- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Search
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API-based Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Watchdog
- Metrics
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- APM Terms and Concepts
- Application Instrumentation
- APM Metrics Collection
- Trace Pipeline Configuration
- Correlate Traces with Other Telemetry
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origin for Spans
- Service Observability
- Endpoint Observability
- Dynamic Instrumentation
- Live Debugger
- Error Tracking
- Data Security
- Guides
- Troubleshooting
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Code Coverage
- PR Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Administration
Entity Types
This product is not supported for your selected Datadog site. ().
Overview
In Software Catalog, an entity represents the smallest building block of modern microservice-based architecture. As of schema definition v3.0+, an entity can be an instrumented APM service, a datastore, a system, an API, a queue, or even a custom-defined entity.
See GitHub for full schema definitions.
Entity types
In APM, a service (kind:service) is a group of related endpoints, queries, or jobs that perform a piece of work for your application. For example, a service could be a group of endpoints, a group of DB queries, or a group of periodic jobs.
Through custom instrumentation in APM, you can create an arbitrary service. In practice, microservice-based architecture includes multiple APM services, each measuring the performance of sub-components of the application through Trace Metrics.
In Software Catalog, you can collect non-instrumented services by declaring them through metadata or importing through external sources like Backstage or ServiceNow.
In Software Catalog, a system (kind:system) is a group of entities that cooperate to perform a broader function. For example, you can group multiple instrumented APM services into a system because they are operated by the same team. You can also use system to represent a full microservice-based architecture, and include components like APIs, datastores, queues, and other common building blocks.
Note: System in Datadog has the same meaning as in Backstage’s System Model.
To define components within a system, you can specify values for the components key in the spec field of the entity’s v3 definition.
Example YAML for kind:system:
entity.datadog.yaml
apiVersion: v3
kind: system
metadata:
name: product-recommendation
description: Surfaces personalized product suggestions in Shopist
displayName: "Product Recommendation"
tags:
- product:recommendations
- business-line:shared-components
owner: shopist
additionalOwners:
- name: Shopist Support Team
type: Operator
spec:
lifecycle: production
tier: "0"
components:
- service: product-recommendation
- service: orders-app
- api: products
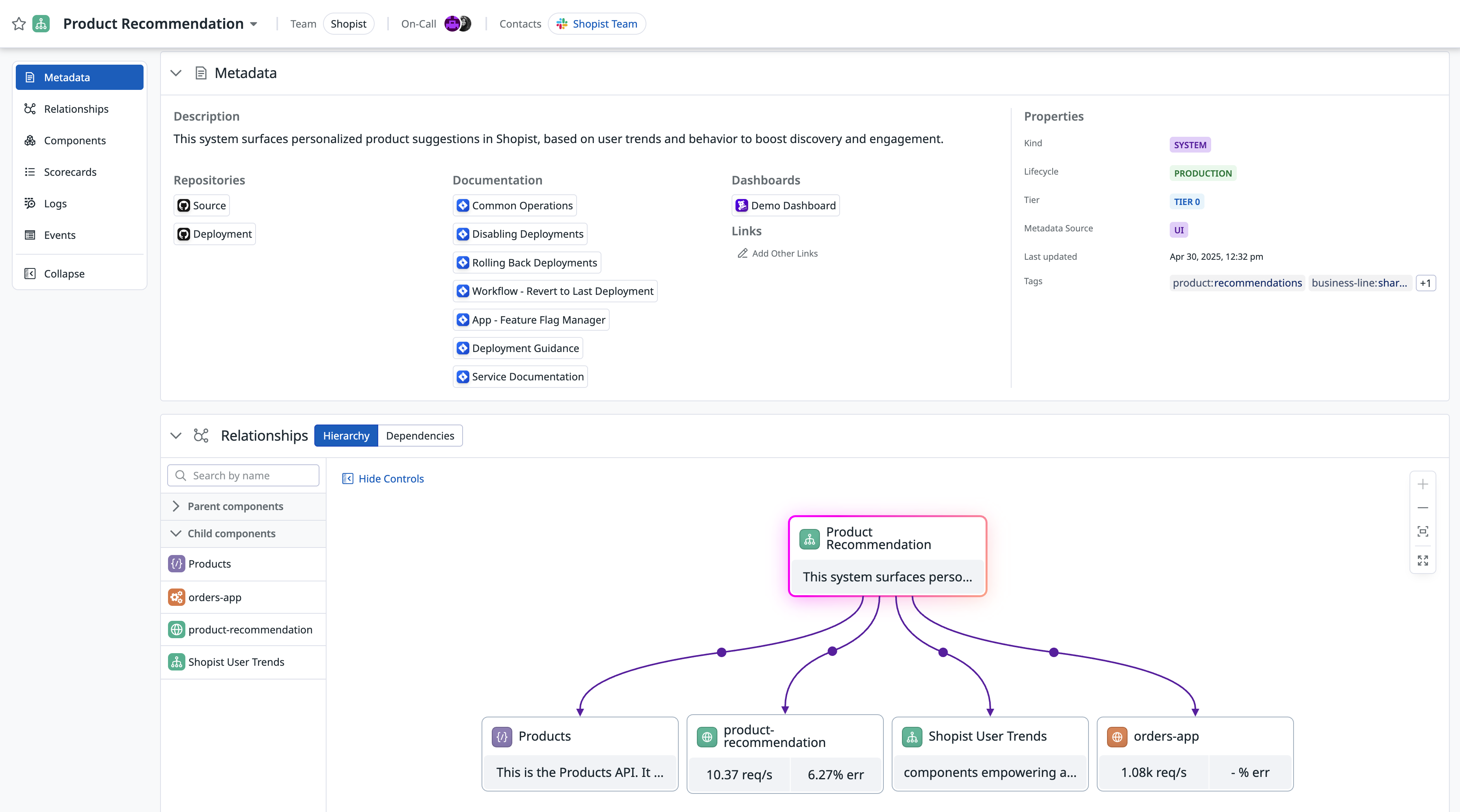
- system: shopist-user-trendsThis user-defined system appears in Software Catalog as shown:
This page holds relationship data of components between the system and upstream/downstream dependencies as well as scorecards, logs, and events aggregated across all system components.
Note: If a single component is part of multiple systems, you must specify that component in the YAML for each system.
In Software Catalog, an API (kind:API) refers to a collection of endpoints that belong together logically. APIs offer an alternative way to group endpoints beyond APM services (the mapping between endpoints and services are not modifiable).
To define components within an API, you can specify values for the components key in the spec field of the entity’s v3 definition.
You can also include an OpenAPI spec in your entity definition in two ways: inline, or through a file reference.
Inline:
Add the OpenAPI definition under the spec field using type: openapi.
entity.datadog.yaml
{
"apiVersion": "v3",
"kind": "api",
"metadata": {
"name": "payments",
"displayName": "Payments",
"owner": "Payments Team",
"links": [
{
"name": "Deployment Information",
"type": "doc",
"url": "https://wiki/products
"
},
{
"name": "Source",
"type": "repo",
"provider": "github",
"url": "https://github.com/"
},
{
"name": "Performance Dashboard",
"type": "dashboard",
"url": "https://datadoghq.com"
}
]
},
"integrations": {
"pagerduty": {
"serviceURL": "https://www.pagerduty.com/service-directory/products"
}
},
"spec": {
"type": "openapi",
"implementedBy": [
"service:payment",
"service:payments-go"
],
"interface": {
"definition": {
"info": {
"title": "Payments"
},
"openapi": "3.0.0",
"paths": {
"/add_item": {
"post": {
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "OK"
}
}
}
},
"/add_purchases": {
"post": {
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "OK"
}
}
}
},
"/admin/update_user": {
"post": {
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "OK"
}
}
}
},
"/carts": {
"get": {
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "OK"
}
}
}
}
}
}
},
"lifecycle": "production",
"tier": "Tier 0"
}
}File reference:
Point to an OpenAPI file stored in GitHub using the fileref field.
entity.datadog.yaml
{
"apiVersion": "v3",
"kind": "api",
"metadata": {
"name": "payments",
"displayName": "Payments",
"owner": "Payments Team",
},
"spec": {
"type": "openapi",
"implementedBy": [
"service:payment",
"service:payments-go"
],
"interface": {
fileRef: https://github.com/openapi.yaml
},
"lifecycle": "production",
"tier": "Tier 0"
}
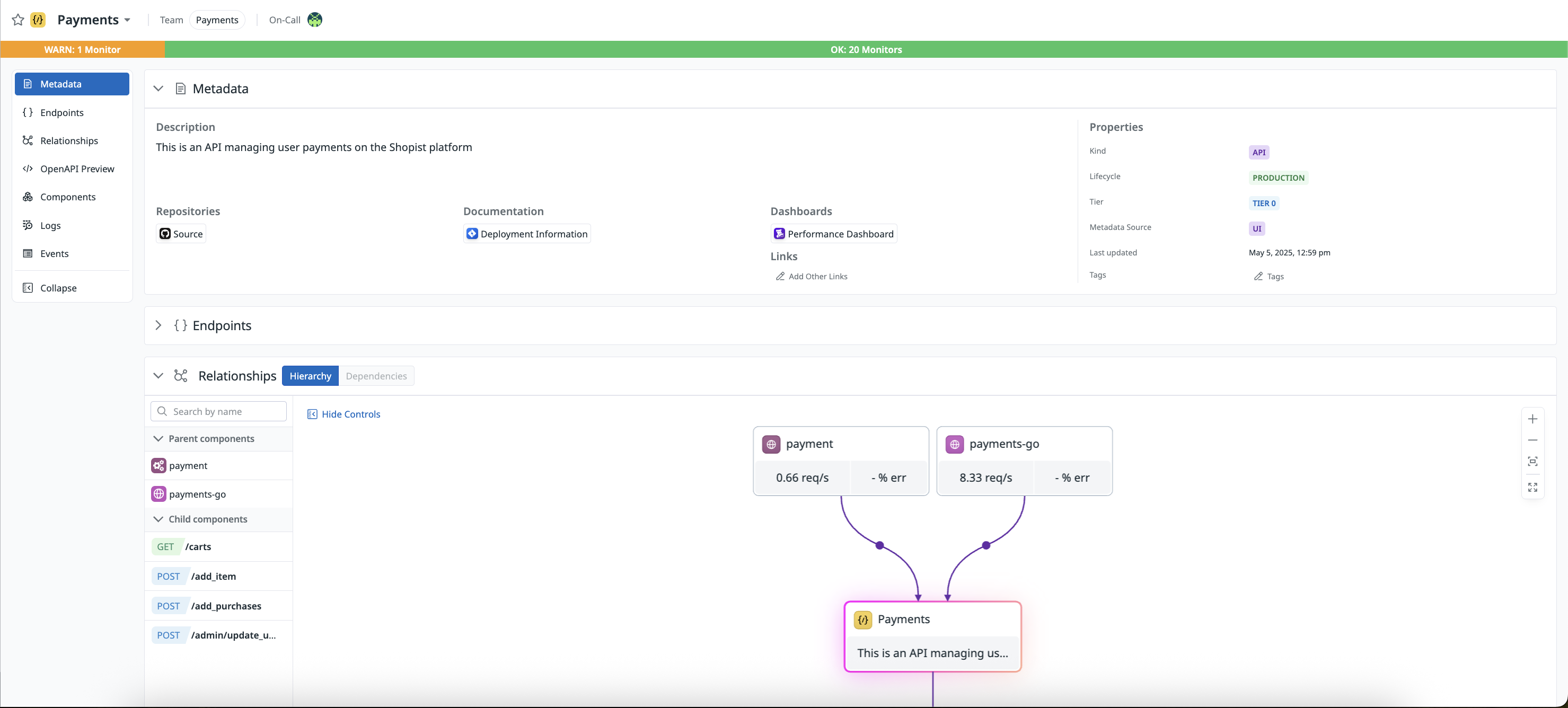
}The user-defined API appears in Software Catalog as shown:
This page holds relationship data of how the API interacts with dependencies, the API components, an OpenAPI preview, and logs and events aggregated across all endpoints.
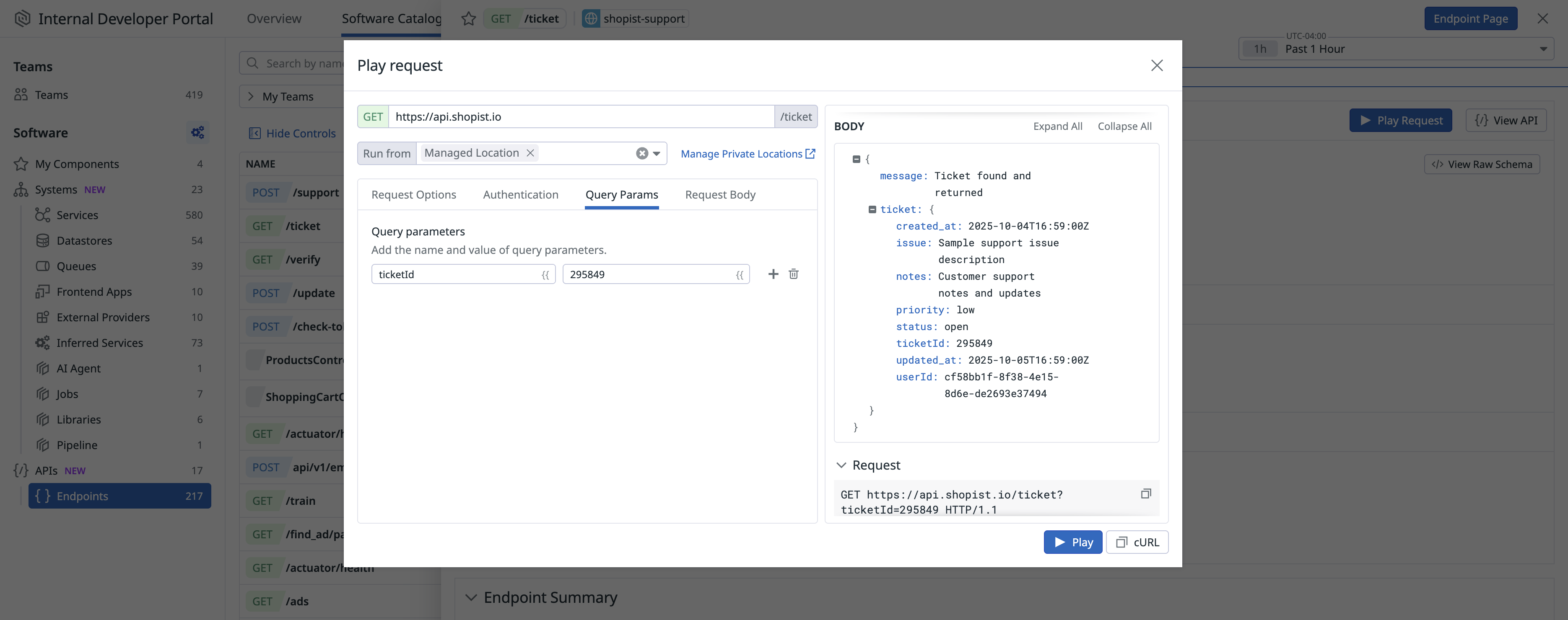
Test API Endpoints
You can use the Play Request feature in Software Catalog to send test HTTP requests to your endpoints and inspect the responses.
To send a test request:
- Navigate to an endpoint in Software Catalog.
- Click an endpoint to open its details in the side panel.
- Click Play Request to configure and send the request.
Before sending the request, you can configure the following:
- Inputs: Provide values for any required query parameters, path variables, or request body fields.
- Authentication: Select an authentication method if required by the endpoint.
- Location: Choose where the request should be sent from:
- Public Location (default)
- Private Location, for APIs accessible only within your private network. These must be configured using Synthetics Private Locations. Any Private Locations you’ve already set up appear automatically in the dropdown.
Note: Software Catalog contains HTTP endpoints that are automatically discovered by APM. The concept of endpoints correspond to APM resources for an APM web service.
In Software Catalog, a datastore (kind:datastore) represents a data storage component or database that services depend on. Datastores can represent relational databases (such as PostgreSQL or MySQL), NoSQL datastores (such as Redis or MongoDB), data warehouses, and caches.
Datastore entities can be:
- Inferred by APM when instrumented services make outbound calls to a database (for example, a PostgreSQL query).
- Manually defined to represent uninstrumented datastores or enrich inferred ones with additional metadata.
Note: If Database Monitoring is enabled, the datastore entity page displays query throughput, latency, and error rates. Otherwise, the page shows basic trace-derived metrics and dependency relationships.
Example YAML definitions
YAML definition for an inferred datastore
YAML definition for an inferred datastore
This example shows a kind:datastore definition for a database automatically detected by APM.
Note: The metadata.name value must exactly match the peer tags used by APM.
apiVersion: v3
kind: datastore
metadata:
name: peer.db.name:web-store-mongo,peer.db.system:mongodb
displayName: "Store Inventory DB (MongoDB)"
description: Stores order transaction data for Shopist e-commerce
owner: shopist
additionalOwners:
- name: infra-team
type: team
links:
- name: "DB Runbook"
type: runbook
url: https://wiki.internal/runbooks/orders-db
- name: "Schema Repo"
type: repo
provider: github
url: https://github.com/org/orders-db-schema
integrations:
pagerduty:
serviceURL: https://pagerduty.com/services/ORD123
spec:
lifecycle: "production"
tier: "Tier 1"
YAML definition for a manually defined datastore
YAML definition for a manually defined datastore
This example shows a kind:datastore definition for a manually declared datastore.
apiVersion: v3
kind: datastore
metadata:
name: web-store-mongo
displayName: "Store Inventory DB (MongoDB)"
description: Stores order transaction data for Shopist e-commerce
owner: shopist
additionalOwners:
- name: infra-team
type: team
links:
- name: "DB Runbook"
type: runbook
url: https://wiki.internal/runbooks/orders-db
- name: "Schema Repo"
type: repo
provider: github
url: https://github.com/org/orders-db-schema
integrations:
pagerduty:
serviceURL: https://pagerduty.com/services/ORD123
spec:
lifecycle: "production"
tier: "Tier 1"
Datastore peer tags
For inferred entities, Datadog uses standard span attributes to construct peer.* tags. The metadata.name value in your entity definition must exactly match the inferred peer tags. Manually defined datastores do not need to follow this convention.
Common peer tags for datastore entities:
| Peer Tag | Source Attributes |
|---|---|
peer.aws.dynamodb.table | tablename |
peer.aws.s3.bucket | bucketname, aws.s3.bucket |
peer.cassandra.contact.points | db.cassandra.contact.points |
peer.couchbase.seed.nodes | db.couchbase.seed.nodes |
peer.db.name | db.name, mongodb.db, db.instance, cassandra.keyspace, db.namespace |
peer.db.system | db.system |
Learn more about peer tags and inferred entities.
In Software Catalog, a queue (kind:queue) represents a message queue or stream-based messaging component that services interact with. Queues can represent systems such as Apache Kafka, Amazon SQS, RabbitMQ, and Google Pub/Sub.
Queue entities can be:
- Inferred by APM when instrumented services produce to or consume from a messaging system.
- Manually defined to represent uninstrumented queues or enrich inferred ones with additional metadata.
Note: If Data Streams Monitoring is enabled, the queue entity page displays metrics such as throughput, service latency, and processing errors. Otherwise, the page shows basic trace-derived metrics and service dependency relationships.
Example YAML definitions
YAML for an inferred queue
YAML for an inferred queue
This example shows a kind:queue definition for a queue automatically detected by APM.
Note: The metadata.name value must exactly match the peer tags used by APM.
apiVersion: v3
kind: queue
metadata:
name: peer.messaging.destination:checkout-events
displayName: "Checkout Events Queue (Kafka)"
description: Captures all checkout-related events for downstream processing
owner: shopist
additionalOwners:
- name: platform-team
type: team
links:
- name: "Queue Runbook"
type: runbook
url: https://wiki.internal/runbooks/checkout-events
- name: "Schema Repo"
type: repo
provider: github
url: https://github.com/org/checkout-schema
integrations:
pagerduty:
serviceURL: https://pagerduty.com/services/MESSAGING123
spec:
lifecycle: "production"
tier: "Tier 1"
YAML for a manually defined queue
YAML for a manually defined queue
This example shows a kind:queue definition for a manually declared queue.
apiVersion: v3
kind: queue
metadata:
name: checkout-events-kafka
displayName: "Checkout Events Queue (Kafka)"
description: Captures all checkout-related events for downstream processing
owner: shopist
additionalOwners:
- name: platform-team
type: team
links:
- name: "Queue Runbook"
type: runbook
url: https://wiki.internal/runbooks/checkout-events
- name: "Schema Repo"
type: repo
provider: github
url: https://github.com/org/checkout-schema
integrations:
pagerduty:
serviceURL: https://pagerduty.com/services/MESSAGING123
spec:
lifecycle: "production"
tier: "Tier 1"
Queue peer tags
For inferred entities, Datadog uses standard span attributes to construct peer.* tags. The metadata.name value in your entity definition must exactly match the inferred peer tags. Manually defined queues do not need to follow this convention.
Common peer tags for kind:queue entities:
| Peer Tag | Source Attributes |
|---|---|
peer.aws.kinesis.stream | streamname |
peer.aws.sqs.queue | queuename |
peer.kafka.bootstrap.servers | messaging.kafka.bootstrap.servers |
peer.messaging.destination | topicname, messaging.destination, messaging.destination.name, messaging.rabbitmq.exchange, amqp.destination, ampqb.queue, amqp.exchange, msmq.queue.path, aws.queue.name |
peer.messaging.system | messaging.system |
Learn more about peer tags and inferred entities.
In Software Catalog, a frontend (kind:frontend) represents a frontend application—such as a browser-based single-page application or mobile app—that interacts with services and APIs. Frontend entities offer a structured way to model user-facing applications in the same catalog alongside backend services.
YAML for RUM app by name
YAML for RUM app by name
This example shows a kind:frontend definition for a frontend application in RUM, linked by the name. You can find the name and ID under Manage Applications, or you can click Add Metadata on an existing frontend app in Software Catalog to autofill the ID.
Example YAML definitions
apiVersion: v3
kind: frontend
metadata:
name: checkout-webapp
displayName: Checkout Web App
description: Main frontend experience for the checkout flow in Shopist
owner: shopist-frontend
additionalOwners:
- name: ux-platform-team
type: team
links:
- name: "UX Design Guidelines"
type: doc
url: https://wiki.internal/checkout-design
- name: "Frontend Source Code"
type: repo
provider: github
url: https://github.com/shopist/checkout-webapp
spec:
type: browser
lifecycle: production
tier: tier1
dependsOn:
- service:checkout-api
- service:payment-service
componentOf:
- system:shopist-checkout-platform
YAML for RUM app by ID
YAML for RUM app by ID
This example shows a kind:frontend definition for a frontend application in RUM, linked by the ID. You can find the name and ID under Manage Applications, or you can click Add Metadata on an existing frontend app in Software Catalog to autofill the ID.
Example YAML definitions
apiVersion: v3
kind: frontend
metadata:
name: rum_application:750904cc-cdde-4d06-b427-5d3fec477219
displayName: Checkout Web App
description: Main frontend experience for the checkout flow in Shopist
owner: shopist-frontend
additionalOwners:
- name: ux-platform-team
type: team
links:
- name: "UX Design Guidelines"
type: doc
url: https://wiki.internal/checkout-design
- name: "Frontend Source Code"
type: repo
provider: github
url: https://github.com/shopist/checkout-webapp
spec:
type: browser
lifecycle: production
tier: tier1
dependsOn:
- service:checkout-api
- service:payment-service
componentOf:
- system:shopist-checkout-platform
YAML for manually defined frontend app
YAML for manually defined frontend app
This example shows a kind:frontend definition for a manually declared frontend app.
Example YAML definitions
apiVersion: v3
kind: frontend
metadata:
name: checkout-webapp
displayName: Checkout Web App
description: Main frontend experience for the checkout flow in Shopist
owner: shopist-frontend
additionalOwners:
- name: ux-platform-team
type: team
links:
- name: "UX Design Guidelines"
type: doc
url: https://wiki.internal/checkout-design
- name: "Frontend Source Code"
type: repo
provider: github
url: https://github.com/shopist/checkout-webapp
spec:
type: browser
lifecycle: production
tier: tier1
dependsOn:
- service:checkout-api
- service:payment-service
componentOf:
- system:shopist-checkout-platform
When this definition is created:
- The frontend app appears under the Frontend Apps section in Software Catalog.
- If a RUM application exists with the same name or ID, its telemetry is automatically linked. You can find the name and ID under Manage Applications, or you can click Add Metadata on an existing frontend app in Software Catalog to autofill the ID.
- The entity aggregates metadata, dependencies, and real-time RUM performance metrics in a unified view.
You can define custom entity types beyond service, system, datastore, queue, and API. Custom entities allow you to represent any component or resource that is important to your organization but does not fit into the standard categories.
First, define the kinds you want to use with this API. Only entities of the kinds you’ve explicitly set up are accepted. After you’ve defined the allowed kinds, entities of that kind can be defined in the UI or programmatically sent through the existing Software Catalog APIs, GitHub integration, and Terraform module. In the example below, a user is declaring a library with links, tags, and owning teams.
Example YAML:
entity.datadog.yaml
apiVersion: v3
kind: library
metadata:
name: my-library
displayName: My Library
tags:
- tag:value
links:
- name: shopping-cart runbook
type: runbook
url: https://runbook/shopping-cart
- name: shopping-cart architecture
provider: gdoc
url: https://google.drive/shopping-cart-architecture
type: doc
- name: shopping-cart Wiki
provider: wiki
url: https://wiki/shopping-cart
type: doc
- name: shopping-cart source code
provider: github
url: http://github/shopping-cart
type: repo
contacts:
- name: Support Email
type: email
contact: team@shopping.com
- name: Support Slack
type: slack
contact: https://www.slack.com/archives/shopping-cart
owner: myteam
additionalOwners:
- name: opsTeam
type: operator
Further reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: