- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- APM Terms and Concepts
- Application Instrumentation
- APM Metrics Collection
- Trace Pipeline Configuration
- Correlate Traces with Other Telemetry
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origins for Spans
- Service Observability
- Endpoint Observability
- Dynamic Instrumentation
- Live Debugger
- Error Tracking
- Data Security
- Guides
- Troubleshooting
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Log Management
- Administration
Cloud Networking Monitor
Overview
Datadog Cloud Network Monitoring (CNM) provides visibility into your network traffic between services, containers, availability zones, and any other tag in Datadog. After you enable CNM, you can create a CNM monitor and get alerted if a TCP network metric crosses a threshold that you have set. For example, you can monitor network throughput between a specific client/server and get alerted if that throughput crosses a threshold.
Monitor creation
To create a CNM monitor in Datadog, use the main navigation: Monitors –> New Monitor –> Cloud Network.
Define the search query
- Construct a search query using the same logic as the CNM analytics search bar.
- Select the tags you want to group your client and server by.
- Choose if you want to show or hide N/A traffic.
- Select a metric you want to measure from the dropdown list. By default, the monitor measures the sum of the metric selected. See which metrics are available for CNM monitors in the metric definitions.
- Set the limit on how many results you want to be included in the query.
Using formulas and functions
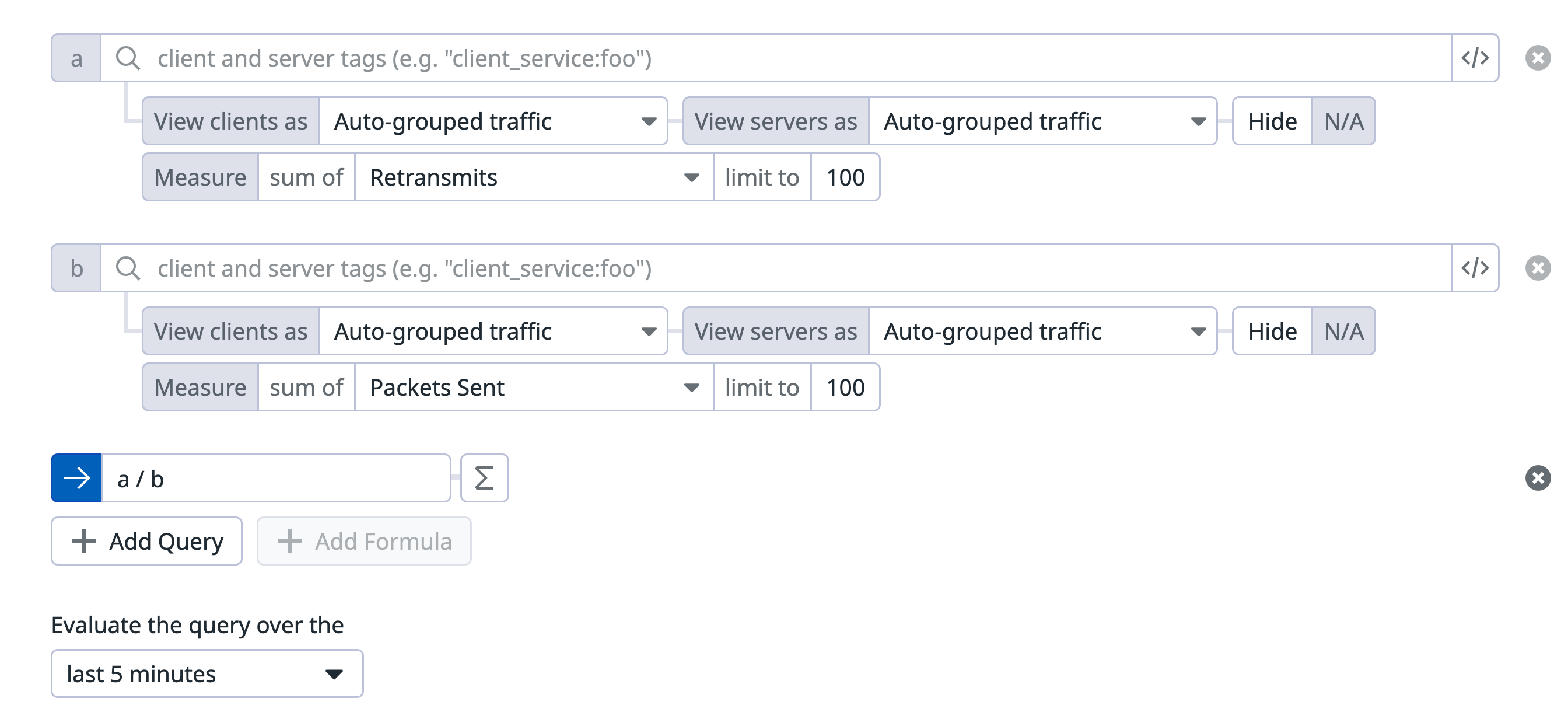
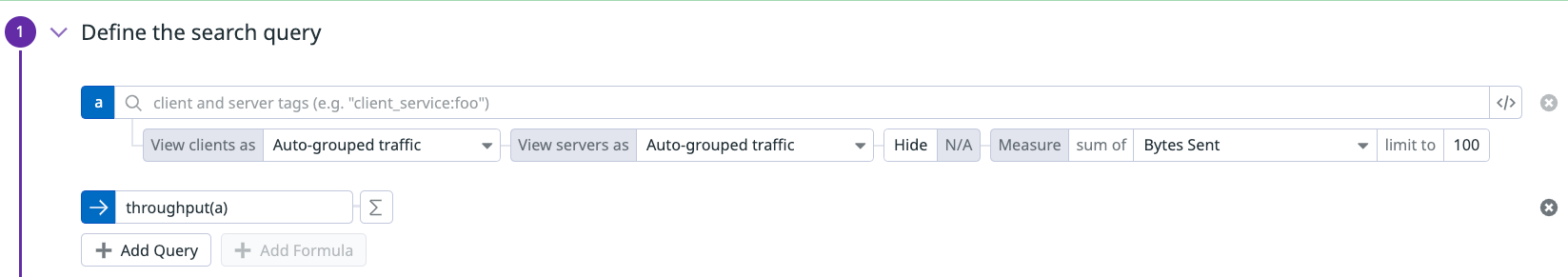
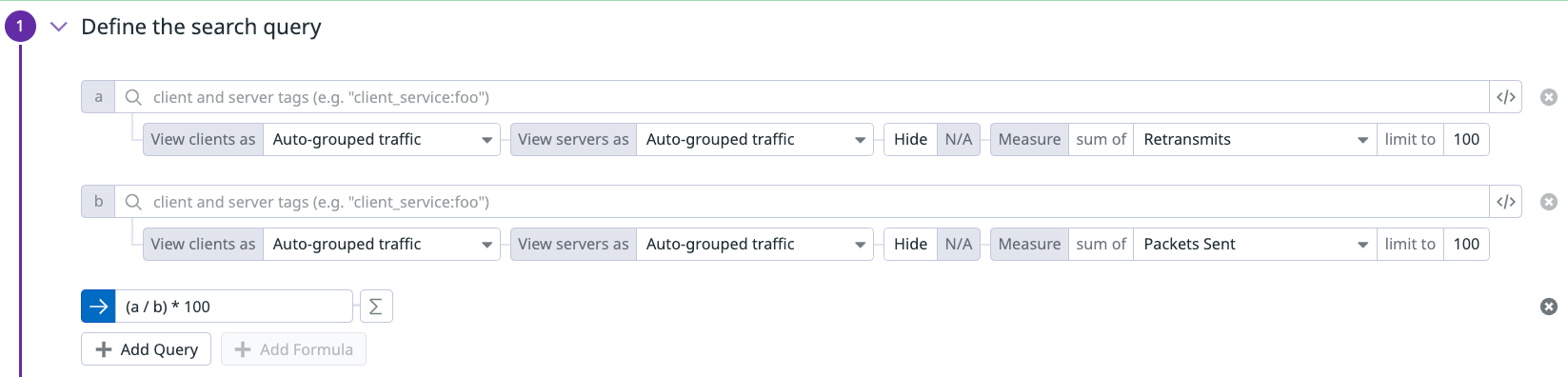
You can create CNM monitors using formulas and functions. This can be used, for example, to create monitors on throughput between a client and server.
The following example shows using a formula to calculate percent retransmits from a client to server.
For more information, see the Functions documentation.
Metric definitions
The following tables list the different CNM metrics you can create monitors on.
Volume
| Metric name | Definition |
|---|---|
| Bytes Received | Bytes received from client. |
| Bytes Sent | Bytes sent from client. |
| Packets Sent | Packets sent from client. |
TCP
| Metric name | Definition |
|---|---|
| Retransmits | Retransmits between client/server. |
| Latency | Average time it takes to make the connection. |
| RTT (Round-Trip Time) | Average time it takes to receive a response. |
| Jitter | Average variance in RTT. |
| TCP Timeouts | The number of TCP connections that timed out from the perspective of the operating system. This can indicate general connectivity and latency issues. |
| TCP Refusals | The number of TCP connections that were refused by the server. Typically this indicates an attempt to connect to an IP/port that isn’t receiving connections, or a firewall/security misconfiguration. |
| TCP Resets | The number of TCP connections that were reset by the server. |
| Established Connections | Establishes connections between client/server. |
| Closed Connections | Closed connections between client/server. |
DNS
| Metric name | Definition |
|---|---|
| DNS Requests | Total number of DNS requests. |
| DNS Failures | Total number of DNS failures. |
| DNS Timeouts | Total number of DNS timeouts. |
| DNS Failed Responses | Total number of DNS failed responses. |
| DNS Successful Responses | Total number of DNS successful responses. |
| DNS Failure Latency | Average DNS failure latency. |
| DNS Success Latency | Average DNS success latency. |
| NXDOMAIN Errors | Total number of NXDOMAIN errors. |
| SERVFAIL Errors | Total number of SERVFAIL errors. |
| Other Errors | Total number of other errors. |
Set alert conditions
Configure monitors to trigger if the query value crosses a threshold and customize advanced alert options for recovery thresholds and evaluations delays. For more information, see Configure Monitors.
Notifications
For detailed instructions on the Configure notifications and automations section, see the Notifications page.
Common monitors
You can start creating monitors on CNM with the following common monitors. These provide a good starting point to track your network and get alerted if your network is experiencing unusual traffic and potentially experiencing unexpected network behavior.
Throughput monitor
The throughput monitor alerts you if throughput between two endpoints specified in the query surpasses a threshold. Monitoring throughput can help you determine if your network is nearing capacity given your network bandwidth. Knowing this can give you enough time to make adjustments to your network to avoid bottlenecks and other effects downstream.
Percent retransmits
Retransmission occurs when packets are either damaged or lost and indicate an unreliable network. The percent retransmits monitor alerts you if the percentage of total packets sent that are resulting in retransmits passes a threshold.
DNS failures
DNS failure monitor tracks DNS server performance to help you identify server-side and client-side DNS issues. Use this monitor to alert you if the sum of DNS failures passes a threshold.
Further Reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: