- Esenciales
- Empezando
- Agent
- API
- Rastreo de APM
- Contenedores
- Dashboards
- Monitorización de bases de datos
- Datadog
- Sitio web de Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Gestión de incidencias
- Integraciones
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitores
- OpenTelemetry
- Generador de perfiles
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless para Lambda AWS
- Software Delivery
- Monitorización Synthetic
- Etiquetas (tags)
- Workflow Automation
- Centro de aprendizaje
- Compatibilidad
- Glosario
- Atributos estándar
- Guías
- Agent
- Arquitectura
- IoT
- Plataformas compatibles
- Recopilación de logs
- Configuración
- Automatización de flotas
- Solucionar problemas
- Detección de nombres de host en contenedores
- Modo de depuración
- Flare del Agent
- Estado del check del Agent
- Problemas de NTP
- Problemas de permisos
- Problemas de integraciones
- Problemas del sitio
- Problemas de Autodiscovery
- Problemas de contenedores de Windows
- Configuración del tiempo de ejecución del Agent
- Consumo elevado de memoria o CPU
- Guías
- Seguridad de datos
- Integraciones
- Desarrolladores
- Autorización
- DogStatsD
- Checks personalizados
- Integraciones
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Crear una integración basada en el Agent
- Crear una integración API
- Crear un pipeline de logs
- Referencia de activos de integración
- Crear una oferta de mercado
- Crear un dashboard de integración
- Create a Monitor Template
- Crear una regla de detección Cloud SIEM
- Instalar la herramienta de desarrollo de integraciones del Agente
- Checks de servicio
- Complementos de IDE
- Comunidad
- Guías
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Aplicación móvil de Datadog
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft
- En la aplicación
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- Editor DDSQL
- Reference Tables
- Hojas
- Monitores y alertas
- Watchdog
- Métricas
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Explorador
- Estados de problemas
- Detección de regresión
- Suspected Causes
- Error Grouping
- Bits AI Dev Agent
- Monitores
- Issue Correlation
- Identificar confirmaciones sospechosas
- Auto Assign
- Issue Team Ownership
- Rastrear errores del navegador y móviles
- Rastrear errores de backend
- Manage Data Collection
- Solucionar problemas
- Guides
- Change Tracking
- Gestión de servicios
- Objetivos de nivel de servicio (SLOs)
- Gestión de incidentes
- De guardia
- Status Pages
- Gestión de eventos
- Gestión de casos
- Actions & Remediations
- Infraestructura
- Cloudcraft
- Catálogo de recursos
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Contenedores
- Processes
- Serverless
- Monitorización de red
- Cloud Cost
- Rendimiento de las aplicaciones
- APM
- Términos y conceptos de APM
- Instrumentación de aplicación
- Recopilación de métricas de APM
- Configuración de pipelines de trazas
- Correlacionar trazas (traces) y otros datos de telemetría
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origin for Spans
- Observabilidad del servicio
- Endpoint Observability
- Instrumentación dinámica
- Live Debugger
- Error Tracking
- Seguridad de los datos
- Guías
- Solucionar problemas
- Límites de tasa del Agent
- Métricas de APM del Agent
- Uso de recursos del Agent
- Logs correlacionados
- Stacks tecnológicos de llamada en profundidad PHP 5
- Herramienta de diagnóstico de .NET
- Cuantificación de APM
- Go Compile-Time Instrumentation
- Logs de inicio del rastreador
- Logs de depuración del rastreador
- Errores de conexión
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Gastos generales de integración del Agent
- Arquitecturas de configuración
- Configuración de Postgres
- Configuración de MySQL
- Configuración de SQL Server
- Configuración de Oracle
- Configuración de MongoDB
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Conexión de DBM y trazas
- Datos recopilados
- Explorar hosts de bases de datos
- Explorar métricas de consultas
- Explorar ejemplos de consulta
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Solucionar problemas
- Guías
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Experiencia digital
- Real User Monitoring
- Pruebas y monitorización de Synthetics
- Continuous Testing
- Análisis de productos
- Entrega de software
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Visibility
- Configuración
- Network Settings
- Tests en contenedores
- Repositories
- Explorador
- Monitores
- Test Health
- Flaky Test Management
- Working with Flaky Tests
- Test Impact Analysis
- Flujos de trabajo de desarrolladores
- Cobertura de código
- Instrumentar tests de navegador con RUM
- Instrumentar tests de Swift con RUM
- Correlacionar logs y tests
- Guías
- Solucionar problemas
- Code Coverage
- Quality Gates
- Métricas de DORA
- Feature Flags
- Seguridad
- Información general de seguridad
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- Observabilidad de la IA
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Gestión de logs
- CloudPrem
- Administración
- Gestión de cuentas
- Seguridad de los datos
- Ayuda
Code Coverage en Datadog
Este producto no es compatible con el sitio Datadog seleccionado. ().
Join the Preview!
Esta función de Test Optimization estará obsoleta y será sustituida por un nuevo producto exclusivo para la cobertura de código. Inscríbete para la vista previa.
Request AccessInformación general
La cobertura de código es una medida del porcentaje total de cobertura de código que ejerce un módulo o sesión.
Asegúrate de que Test Optimization ya está configurado para tu lenguaje.
Informe de cobertura de código
Compatibilidad
dd-trace>=4.45.0ydd-trace>=5.21.0.jest>=24.8.0, sólo cuando se ejecuta conjest-circus.mocha>=5.2.0.cucumber-js>=7.0.0.vitest>=2.0.0.
Nota: El rastreador de DataDog no genera cobertura de código. Si tus tests se ejecutan con la cobertura de código habilitada,
dd-trace lo informa de modo automático en la tag (etiqueta) test.code_coverage.lines_pct para tus sesiones de test.Mocha/Cucumber-js
Sólo se admite la cobertura de código Istanbul para mocha y cucumber-js.
Para informar de la cobertura total del código de tus sesiones de test de mocha y cucumber-js, instala nyc y envuelve tus comandos de test:
- Instala
nyc:
npm install --save-dev nyc
- Envuelve tus comandos de test con
nyc:
{
"scripts": {
"test": "mocha",
"coverage": "nyc npm run test"
}
}
Jest
Jest incluye Istanbul por defecto, por lo que no es necesario instalar nyc. Basta con pasar --coverage:
{
"scripts": {
"coverage": "jest --coverage"
}
}
El único coverageProvider admitido es babel, que es el predeterminado.
Vitest
Vitest requiere dependencias adicionales para ejecutarse con cobertura de código. Consulta documentación de vitest para más información. Una vez instaladas las dependencias, pasa --coverage a tu comando de test:
{
"scripts": {
"coverage": "vitest run --coverage"
}
}
Después de modificar tus comandos de test, ejecuta tus tests con el nuevo comando coverage:
NODE_OPTIONS="-r dd-trace/ci/init" DD_ENV=ci DD_SERVICE=my-javascript-service npm run coverage
Compatibilidad
dd-trace>=2.31.0.
Cuando la cobertura del código está disponible, el rastreador de Datadog (v2.31.0 o posterior) informa de ella en la etiqueta test.code_coverage.lines_pct para tus sesiones de test.
Si utilizas Coverlet para calcular la cobertura del código, indica la ruta del archivo de informe en la variable de entorno DD_CIVISIBILITY_EXTERNAL_CODE_COVERAGE_PATH al ejecutar dd-trace. El archivo de informe debe estar en los formatos OpenCover o Cobertura. Alternativamente, puedes activar el cálculo de cobertura de código integrado en el rastreador de Datadog con la variable de entorno DD_CIVISIBILITY_CODE_COVERAGE_ENABLED=true.
Nota: DD_CIVISIBILITY_EXTERNAL_CODE_COVERAGE_PATH solo se utiliza cuando el comando instrumentado por dd-trace (traza) ci run es dotnet test, dotnet vstest o vstest.console. Por ejemplo, los resultados de la variable se ignoran cuando se ejecuta dd-trace ci run -- coverlet TestAssembly.dll --target dotnet --targetargs "test TestAssembly.dll".
Opciones avanzadas
La cobertura de código incorporada en el rastreador Datadog es compatible con las opciones Coverlet y VS Code Coverage a través del archivo .runsettings.
Estructura del archivo
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RunSettings>
<DataCollectionRunSettings>
<DataCollectors>
<DataCollector friendlyName="DatadogCoverage">
<Configuration>
<!-- Datadog Code Coverage settings -->
...
</Configuration>
</DataCollector>
</DataCollectors>
</DataCollectionRunSettings>
</RunSettings>
Opciones de Coverlet
| Opción | Resumen |
|---|---|
| ExcludeByAttribute | Excluir métodos, clases o ensamblados decorados con atributos de la cobertura de código. |
| ExcludeByFile | Excluir archivos fuente específicos de la cobertura de código. |
| Exclude | Excluir del análisis de cobertura de código mediante expresiones de filtro. |
Atributos
Puedes excluir un método, una clase entera o un ensamblado de la cobertura de código creando y aplicando el atributo ExcludeFromCodeCoverage presente en el espacio de nombres System.Diagnostics.CodeAnalysis.
Excluir atributos adicionales con la propiedad ExcludeByAttribute y el nombre corto del atributo (el nombre del tipo sin el espacio de nombres).
Archivos fuente
Excluye archivos fuente específicos de la cobertura de código con la propiedad ExcludeByFile.
- Utiliza una o varias rutas, separadas por comas.
- Utiliza la ruta del archivo o directorio con un comodín (
*), por ejemplo:dir1/*.cs.
Filtros
Los filtros proporcionan un control preciso sobre lo que se excluye utilizando expresiones de filtro con la siguiente sintaxis:
[<ASSEMBLY_FILTER>]<TYPE_FILTER>
Se admiten comodines:
*=> coincide con cero o más caracteres?=> el carácter prefijado es opcional
Ejemplos:
[*]*=> excluye todos los tipos en todos los ensamblajes (no se instrumenta nada)[coverlet.*]Coverlet.Core.Coverage=> excluye la claseCoveragedel espacio de nombresCoverlet.Coreperteneciente a cualquier ensamblaje que coincida concoverlet.*(por ejemplo,coverlet.core)[*]Coverlet.Core.Instrumentation.*=> Excluye todos los tipos pertenecientes al espacio de nombresCoverlet.Core.Instrumentationen cualquier ensamblaje[coverlet.*.tests?]*=> excluye todos los tipos en cualquier ensamblaje que empiecen porcoverlet.y terminen por.testo.tests(el?hace quessea opcional)[coverlet.*]*,[*]Coverlet.Core*\=> excluye los ensamblajes que coincidan concoverlet.*y excluye todos los tipos pertenecientes al espacio de nombresCoverlet.Coreen cualquier ensamblaje
Opciones de cobertura de código VS
Consulta Personalizar el análisis de cobertura de código en la documentación de Microsoft para obtener información adicional.
| Opción | Resumen |
|---|---|
| Attributes\Exclude | Excluye métodos, clases o ensamblados decorados con atributos de la cobertura de código. |
| Sources\Exclude | Excluir archivos fuente específicos de la cobertura de código. |
Ejemplo de Runsettings
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RunSettings>
<DataCollectionRunSettings>
<DataCollectors>
<DataCollector friendlyName="DatadogCoverage">
<Configuration>
<!-- Coverlet configuration -->
<ExcludeByAttribute>CompilerGeneratedAttribute</ExcludeByAttribute>
<ExcludeByFile>**/Fibonorial.cs</ExcludeByFile>
<Exclude>[myproject.*.tests?]*</Exclude>
<!-- VS Code Coverage configuration -->
<CodeCoverage>
<Attributes>
<Exclude>
<Attribute>^System\.ObsoleteAttribute$</Attribute>
</Exclude>
</Attributes>
<Sources>
<Exclude>
<Source>^MyFile\.cs$</Source>
</Exclude>
</Sources>
</CodeCoverage>
</Configuration>
</DataCollector>
</DataCollectors>
</DataCollectionRunSettings>
</RunSettings>
Compatibilidad
dd-trace-java >= 1.24.2.
Cuando la cobertura de código está disponible, el rastreador de Datadog informa de ella en la etiqueta test.code_coverage.lines_pct para tus sesiones de test.
Jacoco es compatible con la biblioteca de cobertura de código.
Si tu proyecto ya tiene Jacoco configurado, el rastreador de Datadog lo instrumenta e informa los datos de cobertura a Datadog automáticamente.
De lo contrario, puedes configurar el rastreador para añadir Jacoco a tus ejecuciones de tests en tiempo de ejecución.
Utiliza la variable de entorno DD_CIVISIBILITY_JACOCO_PLUGIN_VERSION para especificar qué versión de Jacoco deseas que se inyecte (por ejemplo: DD_CIVISIBILITY_JACOCO_PLUGIN_VERSION=0.8.11).
Compatibilidad
dd-trace>=2.5.0.Python>=3.7.coverage>=4.4.2.pytest>=3.0.0.pytest-cov>=2.7.0.unittest>=3.8.- Sólo se admiten las coberturas de código
coverage.pyypytest-cov.
Cuando los tests se instrumentan con coverage.py o pytest-cov, el rastreador de Datadog informa automáticamente de la cobertura de código bajo la etiqueta test.code_coverage.lines_pct para tus sesiones de test.
Para informar de la cobertura total de código de tus sesiones de test con coverage.py, sigue estos pasos:
- Instala
coverage:
python3 -m pip install coverage
- Ejecuta tu test con el nuevo comando
coverage:
DD_ENV=ci DD_SERVICE=my-python-service coverage run -m pytest
Alternativamente, para informar de la cobertura total de código de tus sesiones de test con pytest-cov, sigue estos pasos:
- Instala
pytest:
python3 -m pip install pytest
- Instala
pytest-cov:
python3 -m pip install pytest-cov
- Ejecuta tu test añadiendo el indicador
--cova tu comandopytest:
DD_ENV=ci DD_SERVICE=my-python-service pytest --cov
Compatibilidad
datadog-ci-rb>=1.7.0simplecov>=0.18.0.
Nota: La biblioteca de DataDog no genera cobertura total de código. Si tus tests se con la cobertura de código habilitada,
datadog-ci-rb lo informa de modo automático en la tag (etiqueta) test.code_coverage.lines_pct para tus sesiones de test.Si tu proyecto tiene configurado simplecov, la biblioteca satadog-ci-rb lo instrumenta e informa los datos de cobertura a Datadog automáticamente bajo la etiqueta test.code_coverage.lines_pct para tus sesiones de test.
Esta función está activada por defecto. Utiliza la variable de entorno DD_CIVISIBILITY_SIMPLECOV_INSTRUMENTATION_ENABLED para desactivar esta función (por ejemplo: DD_CIVISIBILITY_SIMPLECOV_INSTRUMENTATION_ENABLED=0).
Compatibilidad
go test -cover
Nota: La biblioteca de DataDog no genera cobertura total de código. Si tus tests se ejecutan con la cobertura de código habilitada,
dd-trace-go lo informa de modo automático en la tag (etiqueta) test.code_coverage.lines_pct para tus sesiones de test.Si tus tests se ejecutan con el indicador -cover, la biblioteca de Datadog lo instrumenta y automáticamente reporta los datos de cobertura a Datadog bajo la etiqueta test.code_coverage.lines_pct para tus sesiones de test.
Compatibilidad
dd-sdk-swift-testing>=2.5.3.Xcode>=14.3.
Cuando la cobertura de código está activada, el rastreador de Datadog informa de ella en la etiqueta test.code_coverage.lines_pct para tus sesiones de test.
Para habilitar la cobertura de código en proyectos Xcode puedes seguir esta guía de Apple: Habilitar la cobertura de código en tu plan de tests.
Para los tests SPM, añade el parámetro --enable-code-coverage a tu invocación swift test.
Compatibilidad
datadog-ci>=2.17.2.
Puedes cargar un valor de porcentaje de cobertura de código cuando utilices la carga de informes JUnit:
datadog-ci junit upload --service <service_name> --report-measures=test.code_coverage.lines_pct:85 <path>
En este ejemplo, 85 es el porcentaje de líneas cubiertas por tus tests y debe generarse con una herramienta diferente.
El informe de cobertura de código debe generarse en un proceso diferente, de lo contrario las cargas de informes JUnit no generarán informes de cobertura de código. El nombre de la métrica informada debe ser test.code_coverage.lines_pct.
Cobertura del código en gráficos
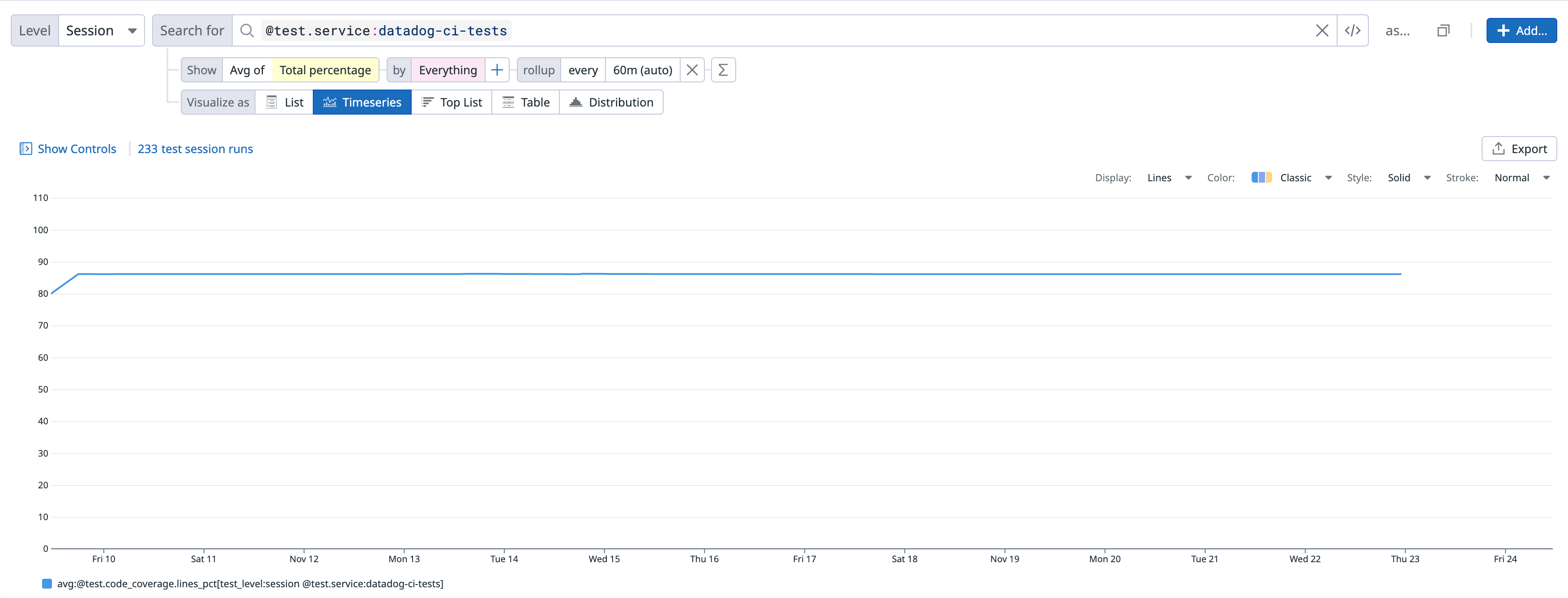
La cobertura de código informada se reporta como @test.code_coverage.lines_pct, que representa el porcentaje total en la faceta, y puede ser graficada como cualquier otra faceta de medida en el CI Visibility Explorer.
Pestaña Cobertura de la sesión de test
La cobertura de código notificada también aparece en la pestaña Coverage (Cobertura) en la página de detalles de una sesión de test:
Exportar el gráfico
Puedes exportar tu gráfico a un dashboard o a un notebook y crear un monitor basado en él haciendo clic en el botón Export (Exportar):
Añadir un monitor
Recibe alertas cada vez que la cobertura de código de tu servicio caiga por debajo de un determinado umbral creando un Monitor de CI Test:
Ver la evolución de la cobertura de código de tu rama
También puedes ver la evolución de la cobertura del código en la página Información general de la rama y comprobar si está mejorando o empeorando:
Mostrar los cambios en la cobertura del código de una solicitud pull
El comentario de resumen del test de la solicitud pull muestra el cambio en la cobertura del código de una solicitud pull de GitHub en comparación con la rama por defecto.
Test Impact Analysis y cobertura total del código
Test Impact Analysis no proporciona automáticamente mediciones de la cobertura total del código, aunque requiere una cobertura del código por test para funcionar.