- Principales informations
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- Tracing
- Conteneurs
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Site Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Intégrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- OpenTelemetry
- Profileur
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Intégrations
- Développeurs
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Application mobile
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Alertes
- Watchdog
- Métriques
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Conteneurs
- Processes
- Sans serveur
- Surveillance réseau
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Termes et concepts de l'APM
- Sending Traces to Datadog
- APM Metrics Collection
- Trace Pipeline Configuration
- Connect Traces with Other Telemetry
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origin for Spans
- Observabilité des services
- Endpoint Observability
- Dynamic Instrumentation
- Live Debugger
- Suivi des erreurs
- Sécurité des données
- Guides
- Dépannage
- Profileur en continu
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Configuration de Postgres
- Configuration de MySQL
- Configuration de SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Données collectées
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Explorer les métriques de requête
- Explorer des échantillons de requêtes
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Dépannage
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- RUM et Session Replay
- Surveillance Synthetic
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Visibility
- Code Coverage
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Securité
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Pipelines d'observabilité
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
Métriques et étiquettes
Ce produit n'est pas pris en charge par le site Datadog que vous avez sélectionné. ().
Ce document présente les métriques Data Streams Monitoring suivantes et leurs tags :
data_streams.latencydata_streams.kafka.lag_secondsdata_streams.kafka.lag_messages
data_streams.latency
Cette métrique mesure la latence entre deux points du pipeline. La valeur peut représenter différents types de latence selon ses tags.
pathway_type- Les informations que représente la valeur de la métrique. Types de pathway possibles :
full: latence de bout en bout entre l’origine des données (start) et un autre point (end) du pipeline- tag
start: origine des données - tag
end: point arbitraire où les données sont suivies pour la dernière fois
- tag
edge: latence entre deux services, connectés via une file d’attente ou directement via HTTP/gRPC. Mesure la durée entre le moment de production chez le producteur (start) et le moment de consommation chez le consommateur (end)- tag
start: le service producteur en amont - tag
end: le service consommateur en aval
- tag
partial_edge: latence entre un service et une file d’attente, si le producteur ou le consommateur n’est pas connu (c’est-à-dire non instrumenté avec Data Streams Monitoring)- tag
start: le service/la file d’attente producteur en amont - tag
end: le service/la file d’attente consommateur en aval
- tag
internal: latence au sein du service. Mesure le temps entre l’opération consume et l’opération produce suivante.
start- Le nom du nœud où Data Streams Monitoring détecte la charge utile pour la première fois. Ce nœud peut être un service (le producteur d’origine) ou une file d’attente (le producteur d’origine n’est pas connu de Data Streams Monitoring).
Lorsque le tagpathway_typeest défini surfull(latence de bout en bout),startfait toujours référence au début du pipeline.
Par exemple :
La requêtestart:serviceA and end:serviceC and pathway_type:fullmesure la latence de bout en bout pour ce pipeline.
La requêtestart:serviceB and end:serviceC and pathway_type:fullne mesure pas la latence pour ce pipeline, car aucune donnée ne provient du Service B. end- Le nom d’un nœud où le pipeline se termine. Vous pouvez utiliser
endpour obtenir des données pour des pipelines partiels.
Par exemple :
Vous pouvez utiliserstart:serviceA and end:serviceB and pathway_type:fullpour mesurer la première partie de ce pipeline. service- Le nom du service où les données sont collectées.
type- Le nom de la technologie de file d’attente pour laquelle les données sont générées, par exemple : Kafka, RabbitMQ, SQS. Pour HTTP et gRPC,
typeest défini surhttpougrpc. topic- Le nom du topic vers lequel les données sont produites ou à partir duquel elles sont consommées, le cas échéant.
direction- La direction du flux de données pour un
serviceparticulier. Valeurs possibles :in: l’opération consume ou la diffusion de données via HTTP/gRPCout: l’opération produce ou l’envoi de données via HTTP/gRPC
env- Environnement dans lequel le service s’exécute
pathway- Une liste ordonnée de services, séparés par
/, par lesquels les données transitent. Si les données passent par le même service plusieurs fois consécutivement, le nom du service n’est ajouté qu’une seule fois. detailed_pathway- Une liste ordonnée de services et de files d’attente, séparés par
/, par lesquels les données transitent. Identique àpathwaymais avec les files d’attente en plus des services. visited_queues- Représente toutes les files d’attente par lesquelles les données transitent. (Les files d’attente directement au début ou à la fin du pipeline sont exclues.) Vous pouvez utiliser ce tag pour affiner votre requête si vos données transitent par plusieurs files d’attente.
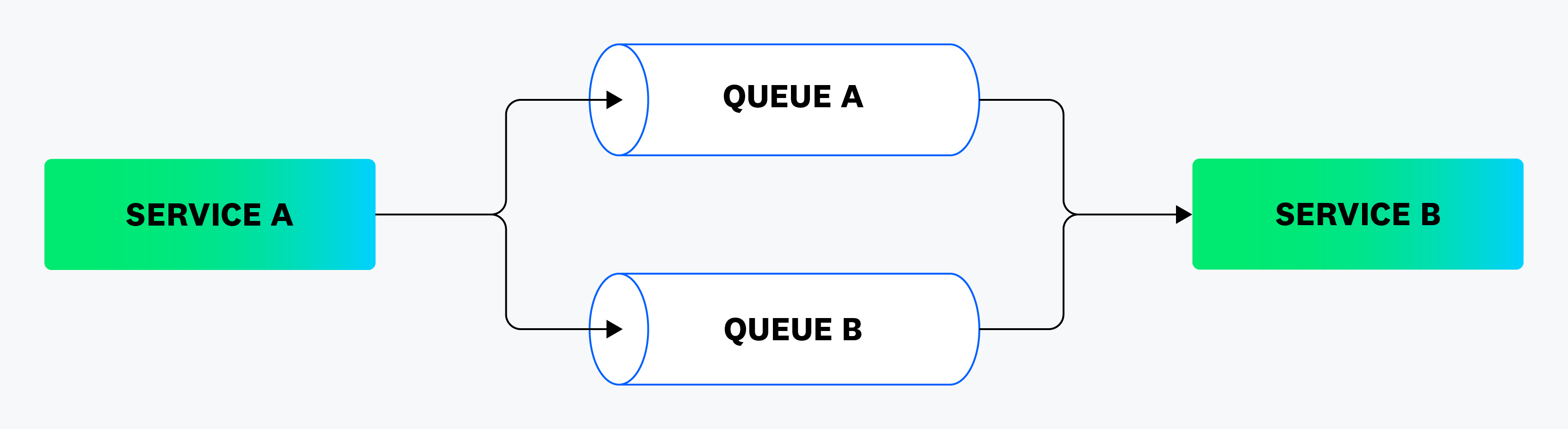
Considérez le pipeline suivant :
Pour mesurer le flux de données de Service A vers Queue A vers Service B, vous pouvez utiliser la requêtestart:serviceA and end:serviceB and visited_queues:queueA.
Pour mesurer le flux de données de Service A vers Queue B vers Service B, vous pouvez utiliser la requêtestart:serviceA and end:serviceB and visited_queues:queueB. visited_services- Représente tous les services par lesquels les données transitent. (Les services directement au début ou à la fin du pipeline sont exclus.)
upstream_service- Le nom du service en amont d’un
serviceparticulier. exchange- Pour RabbitMQ, le nom de l’exchange vers lequel les données sont acheminées.
hash- Un identifiant unique, calculé à partir de diverses valeurs de tags (
type,service,direction,parent_hash, et autres). parent_hash- Le
hashdu nœud en amont du nœud sur le pathway.
data_streams.kafka.lag_seconds
Cette métrique représente le lag (en secondes) entre les dernières opérations produce et consume.
partition- La partition Kafka.
env- L’environnement dans lequel le service consommateur s’exécute.
topic- Le topic Kafka.
consumer_group- Le groupe de consommateurs Kafka.
data_streams.kafka.lag_messages
Cette métrique représente le lag (en offsets) entre les dernières opérations produce et consume.
partition- La partition Kafka.
env- L’environnement dans lequel le service consommateur s’exécute.
topic- Le topic Kafka.
consumer_group- Le groupe de consommateurs Kafka.