- Principales informations
- Getting Started
- Datadog
- Site Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Agent
- Intégrations
- Conteneurs
- Dashboards
- Monitors
- Logs
- Tracing
- Profileur
- Tags
- API
- Service Catalog
- Session Replay
- Continuous Testing
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Incident Management
- Database Monitoring
- Cloud Security Management
- Cloud SIEM
- Application Security Management
- Workflow Automation
- CI Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Intelligent Test Runner
- Code Analysis
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Intégrations
- OpenTelemetry
- Développeurs
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Checks custom
- Intégrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Recommended Monitor
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Checks de service
- IDE Plugins
- Communauté
- Guides
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Application mobile
- CoScreen
- Cloudcraft
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Alertes
- Infrastructure
- Métriques
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Service Catalog
- API Catalog
- Error Tracking
- Service Management
- Infrastructure
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Conteneurs
- Sans serveur
- Surveillance réseau
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Profileur en continu
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Configuration de Postgres
- Configuration de MySQL
- Configuration de SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Données collectées
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Explorer les métriques de requête
- Explorer des échantillons de requêtes
- Dépannage
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Digital Experience
- RUM et Session Replay
- Product Analytics
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Continuous Testing
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Test Visibility
- Exécuteur de tests intelligent
- Code Analysis
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Securité
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Pipelines d'observabilité
- Log Management
- Administration
WebSocket Testing
Cette page n'est pas encore disponible en français, sa traduction est en cours.
Si vous avez des questions ou des retours sur notre projet de traduction actuel, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter.
Si vous avez des questions ou des retours sur notre projet de traduction actuel, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter.
Overview
WebSocket tests allow you to proactively open WebSocket connections on your endpoints to verify responses and defined conditions, such as overall response times or expected headers.
WebSocket tests can run from both managed and private locations depending on your preference for running the test from outside or inside your network. WebSocket tests can run on a schedule, on-demand, or directly within your CI/CD pipelines.
Configuration
You may create a test using one of the following options:
Create a test from a template:
- Hover over one of the pre-populated templates and click View Template. This opens a side panel displaying pre-populated configuration information, including: Test Details, Request Details, Assertions, Alert Conditions, and Monitor Settings.
- Click +Create Test to open the Define Request page, where you can review and edit the pre-populated configuration options. The fields presented are identical to those available when creating a test from scratch.
- Click Save Details to submit your API test.
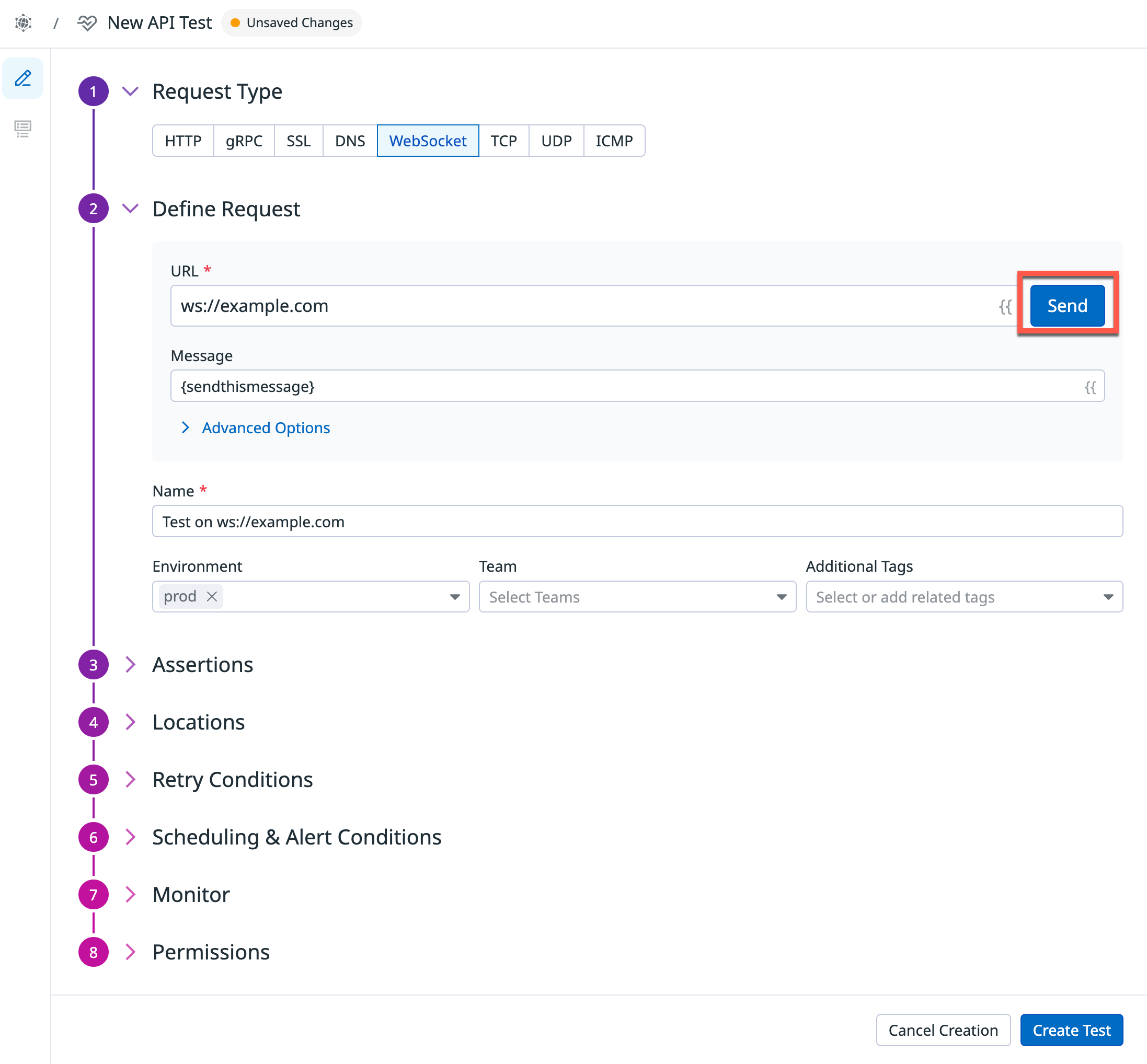
Build a test from scratch:
- To build a test from scratch, click the + Start from scratch template, then select the
WebSocketrequest type. - Specify the URL to run your test on.
- Enter the string you want to send in your test.
- Add Advanced Options (optional) to your test:
- Timeout: Specify the amount of time in seconds before the test times out.
- Request headers: Define headers to add to the HTTP request initiating the WebSocket connection. You can also override the default headers (for example, the
user-agentheader). - Cookies: Define cookies to add to the HTTP request initiating the WebSocket connection. Set multiple cookies using the format
<COOKIE_NAME1>=<COOKIE_VALUE1>; <COOKIE_NAME2>=<COOKIE_VALUE2>.
- HTTP Basic Auth: Add HTTP basic authentication credentials.
- To build a test from scratch, click the + Start from scratch template, then select the
Name your WebSocket test.
Add Environment Tags as well as any other tag to your WebSocket test. You can then use these tags to filter through your Synthetic tests on the Synthetic Monitoring & Continuous Testing page.
Click Send to try out the request configuration. A response preview is displayed on the right side of your screen.
Click Create Test to submit your API test.
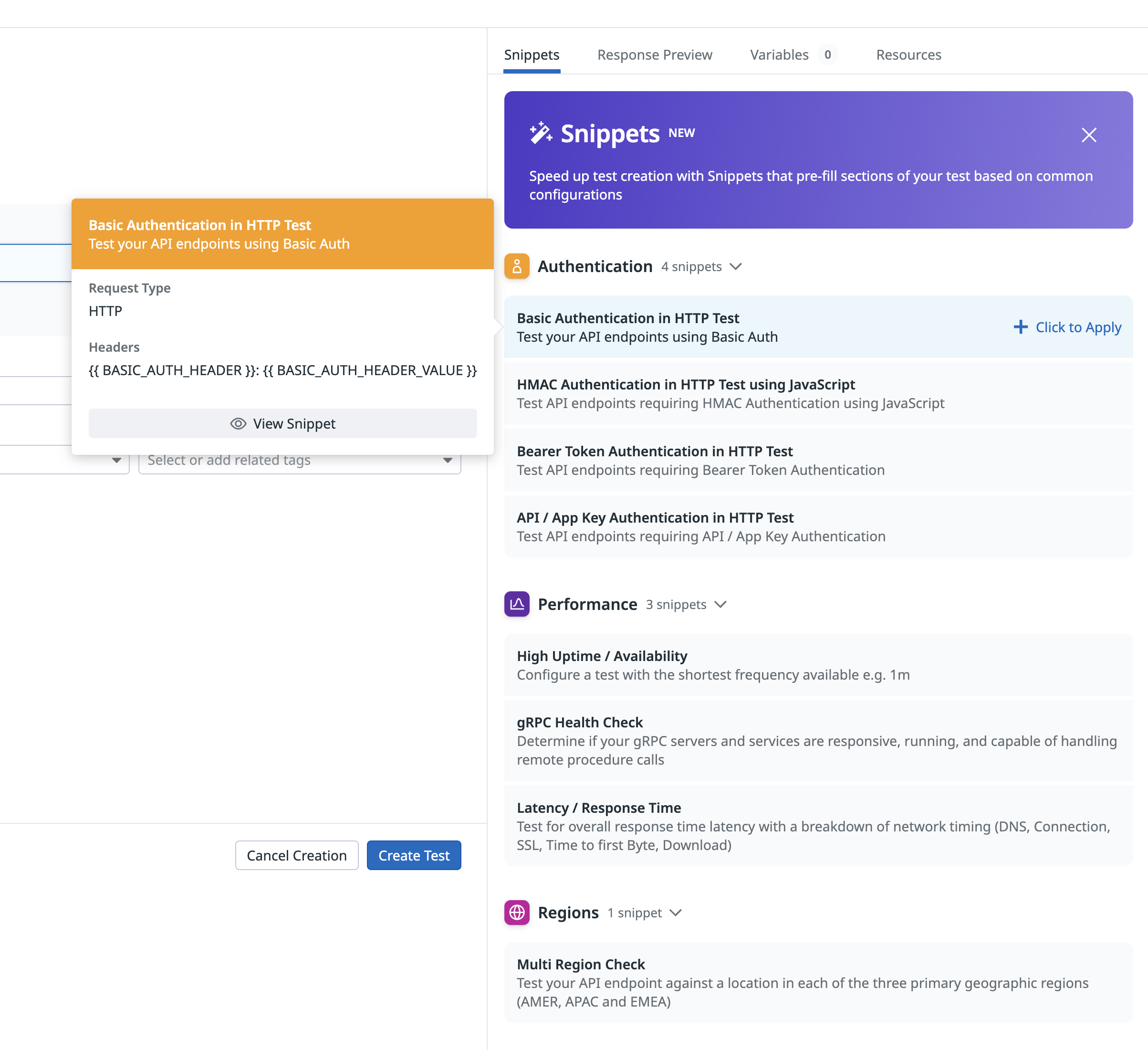
Snippets
When setting up a new Synthetic Monitoring API test, use snippets to automatically fill in basic auth, performance, and regions, rather than selecting these options manually. The following snippets are available:
Basic Auth: Automatically test your APIs using pre-populated basic auth headers, JavaScript, bearer token, and API/app key auth variables.
Performance: Automatically configure a test with the shortest frequency (one minute), perform a gRPC health check, and test for overall response time latency with a breakdown of network timing.
Regions: Automatically test your API endpoint against a location in each of the three primary geographic regions (AMER, APAC and EMEA).
Define assertions
Assertions define what an expected test result is. When you click Test URL, a basic assertion on response time is added. You must define at least one assertion for your test to monitor.
| Type | Operator | Value Type |
|---|---|---|
| response time | is less than | Integer (ms) |
| string response | contains, does not contain, is, is not,matches, does not match | String Regex |
| header | contains, does not contain, is, is not,matches, does not match | String Regex |
Select the response preview directly or click New Assertion to create an assertion. You can create up to 20 assertions per WebSocket test.
To perform OR logic in an assertion, use the matches regex or does not match regex comparators to define a regex with multiple expected values for the same assertion type like (0|100). The test result is successful if the string response or header assertions’ value is 0 or 100.
If a test does not contain an assertion on the response body, the body payload drops and returns an associated response time for the request within the timeout limit set by the Synthetics Worker.
If a test contains an assertion on the response body and the timeout limit is reached, an Assertions on the body/response cannot be run beyond this limit error appears.
Select locations
Select the Locations to run your WebSocket test from. WebSocket tests can run from both managed and private locations depending on your preference for running the test from outside or inside your network.
Datadog’s out-of-the-box managed locations allow you to test public-facing websites and endpoints from regions where your customers are located.
AWS:
| Americas | Asia Pacific | EMEA |
|---|---|---|
| Canada Central | Hong Kong | Bahrain |
| Northern California | Jakarta | Cape Town |
| Northern Virginia | Mumbai | Frankfurt |
| Ohio | Osaka | Ireland |
| Oregon | Seoul | London |
| São Paulo | Singapore | Milan |
| Sydney | Paris | |
| Tokyo | Stockholm |
GCP:
| Americas | Asia Pacific | EMEA |
|---|---|---|
| Dallas | Tokyo | Frankfurt |
| Los Angeles | ||
| Oregon | ||
| Virginia |
Azure:
| Region | Location |
|---|---|
| Americas | Virginia |
The Datadog for Government site (US1-FED) uses the following managed location:
| Region | Location |
|---|---|
| Americas | US-West |
Specify test frequency
WebSocket tests can run:
- On a schedule to ensure your most important endpoints are always accessible to your users. Select the frequency at which you want Datadog to run your WebSocket test.
- Within your CI/CD pipelines to start shipping without fearing faulty code might impact your customers’ experience.
- On-demand to run your tests whenever makes the most sense for your team.
Définir des conditions d’alerte
Définissez des conditions d’alerte afin de spécifier les circonstances dans lesquelles vous souhaitez qu’un test échoue et déclenche une alerte.
Règle d’alerte
Lorsque vous définissez les conditions d’alerte sur An alert is triggered if any assertion fails for X minutes from any n of N locations, une alerte se déclenche uniquement si les deux conditions suivantes se vérifient :
- Au moins un emplacement a donné lieu à un échec (au moins une assertion a échoué) au cours des X dernières minutes
- À un moment au cours des X dernières minutes, au moins n emplacements ont donné lieu à un échec.
Nouvelle tentative rapide
Votre test peut déclencher X nouvelles tentatives après Y ms en cas d’échec. Cet intervalle peut être personnalisé en fonction de vos préférences en matière d’alertes.
La disponibilité d’un emplacement est calculée pour chaque évaluation (quels que soient les résultats du dernier test avant l’évaluation). La disponibilité totale est calculée selon les conditions d’alerte configurées. Les notifications envoyées se basent sur la disponibilité totale.
Configurer le monitor de test
Votre test envoie une notification selon les conditions d’alerte définies au préalable. Cette section vous permet de définir les conditions et le message à envoyer à vos équipes.
Tout comme pour les monitors, sélectionnez les utilisateurs et/ou services qui doivent recevoir des notifications. Pour ce faire, ajoutez
@notificationau message, ou cherchez des membres d’équipe ou des intégrations connectées à l’aide du menu déroulant.Saisissez un message de notification pour le test. Ce champ accepte le format de mise en forme Markdown standard ainsi que les variables conditionnelles suivantes :
Variable conditionnelle Description {{ #is_alert }} S’affiche lorsque le test envoie une alerte. {{ ^is_alert }} S’affiche lorsque le test n’envoie pas d’alerte. {{ #is_recovery }} S’affiche lorsque le test est rétabli depuis un état d’alerte. {{ ^is_recovery }} S’affiche lorsque le test n’est pas rétabli depuis un état d’alerte. {{ #is_renotify }} S’affiche lorsque le monitor renvoie des notifications. {{ ^is_renotify }} S’affiche lorsque le monitor ne renvoie pas de notification. {{ #is_priority }} S’affiche lorsque le monitor correspond à la priorité (P1 à P5). {{ ^is_priority }} S’affiche lorsque le monitor ne correspond pas à la priorité (P1 à P5). Indiquez une fréquence de renvoi du message de notification en cas d’échec d’un test. Si vous ne souhaitez pas renvoyer de notification en cas d’échec, définissez l’option sur
Never renotify if the monitor has not been resolved.Cliquez sur Create pour enregistrer la configuration de votre test et votre monitor.
Pour en savoir plus, consultez la section Utiliser des monitors de test Synthetic.
Create local variables
To create a local variable, click + All steps > Variables. You can select one of the following available builtins to add to your variable string:
- {{ numeric(n) }}
- Generates a numeric string with
ndigits. - {{ alphabetic(n) }}
- Generates an alphabetic string with
nletters. - {{ alphanumeric(n) }}
- Generates an alphanumeric string with
ncharacters. - {{ date(n unit, format) }}
- Generates a date in one of Datadog’s accepted formats with a value corresponding to the UTC date the test is initiated at + or -
nunits. - {{ timestamp(n, unit) }}
- Generates a timestamp in one of Datadog’s accepted units with a value corresponding to the UTC timestamp the test is initiated at +/-
nunits. - {{ uuid }}
- Generates a version 4 universally unique identifier (UUID).
- {{ public-id }}
- Injects the Public ID of your test.
- {{ result-id }}
- Injects the Result ID of your test run.
To obfuscate local variable values in test results, select Hide and obfuscate variable value. Once you have defined the variable string, click Add Variable.
Use variables
You can use the global variables defined on the Settings page in the URL, advanced options, and assertions of your WebSocket tests.
To display your list of variables, type {{ in your desired field.
Test failure
A test is considered FAILED if it does not satisfy one or more assertions or if the request prematurely failed. In some cases, the test can fail without testing the assertions against the endpoint.
These reasons include the following:
CONNRESET- The connection was abruptly closed by the remote server. Possible causes include the web server encountering an error or crashing while responding, or loss of connectivity of the web server.
DNS- DNS entry not found for the test URL. Possible causes include misconfigured test URL or the wrong configuration of your DNS entries.
INVALID_REQUEST- The configuration of the test is invalid (for example, a typo in the URL).
SSL- The SSL connection couldn’t be performed. See the dedicated error page for more information.
TIMEOUT- The request couldn’t be completed in a reasonable time. Two types of
TIMEOUTerrors can happen:TIMEOUT: The request couldn't be completed in a reasonable time.indicates that the request duration hit the test defined timeout (default is set to 60s). For each request only the completed stages for the request are displayed in the network waterfall. For example, in the case ofTotal response timeonly being displayed, the timeout occurred during the DNS resolution.TIMEOUT: Overall test execution couldn't be completed in a reasonable time.indicates that the test duration (request + assertions) hits the maximum duration (60.5s).
WEBSOCKET- The WebSocket connection was closed or cannot be opened. One type of
WEBSOCKETerror can happen:WEBSOCKET: Received message longer than the maximum supported length.indicates that the response message length hits the maximum length (50kb).
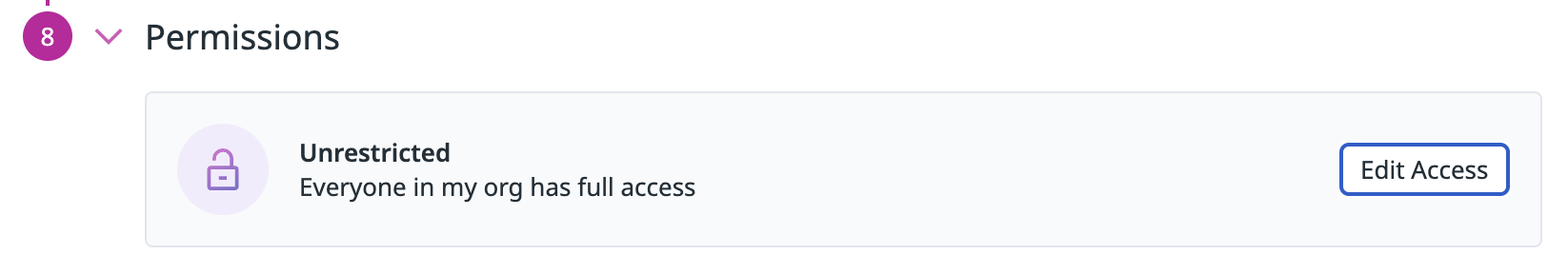
Permissions
By default, only users with the Datadog Admin and Datadog Standard roles can create, edit, and delete Synthetic WebSocket tests. To get create, edit, and delete access to Synthetic WebSocket tests, upgrade your user to one of those two default roles.
If you are using the custom role feature, add your user to any custom role that includes synthetics_read and synthetics_write permissions.
Restrict access
Use granular access control to limit who has access to your test based on roles, teams, or individual users:
- Open the permissions section of the form.
- Click Edit Access.
- Click Restrict Access.
- Select teams, roles, or users.
- Click Add.
- Select the level of access you want to associate with each of them.
- Click Done.
Note: You can view results from a Private Location even without Viewer access to that Private Location.
| Access level | View test configuration | Edit test configuration | View test results | Run test |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No access | ||||
| Viewer | Yes | Yes | ||
| Editor | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Further Reading
Documentation, liens et articles supplémentaires utiles: