- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- APM Terms and Concepts
- Application Instrumentation
- APM Metrics Collection
- Trace Pipeline Configuration
- Correlate Traces with Other Telemetry
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origins for Spans
- Service Observability
- Endpoint Observability
- Dynamic Instrumentation
- Live Debugger
- Error Tracking
- Data Security
- Guides
- Troubleshooting
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Log Management
- Administration
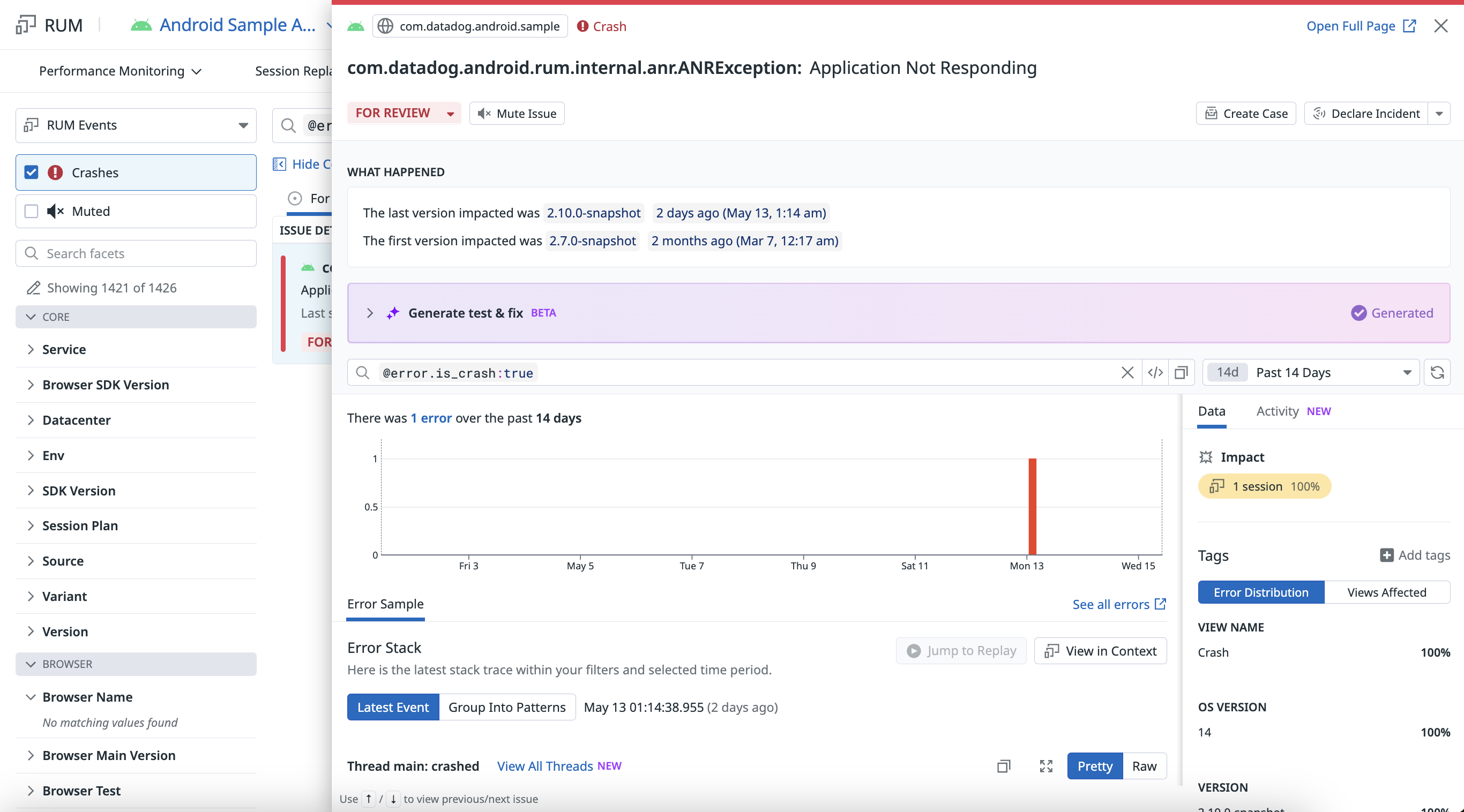
Android Crash Reporting and Error Tracking
Overview
Error Tracking processes errors collected from the Android SDK.
Enable Android Crash Reporting and Error Tracking to get comprehensive crash reports and error trends. With this feature, you can access:
- Aggregated Android crash dashboards and attributes
- Deobfuscated Android crash reports
- Trend analysis with Android error tracking
Your crash reports appear in Error Tracking.
Setup
If you have not set up the Android SDK yet, follow the in-app setup instructions or see the Android setup documentation.
- Add the latest version of the Android SDK to your Gradle dependencies.
- Configure your application’s
envandvariantwhen initializing the SDK. - Run the Gradle tasks to upload your Proguard/R8 mapping file and NDK symbol files to Datadog to access deobfuscated stack traces.
For any given error, you can access the file path, line number, and a code snippet for each frame of the related stack trace.
Add NDK crash reporting
Your Android application may be running native code (C/C++) for performance or code reusability reasons. In order to enable NDK crash reporting, use the Datadog NDK plugin.
Add the Gradle dependency by declaring the library as a dependency in your
build.gradlefile:dependencies { implementation("com.datadoghq:dd-sdk-android-ndk:x.x.x") //(...) }Enable NDK crash collection after initializing the SDK.
NdkCrashReports.enable()
Add ANR reporting
An “Application Not Responding” (ANR) is an Android-specific type of error that gets triggered when the application is unresponsive for too long.
ANRs are only reported through the SDK (not through Logs).
Report fatal ANRs
Fatal ANRs result in crashes. The application reports them when it’s unresponsive, leading to the Android OS displaying a popup dialog to the user, who chooses to force quit the app through the popup.
- In the Error Tracking page, fatal ANRs are grouped based on their similarity, which can result into several individual issues being created
- By default, Datadog catches fatal ANRs through the ApplicationExitInfo API (available since Android 30+), which can be read on the next app launch.
- In Android 29 and below, reporting on fatal ANRs is not possible.
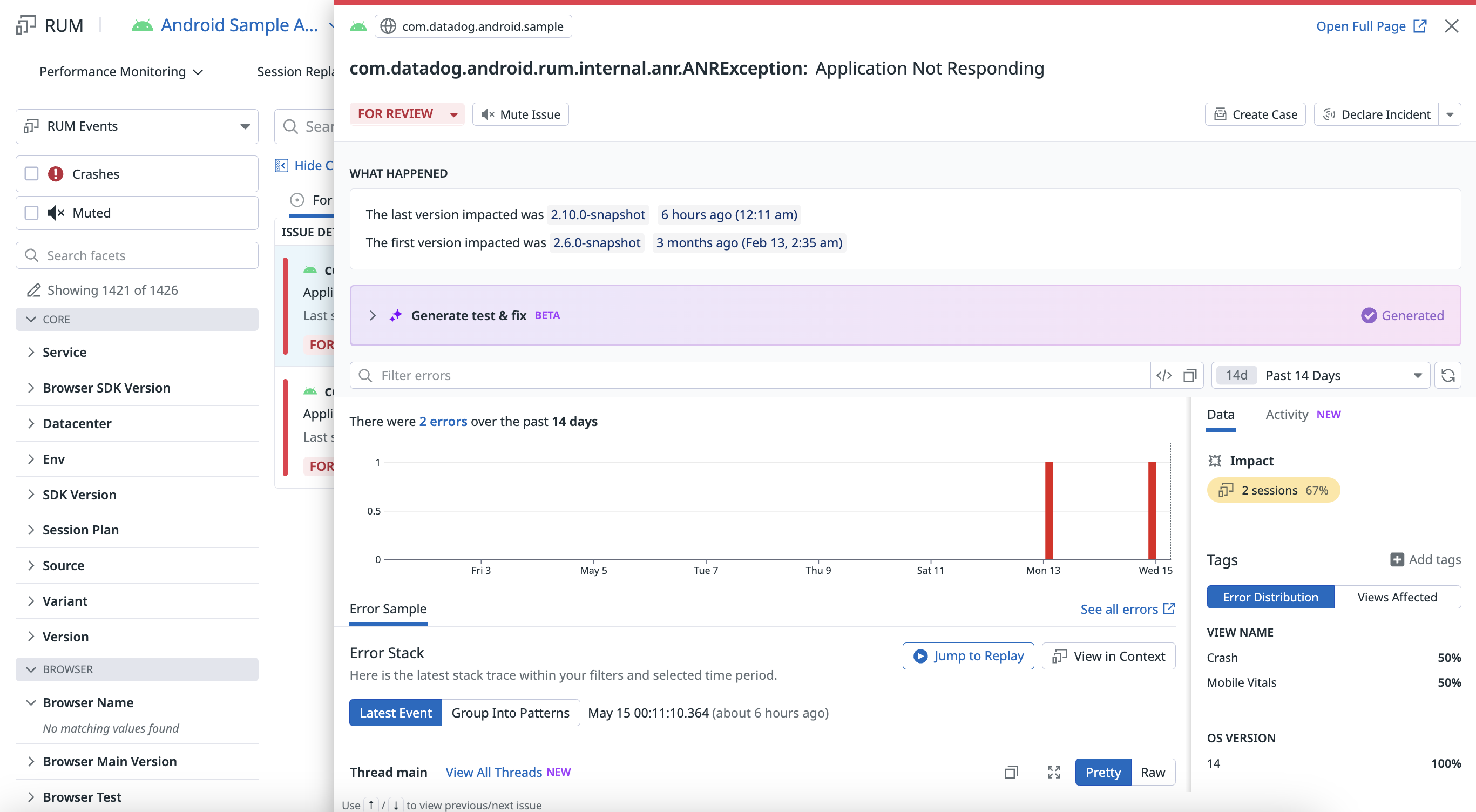
Report non-fatal ANRs
Non-fatal ANRs may or may not have led to the application being terminated (crashing).
- In the Error Tracking page, non-fatal ANRs are grouped under a single issue due to their level of noise.
- By default, the reporting of non-fatal ANRs on Android 30+ is disabled because it would create too much noise over fatal ANRs. On Android 29 and below, however, the reporting of non-fatal ANRs is enabled by default, as fatal ANRs cannot be reported on those versions.
For any Android version, you can override the default setting for reporting non-fatal ANRs by setting trackNonFatalAnrs to true or false when initializing the SDK.
Get deobfuscated stack traces
Mapping files are used to deobfuscate stack traces, which helps in debugging errors. Using a unique build ID that gets generated for each build run, Datadog automatically matches the correct stack traces with the corresponding mapping files. This ensures that regardless of when the mapping file was uploaded (either during pre-production or production builds), the correct information is available for efficient QA processes when reviewing crashes and errors reported in Datadog.
Depending on the Android Gradle plugin version, the matching of stack traces and mapping files relies on different fields:
- Versions 1.13.0 and higher use the
build_idfield (you must use Datadog Android SDK 2.8.0 or later to support this field) - Older versions use a combination of the
service,version, andvariantfields
Upload your mapping file
Note: Re-uploading a source map does not override the existing one if the version has not changed.
Add the Android Gradle Plugin to your Gradle project using the following code snippet.
// In your app's build.gradle script plugins { id("com.datadoghq.dd-sdk-android-gradle-plugin") version "x.y.z" }Create a dedicated Datadog API key and export it as an environment variable named
DD_API_KEYorDATADOG_API_KEY. Alternatively, pass it as a task property, or if you havedatadog-ci.jsonfile in the root of your project, it can be taken from anapiKeyproperty there.Optionally, configure the plugin to upload files to the EU region by configuring the plugin in your
build.gradlescript:datadog { site = "EU1" }Run the upload task after your obfuscated APK builds:
./gradlew uploadMappingReleaseIf running native code, run the NDK symbol upload task:
./gradlew uploadNdkSymbolFilesRelease
Note: If your project uses additional flavors, the plugin provides an upload task for each variant with obfuscation enabled. In this case, initialize the Android SDK with a proper variant name (the necessary API is available in versions 1.8.0 and later).
Add the Android Gradle Plugin to your Gradle project using the following code snippet.
// In your app's build.gradle script plugins { id("com.datadoghq.dd-sdk-android-gradle-plugin") version "x.y.z" }Create a dedicated Datadog API key and export it as an environment variable named
DD_API_KEYorDATADOG_API_KEY. Alternatively, pass it as a task property, or if you havedatadog-ci.jsonfile in the root of your project, it can be taken from anapiKeyproperty there.Configure the plugin to use the EU region by adding the following snippet in your app’s
build.gradlescript file:datadog { site = "EU1" }Run the upload task after your obfuscated APK builds:
./gradlew uploadMappingReleaseIf running native code, run the NDK symbol upload task:
./gradlew uploadNdkSymbolFilesRelease
Note: If your project uses additional flavors, the plugin provides an upload task for each variant with obfuscation enabled. In this case, initialize the Android SDK with a proper variant name (the necessary API is available in versions 1.8.0 and later).
List uploaded mapping files
See the RUM Debug Symbols page to view all uploaded symbols.
Plugin configuration options
There are several plugin properties that can be configured through the plugin extension. In case you are using multiple variants, you can set a property value for a specific flavor in the variant.
For example, for a fooBarRelease variant, you can use the following configuration:
datadog {
foo {
versionName = "foo"
}
bar {
versionName = "bar"
}
fooBar {
versionName = "fooBar"
}
}
The task configuration for this variant is merged from all three flavor configurations provided in the following order:
barfoofooBar
This resolves the final value for the versionName property as fooBar.
| Property name | Description |
|---|---|
versionName | The version name of the application (by default, the version declared in the android block of your build.gradle script). |
serviceName | The service name of the application (by default, the package name of your application as declared in the android block of your build.gradle script). |
site | The Datadog site to upload your data to (US1, US3, US5, EU1, US1_FED, AP1, or AP2). |
remoteRepositoryUrl | The URL of the remote repository where the source code was deployed. If this is not provided, this value is resolved from your Git configuration during the task execution time. |
checkProjectDependencies | This property controls if the plugin should check if the Datadog Android SDK is included in the dependencies. If not, “none” is ignored, “warn” logs a warning, and “fail” fails the build with an error (default). |
Integrate with a CI/CD pipeline
By default, the upload mapping task is independent from other tasks in the build graph. Run the task manually when you need to upload mapping.
If you want to run this task in a CI/CD pipeline, and the task is required as part of the build graph, you can set the upload task to run after the mapping file is generated.
For example:
tasks["minify${variant}WithR8"].finalizedBy { tasks["uploadMapping${variant}"] }
Limitations
File sizing
Mapping files are limited in size to 500 MB each. If your project has a mapping file larger than this, use one of the following options to reduce the file size:
- Set the
mappingFileTrimIndentsoption totrue. This reduces your file size by 5%, on average. - Set a map of
mappingFilePackagesAliases: This replaces package names with shorter aliases. Note: Datadog’s stacktrace uses the same alias instead of the original package name, so it’s better to use this option for third party dependencies.
datadog {
mappingFileTrimIndents = true
mappingFilePackageAliases = mapOf(
"kotlinx.coroutines" to "kx.cor",
"com.google.android.material" to "material",
"com.google.gson" to "gson",
"com.squareup.picasso" to "picasso"
)
}
Collection
When looking at RUM Crash Reporting behaviors for Android, consider the following:
- The crash can only be detected after the SDK is initialised. Given this, the recommendation is to initialize the SDK as soon as possible in your application’s
onCreatemethod. - RUM crashes must be attached to a RUM view. If a crash occurs before a view is visible (typically an Activity or Fragment in an
onResumestate), or after the app is sent to the background by the end-user navigating away from it, the crash is muted and isn’t reported for collection. To mitigate this, use thetrackBackgroundEvents()method in yourRumConfigurationbuilder. - Only crashes that occur in sampled sessions are kept, meaning if a session sampling rate is not 100%, some will not be reported.
Test your implementation
To verify your Android Crash Reporting and Error Tracking configuration, you need to trigger a crash in your application and confirm that the error appears in Datadog.
To test your implementation:
Run your application on an Android emulator or a real device.
Execute some code containing an error or crash. For example:
fun onEvent() { throw RuntimeException("Crash the app") }After the crash happens, restart your application and wait for the Android SDK to upload the crash report in Error Tracking.
Further Reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: