- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- APM Terms and Concepts
- Application Instrumentation
- APM Metrics Collection
- Trace Pipeline Configuration
- Correlate Traces with Other Telemetry
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origins for Spans
- Service Observability
- Endpoint Observability
- Dynamic Instrumentation
- Live Debugger
- Error Tracking
- Data Security
- Guides
- Troubleshooting
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Log Management
- Administration
Set up Tracing on a GitLab Pipeline
This product is not supported for your selected Datadog site. ().
Overview
GitLab is a DevOps platform that automates the software development lifecycle with integrated CI/CD features, enabling automated, continuous deployment of applications with built-in security controls.
Set up tracing in GitLab to collect data on your pipeline executions, analyze performance bottlenecks, troubleshoot operational issues, and optimize your deployment workflows.
Compatibility
| Pipeline Visibility | Platform | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Running pipelines | Running pipelines | View pipeline executions that are running. Queued or waiting pipelines show with status “Running” on Datadog. |
| CI jobs failure analysis | CI jobs failure analysis | Analysis of the root causes of failed CI jobs based on relevant logs using LLM models. |
| Filter CI Jobs on the critical path | Filter CI Jobs on the critical path | Filter by jobs on the critical path. |
| Partial retries | Partial pipelines | View partially retried pipeline executions. |
| Manual steps | Manual steps | View manually triggered pipelines. |
| Queue time | Queue time | View the amount of time pipeline jobs sit in the queue before processing. |
| Logs correlation | Logs correlation | Correlate pipeline spans to logs and enable job log collection. |
| Infrastructure metric correlation | Infrastructure metric correlation | Correlate jobs to infrastructure host metrics for self-hosted GitLab runners. |
| Custom pre-defined tags | Custom pre-defined tags | Set custom tags to all generated pipeline, stages, and job spans. |
| Custom tags and measures at runtime | Custom tags and measures at runtime | Configure custom tags and measures at runtime. |
| Parameters | Parameters | Set custom env or service parameters when a pipeline is triggered. |
| Pipeline failure reasons | Pipeline failure reasons | Identify pipeline failure reasons from error messages. |
| Approval wait time | Approval wait time | View the amount of time jobs and pipelines wait for manual approvals. |
| Execution time | Execution time | View the amount of time pipelines have been running jobs. Gitlab refers to this metric as duration. Duration in Gitlab and execution time may show different values. Gitlab does not take into consideration jobs that failed due to certain kinds of failures (such as runner system failures). |
| Custom spans | Custom spans | Configure custom spans for your pipelines. |
The following GitLab versions are supported:
- GitLab.com (SaaS)
- GitLab >= 14.1 (self-hosted)
- GitLab >= 13.7.0 (self-hosted) with the
datadog_ci_integrationfeature flag enabled
Configure the Datadog integration
Configure the integration on a project or group by going to Settings > Integrations > Datadog for each project or group you want to instrument.
Fill in the integration configuration settings:
- Active
- Enables the integration.
- Datadog site
- Specifies which Datadog site to send data to.
Default:datadoghq.com
Selected site: - API URL (optional)
- Allows overriding the API URL used for sending data directly, only used in advanced scenarios.
Default: (empty, no override) - API key
- Specifies which Datadog API key to use when sending data.
- Enable CI Visibility
- Controls the enablement of CI Visibility features, including pipeline tracing, critical path computation and performance monitoring. Ensure this box is checked to activate these capabilities.
- Service (optional)
- Specifies which service name to attach to each span generated by the integration. Use this to differentiate between GitLab instances.
Default:gitlab-ci - Env (optional)
- Specifies which environment (
envtag) to attach to each span generated by the integration. Use this to differentiate between groups of GitLab instances (for example, staging or production).
Default:none - Tags (optional)
- Specifies any custom tags to attach to each span generated by the integration. Provide one tag per line in the format:
key:value.
Default: (empty, no additional tags)
Note: Available only in GitLab.com and GitLab >= 14.8 self-hosted.
You can test the integration with the Test settings button (only available when configuring the integration on a project). After it’s successful, click Save changes to finish the integration set up. If the button fails, click Save changes and check that the first webhooks sent are successful by looking at the history in the “Recent events” section below.
Configure the integration on a project or group by going to Settings > Integrations > Datadog for each project or group you want to instrument. You can also activate the integration at the GitLab instance level by going to Admin > Settings > Integrations > Datadog.
Fill in the integration configuration settings:
- Active
- Enables the integration.
- Datadog site
- Specifies which Datadog site to send data to.
Default:datadoghq.com
Selected site: - API URL (optional)
- Allows overriding the API URL used for sending data directly, only used in advanced scenarios.
Default: (empty, no override) - API key
- Specifies which Datadog API key to use when sending data.
- Enable CI Visibility
- Controls the enablement of CI Visibility features, including pipeline tracing, critical path computation and performance monitoring. Ensure this box is checked to activate these capabilities. It’s only present starting from GitLab 17.7, and isn’t required in prior versions.
- Service (optional)
- Specifies which service name to attach to each span generated by the integration. Use this to differentiate between GitLab instances.
Default:gitlab-ci - Env (optional)
- Specifies which environment (
envtag) to attach to each span generated by the integration. Use this to differentiate between groups of GitLab instances (for example, staging or production).
Default:none - Tags (optional)
- Specifies any custom tags to attach to each span generated by the integration. Provide one tag per line in the format:
key:value.
Default: (empty, no additional tags)
Note: Available only in GitLab.com and GitLab >= 14.8 self-hosted.
You can test the integration with the Test settings button (only available when configuring the integration on a project). After it’s successful, click Save changes to finish the integration setup. If the button fails, click Save changes and check that the first webhooks sent are successful by looking at the history in the “Recent events” section below.
Enable the datadog_ci_integration feature flag to activate the integration.
Run one of the following commands, which use GitLab’s Rails Runner, depending on your installation type:
From Omnibus Installations:
sudo gitlab-rails runner "Feature.enable(:datadog_ci_integration)"From Source Installations:
sudo -u git -H bundle exec rails runner \
-e production \
"Feature.enable(:datadog_ci_integration)"From Kubernetes Installations:
kubectl exec -it <task-runner-pod-name> -- \
/srv/gitlab/bin/rails runner "Feature.enable(:datadog_ci_integration)"Then, configure the integration on a project by going to Settings > Integrations > Datadog for each project you want to instrument.
Due to a bug in early versions of GitLab, the Datadog integration cannot be enabled at group or instance level on GitLab versions < 14.1, even if the option is available on GitLab's UI.
Fill in the integration configuration settings:
- Active
- Enables the integration.
- Datadog site
- Specifies which Datadog site to send data to.
Default:datadoghq.com
Selected site: - API URL (optional)
- Allows overriding the API URL used for sending data directly, only used in advanced scenarios.
Default: (empty, no override) - API key
- Specifies which Datadog API key to use when sending data.
- Service (optional)
- Specifies which service name to attach to each span generated by the integration. Use this to differentiate between GitLab instances.
Default:gitlab-ci - Env (optional)
- Specifies which environment (
envtag) to attach to each span generated by the integration. Use this to differentiate between groups of GitLab instances (for example, staging or production).
Default:none - Tags (optional)
- Specifies any custom tags to attach to each span generated by the integration. Provide one tag per line in the format:
key:value.
Default: (empty, no additional tags)
Note: Available only in GitLab.com and GitLab >= 14.8 self-hosted.
You can test the integration with the Test settings button (only available when configuring the integration on a project). After it’s successful, click Save changes to finish the integration set up. If the button fails, click Save changes and check that the first webhooks sent are successful by looking at the history in the “Recent events” section below.
Direct support with webhooks is not under development. Unexpected issues could happen. Datadog recommends that you update GitLab instead.
For older versions of GitLab, you can use webhooks to send pipeline data to Datadog.
Go to Settings > Webhooks in your repository (or GitLab instance settings), and add a new webhook:
- URL:
https://webhook-intake./api/v2/webhook/?dd-api-key=<API_KEY>where<API_KEY>is your Datadog API key. - Secret Token: Leave this field empty.
- Trigger: Select
Job eventsandPipeline events.
To set custom env or service parameters, add more query parameters in the webhooks URL. For example, &env=<YOUR_ENV>&service=<YOUR_SERVICE_NAME>.
Set custom tags
To set custom tags to all the pipeline and job spans generated by the integration, add a URL-encoded query parameter tags with key:value pairs separated by commas to the URL.
If a key:value pair contains any commas, surround it with quotes. For example, to add key1:value1,"key2: value with , comma",key3:value3, the following string would need to be appended to the Webhook URL: ?tags=key1%3Avalue1%2C%22key2%3A+value+with+%2C+comma%22%2Ckey3%3Avalue3.
Advanced configuration
Set custom tags
You can set custom tags for all pipeline and job spans from your GitLab projects to improve traceability. For more information, see Custom Tags and Measures.
Integrate with Datadog Teams
To display and filter the teams associated with your pipelines, add team:<your-team> as a custom tag. The custom tag name must match your Datadog Teams team handle exactly.
Correlate infrastructure metrics to jobs
If you are using self-hosted GitLab runners, you can correlate jobs with the infrastructure that is running them.
Datadog infrastructure correlation is possible using different methods:
The GitLab runner must have a tag in the form host:<hostname>. Tags can be added while registering a new runner. As a result, this method is only available when the runner is directly running the job.
This excludes executors that are autoscaling the infrastructure in order to run the job (such as the Kubernetes, Docker Autoscaler, or Instance executors) as it is not possible to add tags dynamically for those runners.
For existing runners:
GitLab >= 15.8: Add tags through the UI by going to Settings > CI/CD > Runners and editing the appropriate runner.
GitLab < 15.8: Add tags by updating the runner’s
config.toml. Or add tags through the UI by going to Settings > CI/CD > Runners and editing the appropriate runner.
After these steps, CI Visibility adds the hostname to each job. To see the metrics, click on a job span in the trace view. In the drawer, a new tab named Infrastructure appears which contains the host metrics.
CI Visibility supports Infrastructure metrics for “Docker Autoscaler” executors. For more information, see the Correlate Infrastructure Metrics with GitLab Jobs guide.
CI Visibility supports Infrastructure metrics for “Instance” executors. For more information, see the Correlate Infrastructure Metrics with GitLab Jobs guide.
CI Visibility supports Infrastructure metrics for the Kubernetes executor. For this, it is necessary to have the Datadog Agent monitoring the Kubernetes Gitlab infrastructure. See Install the Datadog Agent on Kubernetes to install the Datadog Agent in a Kubernetes cluster.
Due to limitations in the Datadog Agent, jobs shorter than the minimum collection interval of the Datadog Agent might not always display infrastructure correlation metrics. To adjust this value, see Datadog Agent configuration template and adjust the variable min_collection_interval to be less than 15 seconds.
CI Visibility does not support Infrastructure metrics for other executors.
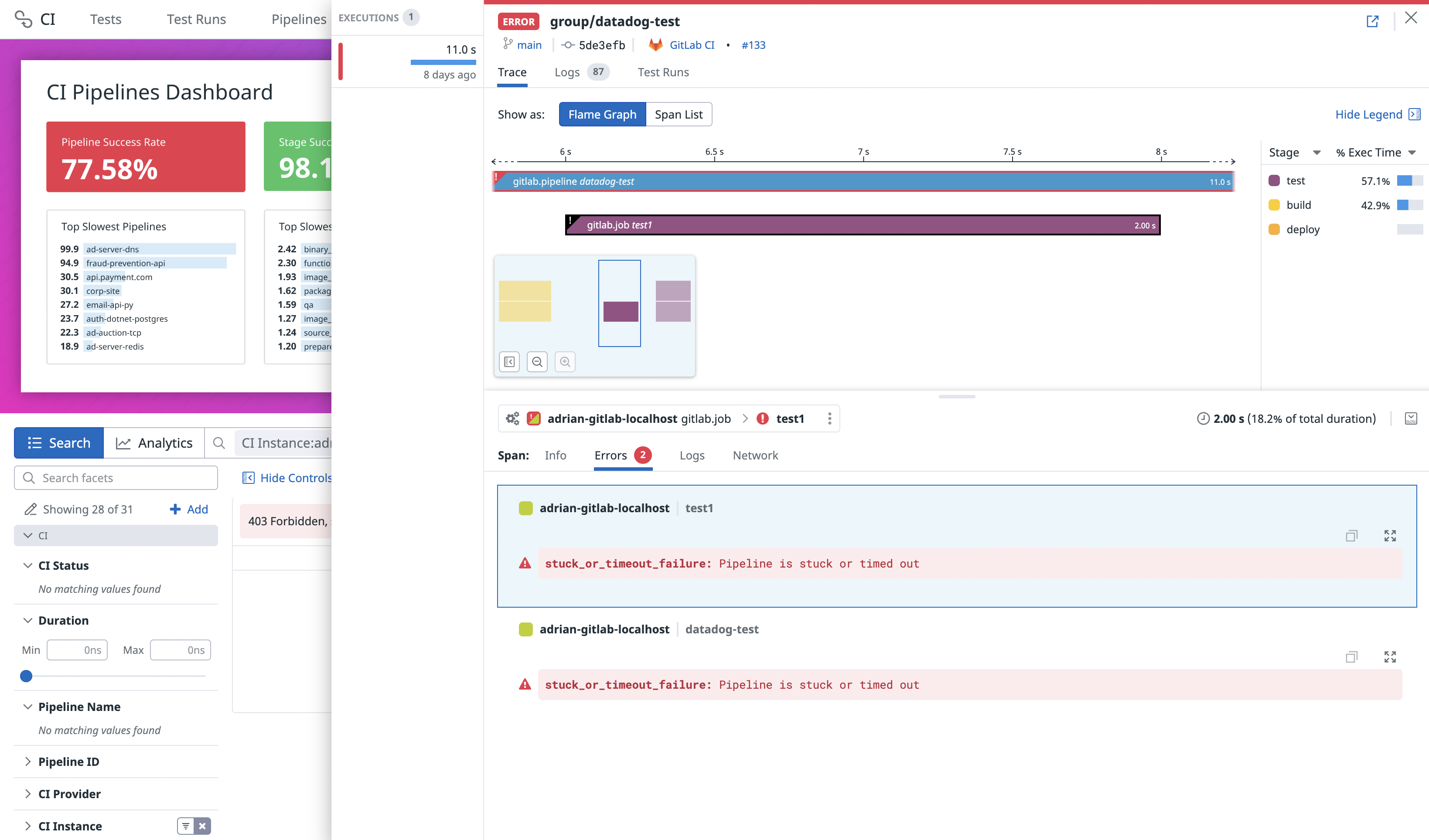
View error messages for pipeline failures
For failed GitLab pipeline executions, each error under the Errors tab within a specific pipeline execution displays a message associated with the error type from GitLab.
CI jobs failure analysis
If job logs collection is enabled, CI Visibility computes analysis using LLM models for failed CI jobs based on relevant logs coming from GitLab.
For a full explanation, see the guide on using CI jobs failure analysis.
Errors provided by GitLab
Error messages are supported for GitLab versions 15.2.0 and above.
The error information provided by GitLab is stored in error.provider_message and error.provider_domain tags.
The following table describes the message and domain correlated with each error type. Any unlisted error type results in a Job failed error message and an unknown error domain.
| Error Type | Error Domain | Error Message |
|---|---|---|
unknown_failure | unknown | Failed due to unknown reason. |
config_error | user | Failed due to error on CI/CD configuration file. |
external_validation_failure | unknown | Failed due to external pipeline validation. |
user_not_verified | user | The pipeline failed due to the user not being verified. |
activity_limit_exceeded | provider | The pipeline activity limit was exceeded. |
size_limit_exceeded | provider | The pipeline size limit was exceeded. |
job_activity_limit_exceeded | provider | The pipeline job activity limit was exceeded. |
deployments_limit_exceeded | provider | The pipeline deployments limit was exceeded. |
project_deleted | provider | The project associated with this pipeline was deleted. |
api_failure | provider | API failure. |
stuck_or_timeout_failure | unknown | Pipeline is stuck or timed out. |
runner_system_failure | provider | Failed due to runner system failure. |
missing_dependency_failure | unknown | Failed due to missing dependency. |
runner_unsupported | provider | Failed due to unsupported runner. |
stale_schedule | provider | Failed due to stale schedule. |
job_execution_timeout | unknown | Failed due to job timeout. |
archived_failure | provider | Archived failure. |
unmet_prerequisites | unknown | Failed due to unmet prerequisite. |
scheduler_failure | provider | Failed due to schedule failure. |
data_integrity_failure | provider | Failed due to data integrity. |
forward_deployment_failure | unknown | Deployment failure. |
user_blocked | user | Blocked by user. |
ci_quota_exceeded | provider | CI quota exceeded. |
pipeline_loop_detected | user | Pipeline loop detected. |
builds_disabled | user | Build disabled. |
deployment_rejected | user | Deployment rejected. |
protected_environment_failure | provider | Environment failure. |
secrets_provider_not_found | user | Secret provider not found. |
reached_max_descendant_pipelines_depth | user | Reached max descendant pipelines. |
ip_restriction_failure | provider | IP restriction failure. |
Collect job logs
The following GitLab versions support collecting job logs:
- GitLab.com (SaaS)
- GitLab >= 15.3 (self-hosted) only if you are using object storage to store job logs
- GitLab >= 14.8 (self-hosted) by enabling the
datadog_integration_logs_collectionfeature flag
Job logs are collected in Log Management and are automatically correlated with the GitLab pipeline in CI Visibility. Log files larger than one GiB are truncated.
To enable collection of job logs:
- Click the Enable job logs collection checkbox in the GitLab integration Settings > Integrations > Datadog.
- Click Save changes.
Datadog downloads log files directly from your GitLab logs object storage with temporary pre-signed URLs.
This means that for Datadog servers to access the storage, the storage must not have network restrictions
The endpoint, if set, should resolve to a publicly accessible URL.
- Click Enable job logs collection checkbox in the GitLab integration under Settings > Integrations > Datadog.
- Click Save changes.
Datadog downloads log files directly from your GitLab logs object storage with temporary pre-signed URLs.
This means that for Datadog servers to access the storage, the storage must not have network restrictions
The endpoint, if set, should resolve to a publicly accessible URL.
- Enable the
datadog_integration_logs_collectionfeature flag in your GitLab. This allows you to see the Enable job logs collection checkbox in the GitLab integration under Settings > Integrations > Datadog. - Click Enable job logs collection.
- Click Save changes.
Logs are billed separately from CI Visibility. Log retention, exclusion, and indexes are configured in Log Management. Logs for GitLab jobs can be identified by the datadog.product:cipipeline and source:gitlab tags.
For more information about processing job logs collected from the GitLab integration, see the Processors documentation.
View partial and downstream pipelines
You can use the following filters to customize your search query in the CI Visibility Explorer.
| Facet Name | Facet ID | Possible Values |
|---|---|---|
| Downstream Pipeline | @ci.pipeline.downstream | true, false |
| Manually Triggered | @ci.is_manual | true, false |
| Partial Pipeline | @ci.partial_pipeline | retry, paused, resumed |
You can also apply these filters using the facet panel on the left hand side of the page.
Visualize pipeline data in Datadog
Once the integration is successfully configured, the CI Pipeline List and Executions pages populate with data after the pipelines finish.
The CI Pipeline List page shows data for only the default branch of each repository. For more information, see Search and Manage CI Pipelines.
Further reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: