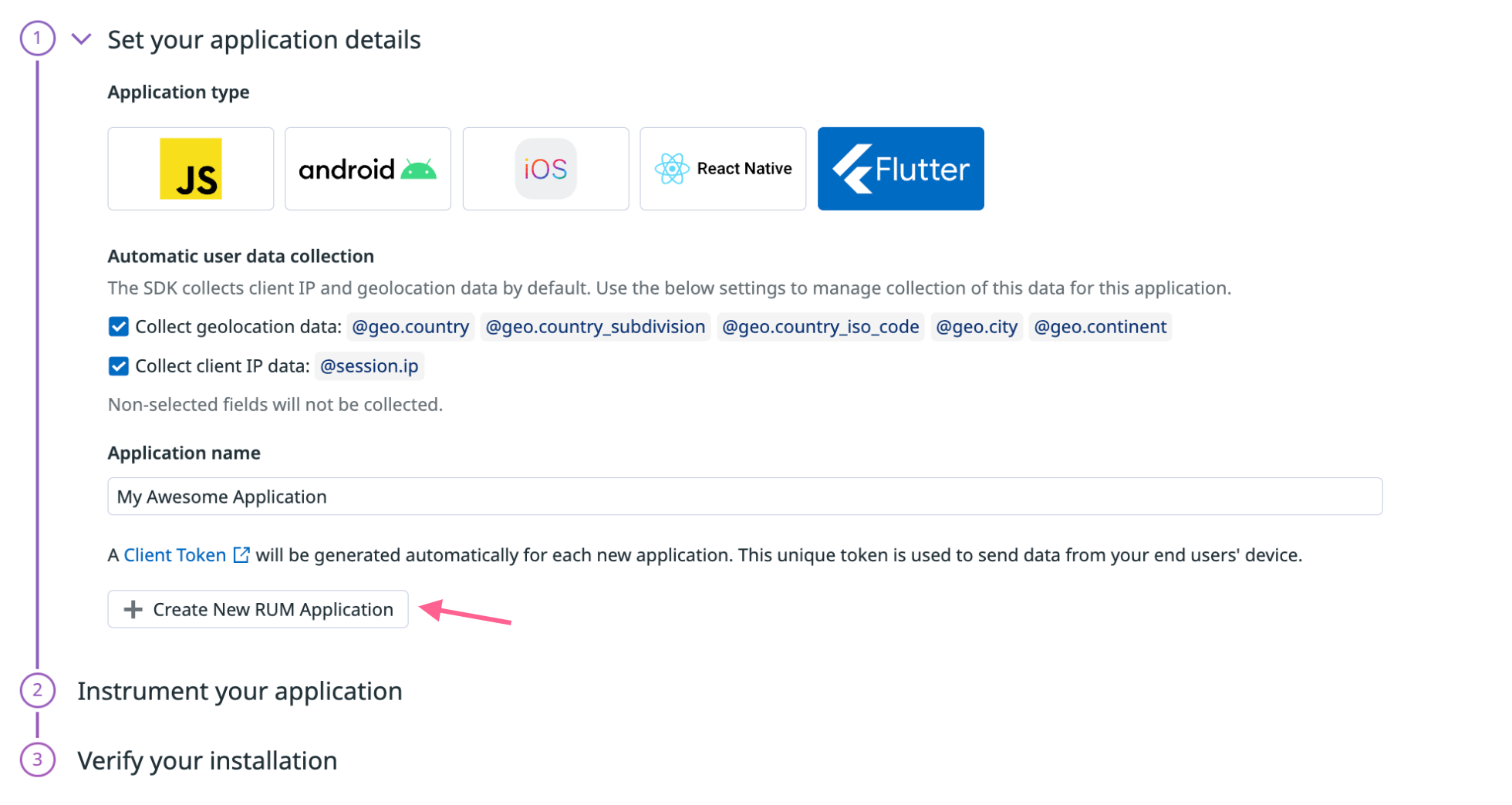
Step 1 - Specify application details in the UI
In Datadog, navigate to Digital Experience > Add an Application.
Choose
Flutteras the application type.Provide an application name to generate a unique Datadog application ID and client token.
To disable automatic user data collection for client IP or geolocation data, uncheck the boxes for those settings. For more information, see Flutter Data Collected.
Navigate to Error Tracking > Settings > Browser and Mobile > Add an Application.
Choose
Flutteras the application type.Provide an application name to generate a unique Datadog application ID and client token.
To disable automatic user data collection for either client IP or geolocation data, uncheck the boxes for those settings. For more information, see Flutter Data Collected.
To ensure the safety of your data, you must use a client token. For more information about setting up a client token, see the Client Token documentation.
Step 2 - Instrument your application
First, ensure that you have your environment set up properly for each platform.
Datadog supports Flutter Monitoring for iOS and Android for Flutter 3.0+.
Datadog does not officially support Flutter Web, but the current Flutter SDK for mobile apps allows you to achieve some out-of-the-box monitoring. Here are known limitations:
- All Actions reported from Flutter are labeled with type
custom. - Long running actions (
startActionandstopAction) are not supported. - Manually reporting RUM resources (
startResourceandstopResource) is not supported. - Event mappers are not supported.
- Tags on loggers are not supported.
addUserExtraInfois not supported.stopSessionis not supported.
No Flutter Web support is planned, but Datadog’s priorities are often re-evaluated based on your feedback. If you have a Flutter Web app and would want to use the Datadog SDK to monitor its performance, reach out to your customer support team and escalate this feature request.
iOS
Your iOS Podfile, located in ios/Podfile, must have use_frameworks! set to true (which is the default in Flutter) and must set its target iOS version >= 11.0.
This constraint is usually commented out on the top line of the Podfile, and should read:
platform :ios, '11.0'
You can replace 11.0 with any minimum version of iOS you want to support that is 11.0 or higher.
Android
For Android, your minSdkVersion version must be >= 21, and if you are using Kotlin, it should be a version >= 1.8.0. These constraints are usually held in your android/app/build.gradle file.
Web
For Web, add the following to your index.html under the head tag, for site:
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://www.datadoghq-browser-agent.com/us1/v5/datadog-logs.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://www.datadoghq-browser-agent.com/us1/v5/datadog-rum-slim.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://www.datadoghq-browser-agent.com/ap1/v5/datadog-logs.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://www.datadoghq-browser-agent.com/ap1/v5/datadog-rum-slim.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://www.datadoghq-browser-agent.com/ap2/v5/datadog-logs.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://www.datadoghq-browser-agent.com/ap2/v5/datadog-rum-slim.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://www.datadoghq-browser-agent.com/eu1/v5/datadog-logs.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://www.datadoghq-browser-agent.com/eu1/v5/datadog-rum-slim.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://www.datadoghq-browser-agent.com/us3/v5/datadog-logs.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://www.datadoghq-browser-agent.com/us3/v5/datadog-rum-slim.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://www.datadoghq-browser-agent.com/us5/v5/datadog-logs.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://www.datadoghq-browser-agent.com/us5/v5/datadog-rum-slim.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://www.datadoghq-browser-agent.com/datadog-logs-v5.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://www.datadoghq-browser-agent.com/datadog-rum-slim-v5.js"></script>
This loads the CDN-delivered Datadog Browser SDKs for Logs and RUM. The synchronous CDN-delivered version of the Browser SDK is the only version supported by the Datadog Flutter Plugin.
Add the plugin
Add the following to your
pubspec.yamlfile:dependencies: datadog_flutter_plugin: ^2.0.0Create a configuration object for each Datadog feature (such as Logs or RUM) with the following snippet. If you do not pass a configuration for a given feature, that feature is disabled.
// Determine the user's consent to be tracked final trackingConsent = ... final configuration = DatadogConfiguration( clientToken: '<CLIENT_TOKEN>', env: '<ENV_NAME>', site: DatadogSite.us1, nativeCrashReportEnabled: true, loggingConfiguration: DatadogLoggingConfiguration(), rumConfiguration: DatadogRumConfiguration( applicationId: '<RUM_APPLICATION_ID>', ) );
For more information on available configuration options, see the DatadogConfiguration object documentation.
To ensure the safety of your data, you must use a client token. You cannot use Datadog API keys to configure the Datadog Flutter Plugin.
- If you are using RUM, set up a Client Token and Application ID.
- If you are only using Logs, initialize the library with a client token.
Step 3 - Initialize the library
You can initialize the library using one of two methods in your main.dart file.
Use
DatadogSdk.runAppto automatically set up Error Tracking.await DatadogSdk.runApp(configuration, TrackingConsent.granted, () async { runApp(const MyApp()); })You can also manually set up Error Tracking and resource tracking.
DatadogSdk.runAppcallsWidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitialized, so if you are not usingDatadogSdk.runApp, you need to call this method prior to callingDatadogSdk.instance.initialize.WidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitialized(); final originalOnError = FlutterError.onError; FlutterError.onError = (details) { DatadogSdk.instance.rum?.handleFlutterError(details); originalOnError?.call(details); }; final platformOriginalOnError = PlatformDispatcher.instance.onError; PlatformDispatcher.instance.onError = (e, st) { DatadogSdk.instance.rum?.addErrorInfo( e.toString(), RumErrorSource.source, stackTrace: st, ); return platformOriginalOnError?.call(e, st) ?? false; }; await DatadogSdk.instance.initialize(configuration, TrackingConsent.granted); runApp(const MyApp());
Sample session rates
To control the data your application sends to Datadog RUM, you can specify a sampling rate for RUM sessions while initializing the Flutter RUM SDK. The rate is a percentage between 0 and 100. By default, sessionSamplingRate is set to 100 (keep all sessions).
For example, to keep only 50% of sessions, use:
final config = DatadogConfiguration(
// other configuration...
rumConfiguration: DatadogRumConfiguration(
applicationId: '<YOUR_APPLICATION_ID>',
sessionSamplingRate: 50.0,
),
);
Set tracking consent (GDPR compliance)
To be compliant with the GDPR regulation, the Datadog Flutter SDK requires the trackingConsent value during initialization.
Set trackingConsent to one of the following values:
TrackingConsent.pending: The Datadog Flutter SDK starts collecting and batching the data but does not send it to Datadog. It waits for the new tracking consent value to decide what to do with the batched data.TrackingConsent.granted: The Datadog Flutter SDK starts collecting the data and sends it to Datadog.TrackingConsent.notGranted: The Datadog Flutter SDK does not collect any data, which means no logs, traces, or events are sent to Datadog.
To change the tracking consent value after the SDK is initialized, use the DatadogSdk.setTrackingConsent API call.
The SDK changes its behavior according to the new value. For example, if the current tracking consent is TrackingConsent.pending:
- You change it to
TrackingConsent.granted, the SDK sends all current and future data to Datadog; - You change it to
TrackingConsent.notGranted, the SDK wipes all current data and does not collect any future data.
Automatically track views
If you are using Flutter Navigator v2.0, your setup for automatic view tracking differs depending on your routing middleware. See Flutter Integrated Libraries for instructions on how to integrate with go_router, AutoRoute, and Beamer.
Flutter Navigator v1
The Datadog Flutter Plugin can automatically track named routes using the DatadogNavigationObserver on your MaterialApp:
MaterialApp(
home: HomeScreen(),
navigatorObservers: [
DatadogNavigationObserver(DatadogSdk.instance),
],
);
This works if you are using named routes or if you have supplied a name to the settings parameter of your PageRoute.
If you are not using named routes, you can use DatadogRouteAwareMixin in conjunction with the DatadogNavigationObserverProvider widget to start and stop your RUM views automatically. With DatadogRouteAwareMixin, move any logic from initState to didPush.
Flutter Navigator v2
If you are using Flutter Navigator v2.0, which uses the MaterialApp.router named constructor, the setup varies based on the routing middleware you are using, if any. Since go_router uses the same observer interface as Flutter Navigator v1, DatadogNavigationObserver can be added to other observers as a parameter to GoRouter.
final _router = GoRouter(
routes: [
// Your route information here
],
observers: [
DatadogNavigationObserver(datadogSdk: DatadogSdk.instance),
],
);
MaterialApp.router(
routerConfig: _router,
// Your remaining setup
)
For examples that use routers other than go_router, see Automatically track views.
Renaming Views
For all setups, you can rename views or supply custom paths by providing a viewInfoExtractor callback. This function can fall back to the default behavior of the observer by calling defaultViewInfoExtractor. For example:
RumViewInfo? infoExtractor(Route<dynamic> route) {
var name = route.settings.name;
if (name == 'my_named_route') {
return RumViewInfo(
name: 'MyDifferentName',
attributes: {'extra_attribute': 'attribute_value'},
);
}
return defaultViewInfoExtractor(route);
}
var observer = DatadogNavigationObserver(
datadogSdk: DatadogSdk.instance,
viewInfoExtractor: infoExtractor,
);
Automatically track actions
Use RumUserActionDetector to track user taps that happen in a given Widget tree:
RumUserActionDetector(
rum: DatadogSdk.instance.rum,
child: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text('RUM'),
),
body: // Rest of your application
),
);
RumUserActionDetector automatically detects tap user actions that occur in its tree and sends them to RUM. It detects interactions with several common Flutter widgets.
For most Button types, the detector looks for a Text widget child, which it uses for the description of the action. In other cases it looks for a Semantics object child, or an Icon with its Icon.semanticsLabel property set.
Alternatively, you can enclose any Widget tree with a RumUserActionAnnotation, which uses the provided description when reporting user actions detected in the child tree, without changing the Semantics of the tree.
Container(
margin: const EdgeInsets.all(8),
child: RumUserActionAnnotation(
description: 'My Image Button',
child: InkWell(
onTap: onTap,
child: Column(
children: [
FadeInImage.memoryNetwork(
placeholder: kTransparentImage,
image: image,
),
Center(
child: Text(
text,
style: theme.textTheme.headlineSmall,
),
)
],
),
),
),
);
Sending data when device is offline
The Flutter SDK ensures availability of data when your user device is offline. In cases of low-network areas, or when the device battery is too low, all events are first stored on the local device in batches. They are sent as soon as the network is available, and the battery is high enough to ensure the Flutter SDK does not impact the end user’s experience. If the network is not available with your application running in the foreground, or if an upload of data fails, the batch is kept until it can be sent successfully.
This means that even if users open your application while offline, no data is lost.
Note: The data on the disk is automatically deleted if it gets too old to ensure the Flutter SDK does not use too much disk space.
Further reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: