- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- Notebooks
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Search
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Extend Datadog
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API-based Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Service Level Objectives
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Event Management
- Incident Response
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- End User Device Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Storage Management
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Session Replay
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Code Coverage
- PR Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Developer Integrations
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- AI Guard
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Configuration
- Sources
- Processors
- Destinations
- Packs
- Akamai CDN
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs
- AWS Application Load Balancer Logs
- AWS CloudTrail
- AWS Elastic Load Balancer Logs
- AWS Network Load Balancer Logs
- Cisco ASA
- Cloudflare
- F5
- Fastly
- Fortinet Firewall
- HAProxy Ingress
- Istio Proxy
- Juniper SRX Firewall Traffic Logs
- Netskope
- NGINX
- Okta
- Palo Alto Firewall
- Windows XML
- ZScaler ZIA DNS
- Zscaler ZIA Firewall
- Zscaler ZIA Tunnel
- Zscaler ZIA Web Logs
- Search Syntax
- Scaling and Performance
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Guides and Resources
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
Google Pub/Sub Destination
This product is not supported for your selected Datadog site. ().
Overview
Use Observability Pipelines’ Google Pub/Sub destination to publish logs to the Google Pub/Sub messaging system, so the logs can be sent to downstream services, data lakes, or custom applications.
When to use this destination
Common scenarios when you might use this destination:
- For analytics pipelines: Route logs downstream into Google BigQuery, Data Lake, or custom machine learning workflows.
- For event-driven processing: Publish logs to a Pub/Sub topic so that Google Cloud Functions, Cloud Run functions, and Dataflow jobs can carry out actions in real time based on the log data.
Prerequisites
Before you configure the destination, you need the following:
- Pub/Sub subscription: Create a Pub/Sub topic and at least one subscription to consume the messages.
- Authentication: Set up a standard Google Cloud authentication method. These options include:
- A service account key (JSON file)
- A workload identity (Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE))
- IAM roles:
roles/pubsub.publisheris required for publishing events.roles/pubsub.vieweris recommended for health checks.- If the role is missing, the error
Healthcheck endpoint forbiddenis logged and the Worker proceeds as usual.
- If the role is missing, the error
- See Available Pub/Sub roles for more information.
Set up a service account for the Worker
A service account in Google Cloud is a type of account used only by applications or services.
- It has its own identity and credentials (a JSON key file).
- You assign it IAM roles so it can access specific resources.
- In this case, the Observability Pipelines Worker uses a service account to authenticate and send logs to Pub/Sub on your behalf.
To authenticate using a service account:
- In the Google Cloud console, navigate to IAM & Admin > Service Accounts.
- Click + Create service account.
- Enter a name and click Create and continue.
- Assign roles:
- Pub/Sub Publisher
- Pub/Sub Viewer
- Click Done.
Authentication methods
After you’ve created the service account with the correct roles, set up one of the following authentication methods:
Option A: Workload Identity method (for GKE, recommended)
- Bind the service account to a Kubernetes service account (KSA).
- Allow the service account to be impersonated by that KSA.
- Annotate the KSA so the GKE knows which service account to use.
- Authentication then comes from the GCP’s metadata server.
Option B: Attach the GSA directly to a VM (for Google Compute Engine)
Use this authentication method if you’re running the Observability Pipelines Worker on a Google Compute Engine (GCE) VM.
- When you create or edit the VM, specify the Google service account under Identity and API access > Service account.
Option C: Run the service as the GSA (for Cloud Run or Cloud Functions)
Use this authentication method if you’re deploying the Worker as a Cloud Run service or Cloud Function.
- In the Cloud Run or Cloud Functions deployment settings, set the Execution service account to the Google service account you created.
Option D: JSON key method (any environment without identity bindings)
- Open the new service account and navigate to Keys > Add key > Create new key.
- Choose the JSON format.
- Save the downloaded JSON file in a secure location.
- After you install the Worker, copy or mount JSON the file into
DD_OP_DATA_DIR/config/. You reference this file in the Google Pub/Sub destination’s Credentials path field when you set up the destination in the Pipelines UI.
Setup
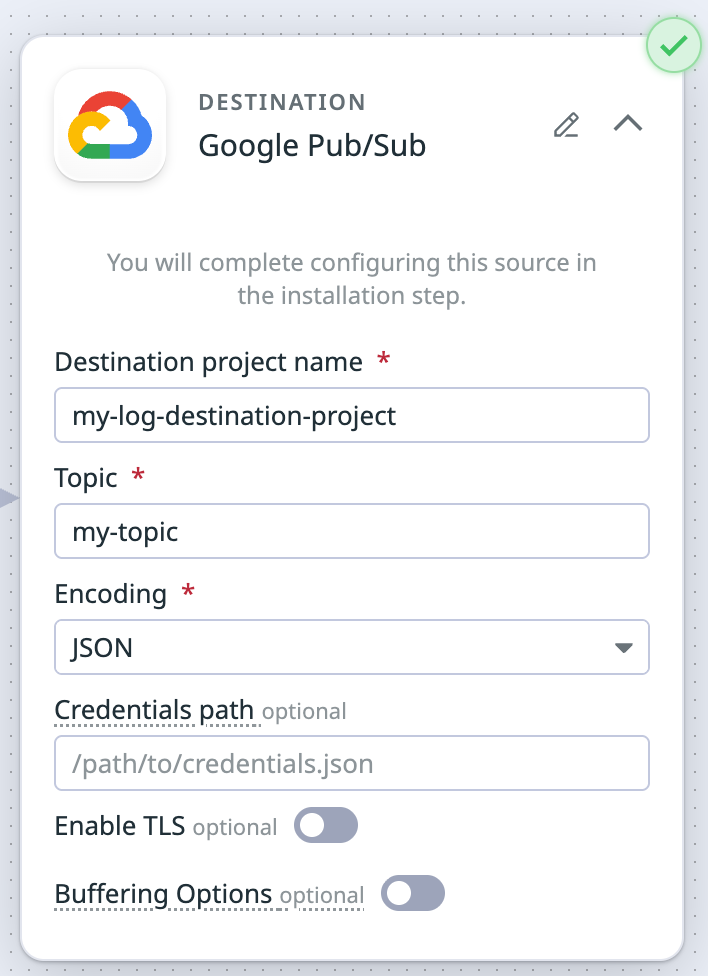
Set up the Google Pub/Sub destination and its environment variables when you set up a pipeline. The information below is configured in the pipelines UI.
Set up the destination
- Enter the destination project name.
- This is the GCP project where your Pub/Sub topic lives.
- Enter the topic.
- This is the Pub/Sub topic to publish logs to.
- In the Encoding dropdown menu, select whether you want to encode your pipeline’s output in JSON or Raw message.
- JSON: Logs are structured as JSON (recommended if downstream tools need structured data).
- Raw: Logs are sent as raw strings (preserves the original format).
- If you have a credentials JSON file, enter the path to your credentials JSON file.
- If you using a service account JSON: enter the path
DD_OP_DATA_DIR/config/<your-service-account>.json. - Or set the
GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALSenvironment variable. - Credentials are automatically managed if you’re using workload identity on GKE.
- If you using a service account JSON: enter the path
Optional settings
Enable TLS
Toggle the switch to Enable TLS if your organization requires secure connections with custom certificates.
Server Certificate Path: The path to the certificate file that has been signed by your Certificate Authority (CA) Root File in DER or PEM (X.509).CA Certificate Path: The path to the certificate file that is your Certificate Authority (CA) Root File in DER or PEM (X.509).Private Key Path: The path to the.keyprivate key file that belongs to your Server Certificate Path in DER or PEM (PKCS#8) format.
Buffering options
Toggle the switch to enable Buffering Options. Enable a configurable buffer on your destination to ensure intermittent latency or an outage at the destination doesn’t create immediate backpressure, and allow events to continue to be ingested from your source. Disk buffers can also increase pipeline durability by writing logs to disk, ensuring buffered logs persist through a Worker restart. See Configurable buffers for destinations for more information.
- If left unconfigured, your destination uses a memory buffer with a capacity of 500 events.
- To configure a buffer on your destination:
- Select the buffer type you want to set (Memory or Disk).
- Enter the buffer size and select the unit.
- Maximum memory buffer size is 128 GB.
- Maximum disk buffer size is 500 GB.
Set secrets
These are the defaults used for secret identifiers and environment variables.
Note: If you enter identifiers for your secrets and then choose to use environment variables, the environment variable is the identifier entered and prepended with DD_OP. For example, if you entered PASSWORD_1 for a password identifier, the environment variable for that password is DD_OP_PASSWORD_1.
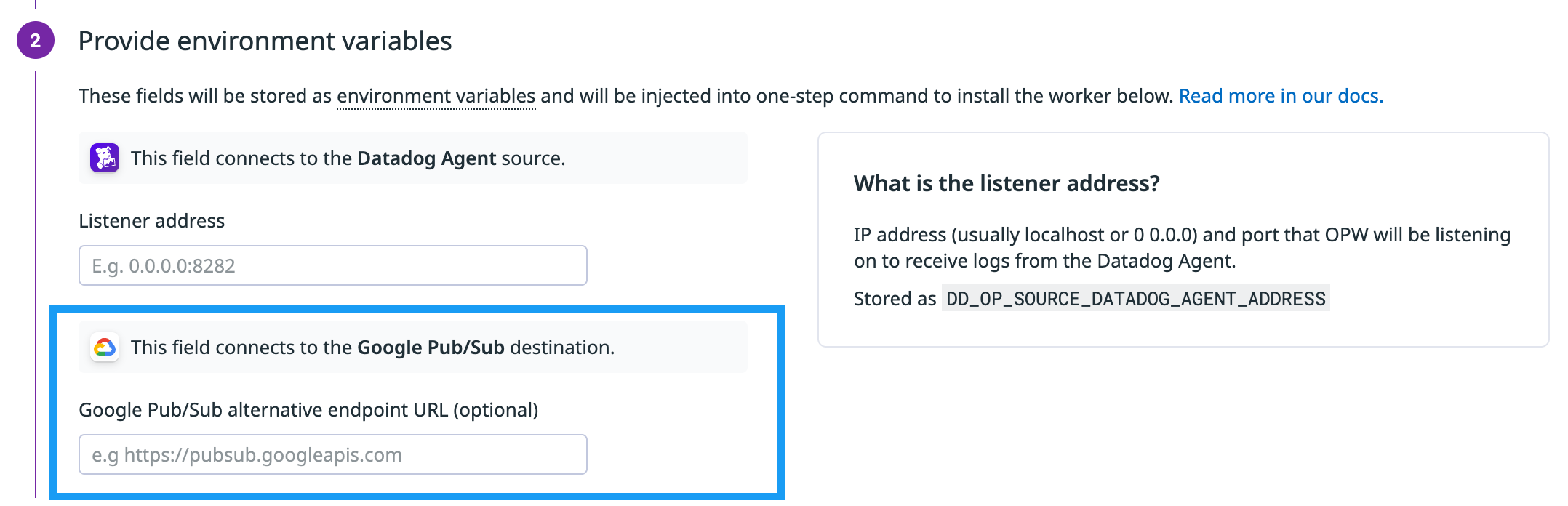
- (Optional) Google Pub/Sub endpoint URL identifier:
- By default the Worker sends data to the global endpoint:
https://pubsub.googleapis.com. - If your Pub/Sub topic is region-specific, configure the Google Pub/Sub alternative endpoint URL with the regional endpoint. See About Pub/Sub endpoints for more information. Enter the configured endpoint URL into your secrets manager.
- The default identifier is
DESTINATION_GCP_PUBSUB_ENDPOINT_URL.
- By default the Worker sends data to the global endpoint:
- Google Pub/Sub TLS passphrase identifier (when TLS is enabled):
- The default identifier is
DESTINATION_GCP_PUBSUB_KEY_PASS.
- The default identifier is
Optional alternative Pub/Sub endpoints
By default the Worker sends data to the global endpoint: https://pubsub.googleapis.com.
If your Pub/Sub topic is region-specific, configure the Google Pub/Sub alternative endpoint URL with the regional endpoint. See About Pub/Sub endpoints for more information.
The default environment variable is DD_OP_DESTINATION_GCP_PUBSUB_ENDPOINT_URL.
TLS (when enabled)
- Google Pub/Sub TLS passphrase:
- The default environment variable is
DD_OP_DESTINATION_GCP_PUBSUB_KEY_PASS.
- The default environment variable is
Troubleshooting
Common issues and fixes:
- Healthcheck forbidden
- Check the
roles/pubsub.viewerIAM role.
- Check the
- Permission denied
- Ensure the service account has
roles/pubsub.publisher.
- Ensure the service account has
- Authentication errors
- Verify the credentials JSON path or GKE Workload Identity setup.
- Dropped events
- Check the
pipelines.component_discarded_events_totalandpipelines.buffer_discarded_events_totalmetrics. - Increase the buffer size or fix misconfigured filters as needed to resolve the issue.
- Check the
- High latency
- Reduce buffer sizer and timeout, or scale your Workers.
- No logs are arriving
- In your Google Pub/Sub destination setup, double-check the topic name, project, and Pub/Sub endpoint (global vs regional).
Metrics
Worker health metrics
See the Observability Pipelines Metrics for a full list of available health metrics.
Component metrics
Monitor the health of your destination with the following key metrics:
pipelines.component_sent_events_total- Events successfully delivered.
pipelines.component_discarded_events_total- Events dropped.
pipelines.component_errors_total- Errors in the destination component.
pipelines.component_sent_events_bytes_total- Total event bytes sent.
pipelines.utilization- Worker resource usage.
Buffer metrics (when enabled)
These metrics are specific to destination buffers, located upstream of a destination. Each destination emits its own respective buffer metrics.
- Use the
component_idtag to filter or group by individual components. - Use the
component_typetag to filter or group by the destination type, such asdatadog_logsfor the Datadog Logs destination.
pipelines.buffer_size_events- Description: Number of events in a destination’s buffer.
- Metric type: gauge
pipelines.buffer_size_bytes- Description: Number of bytes in a destination’s buffer.
- Metric type: gauge
pipelines.buffer_received_events_total- Description: Events received by a destination’s buffer. Note: This metric represents the count per second and not the cumulative total, even though
totalis in the metric name. - Metric type: counter
pipelines.buffer_received_bytes_total- Description: Bytes received by a destination’s buffer. Note: This metric represents the count per second and not the cumulative total, even though
totalis in the metric name. - Metric type: counter
pipelines.buffer_sent_events_total- Description: Events sent downstream by a destination’s buffer. Note: This metric represents the count per second and not the cumulative total, even though
totalis in the metric name. - Metric type: counter
pipelines.buffer_sent_bytes_total- Description: Bytes sent downstream by a destination’s buffer. Note: This metric represents the count per second and not the cumulative total, even though
totalis in the metric name. - Metric type: counter
pipelines.buffer_discarded_events_total- Description: Events discarded by the buffer. Note: This metric represents the count per second and not the cumulative total, even though
totalis in the metric name. - Metric type: counter
- Additional tags:
intentional:truemeans an incoming event was dropped because the buffer was configured to drop the newest logs when it’s full.intentional:falsemeans the event was dropped due to an error. pipelines.buffer_discarded_bytes_total- Description: Bytes discarded by the buffer. Note: This metric represents the count per second and not the cumulative total, even though
totalis in the metric name. - Metric type: counter
- Additional tags:
intentional:truemeans an incoming event was dropped because the buffer was configured to drop the newest logs when it’s full.intentional:falsemeans the event was dropped due to an error.
Deprecated buffer metrics
These metrics are still emitted by the Observability Pipelines Worker for backwards compatibility. Datadog recommends using the replacements when possible.
pipelines.buffer_events- Description: Number of events in a destination’s buffer. Use
pipelines.buffer_size_eventsinstead. - Metric type: gauge
pipelines.buffer_byte_size- Description: Number of bytes in a destination’s buffer. Use
pipelines.buffer_size_bytesinstead. - Metric type: gauge
Event batching
A batch of events is flushed when one of these parameters is met. See event batching for more information.
| Max Events | Max Bytes | Timeout (seconds) |
|---|---|---|
| 1,000 | 10,000,000 | 1 |