- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- Notebooks
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Search
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Extend Datadog
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API-based Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Service Level Objectives
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Event Management
- Incident Response
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- End User Device Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Storage Management
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Session Replay
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Code Coverage
- PR Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Developer Integrations
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- AI Guard
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Configuration
- Sources
- Processors
- Destinations
- Packs
- Akamai CDN
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs
- AWS Application Load Balancer Logs
- AWS CloudTrail
- AWS Elastic Load Balancer Logs
- AWS Network Load Balancer Logs
- Cisco ASA
- Cloudflare
- F5
- Fastly
- Fortinet Firewall
- HAProxy Ingress
- Istio Proxy
- Juniper SRX Firewall Traffic Logs
- Netskope
- NGINX
- Okta
- Palo Alto Firewall
- Windows XML
- ZScaler ZIA DNS
- Zscaler ZIA Firewall
- Zscaler ZIA Tunnel
- Zscaler ZIA Web Logs
- Search Syntax
- Scaling and Performance
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Guides and Resources
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
Databricks
Supported OS
Integration version1.0.0
Overview
Datadog offers several Databricks monitoring capabilities.
Data Observability: Jobs Monitoring provides monitoring for your Databricks jobs and clusters. You can detect problematic Databricks jobs and workflows anywhere in your data pipelines, remediate failed and long-running-jobs faster, and optimize cluster resources to reduce costs.
Cloud Cost Management gives you a view to analyze all your Databricks DBU costs alongside the associated cloud spend.
Log Management enables you to aggregate and analyze logs from your Databricks jobs & clusters. You can collect these logs as part of Data Observability: Jobs Monitoring.
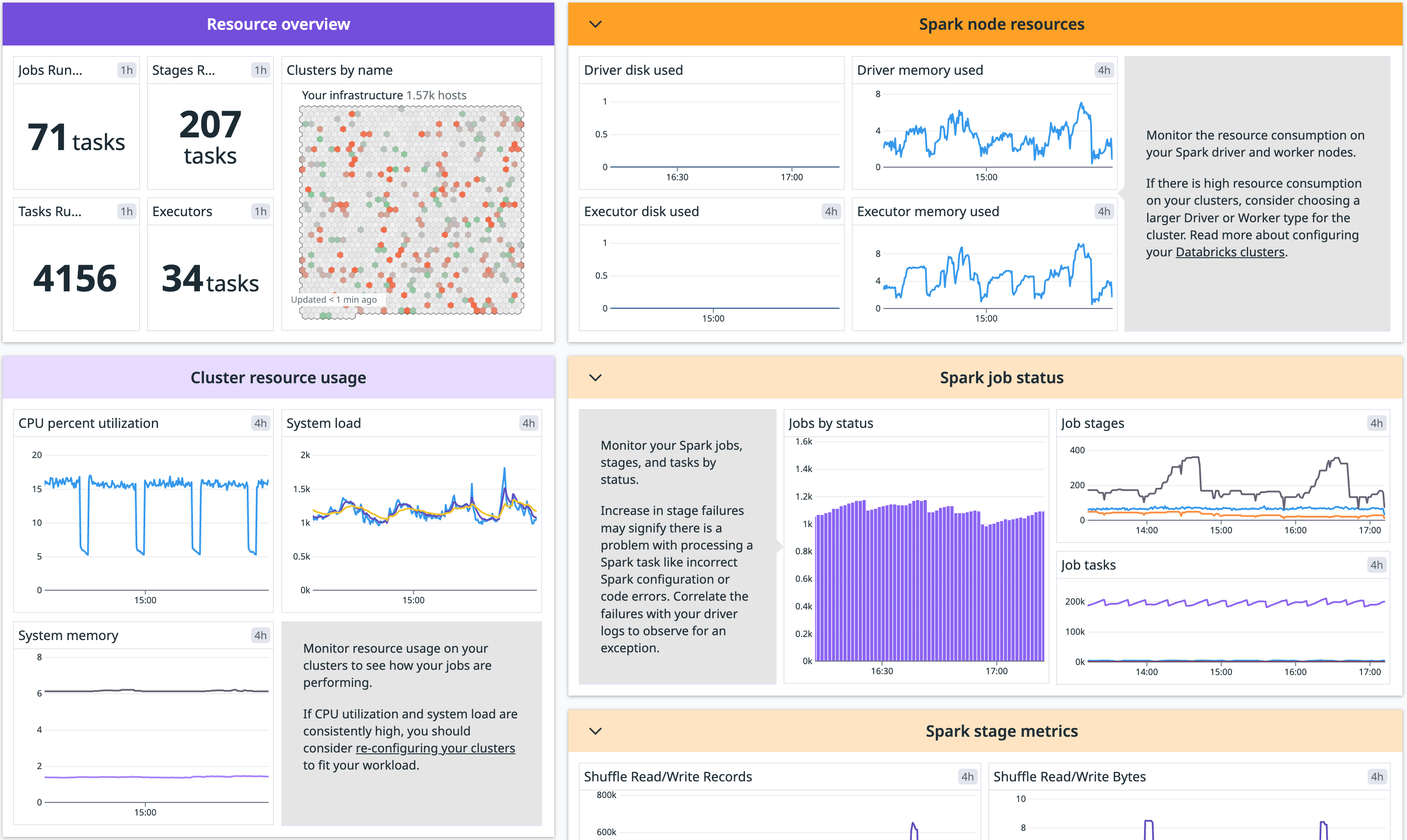
Infrastructure Monitoring gives you a limited subset of the Data Observability: Jobs Monitoring functionality - visibility into the resource utilization of your Databricks clusters and Apache Spark performance metrics.
Reference Tables allow you to import metadata from your Databricks workspace into Datadog. These tables enrich your Datadog telemetry with critical context like workspace names, job definitions, cluster configurations, and user roles.
Data Observability helps data teams detect, resolve, and prevent issues affecting data quality, performance, and cost. It monitors anomalies in volume, freshness, null rates, and distributions, and integrates with pipelines to correlate issues with job runs, data streams, and infrastructure events.
Model serving metrics provide insights into how your Databricks model serving infrastructure is performing. With these metrics, you can detect endpoints that have high error rate, high latency, are over/under provisioned, and more.
Setup
Installation
First, connect a new Databricks workspace in Datadog’s Databricks integration tile. Complete installation by configuring one or more capabilities of the integration: Data Jobs Monitoring, Cloud Cost Management, and Model Serving.
Configuration
Connect to a new Databricks Workspace
New workspaces must authenticate using OAuth. Workspaces integrated with a Personal Access Token continue to function and can switch to OAuth at any time. After a workspace starts using OAuth, it cannot revert to a Personal Access Token.
The following steps must be performed by a Databricks account admin. A workspace admin alone does not have sufficient permissions to create service principals at the account level.
- In your Databricks account console, click User Management in the left menu. Then, under the Service principals tab, click Add service principal.
- Under the Credentials & secrets tab, click Generate secret. Set Lifetime (days) to the maximum value allowed (730), then click Generate. Take note of your client ID and client secret. Also take note of your account ID, which can be found by clicking on your profile in the upper-right corner. (You must be in the account console to retrieve the account ID. The ID will not display inside a workspace.)
- Click Workspaces in the left menu, then select the name of your workspace.
- Go to the Permissions tab and click Add permissions.
- Search for the service principal you created and assign it the Admin permission.
- In Datadog, open the Databricks integration tile.
- On the Configure tab, click Add Databricks Workspace.
- Enter a workspace name, your Databricks workspace URL, account ID, and the client ID and secret you generated.
This option is only available for workspaces created before July 7, 2025. New workspaces must authenticate using OAuth.
In your Databricks workspace, click on your profile in the top right corner and go to Settings. Select Developer in the left side bar. Next to Access tokens, click Manage.
Click Generate new token, enter “Datadog Integration” in the Comment field, remove the default value in Lifetime (days), and click Generate. Take note of your token.
Important:
- Make sure you delete the default value in Lifetime (days) so that the token doesn’t expire and the integration doesn’t break.
- Ensure the account generating the token has CAN VIEW access for the Databricks jobs and clusters you want to monitor.
As an alternative, follow the official Databricks documentation to generate an access token for a service principal.
In Datadog, open the Databricks integration tile.
On the Configure tab, click Add Databricks Workspace.
Enter a workspace name, your Databricks workspace URL, and the Databricks token you generated.
Data Jobs Monitoring
- Connect a workspace in Datadog’s Databricks integration tile.
- In the Select products to set up integration section, set Data Jobs Monitoring to Enabled to start monitoring Databricks jobs and clusters.
- See the docs for Data Jobs Monitoring to complete the configuration.
Note: Ensure that the user or service principal being used has the necessary permissions to access your Databricks cost data.
Cloud Cost Management
- Connect a workspace in Datadog’s Databricks integration tile.
- In the Select products to set up integration section, set Cloud Cost Management to Enabled to view and analyze Databricks DBU costs alongside the associated cloud cost.
Note: Ensure that the user or service principal being used has the necessary permissions to access your Databricks cost data.
Model Serving
- Configure a workspace in Datadog’s Databricks integration tile.
- In the Select resources to set up collection section, set Metrics - Model Serving to Enabled in order to ingest model serving metrics.
Reference Table Configuration
- Configure a workspace in Datadog’s Databricks integration tile.
- In the accounts detail panel, click Reference Tables.
- In the Reference Tables tab, click Add New Reference Table.
- Provide the Reference table name, Databricks table name, and Primary key of your Databricks view or table.
- For optimal results, create a view in Databricks that includes only the specific data you want to send to Datadog. This means generating a dedicated table that reflects the exact scope needed for your use case.
- Click Save.
Data Observability
- Connect a workspace in Datadog’s Databricks integration tile.
- In the Select products to set up integration section, set Data Observability to Enabled to monitor data quality, freshness, and volume anomalies.
- See the docs for Data Observability for more details on configuration and features.
Permissions
For Datadog to access your Databricks cost data in Data Jobs Monitoring or Cloud Cost Management, the user or service principal used to query system tables must have the following permissions:
CAN USEpermission on the SQL Warehouse.- Read access to the system tables within Unity Catalog. This can be granted with:
GRANT USE CATALOG ON CATALOG system TO <service_principal>;
GRANT SELECT ON CATALOG system TO <service_principal>;
GRANT USE SCHEMA ON CATALOG system TO <service_principal>;
The user granting these must have the MANAGE privilege on CATALOG system.
Data Collected
Metrics
Model Serving Metrics
| databricks.model_serving.cpu_usage_percentage (gauge) | Average CPU utilization used across all replicas during the last minute Shown as percent |
| databricks.model_serving.gpu_mem_usage_percentage.avg (gauge) | Average GPU memory usage used across all GPUs during the minute Shown as percent |
| databricks.model_serving.gpu_mem_usage_percentage.max (gauge) | Maximum GPU memory usage used across all GPUs during the minute Shown as percent |
| databricks.model_serving.gpu_mem_usage_percentage.min (gauge) | Minimum GPU memory usage used across all GPUs during the minute Shown as percent |
| databricks.model_serving.gpu_usage_percentage.avg (gauge) | Average GPU utilization used across all GPUs during the minute Shown as percent |
| databricks.model_serving.gpu_usage_percentage.max (gauge) | Maximum GPU utilization used across all GPUs during the minute Shown as percent |
| databricks.model_serving.gpu_usage_percentage.min (gauge) | Minimum GPU utilization used across all GPUs during the minute Shown as percent |
| databricks.model_serving.mem_usage_percentage (gauge) | Average memory utilization used across all replicas during the last minute Shown as percent |
| databricks.model_serving.provisioned_concurrent_requests_total (gauge) | Number of provisioned concurrency during the last minute Shown as request |
| databricks.model_serving.request_4xx_count_total (gauge) | Number of 4xx errors during the last minute Shown as request |
| databricks.model_serving.request_5xx_count_total (gauge) | Number of 5xx errors during the last minute Shown as request |
| databricks.model_serving.request_count_total (gauge) | Number of requests during the last minute Shown as request |
| databricks.model_serving.request_latency_ms.75percentile (gauge) | 75th percentile request latency in milliseconds during the minute Shown as millisecond |
| databricks.model_serving.request_latency_ms.90percentile (gauge) | 90th percentile request latency in milliseconds during the minute Shown as millisecond |
| databricks.model_serving.request_latency_ms.95percentile (gauge) | 95th percentile request latency in milliseconds during the minute Shown as millisecond |
| databricks.model_serving.request_latency_ms.99percentile (gauge) | 99th percentile request latency in milliseconds during the minute Shown as millisecond |
Service Checks
The Databricks integration does not include any service checks.
Events
The Databricks integration does not include any events.
Troubleshooting
You can troubleshoot issues yourself by enabling the Databricks web terminal or by using a Databricks Notebook. Need help? Contact Datadog support.
Further Reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles:
