- Esenciales
- Empezando
- Agent
- API
- Rastreo de APM
- Contenedores
- Dashboards
- Monitorización de bases de datos
- Datadog
- Sitio web de Datadog
- DevSecOps
- Gestión de incidencias
- Integraciones
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitores
- OpenTelemetry
- Generador de perfiles
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless para Lambda AWS
- Software Delivery
- Monitorización Synthetic
- Etiquetas (tags)
- Workflow Automation
- Centro de aprendizaje
- Compatibilidad
- Glosario
- Atributos estándar
- Guías
- Agent
- Arquitectura
- IoT
- Plataformas compatibles
- Recopilación de logs
- Configuración
- Automatización de flotas
- Solucionar problemas
- Detección de nombres de host en contenedores
- Modo de depuración
- Flare del Agent
- Estado del check del Agent
- Problemas de NTP
- Problemas de permisos
- Problemas de integraciones
- Problemas del sitio
- Problemas de Autodiscovery
- Problemas de contenedores de Windows
- Configuración del tiempo de ejecución del Agent
- Consumo elevado de memoria o CPU
- Guías
- Seguridad de datos
- Integraciones
- Desarrolladores
- Autorización
- DogStatsD
- Checks personalizados
- Integraciones
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Crear una integración basada en el Agent
- Crear una integración API
- Crear un pipeline de logs
- Referencia de activos de integración
- Crear una oferta de mercado
- Crear un dashboard de integración
- Create a Monitor Template
- Crear una regla de detección Cloud SIEM
- Instalar la herramienta de desarrollo de integraciones del Agente
- Checks de servicio
- Complementos de IDE
- Comunidad
- Guías
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Aplicación móvil de Datadog
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft
- En la aplicación
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- Editor DDSQL
- Reference Tables
- Hojas
- Monitores y alertas
- Watchdog
- Métricas
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Explorador
- Estados de problemas
- Detección de regresión
- Suspected Causes
- Error Grouping
- Bits AI Dev Agent
- Monitores
- Issue Correlation
- Identificar confirmaciones sospechosas
- Auto Assign
- Issue Team Ownership
- Rastrear errores del navegador y móviles
- Rastrear errores de backend
- Manage Data Collection
- Solucionar problemas
- Guides
- Change Tracking
- Gestión de servicios
- Objetivos de nivel de servicio (SLOs)
- Gestión de incidentes
- De guardia
- Status Pages
- Gestión de eventos
- Gestión de casos
- Actions & Remediations
- Infraestructura
- Cloudcraft
- Catálogo de recursos
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Contenedores
- Processes
- Serverless
- Monitorización de red
- Cloud Cost
- Rendimiento de las aplicaciones
- APM
- Términos y conceptos de APM
- Instrumentación de aplicación
- Recopilación de métricas de APM
- Configuración de pipelines de trazas
- Correlacionar trazas (traces) y otros datos de telemetría
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origin for Spans
- Observabilidad del servicio
- Endpoint Observability
- Instrumentación dinámica
- Live Debugger
- Error Tracking
- Seguridad de los datos
- Guías
- Solucionar problemas
- Límites de tasa del Agent
- Métricas de APM del Agent
- Uso de recursos del Agent
- Logs correlacionados
- Stacks tecnológicos de llamada en profundidad PHP 5
- Herramienta de diagnóstico de .NET
- Cuantificación de APM
- Go Compile-Time Instrumentation
- Logs de inicio del rastreador
- Logs de depuración del rastreador
- Errores de conexión
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Gastos generales de integración del Agent
- Arquitecturas de configuración
- Configuración de Postgres
- Configuración de MySQL
- Configuración de SQL Server
- Configuración de Oracle
- Configuración de MongoDB
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Conexión de DBM y trazas
- Datos recopilados
- Explorar hosts de bases de datos
- Explorar métricas de consultas
- Explorar ejemplos de consulta
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Solucionar problemas
- Guías
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Experiencia digital
- Real User Monitoring
- Pruebas y monitorización de Synthetics
- Continuous Testing
- Análisis de productos
- Entrega de software
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Visibility
- Configuración
- Network Settings
- Tests en contenedores
- Repositories
- Explorador
- Monitores
- Test Health
- Flaky Test Management
- Working with Flaky Tests
- Test Impact Analysis
- Flujos de trabajo de desarrolladores
- Cobertura de código
- Instrumentar tests de navegador con RUM
- Instrumentar tests de Swift con RUM
- Correlacionar logs y tests
- Guías
- Solucionar problemas
- Code Coverage
- Quality Gates
- Métricas de DORA
- Feature Flags
- Seguridad
- Información general de seguridad
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security Management
- Application Security Management
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- Observabilidad de la IA
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Gestión de logs
- CloudPrem
- Administración
- Gestión de cuentas
- Seguridad de los datos
- Ayuda
Set Up Code Coverage
Este producto no es compatible con el sitio Datadog seleccionado. ().
Esta página aún no está disponible en español. Estamos trabajando en su traducción.
Si tienes alguna pregunta o comentario sobre nuestro actual proyecto de traducción, no dudes en ponerte en contacto con nosotros.
Si tienes alguna pregunta o comentario sobre nuestro actual proyecto de traducción, no dudes en ponerte en contacto con nosotros.
Setting up Code Coverage involves the following steps:
- Configure the integration with your source code provider in the Datadog UI.
- Configure code coverage data access permissions in Datadog.
- Optionally, configure a PR Gate to block pull requests based on coverage thresholds.
- Update your CI pipeline to upload code coverage reports to Datadog.
Integrate with source code provider
Code Coverage supports the following:
Follow instructions in the GitHub integration documentation on how to connect your GitHub repositories to Datadog.
Code Coverage requires the following GitHub App permissions:
| Permission | Access Level | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Contents | Read | Show source code in the detailed coverage UI. |
| Pull Requests | Write | Show PR data in coverage UI and write PR comments. |
| Checks | Write | Create coverage PR Gates. |
The following webhooks are required:
| Webhook | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Pull request | Receive PR data updates. |
| Pull request review | Receive PR data updates. |
| Pull request review comment | Receive PR data updates. |
| Push | Receive Git commit metadata. |
If everything is configured correctly, a green check mark is displayed in Datadog’s GitHub Integration page:
If you have a Datadog-managed Marketplace App or a custom app with default settings, the required permissions and webhooks are included.
Follow instructions in the Gitlab Source Code integration documentation on how to connect your Gitlab repositories to Datadog.
See Datadog Source Code Integration Guide for additional context.
Follow instructions in the Datadog Source Code Integration Guide on how to connect your Azure DevOps repositories to Datadog using Azure DevOps Source Code integration.
See Data Collected for details on what data is collected from your source code provider.
Data access permissions
If you are using custom roles rather than Datadog-managed roles, be sure to enable the Code Coverage Read permission for the roles that need to view code coverage data.
Navigate to Roles settings, click Edit on the role you need, add the Code Coverage Read permission to the role, and save the changes.
PR Gates
If you wish to gate on PR coverage, you can configure PR Gates rules in one of two ways:
- Datadog UI: Navigate to PR Gates rule creation and configure a rule to gate on total or patch coverage.
- YAML configuration file: Define gates in your
code-coverage.datadog.ymlfile. This allows you to manage gates as code alongside your repository.
Rules from both sources are evaluated when a pull request is opened or updated. See Configuration for YAML gate syntax and examples.
Upload code coverage reports
Update your CI pipeline to upload code coverage report files to Datadog. This involves installing and running the datadog-ci CLI in your CI environment.
See Data Collected for details on what data is collected during code coverage report upload.
Supported coverage report formats
Datadog supports the following coverage data formats—expand for examples:
LCOV
LCOV
TN:
SF:src/example.c
FN:3,add
FNDA:5,add
FNF:1
FNH:1
DA:3,5
DA:4,5
DA:5,5
DA:8,0
DA:9,0
LF:5
LH:3
BRDA:4,0,0,5
BRDA:4,0,1,0
BRF:2
BRH:1
end_of_recordGo Coverprofile
Go Coverprofile
mode: atomic
example/calculator.go:51.148,53.2 1 0
example/calculator.go:55.190,61.15 3 0
example/calculator.go:61.15,64.3 2 0
example/calculator.go:66.2,67.16 2 0
example/calculator.go:67.16,69.3 1 0
example/clients/api_client.go:27.87,31.2 3 2
example/clients/api_client.go:34.85,36.2 1 3
example/clients/api_client.go:39.126,44.2 4 3
example/clients/api_client.go:47.106,50.2 2 3
example/notifications/notifier.go:49.79,51.2 1 3
example/notifications/notifier.go:60.33,69.2 1 0
example/notifications/notifier.go:79.131,86.15 3 2
example/notifications/notifier.go:104.3,104.10 1 3Cobertura XML
Cobertura XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE coverage SYSTEM "http://cobertura.sourceforge.net/xml/coverage-04.dtd">
<coverage lines-valid="5" lines-covered="3" line-rate="0.6" branches-valid="2" branches-covered="1" branch-rate="0.5" timestamp="1690658886" version="1.9">
<sources>
<source>src</source>
</sources>
<packages>
<package name="example" line-rate="0.6" branch-rate="0.5">
<classes>
<class name="Example" filename="example/Example.java" line-rate="0.6" branch-rate="0.5">
<methods>
<method name="add" signature="(II)I" line-rate="1.0" branch-rate="1.0">
<lines>
<line number="3" hits="5"/>
<line number="4" hits="5" branch="true" condition-coverage="50% (1/2)"/>
<line number="5" hits="5"/>
</lines>
</method>
</methods>
<lines>
<line number="3" hits="5"/>
<line number="4" hits="5" branch="true" condition-coverage="50% (1/2)"/>
<line number="5" hits="5"/>
<line number="8" hits="0"/>
<line number="9" hits="0"/>
</lines>
</class>
</classes>
</package>
</packages>
</coverage>Jacoco XML
Jacoco XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<report name="Example">
<sessioninfo id="SessionId" start="1690658886000" dump="1690658887000"/>
<package name="example">
<sourcefile name="Example.java">
<line nr="3" mi="0" ci="5"/>
<line nr="4" mi="0" ci="5" mb="1" cb="1"/>
<line nr="5" mi="0" ci="5"/>
<line nr="8" mi="1" ci="0"/>
<line nr="9" mi="1" ci="0"/>
</sourcefile>
</package>
</report>Clover XML
Clover XML
<coverage generated="1661852015">
<project timestamp="1661852015">
<file name="/var/www/html/src/App/Console/CronjobRunnerCommand.php">
<class name="App\Console\CronjobRunnerCommand" namespace="global">
<metrics complexity="3" methods="3" coveredmethods="0" conditionals="0" coveredconditionals="0" statements="4" coveredstatements="0" elements="7" coveredelements="0"/>
</class>
<line num="18" type="method" name="__construct" visibility="public" complexity="1" crap="2" count="0"/>
<line num="20" type="stmt" count="1"/>
<line num="27" type="stmt" count="0"/>
<line num="30" type="method" name="execute" visibility="protected" complexity="1" crap="2" count="0"/>
<line num="32" type="stmt" count="0"/>
<metrics loc="35" ncloc="35" classes="1" methods="3" coveredmethods="0" conditionals="0" coveredconditionals="0" statements="4" coveredstatements="0" elements="7" coveredelements="0"/>
</file>
<file name="/var/www/html/src/App/Console/CronjobRunnerCommand2.php">
<line num="42" type="stmt" count="1"/>
</file>
</project>
</coverage>OpenCover XML
OpenCover XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<CoverageSession xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<Modules>
<Module hash="ABC123">
<ModulePath>Example.dll</ModulePath>
<Files>
<File uid="1" fullPath="src\example\Example.cs" />
</Files>
<Classes>
<Class>
<Methods>
<Method visited="true" cyclomaticComplexity="1" sequenceCoverage="100">
<FileRef uid="1"/>
<SequencePoints>
<SequencePoint vc="5" sl="3" />
<SequencePoint vc="5" sl="4" />
<SequencePoint vc="5" sl="5" />
<SequencePoint vc="0" sl="9" />
</SequencePoints>
<BranchPoints>
<BranchPoint vc="5" sl="4" path="0"/>
<BranchPoint vc="0" sl="4" path="1"/>
</BranchPoints>
</Method>
</Methods>
</Class>
</Classes>
</Module>
</Modules>
</CoverageSession>Simplecov JSON
Simplecov JSON
{
"meta": {
"simplecov_version": "0.21.2"
},
"coverage": {
"/path/to/file1.rb": {
"lines": [
null,
1,
2,
0,
null,
1,
null,
null,
null,
"ignored",
"ignored",
"ignored",
null
],
"branches": []
},
"/path/to/file2.rb": {
"lines": [1, 1, null, 0, 1],
"branches": []
}
}
}Install the datadog-ci CLI
Install the datadog-ci CLI globally using npm:
npm install -g @datadog/datadog-ciStandalone binary
If installing Node.js in the CI is an issue, standalone binaries are provided with Datadog CI releases. Only linux-x64, linux-arm64, darwin-x64, darwin-arm64 (MacOS) and win-x64 (Windows) are supported. To install, run the following from your terminal:
curl -L --fail "https://github.com/DataDog/datadog-ci/releases/latest/download/datadog-ci_linux-x64" --output "/usr/local/bin/datadog-ci" && chmod +x /usr/local/bin/datadog-ciThen run any command with datadog-ci:
datadog-ci versioncurl -L --fail "https://github.com/DataDog/datadog-ci/releases/latest/download/datadog-ci_darwin-x64" --output "/usr/local/bin/datadog-ci" && chmod +x /usr/local/bin/datadog-ciThen run any command with datadog-ci:
datadog-ci versionInvoke-WebRequest -Uri "https://github.com/DataDog/datadog-ci/releases/latest/download/datadog-ci_win-x64" -OutFile "datadog-ci.exe"Then run any command with Start-Process -FilePath "datadog-ci.exe":
Start-Process -FilePath "./datadog-ci.exe" -ArgumentList versionDocker image
Alternatively, you can update your CI job to run in a container based on the Datadog CI Docker image.
The image comes with datadog-ci preinstalled and ready to use.
Uploading coverage reports
Datadog automatically aggregates all reports for the same commit on the backend. You don't need to merge coverage reports before uploading them.
To upload your code coverage reports to Datadog, run the following command. Provide a valid Datadog API key (DD_API_KEY), and one or more file paths to either the coverage report files directly or directories containing them:
steps:
- name: Upload coverage reports to Datadog
run: datadog-ci coverage upload .
env:
DD_API_KEY: ${{ secrets.DD_API_KEY }}
DD_SITE:
test:
stage: test
script:
- ... # run your tests and generate coverage reports
- datadog-ci coverage upload . # make sure to add the DD_API_KEY CI/CD variable
- script: datadog-ci coverage upload --format=clover coverage/clover.xml
displayName: 'Upload coverage to Datadog'
env:
DD_API_KEY: $(DD_API_KEY)
DD_SITE: 'datadoghq.com'The command recursively searches the specified directories for supported coverage report files, so specifying the current directory (.) is usually sufficient.
See the datadog-ci documentation for more details on the datadog-ci coverage upload command.
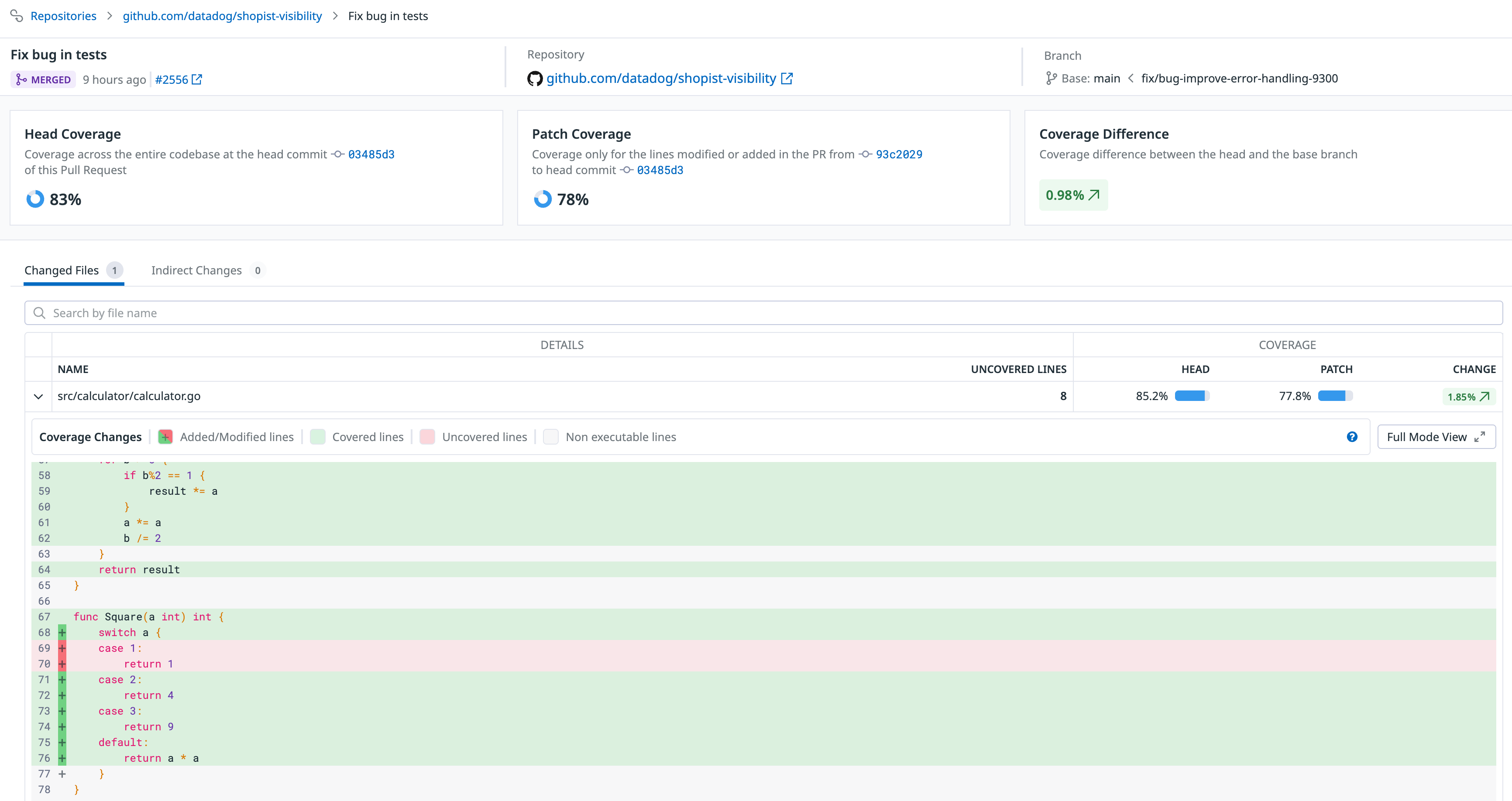
Shortly after the code coverage report upload is finished, Datadog adds a PR comment with code coverage percentage values. You can also view your coverage data aggregated by pull request in the Code Coverage page in Datadog, with the ability to examine individual files and lines of code.
Troubleshooting
Coverage upload command does not detect coverage report files
The datadog-ci coverage upload command automatically detects supported coverage report files in the specified directories using heuristics, such as file names and extensions.
If your coverage report files do not match expected patterns, the command might not detect them automatically. In this case, specify the report format and provide the file paths as positional arguments. For example:
datadog-ci coverage upload --format=lcov \
src/coverage-reports/unit-tests/coverage.info \
src/coverage-reports/e2e-tests/coverage.infoCoverage upload fails with “Format could not be detected” error
The datadog-ci coverage upload command automatically detects the format of the coverage report files based on their content and file extension.
If the command fails with the following error:
Invalid coverage report file [...]: format could not be detected
specify the format explicitly using the --format option, like this:
datadog-ci coverage upload --format=cobertura reports/cobertura.xmlCoverage upload outputs “Could not sync git metadata” error
Git metadata upload is only required if you can’t integrate your CI provider directly with Datadog.
If you are using a source code provider integration, such as Datadog GitHub app or Gitlab integration, you can disable the git metadata upload by passing the --skip-git-metadata-upload=1 flag to the datadog-ci coverage upload command, like this:
datadog-ci coverage upload --skip-git-metadata-upload=1 .Datadog UI does not show changed files in the PR view
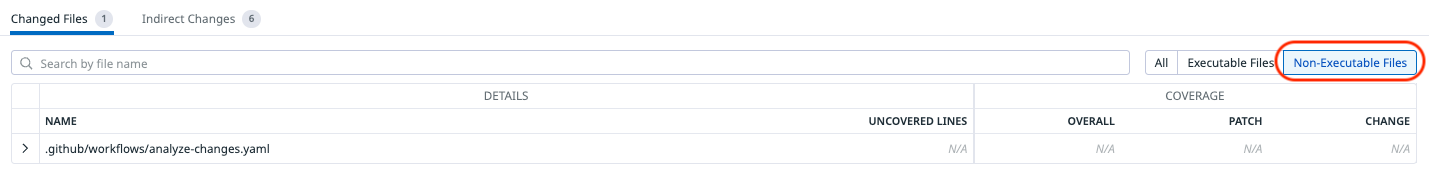
By default, the “Changed files” table only contains executable source code files that are present in the uploaded coverage reports. Select Non-executable files or All in the table header to display all files that were changed in the PR, regardless of whether they are executable or not.
If a source code file is mistakenly marked as non-executable, it is probably missing from your uploaded coverage reports. Make sure that you are uploading all of your relevant reports, and double-check your coverage tool configuration to verify that coverage data is collected for all applicable files.
Test sources are not considered executable files as they are not part of the production codebase being measured for coverage.
Datadog UI shows incorrect file paths
Code Coverage relies on the file paths in coverage reports to be either absolute or relative to the repository root.
If the paths in your report are relative to a different directory in your repository, specify the correct base path (relative to the repo root) with the --base-path option when running the datadog-ci coverage upload command, like this:
datadog-ci coverage upload --base-path=frontend/src .Discrepancy between Datadog UI and coverage report values
Datadog automatically merges coverage reports for the same commit. As a result, the coverage percentage displayed in the Datadog UI may differ from the values in your individual coverage reports, especially if those reports contain overlapping or duplicate source code file entries.
If you use an external tool (such as ReportGenerator) to merge coverage reports before uploading to Datadog, ensure your merged reports do not contain duplicate source code file entries. Datadog deduplicates overlapping files across reports, which can result in differences between your original coverage values and the merged values displayed in the Datadog UI.