- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- APM Terms and Concepts
- Application Instrumentation
- APM Metrics Collection
- Trace Pipeline Configuration
- Correlate Traces with Other Telemetry
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origins for Spans
- Service Observability
- Endpoint Observability
- Dynamic Instrumentation
- Live Debugger
- Error Tracking
- Data Security
- Guides
- Troubleshooting
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Log Management
- Administration
SQL Server
Supported OS
Integration version22.7.0
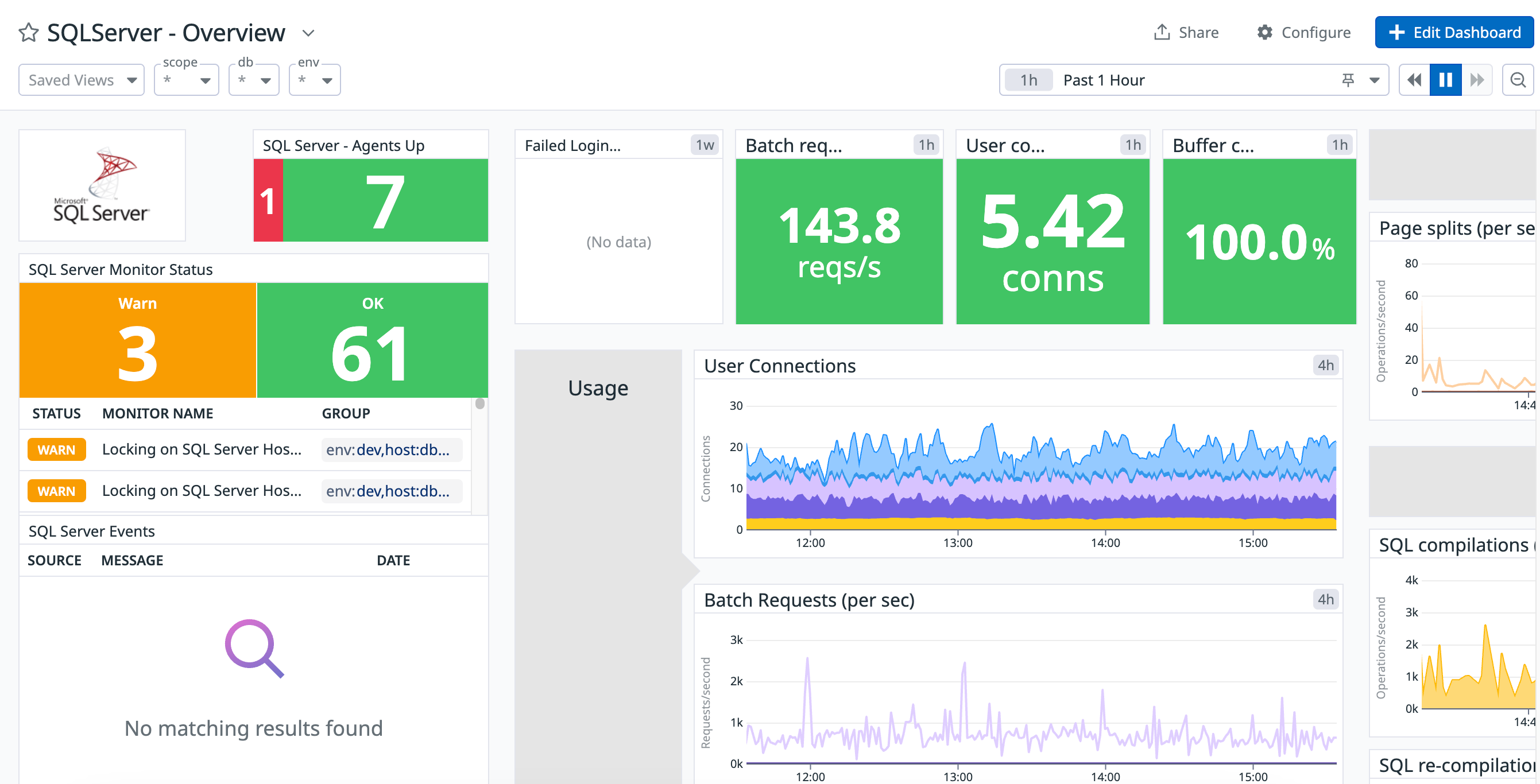
Overview
The SQL Server integration tracks the performance of your SQL Server instances. It collects metrics for number of user connections, rate of SQL compilations, and more.
Enable Database Monitoring (DBM) for enhanced insight into query performance and database health. In addition to the standard integration, Datadog DBM provides query-level metrics, live and historical query snapshots, wait event analysis, database load, query explain plans, and blocking query insights.
SQL Server 2012, 2014, 2016, 2017, 2019, and 2022 are supported.
Setup
This page describes the SQL Server Agent standard integration. If you are looking for the Database Monitoring product for SQL Server, see Datadog Database Monitoring.
Installation
The SQL Server check is included in the Datadog Agent package. No additional installation is necessary on your SQL Server instances.
Make sure that your SQL Server instance supports SQL Server authentication by enabling “SQL Server and Windows Authentication mode” in the server properties:
Server Properties -> Security -> SQL Server and Windows Authentication mode
Prerequisite
Note: To install Database Monitoring for SQL Server, select your hosting solution on the documentation site for instructions.
Supported versions of SQL Server for the SQL Server check are the same as for Database Monitoring. Visit the Setting up SQL Server page to see the currently supported versions under the Self-hosted heading.
Proceed with the following steps in this guide only if you are installing the standard integration alone.
Create a read-only login to connect to your server:
CREATE LOGIN datadog WITH PASSWORD = '<PASSWORD>'; USE master; CREATE USER datadog FOR LOGIN datadog; GRANT SELECT on sys.dm_os_performance_counters to datadog; GRANT VIEW SERVER STATE to datadog;To collect file size metrics per database, ensure the user you created (
datadog) has connect permission access to your databases by running:GRANT CONNECT ANY DATABASE to datadog;(Required for AlwaysOn and
sys.master_filesmetrics) To gather AlwaysOn andsys.master_filesmetrics, grant the following additional permission:GRANT VIEW ANY DEFINITION to datadog;
Configuration
Host
To configure this check for an Agent running on a host:
Edit the
sqlserver.d/conf.yamlfile, in theconf.d/folder at the root of your Agent’s configuration directory. See the sample sqlserver.d/conf.yaml for all available configuration options:init_config: instances: - host: "<SQL_HOST>,<SQL_PORT>" username: datadog password: "<YOUR_PASSWORD>" connector: adodbapi adoprovider: MSOLEDBSQL19 # Replace with MSOLEDBSQL for versions 18 and previousIf you use port autodiscovery, use
0forSQL_PORT. See the example check configuration for a comprehensive description of all options, including how to use custom queries to create your own metrics.Use supported drivers based on your SQL Server setup.
Note: It is also possible to use the Windows Authentication and not specify the username/password with:
connection_string: "Trusted_Connection=yes"
Linux
Extra configuration steps are required to get the SQL Server integration running on a Linux host:
- Install an ODBC SQL Server driver, for example the Microsoft ODBC driver or the FreeTDS driver.
- Copy the
odbc.iniandodbcinst.inifiles into the/opt/datadog-agent/embedded/etcfolder. - Configure the
conf.yamlfile to use theodbcconnector and specify the proper driver as indicated in theodbcinst.inifile.
Log collection
Available for Agent versions >6.0
Collecting logs is disabled by default in the Datadog Agent, enable it in your
datadog.yamlfile:logs_enabled: trueAdd this configuration block to your
sqlserver.d/conf.yamlfile to start collecting your SQL Server logs:logs: - type: file encoding: utf-16-le path: "<LOG_FILE_PATH>" source: sqlserver service: "<SERVICE_NAME>"Change the
pathandserviceparameter values based on your environment. See the sample sqlserver.d/conf.yaml for all available configuration options.
Containerized
For containerized environments, see the Autodiscovery Integration Templates for guidance on applying the parameters below.
Metric collection
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
<INTEGRATION_NAME> | sqlserver |
<INIT_CONFIG> | blank or {} |
<INSTANCE_CONFIG> | {"host": "%%host%%,%%port%%", "username": "datadog", "password": "<UNIQUEPASSWORD>", "connector": "odbc", "driver": "FreeTDS"} |
See Autodiscovery template variables for details on passing <UNIQUEPASSWORD> as an environment variable instead of a label.
Log collection
Available for Agent versions >6.0
Collecting logs is disabled by default in the Datadog Agent. To enable it, see Kubernetes Log Collection.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
<LOG_CONFIG> | {"source": "sqlserver", "service": "sqlserver"} |
Validation
Run the Agent’s status subcommand and look for sqlserver under the Checks section.
Data Collected
Metrics
| sqlserver.access.full_scans (gauge) | Number of unrestricted full scans per second. These can be either base-table or full-index scans. (Perf. Counter: Access Methods - Full Scans/sec)Shown as operation |
| sqlserver.access.index_searches (gauge) | Number of index searches per second. These are used to start a range scan, reposition a range scan, revalidate a scan point, fetch a single index record, and search down the index to locate where to insert a new row. (Perf. Counter: Access Methods - Index Searches/sec)Shown as operation |
| sqlserver.access.page_splits (gauge) | The number of page splits per second. (Perf. Counter: Access Methods - Page Splits/sec)Shown as operation |
| sqlserver.access.probe_scans (gauge) | Number of probe scans per second that are used to find at most one single qualified row in an index or base table directly. (Perf. Counter: Access Methods - Probe Scans/sec)Shown as operation |
| sqlserver.access.range_scans (gauge) | Number of qualified range scans through indexes per second. (Perf. Counter: Access Methods - Range Scans/sec)Shown as operation |
| sqlserver.agent.active_jobs.duration (gauge) | Duration of currently running jobs on sqlserver agent (DBM Only) Shown as second |
| sqlserver.agent.active_jobs.step_info (gauge) | Presence of a most recent completed step for active jobs running on the sqlserver agent (DBM Only) |
| sqlserver.agent.completed_jobs.duration (gauge) | Duration of completed jobs on sqlserver agent (DBM Only) Shown as second |
| sqlserver.agent.completed_jobs.executions (gauge) | Number of executions of completed jobs on sqlserver agent (DBM Only) Shown as execution |
| sqlserver.ao.ag_sync_health (gauge) | Availability group synchronization health: 0 = Not healthy, 1 = Partially healthy, 2 = Healthy. Tags: availability_group, availability_group_name, synchronization_health_desc |
| sqlserver.ao.filestream_send_rate (gauge) | The rate at which the FILESTREAM files are shipped to the secondary replica. Tags: availability_group, availability_group_name, replica_server_name, failover_mode, availability_mode, db, replica_id, database_id, database_state, synchronization_state, failover_cluster, replica_roleShown as byte |
| sqlserver.ao.is_primary_replica (gauge) | Denotes if a replica is a primary(1) or secondary(0). Tags: availability_group, availability_group_name, replica_server_name, failover_mode, availability_mode, db, replica_id, database_id, database_state, synchronization_state, failover_cluster, replica_role |
| sqlserver.ao.log_send_queue_size (gauge) | Amount of log records of the primary database that has not been sent to the secondary databases. Tags: availability_group, availability_group_name, replica_server_name, failover_mode, availability_mode, db, replica_id, database_id, database_state, synchronization_state, failover_cluster, replica_roleShown as byte |
| sqlserver.ao.log_send_rate (gauge) | Average rate at which primary replica instance sent data during last active period. Tags: availability_group, availability_group_name, replica_server_name, failover_mode, availability_mode, db, replica_id, database_id, database_state, synchronization_state, failover_cluster, replica_roleShown as byte |
| sqlserver.ao.low_water_mark_for_ghosts (gauge) | A monotonically increasing number for the database indicating a low water mark used by ghost cleanup on the primary database. Tags: availability_group, availability_group_name, replica_server_name, failover_mode, availability_mode, db, replica_id, database_id, database_state, synchronization_state, failover_cluster, replica_role |
| sqlserver.ao.member.number_of_quorum_votes (gauge) | Number of quorum votes possessed by this quorum member. Tags: member_name, member_type, member_state, failover_cluster |
| sqlserver.ao.member.state (gauge) | The state of a member that’s a part of the WSFC quorum. Tags: member_name, member_type, member_state, failover_cluster |
| sqlserver.ao.member.type (gauge) | The type of member that’s a part of the WSFC quorum. Tags: member_name, member_type, member_state, failover_cluster |
| sqlserver.ao.primary_replica_health (gauge) | Recovery health of primary replica: 0 = In progress, 1 = Online. The metric is not emitted if on a secondary replica. Tags: availability_group, availability_group_name, synchronization_health_desc |
| sqlserver.ao.quorum_state (gauge) | State of the WSFC quorum. Tags: quorum_type, quorum_state, failover_cluster |
| sqlserver.ao.quorum_type (gauge) | Type of quorum used by the WSFC cluster. Tags: quorum_type, quorum_state, failover_cluster |
| sqlserver.ao.redo_queue_size (gauge) | Amount of log records in the log files of the secondary replica that has not yet been redone. Tags: availability_group, availability_group_name, replica_server_name, failover_mode, availability_mode, db, replica_id, database_id, database_state, synchronization_state, failover_cluster, replica_roleShown as byte |
| sqlserver.ao.redo_rate (gauge) | Average rate at which the log records are being redone on a given secondary database. Tags: availability_group, availability_group_name, replica_server_name, failover_mode, availability_mode, db, replica_id, database_id, database_state, synchronization_state, failover_cluster, replica_roleShown as byte |
| sqlserver.ao.replica_failover_mode (gauge) | Replica failover mode: 0 = Automatic failover, 1 = Manual failover. Tags: replica_server_name, availability_group, availability_group_name, failover_mode_desc |
| sqlserver.ao.replica_failover_readiness (gauge) | Replica failover readiness: 0 = Not ready for failover, 1 = Ready for failover. Tags: replica_server_name, availability_group, availability_group_name, failover_mode_desc |
| sqlserver.ao.replica_status (gauge) | Denotes an Availability Group replica’s status. Tags: availability_group, availability_group_name, replica_server_name, failover_mode, availability_mode, db, replica_id, database_id, database_state, synchronization_state, failover_cluster, replica_role |
| sqlserver.ao.replica_sync_state (gauge) | Replica synchronization state: 0 = Not synchronizing, 1 = Synchronizing, 2 = Synchronized, 3 = Reverting, 4 = Initializing. Tags: availability_group, availability_group_name, synchronization_health_desc |
| sqlserver.ao.secondary_lag_seconds (gauge) | The number of seconds that the secondary replica is behind the primary replica during synchronization. Tags: availability_group, availability_group_name, replica_server_name, failover_mode, availability_mode, db, replica_id, database_id, database_state, synchronization_state, failover_cluster, replica_roleShown as second |
| sqlserver.ao.secondary_replica_health (gauge) | Recovery health of secondary replica: 0 = In progress, 1 = Online. The metric is not emitted if on a primary replica. Tags: availability_group, availability_group_name, synchronization_health_desc |
| sqlserver.buffer.cache_hit_ratio (gauge) | The ratio of data pages found and read from the buffer cache over all data page requests. (Perf. Counter: Buffer Manager - Buffer cache hit ratio)Shown as fraction |
| sqlserver.buffer.checkpoint_pages (gauge) | The number of pages flushed to disk per second by a checkpoint or other operation that require all dirty pages to be flushed. (Perf. Counter: Buffer Manager - Checkpoint pages/sec)Shown as page |
| sqlserver.buffer.page_life_expectancy (gauge) | Duration that a page resides in the buffer pool. (Perf. Counter: Buffer Manager - Page life expectancy)Shown as second |
| sqlserver.buffer.page_reads (gauge) | Indicates the number of physical database page reads that are issued per second. This statistic displays the total number of physical page reads across all databases. (Perf. Counter: Buffer Manager - Page reads/sec)Shown as page |
| sqlserver.buffer.page_writes (gauge) | Indicates the number of physical database page writes that are issued per second. (Perf. Counter: Buffer Manager - Page writes/sec)Shown as page |
| sqlserver.cache.object_counts (gauge) | Number of cache objects in the cache. (Perf. Counter: Plan Cache - Cache Object Counts)Shown as object |
| sqlserver.cache.pages (gauge) | Number of 8-kilobyte (KB) pages used by cache objects. (Perf. Counter: Plan Cache - Cache Pages)Shown as object |
| sqlserver.database.active_transactions (gauge) | Number of active transactions across all databases on the SQL Server instance. Tags: db. (Perf. Counter: Databases - Active Transactions).Shown as transaction |
| sqlserver.database.avg_fragment_size_in_pages (gauge) | The average number of pages in one fragment on the leaf level of an IN_ROW_DATA allocation unit. Tags: db, object_name, schema, index_id, index_name |
| sqlserver.database.avg_fragmentation_in_percent (gauge) | Logical fragmentation for indexes, or extent fragmentation for heaps in the IN_ROW_DATA allocation unit. Tags: db, object_name, schema, index_id, index_name |
| sqlserver.database.backup_count (gauge) | The total count of successful backups made for a database. Note: This metric is not emitted on Azure managed databases. Tags: db |
| sqlserver.database.backup_restore_throughput (gauge) | Read/write throughput for backup and restore operations of a database per second. Tags: db. (Perf. Counter: Databases - Backup/Restore Throughput/sec) |
| sqlserver.database.files.size (gauge) | Current size of the database file. Tags: db, file_id, file_type, file_name, file_location, database_files_state_descShown as kibibyte |
| sqlserver.database.files.space_used (gauge) | Current used space of the database file. Tags: db, file_id, file_type, file_name, file_location, database_files_state_descShown as kibibyte |
| sqlserver.database.files.state (gauge) | Database file state: 0 = Online, 1 = Restoring, 2 = Recovering, 3 = Recovery_Pending, 4 = Suspect, 5 = Unknown, 6 = Offline, 7 = Defunct. Tags: db, file_id, file_type, file_name, file_location, database_files_state_desc |
| sqlserver.database.fragment_count (gauge) | The number of fragments in the leaf level of an IN_ROW_DATA allocation unit. Tags: db, object_name, schema, index_id, index_name |
| sqlserver.database.index_page_count (gauge) | Total number of index or data pages. Tags: db, object_name, schema, index_id, index_name |
| sqlserver.database.is_in_standby (gauge) | Whether or not the database is read-only for restore log. Tags: db, database_state_desc, database_recovery_model_desc |
| sqlserver.database.is_read_only (gauge) | Whether or not the database is marked as READ_ONLY. 0 = READ_WRITE, 1 = READ_ONLY. Tags: db, database_state_desc, database_recovery_model_desc |
| sqlserver.database.is_sync_with_backup (gauge) | Whether or not the database is marked for replication synchronization with backup. 0 = Not marked for replication sync, 1 = Marked for replication sync. Tags: db, database_state_desc, database_recovery_model_desc |
| sqlserver.database.log_bytes_flushed (gauge) | Total number of log bytes flushed. Tags: db. (Perf. Counter: Databases - Log Bytes Flushed/sec)Shown as byte |
| sqlserver.database.log_flush_wait (gauge) | Total wait time (in milliseconds) to flush the log. On an Always On secondary database, this value indicates the wait time for log records to be hardened to disk. Tags: db. (Perf. Counter: Databases - Log Flush Wait Time)Shown as millisecond |
| sqlserver.database.log_flushes (gauge) | Number of log flushes per second. Tags: db. (Perf. Counter: Databases - Log Flushes/sec)Shown as flush |
| sqlserver.database.master_files.size (gauge) | Current size of the database file. For a database snapshot, size reflects the maximum space that the snapshot can ever use for the file. Note: Use sqlserver.database.files.size for the actual size of FILESTREAM containers. Tags: db, file_id, file_type, file_location, database_files_state_descShown as kibibyte |
| sqlserver.database.master_files.state (gauge) | Database file state: 0 = Online, 1 = Restoring, 2 = Recovering, 3 = Recovery_Pending, 4 = Suspect, 5 = Unknown, 6 = Offline, 7 = Defunct. Tags: db, file_id, file_type, file_location, database_files_state_desc |
| sqlserver.database.replica.transaction_delay (gauge) | Total delay in waiting for unterminated commit acknowledgment for all the current transactions, in milliseconds. Tags: db. (Perf. Counter: Database Replica - Transaction Delay)Shown as millisecond |
| sqlserver.database.state (gauge) | Database state: 0 = Online, 1 = Restoring, 2 = Recovering, 3 = Recovery_Pending, 4 = Suspect, 5 = Emergency, 6 = Offline, 7 = Copying, 10 = Offline_Secondary. Tags: db, database_state_desc, database_recovery_model_desc |
| sqlserver.database.transactions (gauge) | Number of transactions started for the SQL Server instance per second. Tags: db. (Perf. Counter: Databases - Transactions/sec)Shown as transaction |
| sqlserver.database.write_transactions (gauge) | Number of transactions that wrote to all databases on the SQL Server instance and committed, in the last second. Tags: db. (Perf. Counter: Databases - Write Transactions/sec)Shown as transaction |
| sqlserver.fci.is_current_owner (gauge) | Whether or not this node is the current owner of the SQL Server FCI. Tags: node_name, status, failover_cluster |
| sqlserver.fci.status (gauge) | Status of the node in a SQL Server failover cluster instance. Tags: node_name, status, failover_cluster |
| sqlserver.files.io_stall (count) | Total time that users waited for I/O to complete on the file. Tags: logical_name, file_location, db, stateShown as millisecond |
| sqlserver.files.read_bytes (count) | Bytes read from the file. Tags: logical_name, file_location, db, stateShown as byte |
| sqlserver.files.read_io_stall (count) | Total time that users waited for reads on the file. Tags: logical_name, file_location, db, stateShown as millisecond |
| sqlserver.files.read_io_stall_queued (count) | Total latency from IO governance pools for reads on the file. Tags: logical_name, file_location, db, stateShown as millisecond |
| sqlserver.files.reads (count) | Number of reads issued on the file. Tags: logical_name, file_location, db, stateShown as read |
| sqlserver.files.size_on_disk (gauge) | Number of bytes used on the disk for this file. Tags: logical_name, file_location, db, stateShown as byte |
| sqlserver.files.write_io_stall (count) | Total time that users waited for writes on the file. Tags: logical_name, file_location, db, stateShown as millisecond |
| sqlserver.files.write_io_stall_queued (count) | Total latency from IO governance pools for writes on the file. Tags: logical_name, file_location, db, stateShown as millisecond |
| sqlserver.files.writes (count) | Number of writes issued on the file. Tags: logical_name, file_location, db, stateShown as write |
| sqlserver.files.written_bytes (count) | Bytes written to the file. Tags: logical_name, file_location, db, stateShown as byte |
| sqlserver.index.user_lookups (count) | Number of bookmark lookups by user queries. Tags: db, table, index_name, schemaShown as occurrence |
| sqlserver.index.user_scans (count) | Number of scans by user queries that did not use ‘seek’ predicate. Tags: db, table, index_name, schemaShown as scan |
| sqlserver.index.user_seeks (count) | Number of seeks by user queries. Tags: db, table, index_name, schemaShown as occurrence |
| sqlserver.index.user_updates (count) | Number of updates by user queries. This includes Insert, Delete, and Updates representing the number of operations done, not the actual rows affected. Tags: db, table, index_name, schemaShown as update |
| sqlserver.latches.latch_wait_time (gauge) | Average latch wait time (in milliseconds) for latch requests that had to wait. (Perf. Counter: Locks - Average Latch Wait Time (ms))Shown as millisecond |
| sqlserver.latches.latch_waits (gauge) | Number of latch requests that could not be granted immediately. (Perf. Counter: Locks - Latch Waits/sec)Shown as request |
| sqlserver.locks.deadlocks (gauge) | Number of lock requests per second that resulted in a deadlock. (Perf. Counter: Locks - Number of Deadlocks/sec)Shown as request |
| sqlserver.log_shipping_primary.backup_threshold (gauge) | Seconds allowed to elapse between backup operations before a SQL Server job alert is generated. (Tags: primary_db, primary_server, primary_id)Shown as second |
| sqlserver.log_shipping_primary.time_since_backup (gauge) | Seconds since the last transaction log backup operation on the primary server. (Tags: primary_db, primary_server, primary_id)Shown as second |
| sqlserver.log_shipping_secondary.last_restored_latency (gauge) | The amount of time, in seconds, that elapsed between when the log backup was created on the primary and when it was restored on the secondary. (Tags: primary_db, primary_server, secondary_db, secondary_server, secondary_id)Shown as second |
| sqlserver.log_shipping_secondary.restore_threshold (gauge) | Seconds allowed to elapse between restore operations before a SQL Server job alert is generated. (Tags: primary_db, primary_server, secondary_db, secondary_server, secondary_id)Shown as second |
| sqlserver.log_shipping_secondary.time_since_copy (gauge) | Seconds since last copy operation to the secondary server. (Tags: primary_db, primary_server, secondary_db, secondary_server, secondary_id)Shown as second |
| sqlserver.log_shipping_secondary.time_since_restore (gauge) | Seconds since the last restore operation on the secondary server. (Tags: primary_db, primary_server, secondary_db, secondary_server, secondary_id)Shown as second |
| sqlserver.memory.connection (gauge) | Specifies the total amount of dynamic memory the server is using for maintaining connections. (Perf. Counter: Memory Manager - Connection Memory (KB))Shown as kibibyte |
| sqlserver.memory.database_cache (gauge) | Specifies the amount of memory the server is currently using for the database pages cache. (Perf. Counter: Memory Manager - Database Cache Memory (KB))Shown as kibibyte |
| sqlserver.memory.granted_workspace (gauge) | Specifies the total amount of memory currently granted to executing processes, such as hash, sort, bulk copy, and index creation operations. (Perf. Counter: Memory Manager - Granted Workspace Memory (KB))Shown as kibibyte |
| sqlserver.memory.grants_outstanding (gauge) | Specifies the total number of processes that have successfully acquired a workspace memory grant. (Perf. Counter: Memory Manager - Memory Grants Outstanding) |
| sqlserver.memory.lock (gauge) | Specifies the total amount of dynamic memory the server is using for locks. (Perf. Counter: Memory Manager - Lock Memory (KB))Shown as kibibyte |
| sqlserver.memory.log_pool_memory (gauge) | Total amount of dynamic memory the server is using for Log Pool. (Perf. Counter: Memory Manager - Log Pool Memory (KB))Shown as kibibyte |
| sqlserver.memory.memory_grants_pending (gauge) | Specifies the total number of processes waiting for a workspace memory grant (Perf. Counter: Memory Manager - Memory Grants Pending) |
| sqlserver.memory.optimizer (gauge) | Specifies the total amount of dynamic memory the server is using for query optimization. (Perf. Counter: Memory Manager - Optimizer Memory (KB))Shown as kibibyte |
| sqlserver.memory.sql_cache (gauge) | Specifies the total amount of dynamic memory the server is using for the dynamic SQL cache. (Perf. Counter: Memory Manager - SQL Cache Memory (KB))Shown as kibibyte |
| sqlserver.memory.stolen (gauge) | Specifies the amount of memory the server is using for purposes other than database pages. (Perf. Counter: Memory Manager - Stolen Server Memory (KB))Shown as kibibyte |
| sqlserver.memory.total_server_memory (gauge) | Specifies the amount of memory the server has committed using the memory manager. (Perf. Counter: Memory Manager - Total Server Memory (KB))Shown as kibibyte |
| sqlserver.procedures.count (count) | Total count of executed stored procedures per procedure (DBM only). Tags: db, procedure_name.Shown as query |
| sqlserver.procedures.logical_reads (count) | Total number of logical reads performed by executed stored procedures per procedure (DBM only). Tags: db, procedure_name.Shown as read |
| sqlserver.procedures.logical_writes (count) | Total number of logical writes performed by executed stored procedures per procedure (DBM only). Tags: db, procedure_name.Shown as write |
| sqlserver.procedures.physical_reads (count) | Total number of physical reads performed by executed stored procedures per procedure (DBM only). Tags: db, procedure_name.Shown as read |
| sqlserver.procedures.spills (count) | The total number of pages spilled by execution of this stored procedure per procedure (DBM only). Tags: db, procedure_name. |
| sqlserver.procedures.time (count) | Total elapsed time for executed stored procedures per procedure (DBM only) Shown as nanosecond |
| sqlserver.procedures.worker_time (count) | Total CPU time consumed by executed stored procedures per procedure (DBM only). Tags: db, procedure_name.Shown as nanosecond |
| sqlserver.queries.clr_time (count) | Total time consumed inside Microsoft .NET Framework common language runtime (CLR) objects for executed queries per query (DBM only) Shown as nanosecond |
| sqlserver.queries.columnstore_segment_reads (count) | Total columnstore segments read by executed queries per query (DBM only) Shown as segment |
| sqlserver.queries.columnstore_segment_skips (count) | Total columnstore segments skipped by executed queries per query (DBM only) Shown as segment |
| sqlserver.queries.count (count) | Total count of executed queries per query (DBM only) Shown as query |
| sqlserver.queries.dop (count) | The total sum of degree of parallelism used by executions of this query per query (DBM only) |
| sqlserver.queries.duration.max (gauge) | The age of the longest running query per user, db, and app. (DBM only) Shown as nanosecond |
| sqlserver.queries.duration.sum (gauge) | The sum of the age of all running queries per user, db, and app. (DBM only) Shown as nanosecond |
| sqlserver.queries.ideal_memory_grant (count) | The total amount of ideal memory grant estimated by executions of this query per query (DBM only) Shown as kilobyte |
| sqlserver.queries.logical_reads (count) | Total number of logical reads performed by executed queries per query (DBM only) Shown as read |
| sqlserver.queries.logical_writes (count) | Total number of logical writes performed by executed queries per query (DBM only) Shown as write |
| sqlserver.queries.memory_grant (count) | The total amount of reserved memory received by executions of this query per query. It will always be 0 for querying a memory-optimized table (DBM only). Shown as kilobyte |
| sqlserver.queries.physical_reads (count) | Total number of physical reads performed by executed queries per query (DBM only) Shown as read |
| sqlserver.queries.reserved_threads (count) | The total sum of reserved parallel threads used by executions of this query per query (DBM only) Shown as thread |
| sqlserver.queries.rows (count) | Total number of rows returned by executed queries per query (DBM only) Shown as row |
| sqlserver.queries.spills (count) | The total number of pages spilled by execution of this query per query (DBM only) |
| sqlserver.queries.time (count) | Total elapsed time for executed queries per query (DBM only) Shown as nanosecond |
| sqlserver.queries.used_memory_grant (count) | The total amount of reserved memory used by executions of this query per query. It will always be 0 for querying a memory-optimized table (DBM only). Shown as kilobyte |
| sqlserver.queries.used_threads (count) | The total sum of used parallel threads used by executions of this query per query (DBM only) Shown as thread |
| sqlserver.queries.worker_time (count) | Total CPU time consumed by executed queries per query (DBM only) Shown as nanosecond |
| sqlserver.replica.flow_control_sec (gauge) | Number of times flow-control initiated in the last second. Flow Control Time (ms/sec) divided by Flow Control/sec is the average time per wait. (Perf. Counter: Database Replica - Flow Control/sec) |
| sqlserver.replica.transaction_delay (gauge) | Total delay in waiting for unterminated commit acknowledgment for all the current transactions, in milliseconds. (Perf. Counter: Database Replica - Transaction Delay)Shown as millisecond |
| sqlserver.scheduler.active_workers_count (gauge) | Number of workers that are active. An active worker is never preemptive, must have an associated task, and is either running, runnable, or suspended. Tags: ‘scheduler_id’, parent_node_idShown as worker |
| sqlserver.scheduler.current_tasks_count (gauge) | Number of current tasks that are associated with this scheduler. Tags: ‘scheduler_id’, parent_node_idShown as task |
| sqlserver.scheduler.current_workers_count (gauge) | Number of workers that are associated with this scheduler. Tags: ‘scheduler_id’, parent_node_idShown as worker |
| sqlserver.scheduler.runnable_tasks_count (gauge) | Number of workers, with tasks assigned to them, that are waiting to be scheduled on the runnable queue. Tags: ‘scheduler_id’, parent_node_idShown as task |
| sqlserver.scheduler.work_queue_count (gauge) | Number of tasks in the pending queue. These tasks are waiting for a worker to pick them up. Tags: ‘scheduler_id’, parent_node_idShown as unit |
| sqlserver.server.committed_memory (gauge) | The amount of memory committed to the memory manager Shown as byte |
| sqlserver.server.cpu_count (gauge) | The number of logical CPUs or vCPUs on the server. Shown as byte |
| sqlserver.server.physical_memory (gauge) | Total physical memory on the machine Shown as byte |
| sqlserver.server.target_memory (gauge) | Amount of memory that can be consumed by the memory manager. When this value is larger than the committed memory, then the memory manager will try to obtain more memory. When it is smaller, the memory manager will try to shrink the amount of memory committed. Shown as byte |
| sqlserver.server.uptime (gauge) | Total time elapsed since the last computer restart. Shown as second |
| sqlserver.server.virtual_memory (gauge) | Amount of virtual memory available to the process in user mode. Shown as byte |
| sqlserver.stats.auto_param_attempts (gauge) | Number of auto-parameterization attempts per second. (Perf. Counter: SQL Statistics - Auto-Param Attempts/sec)Shown as attempt |
| sqlserver.stats.batch_requests (gauge) | The number of batch requests per second. (Perf. Counter: Buffer Manager - Batch Requests/sec)Shown as request |
| sqlserver.stats.connections (gauge) | The number of user connections. If DBM is enabled, this metric is tagged with status, db, and user. Shown as connection |
| sqlserver.stats.failed_auto_param_attempts (gauge) | Number of failed auto-parameterization attempts per second. (Perf. Counter: SQL Statistics - Failed Auto-Params/sec)Shown as attempt |
| sqlserver.stats.lock_waits (gauge) | The number of times per second that SQL Server is unable to retain a lock right away for a resource. (Perf. Counter: Locks - Lock Waits/sec)Shown as lock |
| sqlserver.stats.procs_blocked (gauge) | The number of processes blocked. (Perf. Counter: General Statistics - Processes blocked)Shown as process |
| sqlserver.stats.safe_auto_param_attempts (gauge) | Number of safe auto-parameterization attempts per second. (Perf. Counter: SQL Statistics - Safe Auto-Params/sec)Shown as attempt |
| sqlserver.stats.sql_compilations (gauge) | The number of SQL compilations per second. (Perf. Counter: SQL Statistics - SQL Compilations/sec)Shown as operation |
| sqlserver.stats.sql_recompilations (gauge) | The number of SQL re-compilations per second. (Perf. Counter: SQL Statistics - SQL Re-Compilations/sec)Shown as operation |
| sqlserver.table.data_size (gauge) | The size in kibibytes of data stored in this table excluding internal index pages and allocation-management pages. Tags: database schema tableShown as kibibyte |
| sqlserver.table.row_count (gauge) | The number of rows in this table. Tags: database schema tableShown as row |
| sqlserver.table.total_size (gauge) | The total size of the table in kibibytes. Tags: database schema tableShown as kibibyte |
| sqlserver.table.used_size (gauge) | The size in kibibytes of data stored in this table including internal index pages and allocation-management pages. Tags: database schema tableShown as kibibyte |
| sqlserver.task.context_switches_count (gauge) | Number of scheduler context switches that this task has completed. Tags: ‘scheduler_id’ Shown as unit |
| sqlserver.task.pending_io_byte_average (gauge) | Average byte count of I/Os that are performed by this task. Tags: ‘scheduler_id’ Shown as byte |
| sqlserver.task.pending_io_byte_count (gauge) | Total byte count of I/Os that are performed by this task. Tags: ‘scheduler_id’ Shown as byte |
| sqlserver.task.pending_io_count (gauge) | Number of physical I/Os that are performed by this task. Tags: ‘scheduler_id’ Shown as unit |
| sqlserver.tempdb.file_space_usage.free_space (gauge) | The amount of free space in the tempdb database file. Note: This metric is not emitted on Azure managed databases. Tags: dbShown as mebibyte |
| sqlserver.tempdb.file_space_usage.internal_object_space (gauge) | The amount of space used by internal objects in the tempdb database file. Note: This metric is not emitted on Azure managed databases. Tags: dbShown as mebibyte |
| sqlserver.tempdb.file_space_usage.mixed_extent_space (gauge) | The amount of space used by mixed extents in the tempdb database file. Note: This metric is not emitted on Azure managed databases. Tags: dbShown as mebibyte |
| sqlserver.tempdb.file_space_usage.user_object_space (gauge) | The amount of space used by user objects in the tempdb database file. Note: This metric is not emitted on Azure managed databases. Tags: dbShown as mebibyte |
| sqlserver.tempdb.file_space_usage.version_store_space (gauge) | The amount of space used by the version store in the tempdb database file. Note: This metric is not emitted on Azure managed databases. Shown as mebibyte |
| sqlserver.transactions.longest_transaction_running_time (gauge) | The time (in seconds) that the oldest active transaction has been running. Only works if database is under read committed snapshot isolation level. (Perf. Counter: Transactions - Longest Transaction Running Time)Shown as second |
| sqlserver.transactions.version_cleanup_rate (gauge) | The cleanup rate of the version store in tempdb. (Perf. Counter: Transactions - Version Cleanup rate (KB/s))Shown as kibibyte |
| sqlserver.transactions.version_generation_rate (gauge) | The generation rate of the version store in tempdb. (Perf. Counter: Transactions - Version Generation rate (KB/s))Shown as kibibyte |
| sqlserver.transactions.version_store_size (gauge) | The size of the version store in tempdb. (Perf. Counter: Transactions - Version Store Size (KB))Shown as kibibyte |
| sqlserver.xe.events_not_in_xml (gauge) | Number of generated events that are missing in the XML representation of the ring buffer. Tags: session_nameShown as event |
| sqlserver.xe.session_status (gauge) | Status of the node in a SQL Server failover cluster instance. Tags: session_name |
Most of these metrics come from your SQL Server’s sys.dm_os_performance_counters table.
Events
The SQL server check does not include any events.
Service Checks
sqlserver.can_connect
Returns CRITICAL if the Agent is unable to connect to the monitored SQL Server instance. Returns OK otherwise.
Statuses: ok, critical
sqlserver.database.can_connect
Returns CRITICAL if the Agent is unable to connect to the autodiscovered SQL Server Database. Returns OK otherwise.
Statuses: ok, critical
Troubleshooting
Need help? Contact Datadog support.
If you are running the Agent on an ARM aarch64 processor, there is a known issue starting in version 14.0.0 of this check, which is bundled with Agent version 7.48.0. A Python dependency fails to load, and you’ll see the following message when running the Agent’s status subcommand:
Loading Errors
==============
sqlserver
---------
Core Check Loader:
Check sqlserver not found in Catalog
JMX Check Loader:
check is not a jmx check, or unable to determine if it's so
Python Check Loader:
unable to import module 'sqlserver': No module named 'sqlserver'
This is fixed in version 15.2.0 of the check and in Agent versions 7.49.1 and above.
Further Reading
- Monitor your Azure SQL Databases with Datadog
- Key metrics for SQL Server monitoring
- SQL Server monitoring tools
- Monitor SQL Server performance with Datadog
- Custom SQL Server metrics for detailed monitoring
- Strategize your Azure migration for SQL workloads with Datadog
- Optimize SQL Server performance with Datadog Database Monitoring
