- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- APM Terms and Concepts
- Application Instrumentation
- APM Metrics Collection
- Trace Pipeline Configuration
- Correlate Traces with Other Telemetry
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origins for Spans
- Service Observability
- Endpoint Observability
- Dynamic Instrumentation
- Live Debugger
- Error Tracking
- Data Security
- Guides
- Troubleshooting
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Log Management
- Administration
Ruby Tests
This product is not supported for your selected Datadog site. ().
Compatibility
Supported languages:
| Language | Version |
|---|---|
| Ruby | >= 2.7 |
| JRuby | >= 9.4 |
Supported test frameworks:
| Test Framework | Version |
|---|---|
| RSpec | >= 3.0.0 |
| Minitest | >= 5.0.0 |
| Cucumber | >= 3.0 |
Supported test runners:
| Test runner | Version |
|---|---|
| Knapsack Pro | >= 7.2.0 |
| parallel_tests | >= 4.0.0 |
| ci-queue | >= 0.53.0 |
Configuring reporting method
To report test results to Datadog, you need to configure the datadog-ci gem:
We support auto-instrumentation for the following CI providers:
| CI Provider | Auto-Instrumentation method |
|---|---|
| GitHub Actions | Datadog Test Visibility Github Action |
| Jenkins | UI-based configuration with Datadog Jenkins plugin |
| GitLab | Datadog Test Visibility GitLab Script |
| CircleCI | Datadog Test Visibility CircleCI Orb |
If you are using auto-instrumentation for one of these providers, you can skip the rest of the setup steps below.
Note: Auto-instrumentation is not supported for JRuby. Follow the manual instrumentation steps instead.
If you are using a cloud CI provider without access to the underlying worker nodes, such as GitHub Actions or CircleCI, configure the library to use the Agentless mode. For this, set the following environment variables:
DD_CIVISIBILITY_AGENTLESS_ENABLED=true(Required)- Enables or disables Agentless mode.
Default:false DD_API_KEY(Required)- The Datadog API key used to upload the test results.
Default:(empty)
Additionally, configure the Datadog site to which you want to send data.
DD_SITE(Required)- The Datadog site to upload results to.
Default:datadoghq.com
If you are running tests on an on-premises CI provider, such as Jenkins or self-managed GitLab CI, install the Datadog Agent on each worker node by following the Agent installation instructions. This is the recommended option as it allows you to automatically link test results to logs and underlying host metrics.
If you are using a Kubernetes executor, Datadog recommends using the Datadog Operator. The operator includes Datadog Admission Controller which can automatically inject the tracer library into the build pods. Note: If you use the Datadog Operator, there is no need to download and inject the tracer library since the Admission Controller can do this for you, so you can skip the corresponding step below. However, you still need to make sure that your pods set the environment variables or command-line parameters necessary to enable Test Visibility.
If you are not using Kubernetes or can’t use the Datadog Admission Controller and the CI provider is using a container-based executor, set the DD_TRACE_AGENT_URL environment variable (which defaults to http://localhost:8126) in the build container running the tracer to an endpoint that is accessible from within that container. Note: Using localhost inside the build references the container itself and not the underlying worker node or any container where the Agent might be running in.
DD_TRACE_AGENT_URL includes the protocol and port (for example, http://localhost:8126) and takes precedence over DD_AGENT_HOST and DD_TRACE_AGENT_PORT, and is the recommended configuration parameter to configure the Datadog Agent’s URL for CI Visibility.
If you still have issues connecting to the Datadog Agent, use the Agentless Mode. Note: When using this method, tests are not correlated with logs and infrastructure metrics.
Installing the Ruby test optimization library
To install the Ruby test optimization gem run:
bundle add datadog-ci --group "test"
Alternatively, add it to your Gemfile manually:
- Add the
datadog-cigem to yourGemfile:
Gemfile
gem "datadog-ci", "~> 1.0", group: :test- Install the gem by running
bundle install
Instrumenting your tests
Follow these steps if your CI Provider is not supported for auto-instrumentation (see Configuring reporting method).
- Set the following environment variables to configure the tracer:
DD_CIVISIBILITY_ENABLED=true(Required)- Enables the Test Optimization product.
DD_TEST_SESSION_NAME- Use this to identify a group of tests (for example:
unit-testsorintegration-tests). DD_ENV(Required)- Environment where the tests are being run (for example:
localwhen running tests on a developer workstation orciwhen running them on a CI provider). DD_SERVICE(Optional)- Name of the service or library being tested.
- Prepend your test command with this datadog-ci CLI wrapper:
bundle exec ddcirb exec bundle exec rake test
Alternatively, set RUBYOPT environment variable to "-rbundler/setup -rdatadog/ci/auto_instrument" and don’t modify your test command.
Adding custom tags to tests
You can add custom tags to your tests by using the current active test:
require "datadog/ci"
# inside your test
Datadog::CI.active_test&.set_tag("test_owner", "my_team")
# test continues normally
# ...
To create filters or group by fields for these tags, you must first create facets. For more information about adding tags, see the Adding Tags section of the Ruby custom instrumentation documentation.
Adding custom measures to tests
Like tags, you can add custom measures to your tests by using the current active test:
require "datadog/ci"
# inside your test
Datadog::CI.active_test&.set_metric("memory_allocations", 16)
# test continues normally
# ...
For more information on custom measures, see the Add Custom Measures Guide.
Configuration settings
The following is a list of the most important configuration settings that can be used with the test optimization library, either in code by using a Datadog.configure block, or using environment variables:
service- Name of the service or library under test.
Environment variable:DD_SERVICE
Default:$PROGRAM_NAME
Example:my-ruby-app env- Name of the environment where tests are being run.
Environment variable:DD_ENV
Default:none
Examples:local,ci
For more information about service and env reserved tags, see Unified Service Tagging.
The following environment variable can be used to configure the location of the Datadog Agent:
DD_TRACE_AGENT_URL- Datadog Agent URL for trace collection in the form
http://hostname:port.
Default:http://localhost:8126
All other Datadog Tracer configuration options can also be used.
Using additional instrumentation
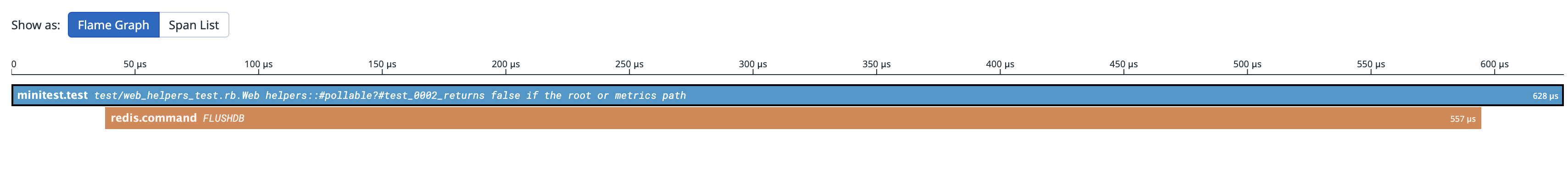
It can be useful to have rich tracing information about your tests that includes time spent performing database operations or other external calls, as seen in the following flame graph:
To achieve this, configure additional instrumentation in your configure block:
if ENV["DD_ENV"] == "ci"
Datadog.configure do |c|
# ... ci configs and instrumentation here ...
c.tracing.instrument :redis
c.tracing.instrument :pg
# ... any other instrumentations supported by datadog gem ...
end
end
Alternatively, you can enable automatic APM instrumentation in test_helper/spec_helper:
require "datadog/auto_instrument" if ENV["DD_ENV"] == "ci"
Note: In CI mode, these traces are submitted to Test Optimization, and they do not show up in Datadog APM.
For the full list of available instrumentation methods, see the tracing documentation
Collecting Git metadata
Datadog uses Git information for visualizing your test results and grouping them by repository, branch, and commit. Git metadata is automatically collected by the test instrumentation from CI provider environment variables and the local .git folder in the project path, if available.
If you are running tests in non-supported CI providers or with no .git folder, you can set the Git information manually using environment variables. These environment variables take precedence over any auto-detected information. Set the following environment variables to provide Git information:
DD_GIT_REPOSITORY_URL- URL of the repository where the code is stored. Both HTTP and SSH URLs are supported.
Example:git@github.com:MyCompany/MyApp.git,https://github.com/MyCompany/MyApp.git DD_GIT_BRANCH- Git branch being tested. Leave empty if providing tag information instead.
Example:develop DD_GIT_TAG- Git tag being tested (if applicable). Leave empty if providing branch information instead.
Example:1.0.1 DD_GIT_COMMIT_SHA- Full commit hash.
Example:a18ebf361cc831f5535e58ec4fae04ffd98d8152 DD_GIT_COMMIT_MESSAGE- Commit message.
Example:Set release number DD_GIT_COMMIT_AUTHOR_NAME- Commit author name.
Example:John Smith DD_GIT_COMMIT_AUTHOR_EMAIL- Commit author email.
Example:john@example.com DD_GIT_COMMIT_AUTHOR_DATE- Commit author date in ISO 8601 format.
Example:2021-03-12T16:00:28Z DD_GIT_COMMIT_COMMITTER_NAME- Commit committer name.
Example:Jane Smith DD_GIT_COMMIT_COMMITTER_EMAIL- Commit committer email.
Example:jane@example.com DD_GIT_COMMIT_COMMITTER_DATE- Commit committer date in ISO 8601 format.
Example:2021-03-12T16:00:28Z
Manually instrumenting your tests
Attention: when using manual instrumentation, run your tests like you normally do:
don't change `RUBYOPT` env variable and don't prepend `bundle exec ddcirb exec` to your test command
Auto-instrumentation adds additional performance overhead at the code loading stage. It can be especially noticeable for large repositories with a lot of dependencies. If your project takes 20+ seconds to start, you are likely to benefit from manually instrumenting your tests.
The RSpec integration traces all executions of example groups and examples when using the rspec test framework.
To activate your integration, add this to the spec_helper.rb file:
require "rspec"
require "datadog/ci"
# Only activates test instrumentation on CI
if ENV["DD_ENV"] == "ci"
Datadog.configure do |c|
# enables test optimization
c.ci.enabled = true
# The name of the service or library under test
c.service = "my-ruby-app"
# Enables the RSpec instrumentation
c.ci.instrument :rspec
end
end
Run your tests as you normally do, specifying the environment where tests are being run in the DD_ENV environment variable.
You could use the following environments:
localwhen running tests on a developer workstationciwhen running them on a CI provider
For example:
DD_ENV=ci bundle exec rake spec
The Minitest integration traces all executions of tests when using the minitest framework.
To activate your integration, add this to the test_helper.rb file:
require "minitest"
require "datadog/ci"
# Only activates test instrumentation on CI
if ENV["DD_ENV"] == "ci"
Datadog.configure do |c|
# enables test optimization
c.ci.enabled = true
# The name of the service or library under test
c.service = "my-ruby-app"
c.ci.instrument :minitest
end
end
Run your tests as you normally do, specifying the environment where tests are being run in the DD_ENV environment variable.
You could use the following environments:
localwhen running tests on a developer workstationciwhen running them on a CI provider
For example:
DD_ENV=ci bundle exec rake test
Note: When using `minitest/autorun`, ensure that `datadog/ci` is required before `minitest/autorun`.
Example configuration with minitest/autorun:
require "datadog/ci"
require "minitest/autorun"
if ENV["DD_ENV"] == "ci"
Datadog.configure do |c|
c.ci.enabled = true
c.service = "my-ruby-app"
c.ci.instrument :minitest
end
end
The Cucumber integration traces executions of scenarios and steps when using the cucumber framework.
To activate your integration, add the following code to your application:
require "cucumber"
require "datadog/ci"
# Only activates test instrumentation on CI
if ENV["DD_ENV"] == "ci"
Datadog.configure do |c|
# enables test optimization
c.ci.enabled = true
# The name of the service or library under test
c.service = "my-ruby-app"
# Enables the Cucumber instrumentation
c.ci.instrument :cucumber
end
end
Run your tests as you normally do, specifying the environment where tests are being run in the DD_ENV environment variable.
You could use the following environments:
localwhen running tests on a developer workstationciwhen running them on a CI provider
For example:
DD_ENV=ci bundle exec rake cucumber
Using library’s public API for unsupported test frameworks
If you use RSpec, Minitest, or Cucumber, do not use the manual testing API, as Test Optimization automatically instruments them and sends the test results to Datadog. The manual testing API is incompatible with already supported testing frameworks.
Use the manual testing API only if you use an unsupported testing framework or have a different testing mechanism. Full public API documentation is available on YARD site.
Domain model
The API is based around four concepts: test session, test module, test suite, and test.
Test session
A test session represents a test command run.
To start a test session, call Datadog::CI.start_test_session and pass the Datadog service and tags (such as the test framework
you are using).
When all your tests have finished, call Datadog::CI::TestSession#finish, which closes the session and sends the session
trace to the backend.
Test module
A test module represents a smaller unit of work within a session. For supported test frameworks, test module is always same as test session. For your use case, this could be a package in your componentized application.
To start a test module, call Datadog::CI.start_test_module and pass the name of the module.
When the module run has finished, call Datadog::CI::TestModule#finish.
Test suite
A test suite comprises a set of tests that test similar functionality. A single suite usually corresponds to a single file where tests are defined.
Create test suites by calling Datadog::CI#start_test_suite and passing the name of the test suite.
Call Datadog::CI::TestSuite#finish when all the related tests in the suite have finished their execution.
Test
A test represents a single test case that is executed as part of a test suite. Usually it corresponds to a method that contains testing logic.
Create tests in a suite by calling Datadog::CI#start_test or Datadog::CI.trace_test and passing the name of the test and name of the test suite. Test suite name must be the same as name of the test suite started in previous step.
Call Datadog::CI::Test#finish when a test has finished execution.
Code example
The following code represents example usage of the API:
require "datadog/ci"
Datadog.configure do |c|
c.service = "my-test-service"
c.ci.enabled = true
end
def run_test_suite(tests, test_suite_name)
test_suite = Datadog::CI.start_test_suite(test_suite_name)
run_tests(tests, test_suite_name)
test_suite.passed!
test_suite.finish
end
def run_tests(tests, test_suite_name)
tests.each do |test_name|
Datadog::CI.trace_test(test_name, test_suite_name) do |test|
test.passed!
end
end
end
Datadog::CI.start_test_session(
tags: {
Datadog::CI::Ext::Test::TAG_FRAMEWORK => "my-framework",
Datadog::CI::Ext::Test::TAG_FRAMEWORK_VERSION => "0.0.1",
}
)
Datadog::CI.start_test_module("my-test-module")
run_test_suite(["test1", "test2", "test3"], "test-suite-name")
Datadog::CI.active_test_module&.passed!
Datadog::CI.active_test_module&.finish
Datadog::CI.active_test_session&.passed!
Datadog::CI.active_test_session&.finish
Best practices
Test session name DD_TEST_SESSION_NAME
Use DD_TEST_SESSION_NAME to define the name of the test session and the related group of tests. Examples of values for this tag would be:
unit-testsintegration-testssmoke-testsflaky-testsui-testsbackend-tests
If DD_TEST_SESSION_NAME is not specified, the default value used is a combination of the:
- CI job name
- Command used to run the tests (such as
yarn test)
The test session name needs to be unique within a repository to help you distinguish different groups of tests.
When to use DD_TEST_SESSION_NAME
There’s a set of parameters that Datadog checks to establish correspondence between test sessions. The test command used to execute the tests is one of them. If the test command contains a string that changes for every execution, such as a temporary folder, Datadog considers the sessions to be unrelated to each other. For example:
yarn test --temp-dir=/var/folders/t1/rs2htfh55mz9px2j4prmpg_c0000gq/Tpnpm vitest --temp-dir=/var/folders/t1/rs2htfh55mz9px2j4prmpg_c0000gq/T
Datadog recommends using DD_TEST_SESSION_NAME if your test commands vary between executions.
Further reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: