- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- Notebooks
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Search
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Extend Datadog
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API-based Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Service Level Objectives
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Event Management
- Incident Response
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- End User Device Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Storage Management
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Session Replay
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Code Coverage
- PR Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Developer Integrations
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- AI Guard
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Configuration
- Sources
- Processors
- Destinations
- Packs
- Akamai CDN
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs
- AWS Application Load Balancer Logs
- AWS CloudTrail
- AWS Elastic Load Balancer Logs
- AWS Network Load Balancer Logs
- Cisco ASA
- Cloudflare
- F5
- Fastly
- Fortinet Firewall
- HAProxy Ingress
- Istio Proxy
- Juniper SRX Firewall Traffic Logs
- Netskope
- NGINX
- Okta
- Palo Alto Firewall
- Windows XML
- ZScaler ZIA DNS
- Zscaler ZIA Firewall
- Zscaler ZIA Tunnel
- Zscaler ZIA Web Logs
- Search Syntax
- Scaling and Performance
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Guides and Resources
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
Google Cloud Log Forwarding Setup
Overview
Forwarding logs from your Google Cloud environment enables near real-time monitoring of the resources and activities taking place in your organization or folder. You can set up log monitors to be notified of issues, use Cloud SIEM to detect threats, or leverage Watchdog to identify unknown issues or anomalous behavior.
Logs are forwarded by Google Cloud Dataflow using the Datadog Dataflow template. This approach offers batching and compression of your log events before forwarding them to Datadog, which is the most network-efficient way to forward your logs. You can specify which logs are forwarded with inclusion and exclusion filters.
Setup
Quick Start (recommended)
Quick Start (recommended)
Choose the Quick Start setup method if…
- You are setting up log forwarding from Google Cloud for the first time.
- You prefer a UI-based workflow and want to minimize the time it takes to create and configure the necessary resources.
- You want to automate setup steps in scripts or CI/CD pipelines.
Prerequisite permissions
You must have the following permissions to complete the setup:
In Google Cloud:
- roles/pubsub.admin
- roles/storage.admin
- roles/secretmanager.admin
- roles/resourcemanager.projectIamAdmin
- roles/logging.configWriter
- roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageAdmin
- roles/dataflow.developer
In Datadog:
Your Datadog user account must have either the Datadog Admin role, or, if using custom roles, the following permissions:
api_keys_readapi_keys_write
Instructions
- In the Google Cloud integration tile, click the Configure Log Collection button.
- Select Quick Start. A setup script, configured with your Datadog credentials and site, is automatically generated.
- Copy the setup script. You can run the script locally or in Google Cloud Shell:
- Locally: May be faster, but requires your Google Cloud credentials and the gcloud CLI installed on your machine.
- Google Cloud Shell: Click Open Google Cloud Shell to run the script.
- After running the script, return to the Google Cloud integration tile.
- In the Select Projects section, select the folders and projects to forward logs from. If you select a folder, logs are forwarded from all of its child projects.
Note: Only folders and projects that you have the necessary access and permissions for appear in this section. Likewise, folders and projects without a display name do not appear. - In the Dataflow Job Configuration section, specify configuration options for the Dataflow job:
- Select deployment settings (Google Cloud region and project to host the created resources—Pub/Sub topics and subscriptions, a log routing sink, a Secret Manager entry, a service account, a Cloud Storage bucket, and a Dataflow job)
- Select scaling settings (number of workers and maximum workers)
- Select performance settings (maximum number of parallel requests and batch size)
- Select execution options
- In the Advanced Configuration section, optionally specify the machine type for your Dataflow worker VMs. If no machine type is selected, Dataflow automatically chooses an appropriate machine type based on your job requirements.
- Optionally, choose to specify inclusion and exclusion filters using Google Cloud’s logging query language.
- Review the steps to be executed in the Complete Setup section. If everything is satisfactory, click Complete Setup.
Terraform
Terraform
Choose the Terraform setup method if…
- You manage infrastructure as code and want to keep the Datadog Google Cloud integration under version control.
- You need to configure multiple folders or projects consistently with reusable provider blocks.
- You want a repeatable, auditable deployment process that fits into your Terraform-managed environment.
Prerequisite permissions
You must have the following permissions to complete the setup:
In Google Cloud:
- roles/pubsub.admin
- roles/storage.admin
- roles/secretmanager.admin
- roles/resourcemanager.projectIamAdmin
- roles/logging.configWriter
- roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageAdmin
- roles/dataflow.developer
In Datadog:
Your Datadog user account must have either the Datadog Admin role, or, if using custom roles, the following permissions:
api_keys_readapi_keys_write
Instructions
- In the Google Cloud integration tile, click the Configure Log Collection button.
- Select Terraform.
- In the Select Projects section, select the folders and projects to forward logs from. If you select a folder, logs are forwarded from all of its child projects.
Note: Only folders and projects that you have the necessary access and permissions for appear in this section. Likewise, folders and projects without a display name do not appear. - In the Dataflow Job Configuration section, specify configuration options for the Dataflow job:
- Select deployment settings (Google Cloud region and project to host the created resources—Pub/Sub topics and subscriptions, a log routing sink, a Secret Manager entry, a service account, a Cloud Storage bucket, and a Dataflow job)
- Select scaling settings (maximum workers)
- Select performance settings (maximum number of parallel requests and batch size)
- Select execution options (Streaming Engine is enabled by default; read more about its benefits)
- In the Advanced Configuration section, optionally specify the machine type for your Dataflow worker VMs. If no machine type is selected, Dataflow automatically chooses an appropriate machine type based on your job requirements.
- Optionally, choose to specify inclusion and exclusion filters using Google Cloud’s logging query language.
See the instructions on the terraform-gcp-datadog-integration repo to set up and manage the necessary infrastructure through Terraform.
Manual
Manual
The instructions in this section guide you through the process of:
- Creating a Pub/Sub topic and pull subscription to receive logs from a configured log sink
- Creating a custom Dataflow worker service account to provide least privilege to your Dataflow pipeline workers
- Creating a log sink to publish logs to the Pub/Sub topic
- Creating a Dataflow job using the Datadog template to stream logs from the Pub/Sub subscription to Datadog
You have full control over which logs are sent to Datadog through the logging filters you create in the log sink, including GCE and GKE logs. See Google’s Logging query language page for information about writing filters. For a detailed examination of the created architecture, see Stream logs from Google Cloud to Datadog in the Cloud Architecture Center.
Note: You must enable the Dataflow API to use Google Cloud Dataflow. See Enabling APIs in the Google Cloud documentation for more information.
To collect logs from applications running in GCE or GKE, you can also use the Datadog Agent.
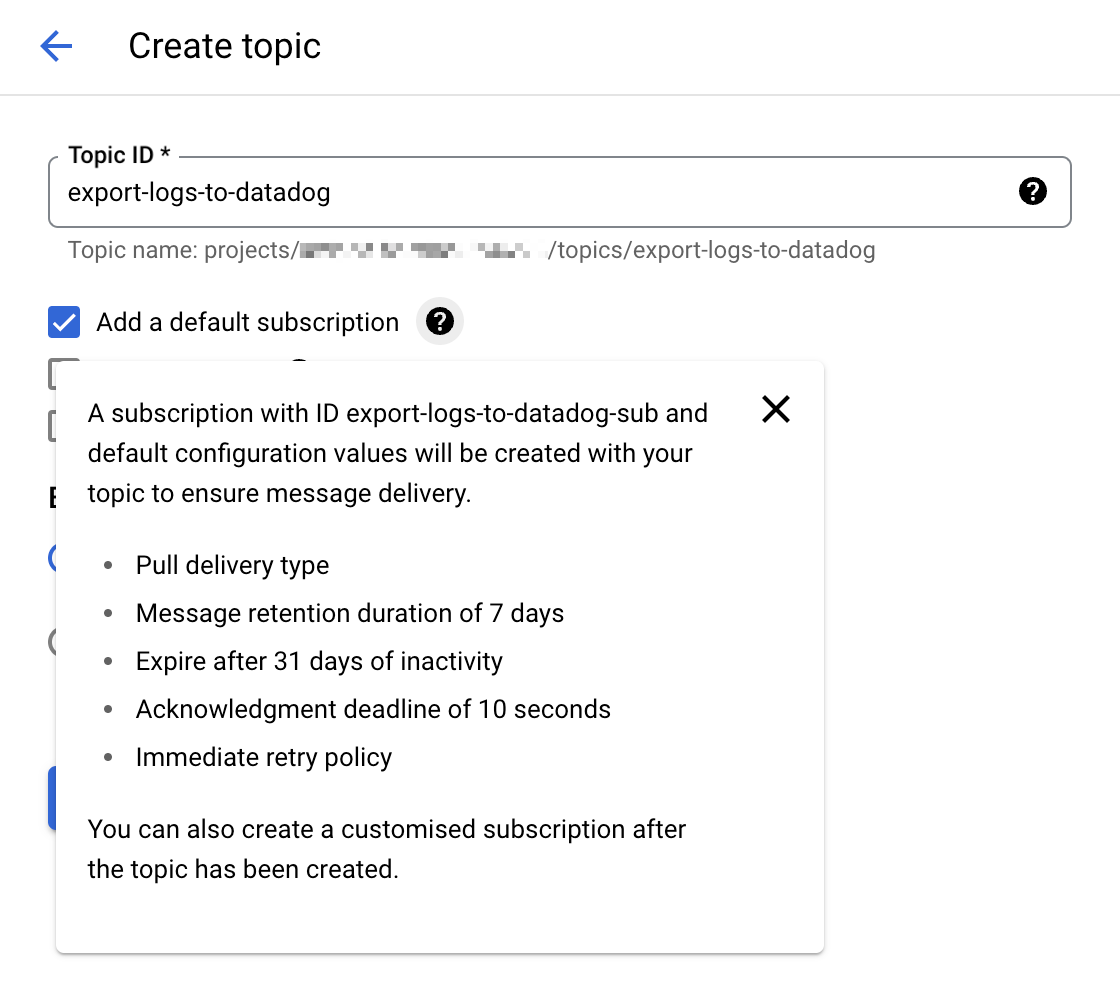
1. Create a Cloud Pub/Sub topic and subscription
Go to the Cloud Pub/Sub console and create a new topic. Select the option Add a default subscription to simplify the setup.
Note: You can also manually configure a Cloud Pub/Sub subscription with the Pull delivery type. If you manually create your Pub/Sub subscription, leave the
Enable dead letteringbox unchecked. For more details, see Unsupported Pub/Sub features.
Give that topic an explicit name such as
export-logs-to-datadogand click Create.Create an additional topic and default subscription to handle any log messages rejected by the Datadog API. The name of this topic is used within the Datadog Dataflow template as part of the path configuration for the
outputDeadletterTopictemplate parameter. When you have inspected and corrected any issues in the failed messages, send them back to the originalexport-logs-to-datadogtopic by running a Pub/Sub to Pub/Sub template job.Datadog recommends creating a secret in Secret Manager with your valid Datadog API key value, for later use in the Datadog Dataflow template.
Cloud Pub/Subs are subject to Google Cloud quotas and limitations. If the number of logs you have exceeds those limitations, Datadog recommends you split your logs over several topics. See the Monitor the Pub/Sub Log Forwarding section for information on setting up monitor notifications if you approach those limits.
2. Create a custom Dataflow worker service account
The default behavior for Dataflow pipeline workers is to use your project’s Compute Engine default service account, which grants permissions to all resources in the project. If you are forwarding logs from a Production environment, you should instead create a custom worker service account with only the necessary roles and permissions, and assign this service account to your Dataflow pipeline workers.
- Go to the Service Accounts page in the Google Cloud console and select your project.
- Click CREATE SERVICE ACCOUNT and give the service account a descriptive name. Click CREATE AND CONTINUE.
- Add the roles in the required permissions table and click DONE.
Required permissions
- Dataflow Admin
roles/dataflow.admin
Allow this service account to perform Dataflow administrative tasks.- Dataflow Worker
roles/dataflow.worker
Allow this service account to perform Dataflow job operations.- Pub/Sub Viewer
roles/pubsub.viewer
Allow this service account to view messages from the Pub/Sub subscription with your Google Cloud logs.- Pub/Sub Subscriber
roles/pubsub.subscriber
Allow this service account to consume messages from the Pub/Sub subscription with your Google Cloud logs.- Pub/Sub Publisher
roles/pubsub.publisher
Allow this service account to publish failed messages to a separate subscription, which allows for analysis or resending the logs.- Secret Manager Secret Accessor
roles/secretmanager.secretAccessor
Allow this service account to access the Datadog API key in Secret Manager.- Storage Object Admin
roles/storage.objectAdmin
Allow this service account to read and write to the Cloud Storage bucket specified for staging files.
Note: If you don’t create a custom service account for the Dataflow pipeline workers, ensure that the default Compute Engine service account has the required permissions above.
3. Export logs from Google Cloud Pub/Sub topic
Go to the Logs Explorer page in the Google Cloud console.
From the Log Router tab, select Create Sink.
Provide a name for the sink.
Choose Cloud Pub/Sub as the destination and select the Cloud Pub/Sub topic that was created for that purpose. Note: The Cloud Pub/Sub topic can be located in a different project.
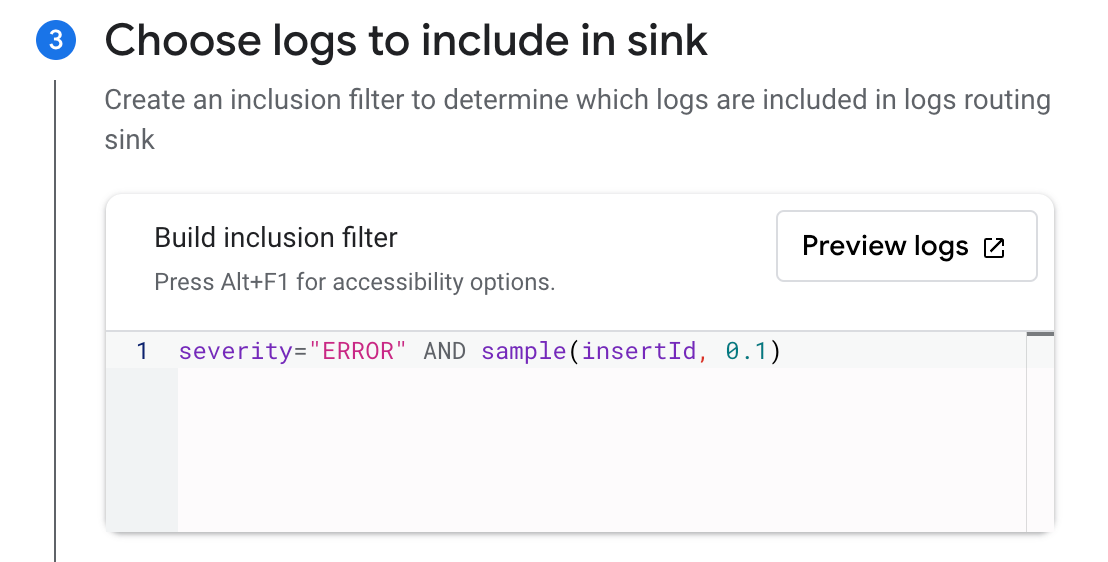
Choose the logs you want to include in the sink with an optional inclusion or exclusion filter. You can filter the logs with a search query, or use the sample function. For example, to include only 10% of the logs with a
severitylevel ofERROR, create an inclusion filter withseverity="ERROR" AND sample(insertId, 0.1).Click Create Sink.
Note: It is possible to create several exports from Google Cloud Logging to the same Cloud Pub/Sub topic with different sinks.
4. Create and run the Dataflow job
Go to the Create job from template page in the Google Cloud console.
Give the job a name and select a Dataflow regional endpoint.
Select
Pub/Sub to Datadogin the Dataflow template dropdown, and the Required parameters section appears.Select the input subscription in the Pub/Sub input subscription dropdown.
Enter the following in the Datadog Logs API URL field:
https://
Note: Ensure that the Datadog site selector on the right of the page is set to your Datadog site before copying the URL above.
Select the topic created to receive message failures in the Output deadletter Pub/Sub topic dropdown.
Specify a path for temporary files in your storage bucket in the Temporary location field.
Under Optional Parameters, check
Include full Pub/Sub message in the payload.If you created a secret in Secret Manager with your Datadog API key value as mentioned in step 1, enter the resource name of the secret in the Google Cloud Secret Manager ID field.
See Template parameters in the Dataflow template for details on using the other available options:
apiKeySource=KMSwithapiKeyKMSEncryptionKeyset to your Cloud KMS key ID andapiKeyset to the encrypted API key- Not recommended:
apiKeySource=PLAINTEXTwithapiKeyset to the plaintext API key
If you created a custom worker service account, select it in the Service account email dropdown.
Click RUN JOB.
Note: If you have a shared VPC, see the Specify a network and subnetwork page in the Dataflow documentation for guidelines on specifying the Network and Subnetwork parameters.
Pub/Sub Push subscription (legacy)
Pub/Sub Push subscription (legacy)
Collecting Google Cloud logs with a Pub/Sub Push subscription is in the process of being deprecated.
The above documentation for the Push subscription is only maintained for troubleshooting or modifying legacy setups.
Datadog recommends instead using a Pull subscription with the Datadog Dataflow template, as described in the Quick Start and Terraform setup sections.
See the Stream logs from Google Cloud to Datadog guide in the Google Cloud architecture center for a more detailed explanation of the steps and architecture involved in log forwarding. For a deep dive into the benefits of the Pub/Sub to Datadog template, read Stream your Google Cloud logs to Datadog with Dataflow in the Datadog blog.
Validation
New logging events delivered to the Cloud Pub/Sub topic appear in the Datadog Log Explorer.
Note: You can use the Google Cloud Pricing Calculator to calculate potential costs.
Monitor the Cloud Pub/Sub log forwarding
The Google Cloud Pub/Sub integration provides helpful metrics to monitor the status of the log forwarding:
gcp.pubsub.subscription.num_undelivered_messagesfor the number of messages pending deliverygcp.pubsub.subscription.oldest_unacked_message_agefor the age of the oldest unacknowledged message in a subscription
Use the metrics above with a metric monitor to receive alerts for the messages in your input and deadletter subscriptions.
Monitor the Dataflow pipeline
Use Datadog’s Google Cloud Dataflow integration to monitor all aspects of your Dataflow pipelines. You can see all your key Dataflow metrics on the out-of-the-box dashboard, enriched with contextual data such as information about the GCE instances running your Dataflow workloads, and your Pub/Sub throughput.
You can also use a preconfigured Recommended Monitor to set up notifications for increases in backlog time in your pipeline. For more information, read Monitor your Dataflow pipelines with Datadog in the Datadog blog.
Further reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: