- Principales informations
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- Tracing
- Conteneurs
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Site Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Intégrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- OpenTelemetry
- Profileur
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Intégrations
- Développeurs
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Application mobile
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Alertes
- Watchdog
- Métriques
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Conteneurs
- Processes
- Sans serveur
- Surveillance réseau
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Termes et concepts de l'APM
- Sending Traces to Datadog
- APM Metrics Collection
- Trace Pipeline Configuration
- Connect Traces with Other Telemetry
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origin for Spans
- Observabilité des services
- Endpoint Observability
- Dynamic Instrumentation
- Live Debugger
- Suivi des erreurs
- Sécurité des données
- Guides
- Dépannage
- Profileur en continu
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Configuration de Postgres
- Configuration de MySQL
- Configuration de SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Données collectées
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Explorer les métriques de requête
- Explorer des échantillons de requêtes
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Dépannage
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- RUM et Session Replay
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Visibility
- Code Coverage
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Securité
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Pipelines d'observabilité
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
Test Impact Analysis for Go
Ce produit n'est pas pris en charge par le site Datadog que vous avez sélectionné. ().
Cette page n'est pas encore disponible en français, sa traduction est en cours.
Si vous avez des questions ou des retours sur notre projet de traduction actuel, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter.
Si vous avez des questions ou des retours sur notre projet de traduction actuel, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter.
Compatibility
Test Impact Analysis is only supported on orchestrion >= 0.9.4 + dd-trace-go >= 1.70.0.
Setup
Test Optimization
Prior to setting up Test Impact Analysis, set up Test Optimization for Go. If you are reporting data through the Agent, use v6.40 and later or v7.40 and later.
Activate Test Impact Analysis for the test service
You, or a user in your organization with the Intelligent Test Runner Activation (intelligent_test_runner_activation_write) permission, must activate Test Impact Analysis on the Test Service Settings page.
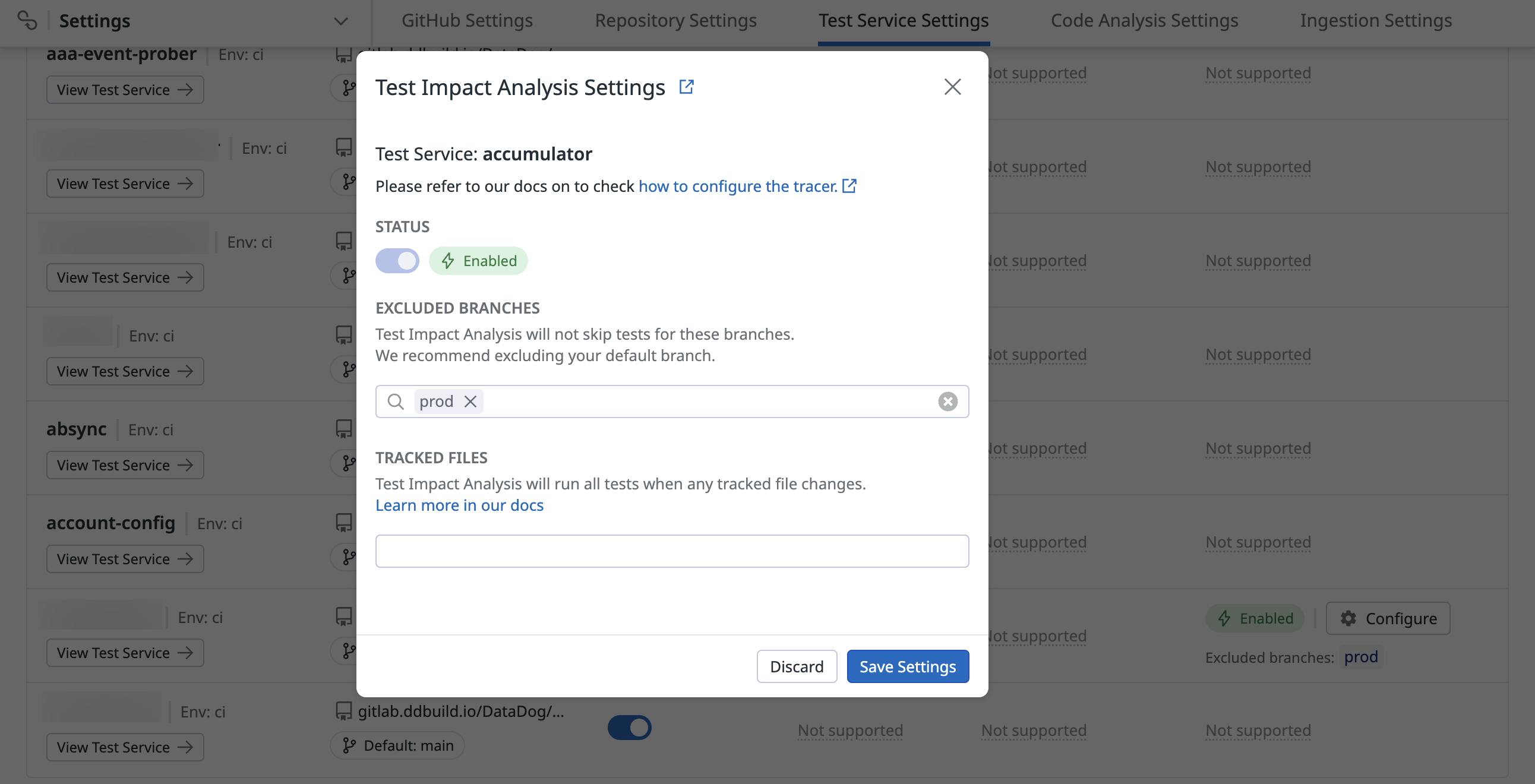
Run tests with Test Impact Analysis enabled
After completing setup, run your tests by using go test with the following code coverage options:
orchestrion go test ./... -cover -covermode=count -coverpkg ./...
-cover: The Test Impact Analysis feature uses the built-in Go’s code coverage processor, so you need to enable code coverage collection in thego testcommand.-covermode: must be eithercountoratomic. Becausesetis not supported, setting this value disables test impact analysis.-coverpkg: the code coverage analysis for each test must be configured to apply in all package dependencies and not only for the package being tested. This way, if a dependency changes, you can track the test affected by this change. If you run the test command from the root of the project (where the go.mod file is), you can use the./...wildcard. If not, you must manually list all package dependencies comma separated (pattern1, pattern2, pattern3, ...). For that, you could use thego list ./...command to get all the package names.
Having an incorrect -coverpkg value affects the ability of Test Impact Analysis to correctly track test coverage.
Disable skipping for specific tests
You can override the Test Impact Analysis behavior and prevent specific tests from being skipped. These tests are referred to as unskippable tests.
Why make tests unskippable?
Test Impact Analysis uses code coverage data to determine whether or not tests should be skipped. In some cases, this data may not be sufficient to make this determination.
Examples include:
- Tests that read data from text files.
- Tests that interact with APIs outside of the code being tested (such as remote REST APIs).
- Designating tests as unskippable ensures that Test Impact Analysis runs them regardless of coverage data.
Marking tests as unskippable
Individual test case
Add the //dd:test.unskippable comment to your test case to mark it as unskippable.
import (
"testing"
)
//dd:test.unskippable
func TestMyCustomTest(t *testing.T) {
...
}
Test suite
Add the //dd:suite.unskippable comment at the begining of the file to mark it as unskippable.
If a suite is marked as unskippable, none of the test cases from that suite can be skipped by Test Impact Analysis.
import (
"testing"
)
//dd:suite.unskippable
func TestMyCustomTest(t *testing.T) {
...
}
func TestMyCustomTest2(t *testing.T) {
...
}
Further Reading
Documentation, liens et articles supplémentaires utiles:
