- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- Notebooks
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Search
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API-based Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Service Level Objectives
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Event Management
- Incident Response
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- End User Device Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Storage Management
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Session Replay
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Code Coverage
- PR Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- AI Guard
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Configuration
- Sources
- Processors
- Destinations
- Packs
- Akamai CDN
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs
- AWS Application Load Balancer Logs
- AWS CloudTrail
- AWS Elastic Load Balancer Logs
- AWS Network Load Balancer Logs
- Cisco ASA
- Cloudflare
- F5
- Fastly
- Fortinet Firewall
- HAProxy Ingress
- Istio Proxy
- Juniper SRX Firewall Traffic Logs
- Netskope
- NGINX
- Okta
- Palo Alto Firewall
- Windows XML
- ZScaler ZIA DNS
- Zscaler ZIA Firewall
- Zscaler ZIA Tunnel
- Zscaler ZIA Web Logs
- Search Syntax
- Scaling and Performance
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Guides and Resources
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
Metrics and Tags
Data Streams Monitoring is not available for the site.
This document discusses the following Data Streams Monitoring metrics and their tags:
data_streams.latencydata_streams.kafka.lag_secondsdata_streams.kafka.lag_messagesdata_streams.sqs.dead_letter_queue.messagesdata_streams.payload_size
data_streams.latency
This metric measures latency between two points in the pipeline. The value can represent different types of latency, depending on its tags.
pathway_type- What information the metric value represents. Possible pathway types:
full: end-to-end latency between data origin (start) and another point (end) in the pipelinestarttag: data originendtag: arbitrary point where data is last tracked
edge: latency between two services, connected through a queue or directly over HTTP/gRPC. Measures duration between time of produce in the producer (start) and time of consume in the consumer (end)starttag: the upstream producer serviceendtag: the downstream consumer service
partial_edge: latency between a service and a queue, if the producer or consumer is not known (that is, not instrumented with Data Streams Monitoring)starttag: the upstream producer service/queueendtag: the downstream consumer service/queue
internal: latency within the service. Measures time between consume and the folllowing produce operation.
start- The name of the node where Data Streams Monitoring first detects the payload. This node can be a service (the original producer) or a queue (the original producer is not known to Data Streams Monitoring).
When thepathway_typetag is set tofull(end-to-end latency),startalways refers to the start of the pipeline.
For example:
The querystart:serviceA and end:serviceC and pathway_type:fullmeasures end-to-end latency for this pipeline.
The querystart:serviceB and end:serviceC and pathway_type:fulldoes not measure latency for this pipeline, as there is no data originating at Service B. end- The name of a node where the pipeline ends. You can use
endto get data for partial pipelines.
For example:
You can usestart:serviceA and end:serviceB and pathway_type:fullto measure the first part of this pipeline. service- The name of the service where data is collected.
type- The name of the queueing technology for which the data is generated, for example: Kafka, RabbitMQ, SQS. For HTTP and gRPC,
typeis set tohttporgrpc. topic- The name of the topic the data is produced to or consumed from, if any.
direction- The direction of data flow for a particular
service. Possible values:in: the consume operation or serving data over HTTP/gRPCout: the produce operation or sending data over HTTP/gRPC
env- Environment in which the service is running
pathway- An ordered list of services, separated by
/, that the data travels through. If the data goes through the same service multiple times consecutively, the service name is added only once. detailed_pathway- An ordered list of services and queues, separated by
/, that the data travels through. The same aspathwaybut with queues in addition to services. visited_queues- Represents all queues the data goes through. (Queues directly at the start or end of the pipeline are excluded.) You can use this tag to make your query more specific if your data is flowing through multiple queues.
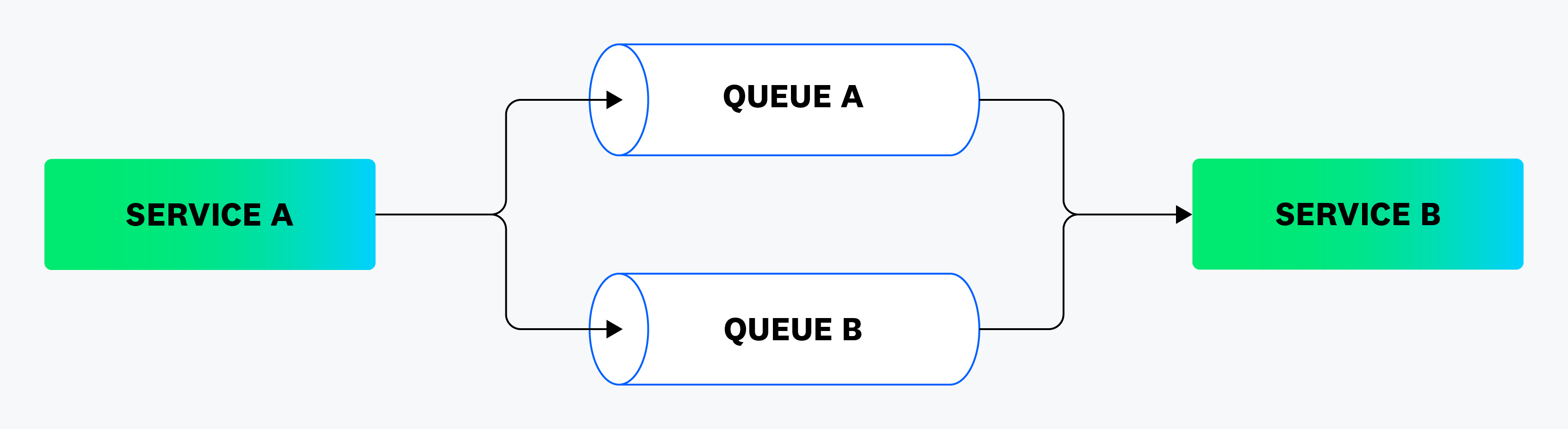
Consider the following pipeline:
To measure data flow from Service A to Queue A to Service B, you can querystart:serviceA and end:serviceB and visited_queues:queueA.
To measure data flow from Service A to Queue B to Service B, you can querystart:serviceA and end:serviceB and visited_queues:queueB. visited_services- Represents all services the data goes through. (Services directly at the start or end of the pipeline are excluded.)
upstream_service- The name of the service upstream from a particular
service. exchange- For RabbitMQ, the name of the exchange the data went to.
hash- A unique identifier, computed using various tag values (
type,service,direction,parent_hash, and others). parent_hash- The
hashof the node upstream from the node on the pathway.
data_streams.kafka.lag_seconds
This metric represents the lag (in seconds) between the last produce and consume operations.
partition- The Kafka partition.
env- The environment in which the consumer service is running.
topic- The Kafka topic.
consumer_group- The Kafka consumer group.
data_streams.kafka.lag_messages
This metric represents the lag (in offsets) between the last produce and consume operations.
partition- The Kafka partition.
env- The environment in which the consumer service is running.
topic- The Kafka topic.
consumer_group- The Kafka consumer group.
data_streams.payload_size
This metric is a distribution metric representing the message size distribution in bytes of messages going through the Data Streams.
The tags are the same as for the data_streams.latency metric.
data_streams.sqs.dead_letter_queue.messages
This metric represents the number of a messages in an SQS dead-letter queue. It is used to to measure the number of dead-lettered messages for a given queue.
arn- The ARN (Amazon Resource Name) of the queue.
aws_account- The AWS Account number of the queue (and dead-letter queue).
dlq- The ARN of the dead letter queue that messages are being sent to.
queue- The name of the queue.
region- The AWS region of the queue (and dead-letter queue).