- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- Notebooks
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Search
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API-based Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Service Level Objectives
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Event Management
- Incident Response
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- End User Device Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Storage Management
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Session Replay
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Code Coverage
- PR Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Developer Integrations
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- AI Guard
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Configuration
- Sources
- Processors
- Destinations
- Packs
- Akamai CDN
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs
- AWS Application Load Balancer Logs
- AWS CloudTrail
- AWS Elastic Load Balancer Logs
- AWS Network Load Balancer Logs
- Cisco ASA
- Cloudflare
- F5
- Fastly
- Fortinet Firewall
- HAProxy Ingress
- Istio Proxy
- Juniper SRX Firewall Traffic Logs
- Netskope
- NGINX
- Okta
- Palo Alto Firewall
- Windows XML
- ZScaler ZIA DNS
- Zscaler ZIA Firewall
- Zscaler ZIA Tunnel
- Zscaler ZIA Web Logs
- Search Syntax
- Scaling and Performance
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Guides and Resources
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
Test Impact Analysis for Ruby
This product is not supported for your selected Datadog site. ().
Compatibility
Test Impact Analysis is only supported in the following versions and testing frameworks:
datadog-ci >= 1.0Ruby >= 2.7- JRuby is not supported.
rspec >= 3.0.0minitest >= 5.0.0cucumber >= 3.0.0
Setup
Test Optimization
Prior to setting up Test Impact Analysis, set up Test Optimization for Ruby. If you are reporting data through the Agent, use v6.40 and later or v7.40 and later.
Activate Test Impact Analysis for the test service
You, or a user in your organization with the Intelligent Test Runner Activation (intelligent_test_runner_activation_write) permission, must activate Test Impact Analysis on the Test Service Settings page.
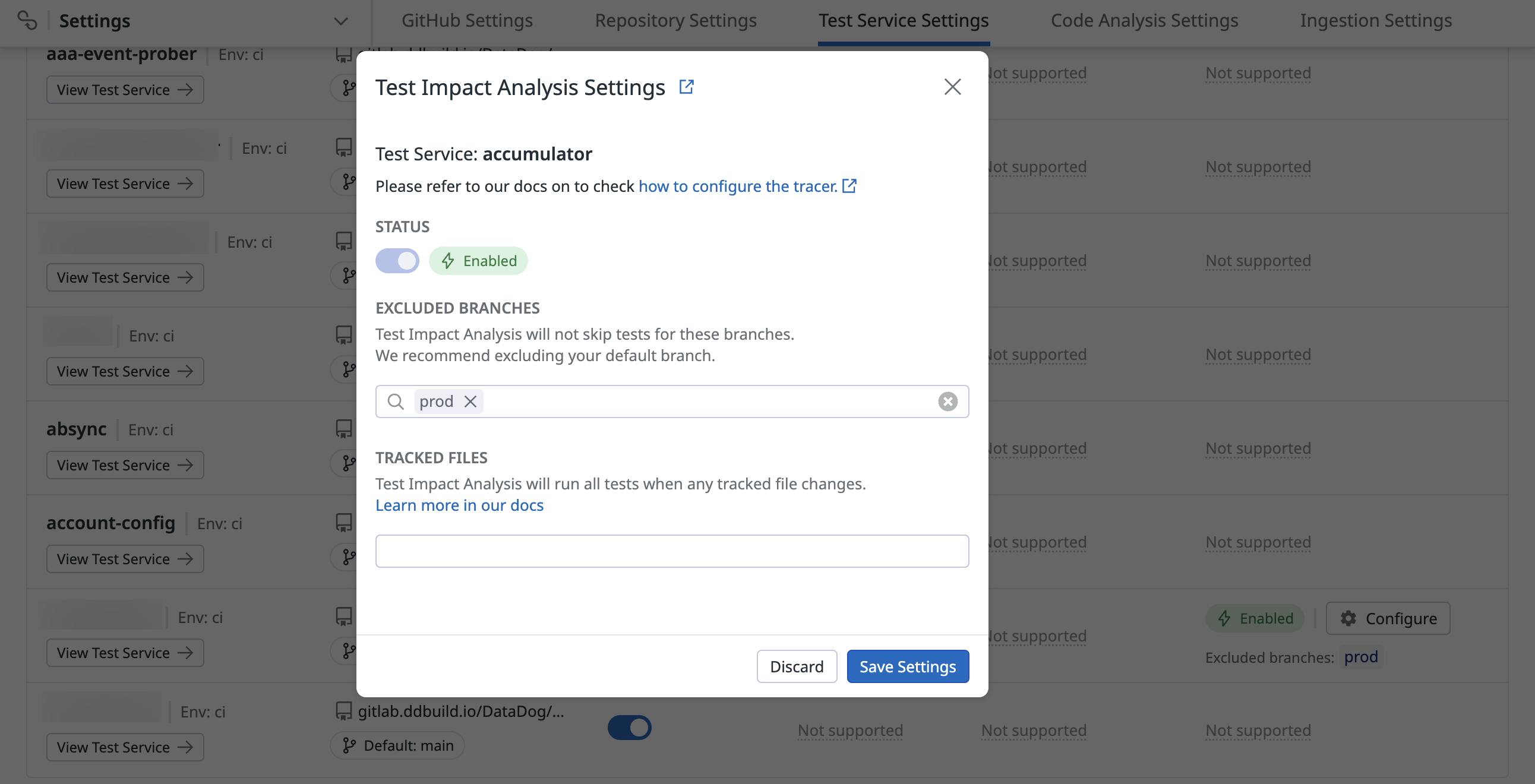
Run tests with Test Impact Analysis enabled
After completing setup, run your tests as you normally do.
Known limitations
Test Impact Analysis uses code coverage data to determine whether or not tests should be skipped. In certain situations, code coverage data alone is not enough to determine whether to skip a test.
Coverage limitations
The following limitations apply to how code coverage is collected:
- Non-Ruby files are not tracked by default: Changes to non-Ruby files such as fixtures, YAML configuration, i18n translation files, or other data files are not detected by code coverage. Tests that read data from these files may be incorrectly skipped when these files change.
- Suite-level hooks: Code coverage for suite-level hooks (for example,
before(:all)orbefore(:context)in RSpec) is attributed to the entire test suite rather than individual tests. This may affect skip decisions for tests that depend on setup performed in these hooks. - Forked processes: Per-test code coverage only collects coverage for the main process. Tests that spawn child processes or use forked execution do not have coverage collected for code running in those processes.
- Constant references across files: Accessing a constant defined in another file does not count as covered code. If a test’s behavior depends on constants defined elsewhere, changes to those constants may not trigger the test to run. This is supported as an experimental feature. See Static dependencies analysis for more information.
External dependencies
Tests that interact with external systems may be incorrectly skipped:
- Tests that make calls to external APIs or services (such as remote REST APIs)
- Tests that run external processes or shell commands
- Tests that depend on global shared state (for example, caches, databases, or files created by a different test or process)
Recommendations
When you encounter these limitations, consider the following approaches:
- Mark tests as unskippable: For tests that make external calls, fork processes, or depend on global shared state, mark them as unskippable to ensure they always run.
- Configure tracked files: If your tests depend on non-Ruby files like fixtures, i18n files, or configuration files, add these files to your tracked files configuration. This causes all tests to run when these files change.
Rails system tests
Test Impact Analysis supports Rails system tests that use ActionDispatch::SystemTestCase or ApplicationSystemTestCase, as long as the server runs in the same process as the test code. This is the default behavior in Rails system tests.
Static dependencies analysis (experimental)
By default, Ruby’s code coverage does not track constant references across files. When a test accesses a constant defined in another file, changes to that constant’s file may not trigger the test to run.
Static dependencies analysis addresses this limitation by analyzing Ruby’s compiled bytecode to find constant references and resolve them to source files.
Compatibility
Static dependencies analysis requires:
datadog-ci >= 1.26.0Ruby >= 3.2
Enabling static dependencies analysis
To enable this experimental feature, set the following environment variable in your CI configuration:
DD_TEST_OPTIMIZATION_TIA_STATIC_DEPS_COVERAGE_ENABLED(Optional)- Enable static dependencies analysis to track constant references across files.
Default:false
Limitations
The following limitations apply to static dependencies analysis:
- Requires eager loading: Only works when your code is eager loaded in tests. If constants are loaded dynamically, their source locations cannot be resolved correctly.
- Dynamic lookups not supported: Constants accessed through metaprogramming (such as
const_getorconstantize) are not detected. - Unqualified constant names: Constants accessed without their full namespace path may not be resolved correctly (for example
MyConstinstead ofMyModule::MyConst)
Unskippable tests
You can override the Test Impact Analysis’s behavior and prevent specific tests from being skipped. These tests are referred to as unskippable tests.
Marking tests as unskippable
To ensure that RSpec tests within a specific block are not skipped, add the metadata key datadog_itr_unskippable with the value true to any describe, context, or it block. This marks all tests in that block as unskippable.
# mark the whole file as unskippable
RSpec.describe MyClass, datadog_itr_unskippable: true do
describe "#my_method" do
context "when called without arguments" do
it "works" do
end
end
end
end
# mark one test as unskippable
RSpec.describe MyClass do
describe "#my_method" do
context "when called without arguments" do
it "works", datadog_itr_unskippable: true do
end
end
end
end
# mark specific block as unskippable
RSpec.describe MyClass do
describe "#my_method", datadog_itr_unskippable: true do
context "when called without arguments" do
it "works" do
end
end
end
end
To mark an entire feature file as unskippable in Cucumber, use the @datadog_itr_unskippable tag. This prevents Test Impact Analysis from skipping any of the scenarios defined in that feature file.
To make only specific scenarios unskippable, apply this tag directly to the desired scenario.
@datadog_itr_unskippable
Feature: Unskippable feature
Scenario: Say greetings
When the greeter says greetings
Then I should have heard "greetings"
Feature: An unskippable scenario
@datadog_itr_unskippable
Scenario: Unskippable scenario
When the ITR wants to skip this scenario
Then it will never be skipped
Scenario: Skippable scenario
When the ITR wants to skip this scenario
Then it will be skipped
To make an entire Minitest subclass unskippable, use the datadog_itr_unskippable method. If you want to mark specific tests within the subclass as unskippable, provide the names of these test methods as arguments to the datadog_itr_unskippable method call.
# mark the whole class unskippable
class MyTest < Minitest::Test
datadog_itr_unskippable
def test_my_method
end
end
# here only test1 and test2 are unskippable
class MyTest < Minitest::Test
datadog_itr_unskippable "test1", "test2"
def test1
end
def test2
end
def test3
end
end
Temporarily disabling Test Impact Analysis
Test Impact Analysis can be disabled locally by setting the DD_CIVISIBILITY_ITR_ENABLED environment variable to false or 0.
DD_CIVISIBILITY_ITR_ENABLED(Optional)- Enable the Test Impact Analysis coverage and test skipping features
Default:(true)
Further Reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles:
